IJCRR - 12(18), September, 2020
Pages: 48-54
Date of Publication: 22-Sep-2020
Print Article
Download XML Download PDF
Green Tea Enhances Nutritional and Antioxidant Potential of Pearl Millet Based Cookies: A Healthy Approach
Author: Jigisha Anand, Gargi Kandwal, Manya Nath, Vijay Kumar, Jaya Sinha, Sanjay Kumar, Nishant Rai
Category: Healthcare
Abstract:Background: The study aimed to prepare cookies with high-quality ingredients which are a rich source of nutrition and have a good shelf life. The study proposed a healthy composition of cookies by incorporating antioxidant-rich green tea while replacing usual principal ingredients like all-purpose flour with cereals like Pearl Millet (Bajra) and oats while substituting unhealthy refined sugar with healthy powdered jaggery. The study thus evaluated the health benefits of green tea cookies based on their nutritional value and sensory analysis. Method and Materials: Cookies composed of five different compositions with varying concentrations of green tea, pearl millets, oats, jaggery, and other ingredients were prepared. Their physicochemical studies like change in width, density, thickness, volume, spread ratio, baking weight loss, fat, and ash contents were evaluated using standard protocols. Total flavonoid content, total phenolic content, and antioxidant activities of all cookies were determined. The sensory analysis was performed for all the five samples of cookies by Preference Tests-9 point hedonic rating. Results: There was a significant increase in TPC, TFC, and antioxidant activity. The sensory profile showed likeliness for these cookies. Conclusion: It can be inferred from the study that substituting pearl millet, oats, and jaggery with the normal ingredients enhanced the nutritional value and the likeliness of the cookies. Further incorporating green tea extract improved the quality of cookies and thus these cookies could be the promising source of healthy antioxidants.
Keywords: Antioxidant, Cookies, Green tea, Jaggery, Pearl millet, Sesame.
Full Text:
INTRODUCTION
In today’s lifestyle, continuous stress, and negligence of a healthy diet have led to cause many diseases such as hypertension, diabetes, obesity etc.1. Cookies are one of the convenient and tasteful delicacies in our daily appetite. Moreover, owing to its wide utility, health prospect has become an important aspect and therefore emphasis is being made to enhance the nutritive value of the cookies2, 3.
The market of cookies is one of the rapidly growing sectors in the fast-moving consumer goods (FMCG) category, while it is expected that the compound annual growth rate of the global packaged bakery products market will be 4.6% during the period 2017-20254. It is known that many cookies contain industrial pollution or they are made from unhealthy all-purpose flour5. Health experts never support the idea of having cookies made from all-purpose flour due to its side effects. Therefore this research is based on making cookies that are baked and contain a high nutritional value which imposes beneficial health effects of rich antioxidants.
In the past several years, the concept of multigrain cookies has emerged tremendously and claimed to be rich in energy, fiber, and carbohydrates; these cookies are now widely accepted by the consumers. Nutritious cookies could be made by substituting all-purpose flour with some other products like Pearl Millet Bajra, oats which are rich in fiber and filled with nutrition6.
Green tea is now considered as the world’s healthiest drink because of the presence of the highest amounts of antioxidants of any tea. Green tea contains 20-45 percent polyphenols of which 60-80 percent are catechins such as epigallocatechin gallate (EGCG) which are credited with its rich antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and anti-carcinogenic effects7.
The EGCG contains healthy bioactive compounds that increase metabolism and reduces the rate of diseases such as diabetes, Alzheimer’s, heart disease and maintain the blood pressure7, 8. Likewise, sesame seed provides a good source of vitamin E, boost digestion, strengthens bones, and prevent disease such as cancer9. Jaggery (gur) is a natural sweetener that is made up of concentrated sugarcane juice. Jaggery contains minerals and vitamins which are good for our health and it is also called “medicinal sugar” because of its use in Ayurveda10.
