IJCRR - 12(18), September, 2020
Pages: 180-187
Date of Publication: 22-Sep-2020
Print Article
Download XML Download PDF
Behavioral Intervention with Fine Motor Training for Dysgraphia in School Going Children
Author: Yanjana, Promila Singh, Mahendra Kumar
Category: Healthcare
Abstract:Aim: The main objective of this study was to examine the effectiveness of Behavioral Intervention with fine motor training on behavioral problems and learning disabilities in children with writing difficulties (dysgraphia). Materials and Methods: Those school going children who were average IQ, low academic performance and scored less than 50 on diagnostic test of learning disability (DTLD) and less than 5 on Eye-hand Coordination (EHC) subtest of DTLD were identified as subjects with writing difficulties. Subjects were also rated by teachers on behavioural problem checklist in pre-post condition. Seventy children with dysgraphia taken for intervention from the age group of 8-11 years (out of these 14 were dropouts). The quasi-experimental design was used. Hence, 28 subjects were part of the experimental group and the rest of the subjects were included in the placebo group. Three-month intervention (behavioural intervention with fine motor training) with 2 sessions per week was given to the experimental group through group and individual sessions. Placebo group were only involved in daily routine activities. After the intervention, all measurements were again administered. SPSS 16 V. was used for statistical analysis. Results: The results in eye-hand coordination (Wilcoxon W=28.000;Z=-4.059;p=.000) and diagnostic test of learning disability total score (F=4.656, p=.035) show a significant increase on post-intervention for the experimental group. The results in behavioural problems show a significant decrease in post-intervention for the experimental group (F=40.179; p=.000). Conclusions: Behavioral intervention with activity-based fine motor training to be useful in the classroom. The research empirically proves that activity had a positive effect in enhancing the EHC and overall psychological health with reducing behavioural problems in Children with writing difficulties.
Keywords: Learning disability, Intelligence, Behavioral Problem, Behavioral Intervention, Fine Motor Training
Full Text:
Introduction:
Writing difficulties or dysgraphia is a type of learning disability that frequently interferes with the student's ability to form letters and words when writing. Dysgraphia can affect writing ability and fine motor skills, it can produce illegible writing, misspell words, inaccurately copy words and letters, and write in incoherent sentences. In a survey, more than 1,83,000 children below 14 cannot read and write. Total 37 % children studying in government schools in the age group of 7 to 10 years cannot read simple words and 52 % cannot even recognize numbers1. Students with learning disabilities may suffer from emotional problems and behavioural problem2,3 and associated with psychological co morbidities4. Most of the students withdraw from social interaction and involved in drugs or alcohol abused for relief from feelings of low self-worth and approximately 35% of students with learning disorders, drop out from High School5. Dyslexic students are highly thinking about to attempt suicide compared to other young people6. Youth suffer from poor reading ability were more possibility to suicide attempts or experience suicidal thought and high risk on and more probability to drop out of school than youth with typical reading7.
The researcher observed in children who were developmentally delayed, a common thread-their cognitive development as well as their fine motor development. Students struggling have poorly developed fine motor skills like poor handwriting, poor cutting and colouring skills, problem copying from the board, low skills in visual-perception, complexity with puzzles and mazes, trouble identifying letters and numerals, as well as poor ability in reading and writing. A student with dysgraphia might have fine motor difficulties such as trouble holding the pencil correctly, inability to use scissors well, or colouring inside the lines8. Fine motor skills are necessary for both reading and writing. Students need fine motor Placebo for eye muscles to focus and distinguish letters, crossing midline, and tracking all essential skills for reading and writing. They need eye-hand placebo to develop good handwriting skills so that they can express themselves in written form.
The cognitive-based remediation program has the potential for substantially improving comprehension and its underlying cognitive process among English-as-a-second-language children 9,10. This method also reported continued improvement in their reading skills, notably in comprehension11. In another study, significant improvement was observed in word identification and word attack pre-post test12. Positive effects of specific writing treatments were observed for struggling writers and students of LD in several studies13-16. Impact of experimental studies on the writing of students with LD in Grades 1 to 9 has examined and they reported instructional components were essential for effective writing instruction for students with LD17.