Pearl millet, commonly known as ‘Bajra’ in the Indian sub-continent, is a high energy cereal known for its rich nutritive value. It comprises of protein (12-16%), fats (4-6%), vitamin B1(0.25mg), vitamin B2 (0.20mg), Vitamin B3(0.86mg), vitamin B6 (0.50mg), carotenoids (293µg), carbohydrates (0.81g), and minerals, dietary fiber and polyphenols (0.2-0.3%)11. Besides, their rich nutritional attributes, millets confer increase antioxidant activity and helps in curing metabolic diseases, cardiovascular disorders, diabetes etc12.
Oats are known scientifically as Avena sativa and contain many components contributing to health benefits. The soluble fiber in oats is β-glucan, which helps in slow digestion, increase sufficiency, and subdue appetite. β-glucan binds with the cholesterol-rich bile acids present in the intestine and transports it through the digestive tract and at the end out of the body13. Whole oats commonly called rolled oats contain phenolic compounds and phytoestrogens having antioxidant properties that reduce the damaging effects of chronic inflammation which is associated with various diseases like cardiovascular disease and diabetes14.
Jaggery contains more nutrients than refined sugar because of its molasses content and is a sweetener now popular as a "healthy" replacement for sugar. Molasses is a nutritious by-product of the sugar-making process and, unlike refined sugar; it is rich in micronutrients, minerals, and vitamins15.
Sesame seed or “Til’, is a rich source of protein. It has a non-culinary application. The seeds contain Sesamin and Sesamolin having a cholesterol-lowering effect in humans and the prevention of high blood pressure16.
Fennel seeds or “Suaf’ indeed contain numerous flavonoids, anti-oxidant like kaempferol and quercetin. These compounds function as a powerful antioxidant agent. Fennel seeds are also a rich source of dietary fibre, resistant to digestion and re-absorption in the colon which contributes to lowering serum LDL cholesterol levels17.
The present study addresses the enhancement of green tea, pearl millet, oats, sesame seed, fennel seeds, and jaggery in green tea-based cookies (GTC) preparation. The study aims to investigate the effect of all the above ingredients on quality attributes of green tea-based cookies (GTC).
MATERIALS AND METHOD
The materials used for making cookies i.e. green tea, pearl millet flour, oats, jaggery, sesame seeds, fennel seeds, refined flour, and unsalted butter were procured from the local market Dehradun. All the chemicals used in the present study were purchased from Hi-Media, India.
Preparation of Green tea cookies (GTC)
The green tea cookies i.e. GTC-A, GTC-B, GTC-C, GTC-D, and GTC-E were prepared by mixing all the ingredients in a proper ratio and baked it at 170°C for 15-20 min5. The prepared green tea cookies were packed in food grade bags and stored at room temperature in an airtight container for further analysis (Table 1).
Physicochemical analysis of Green tea cookies (GTC)
The prepared cookies were analyzed based on the change in density, thickness, width, volume, spread factor, baking weight loss18. Density was calculated using the formula; Density= Mass/Volume. The diameter was measured using a vernier calliper. The thickness of biscuits (T) was measured in triplicate and means were recorded. Spread ratio (Sr) was calculated using the formula:
Sr= D/T
Volume (V) was calculated using the formula:
V = (D2 π T)/4
Baking weight loss (BWL) was determined by measuring the weight of the biscuit before and after baking.
It was calculated using equation:
BWL (%) = (w0-wt)/w0 × 100
where, w0 = initial weight (g) of cookie and wt = weight (g) after baking19.
Moisture content was measured by hot air oven drying method20.
Total ash and fat content were determined by AOAC method21.
Total flavonoid content:
For TFC estimation, calibration curve was plotted at 0.0156, 00312, 0.0625, 0.125, 0.25, 0.5, and 1.0 mg/ml concentration of hydrated catechins (as standard) respectively. 100 µl of the GTC sample at the concentration of 1 mg/ml was taken and mixed with 400 µl of distilled water. To the above mix, 30 µl of 7% sodium nitrate was added and was incubated for 5min. Further 30µl of 10% aluminium chloride was added and incubated for 5 min. Then, 20 µl of 4% NaOH was added. Volume makeup was done to 1 ml by adding 420 µl of distilled water. To calculate the TFC optical density was recorded at 570 nm. Triplicate measurements were carried out and total phenolic content was expressed as milligram of catechin22.