The study reported knowledge about behavioural disorders is poor among primary school teachers in India18. Early identification of such students can help in the early institution of intervention and suitable modifications in teaching techniques19. In India, limited studies are focused on the prevention of mental health problem and limited attention is given to child mental health promotion in LD students. Research has shown Behavioral intervention to be effective in the prevention of mental health problems in children but there are very few studies focused on behavioural intervention for LD with mental health promotion among LD students. There is an also need to examine our lack of focus on fine motor development. For this purpose this study was undertaken to examine the effectiveness of behavioural intervention with fine motor training on behavioural problems, learning disability and intelligence among children with writing difficulties.
Materials and Methods:
Participants
Seventy children of writing disabled were selected from the government school of Chhattisgarh (age range 8 -11 years). The purposive sampling technique was used. All the students are from the same pattern of education i.e. Chhattisgarh Board of Secondary Education.
Inclusion criteria:
-
The sample comprised of school-going children.
-
Age range 08 - 11
-
Student of rural & urban school both
-
Children identified by teachers as having difficulties in learning and poor academic performance.
-
Children study in schools would be Hindi is the medium of instruction.
-
Children going to school with at least 62 to75% attendance.
-
Willingness to participate in the study.
Exclusion criteria:
-
Children with mental retardation.
-
Children with gross and uncorrected visual or auditory sensory handicaps which could influence school performance.
-
Children with medical conditions such as epilepsy and a head injury which could impair the ability to learn.
-
Breathing-related sleep disorder;
-
Occurrences of progressive medical sickness i.e. (cancer, dementia); (d) mental disorder
-
Direct physiological effects of drugs (e.g., a drug of abuse, a medication) or a general medical condition.
Seventy participants were selected based on a priori power analysis by G∗Power computer program. Using parameters of 0.80 power, 0.80 large sizes, and 0.05 alpha, the sample size for F-test needed per group was 21 participants.
Randomization: after the enrollment of the participants, following the random sequence generation technique these 70 participates were divided into two groups as the experimental group and placebo group, each constitutes 35 participants. 56 participants were completed (28 in the experimental group and 28 in the placebo group). Figure 1 represents the CONSORT diagram showing the flow of participants through each stage of the trial.
Tools
1. Coloured Progressive matrices
Intelligence was measured by Raven’s coloured progressive matrices. In the present test, split-half reliability was found at 0.90. Coloured Progressive matrices is a suitable IQ test for the children in the age range of 6 years to 11 years20.
2. Diagnostic Test of Learning Disability (DTLD).
It is to be individually administered as well as a group on the age group 8-11 years old. A deficit in any of the area or areas or a combination of any would lead to a learning problem. It consists of 10 sub-tests: Eye-hand Co-ordination(ECH), Figure-Ground Perception (FG), Figure Constancy(FC), Position-in-Space(PS), Spatial Relations(SR), Auditory Perception(AP), Cognitive Abilities(CA), Memory(M), Receptive Language(RL), Expressive Language(EL). Eye-hand co-ordination subtest measures the ability to coordinate vision with the movement of the hands for effective use. A subject having handwriting problems because of dysgraphia will score low on this subtest21.
3. Behavioural problems checklist (BP)
To measures, the behavioural problem of the children, child behaviour checklist was used (Anuradha & Parimu, 2005). Behavioural problems were rated by the class teacher and parents based on Behavioral problems checklist. In this checklist, 30 items were included. Scores were obtained by (e.g., Yes = 1 & No = 0) and then summing all 30 items. High score reported a high level of Behavioral problems22.
Information related to their demographic (age, sex, birth order, family status, mother occupation, father occupation) variations were obtained by taking their bio-data record.
Procedure
First of all the authorities of the different school were requested to permit collecting data from the students. After getting permission, the informed consent form was taken from parents. Firstly 1200 students were assessed on intelligence test from 3rd, 4th and 5th class school going students. Students who have difficulties in learning with low academic performance were identified by the teacher. Further 570 students of average and above-average IQ with low academic performance were selected for the identification of writing disabilities. Behaviour problem checklists with a demographic and diagnostic test of learning disabilities (DTLD) were administered on 570 students. Before administering the above measure printed instructions were made clear to them when they understood the instructions completely, the measures were administered to them and response sheets were collected.
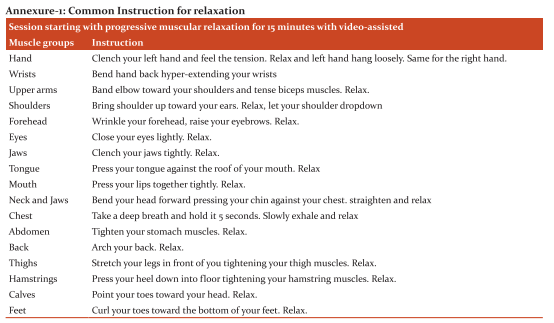
The 70 participants (n=70) who were positive in the area of difficulty in the writing and low score less than 50 on DTLD and less than 5 on Eye-hand Coordination (EHC) subtest of diagnostic tests of Learning Disability were identified as subjects with writing difficulties (dysgraphia). The participants (n=70) who were writing difficulties (dysgraphia) were considered for Intervention. The parents of the identified participants were approached for the consent, to be the part of the research. Figure-1 show 56 children were completed this intervention study in two groups (experimental group and placebo group). Three-month intervention with 2 sessions per week (1-2 hour per session) was done in a school with the experimental group through group sessions and individual (see annexure 1 and 2). Each task of the intervention was administered twice on all the 28 participants to refine their skills. The placebo group subjects only involved in daily routine activities they were not receiving any type of intervention during the period. After completing all the intervention sessions, all measurements (Raven’s coloured progressive matrices, behavioural problem checklist and DTLD) were again administered on both the groups for the postcondition data. The responses were coded by the scoring pattern given in the manual. Three months after the end of intervention sessions, a post-test assessment was done by questionnaire for both groups.
Statistical Analysis
The data were analyzed by ANOVA, Wilcoxon signed-rank test statistics on the pre-post scores of learning disability test, intelligence scale and behavioural problem for Indian children with the help of SPSS 16 V. The level of statistical significance was set at a p-value less than 0.05.
Results
The participants in this study, who were residents of Chhattisgarh, included 56 students with writing disabilities between the ages of 8 and 11 years (male, n=31; female, n=25) who were attending schools education in Chhattisgarh. Details of the participant with regards to demographics are shown in Table 1 (see table-1).
The Kolmogorov-Smirnov test and Levene's test were used to determine the normal distribution and Homogeneity of Variances of data. Due to the normality of data distribution of the Placebo group, parametric tests were used to analyze the data.
The Significant value of Levene's test of homogeneity of variance indicates that the finding would alert us to the fact that the sampling distribution might be not normal in overall EHC score of the experimental group. Further normality test of normal distribution in EHC subtest also reveals that the data is not normally distributed this permission to use the non-parametric test. For this purpose the nonparametric test of difference viz. Wilcoxon Signed Ranks Test was worked out to find the significance of the difference between pre and post condition in EHC subtest of the experimental group.
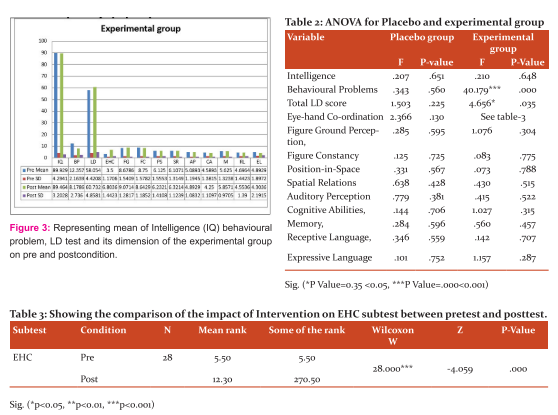
Figure-2 and table-2 show the results of the mean value of intelligence, behavioural problems, learning disability and its dimensions. Table-2 shows a small non-significant change in mean value on post-intervention for the placebo group.
The results in behavioural problems show a significant decrease in post-intervention for the experimental group (see table-2). The mean of post-intervention behavioural problems score was lower than the mean of pre-intervention behavioural problems scores (see figure-2). The results in the total LD score show a significant increase in post-intervention for the experimental group (see table-2). The mean of post-intervention total LD scores was slightly higher than the mean of pre-intervention total LD scores (see figure-3). But, the results in figure-ground perception, figure constancy, position-in-space, spatial relations, auditory perception, cognitive abilities, memory, receptive language, expressive language and intelligence showed a small non-significant change on post-intervention for the experimental group (see figure-2 and table-2).
The results in eye-hand coordination show a significant increase in post-intervention for the experimental group (see table-3). The mean rank of post-intervention eye-hand coordination scores was higher than the mean rank of pre-intervention eye-hand coordination scores (see figure-2).
Discussion
The main objective of the present study was to examine the effectiveness of Behavioral Intervention with fine motor training on learning disability test, behavioural problem and intelligence among children with Dysgraphia. These results demonstrate that increased eye-hand coordination (EHC) with fine motor development help to reduce behavioural problems. Regular physical activity and exercise help to increase adaptation and emotional stability by relieving psychological tension, anxiety, and fatigue23,24. The basic reason for the results is relaxation training because the study reported four weeks of relaxation training affects HPA- Hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal Axis by decreasing the level of Salivary Cortisol. Cortisol is a reliable physiological marker of stress. Cortisol play important role in the development and expression of a sequence of behavioural changes25.
The experimental group reported an increase in their scores in EHC sub-tests. This study has consisted of the findings of previous studies who reported that the EHC can be enhanced through exercises or EHC training26,27. The significant difference was reported between Pre-Test and Post-Test scores of children concerning the four components of fine motor skills after Activity-based program28. Reasons for this result which could be attributed by the fine motor training and to the growing age. Some children immediate increase from their pre-class to next grade class or they pass from first-class to another class so that their brain, cognition and motivational beliefs (MB) develop and it may prevent the difficulties in writing. Influential effect on the improvement of their individual and educational behaviour can be produced by awareness of the quality of MB creation in the children29. Research related to the brain has shown that as learners to be able to connect to our world through our senses and continually make more sense of it through strengthening and building upon neural pathways. The study reported coordination of small muscle movement which occurs in fingers in coordination with the movement of eyes can be defined as fine motor skills30. The utility of writing, grasping small objects and fastening clothing skills involved in the small muscles of the body31,32. The fine motor skills involve strength, fine motor control, and dexterity. In this study, Fine Motor training includes; the ability of the eyes to follow and focus on an object in the field of vision as required for Ocular Motor Placebo and activities with the hands guided by the eyes requiring accuracy in placement direction and spatial awareness to execute hand-eye coordination. Accurately manipulate the hands and fingers for neat handwriting, drawing, typing skills ability can improve manual dexterity. The intervention group did not found any significant change in IQ. Because the review of the literature does not found in the improvement in the Intelligence yet the tasks included are aimed at delivering the cognitive stimulation which may affect the intelligence scores of the subject. The studies in which the fine motor training is used as an intervention module are also tested on the IQ but that is on the cognitive assessment system, which does not provide the traditional IQ scores. Therefore, it cannot be generalized that this behavioural intervention with the fine motor can enhance the IQ scores. Limitations of this study include the administration of assessment tools that have been not been specifically validated in a Hindi medium Indian context. Another limitation was the underrepresentation of ages (8-11) in the sample which could limit the generalisability across ages. The lesser number of participants may have affected the statistical result.
Conclusions
Findings of the research empirically prove that activity had a positive effect in enhancing the EHC and reducing the behavioral problem in children with Dysgraphia. Overall this study’s findings point behavioural intervention with activity-based fine motor training as a possible useful technique, with good acceptance by children, which can be used by campus health services to create a response to reduce students’ behavioural problems.
Abbreviations:
Diagnostic test of learning disabilities (DTLD); Eye-hand Co-ordination(ECH); Figure Ground Perception(FG); Figure Constancy(FC); Position-in-Space(PS); Spatial Relations(SR); Auditory Perception(AP); Cognitive Abilities(CA); Memory(M); Receptive Language(RL); Expressive Language(EL); Behavioral Problems(BP); Intelligence(IQ) .
Acknowledgement:
Authors acknowledge the immense help received from the scholars whose articles are cited and included in references to this manuscript. The authors are also grateful to authors/editors/publishers of all those articles, journals and books from where the literature for this article has been reviewed and discussed.
Contribution of authors:
All the authors equally contributed in planning, data collection, data processing and writing the manuscript.
Conflict of interest
There were no conflicts of interest to declare.
Sources of financial support- None
Compliance with Ethical Standards
Informed consent: All participants gave written informed consent.
Ethical consideration: The study was approved by the Institutional Ethics Committee, (Pt. Ravishankar Shukla University Raipur, India No.6917/Acad.Ph.D./2018).
What is already known?
• Students of learning disabilities may suffer from emotional problems and behavioural problem and associated with psychological comorbidities
Novelty
• Behavioral intervention with activity-based fine motor training to be useful in the classroom.
• The research empirically proves that activity had a positive effect in enhancing the EHC and overall psychological health with reducing behavioural problems.
What are the future clinical and research implications of the study findings?
-
Overall this study’s findings point behavioural intervention with activity-based fine motor training as a possible useful technique, with good acceptance by children, which can be used by campus health services to create a response to reduce students’ behavioural problems.


References:
-
Himanshu. Delhi performs poorly on development, Hindustan Times, 25 August, 3. 2006.
-
McGee R, William S, Share DL, Anderson J, Silva P. The relationship between specific reading retardation, general reading backwardness and behavioural problems in a large sample of Dunedin boys: A longitudinal study from 5-11 years. J Child Psychol Psychiatry. 1986; 27: 597.
-
Rutter M. Emotional disorder and educational underachievement. Arch Dis Child. 1974; 49: 249-56.
-
Willcutt EG, Pennington BF. Psychiatric comorbidity in children and adolescents with reading disability. J Child Psychol Psychiatry. 2000; 41: 1039-48.
-
Girod CM. Diseases and disorders: Learning disabilities. 2001; SanDiego: Lucent Books.
-
Landau E. Dyslexia. New York: Franklin Watts. National Dissemination Center for Children with Disabilities.2004; http://nichcy.org/disability/specific/ohi
-
Daniel SS, Walsh AK, Goldston DB, Arnold EM, Reboussin BA, Wood FB. Suicidality, school dropout, and reading problems among adolescents. J Learn Disabil. 2006; 39(6): 507-14.
-
Kohli A, Sharma S, Padhy SK. Specific learning disabilities: Issues that remain unanswered. Indian J Psychol Med. 2018; 40: 399-405.
-
Das JP, Denyse VH, George KG, Troy J, Boora N. Comparing the effectiveness of two reading intervention programs for children with reading disabilities, Educaciony Diversidad. 2009; 3: 15-36.
-
Mahapatra S, Das JP, Stack-Cutler H, Parri S, la R. Remediating reading comprehension difficulties. A cognitive processing approach. Reading Psychology. 2010; 31: 428- 453.
-
Das JP, Hayward DV, Georgiou GK. Comparing the effectiveness of two reading intervention programs for children with reading disabilities. Education y Diversidad 2009; 3:15-36.
-
Das JP, Mishra RK, Pool JE. An Experiment in Cognitive Remediation of Word-Reading Difficulty. Journal of Learning Disabilities. 1995; 28: 66-79.
-
Graham S. Strategy instruction and the teaching of writing, In C. MacArthur, S. Graham, 472 Summer & J. Fitzgerald (Eds.), Handbook of writing research: New York, NY: Guilford.2014: 187–207.
-
Graham S, Harris KR. Students with learning disabilities and the process of writing: A meta-analysis of SRSD studies (Eds.). Handbook of learning disabilities, New York, NY: Guilford. 2003; 323–344.
-
Graham S, McKeown D, Kiuhara, SA, Harris KR. A meta-analysis of writing instruction for students in the elementary grades. Journal of Educational Psychology. 2012; 104:879-896.
-
Graham S, Perin D. A meta-analysis of writing instruction for adolescent students. Journal of Educational Psychology. 2007; 99: 445–476.
-
Gersten R, and Baker S. Teaching expressive writing to students with learning disabilities: A meta-analysis. The Elementary School Journal. 2001; 101: 251–272.
-
Shetty A, Rai BS. Awareness and knowledge of attention deficit hyperactivity disorders among primary school teachers in India. International journal of current research review 2014; 6(09):30-36.
-
Padhy SK, Goel S, Das SS, Sarkar S, Sharma V, Panigrahi M. Prevalence and Patterns of Learning Disabilities in School Children. Indian J Pediatr. 2016; 83(4): 300-6.
-
Pueyo R. Junque C. Vendrell P. Narberhaus A. Segarra D. Raven's Coloured Progressive Matrices as a measure of cognitive functioning in Cerebral Palsy. Journal of intellectual disability research 2008; 52 (5): 437-445.
-
Swarup S, Mehta DH. The diagnostic test of learning disability, Manual (16-0231-M). Prasad Psycho Corporation. 2008.
-
Parimu B, Anuradha S. Effect of Intervention Strategies on Learning Disabilities and Associated Problems. 2011 https://shodhganga.inflibnet.ac.in/handle/10603/58193
-
Park SH, Kim EH. Emotional and behaviour problems expressing in male and female student with intellectual disabilities. J Intellect Disablil. 2012;14:157-176.
-
Jeoung BJ. Effect of SPARK program on health-related physical fitness and CBCL (child behaviour checklist) of students with intellectual disabilities. J Korean Phys Edu Society 2014; 28(4): 167-177.
-
Burgese DF, Bassitt DP. Variation of plasma cortisol levels in patients with depression after treatment with bilateral electroconvulsive therapy. Trends Psychiatry Psychother. 2015; 37(1): 27-36.
-
Lee KY. Hui-Chan CW, Tsang WW. The effects of practising sitting Tai Chi on balance control and eye-hand coordination in older adults: a randomized controlled trial. Disabil Rehabil. 2015; 37(9):790–4.
-
Tsang WW, Wong GC, Gao, KL. Mahjong playing and eye-hand coordination in older adults- A cross-sectional study. J Phys Ther Sci. 2016; 28(10): 2955–60.
-
Kareem J. Shruthi, Shree N. Effectiveness of the activity-based program in enhancing fine motor skills of children with dyspraxia. Scholedge international journal of multidisciplinary & allied studies 2015; 2(5):2394-336.
-
Ghorbanshiroudi S. Comparison of Motivational Beliefs in Self-regulation Learning between Intelligent, Learning-Disabled And Normal Students In Primary School In Rasht. International Journal of Current Research and Review 2012; 4(6):6-19.
-
Rogers L, Graham S. A meta-analysis of single-subject design writing intervention research. Journal of Educational Psychology 2008; 100: 879–906.
-
Kids Health. "Movement, Coordination, and Your Newborn. 2012. http://www.kidshealth.org/parent/growth/movement/movenewborn.html.
-
Gopalakrishnan Nair TR, Sowjanya Rao N, Bukkambudhi A. Enhancing Fine Motor Skills of Wards with Special Needs Using Cluster Model of Cognition. International Conference - TeamTech Bangalore, 2009.
|






 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License