Total phenolic content:
Determination of total phenolic content was carried out using Folin–Ciocalteu reagent (FCR) assay. 20 µl of the cookies (stock solution 1mg/ml) was dissolved in 80 µl of water and 500 µl of FCR was added. The solutions were mixed followed by incubation in dark at room temperature for 5 minutes. After incubation, 400 µl of 7.5% Na2CO3 solution was added and kept for further incubation in dark for 30 minutes at room temperature. The absorbance was recorded at 765 nm using a colourimeter. Gallic acid (as standard) was used for the calibration curve that is plotted at 0.0156, 00312, 0.0625, 0.125, 0.25, 0.5, and 1.0 mg/ml of concentration respectively. The measurements were taken in triplicate and total phenolic content was expressed as milligram of gallic acid equivalents (GAE) per gram of samples22.
DPPH
DPPH is highly photosensitive; therefore all the procedures were done in dark. DPPH solution was prepared by dissolving 2.4 mg of DPPH in 50 ml of 100% methanol. Ascorbic acid served as the standard. Both samples and standards were prepared in a concentration of 1mg/ml. The standard was then diluted by using half fold dilution method. 100µl of GTC sample was taken and 1900 µl of DPPH solution was added. All the treated test samples and standard dilutions were incubated for 2 hours in dark. After incubation, the O.D was recorded at 517nm. The calibration curve of standard was plotted at 0.0156, 00312, 0.0625, 0.125, 0.25, 0.5, and 1.0 mg/ml of concentration respectively22. Measurements were taken in triplicate and the percentage scavenging effect was determined using the formula:
scavenging rate (%) = [(A0 - A1)/A0] / 100
where A0 = Absorbance of the control (without extract)
A1 =Absorbance in the presence of the extract
Sensory analysis
Sensory analysis was performed for all the five samples of cookies by Preference Tests -9 point hedonic rating. Nine different people and their responses were recorded in context to the three main attributes that are colour, taste, and flavour23.
Statistical analysis:
All the estimated data was statistically analyzed accordingly using ANONA two-way analysis (with duplicates) and t-test. All the parameter scores were expressed in terms of Mean ±SD 2The statistical significance was set at a 5% level of significance (p<0.05).
RESULTS
Density, spread ratio, and baking weight loss
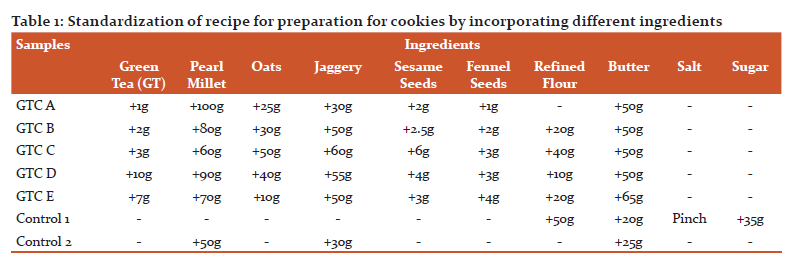
After baking it was observed that the thicknesses of cookies were increased thus the spread ratio of GTC and control cookies decreases after baking. The spread ratio ranges from 2.41 – 2.67 (Table 2) which are in the range of control cookies. P-value was observed less than 0.05, thus there is a significant difference in the values of spread ratio studies for different GTC and control cookies samples. The changes in the spread ratio are represented in Figure 1.
Due to loss in baking weight the density of control and GTC cookies after baking is less than before baking. The density ranges from 0.69 to 0.78 g/cm3 which are in the range of control cookies (table 2). The P-value was observed less than 0.05, thus there is a significant difference in the values of densities studies for different GTC and control cookies samples. The changes in the density are represented in Figure 2.
The baking weight loss of different GTC and control cookies ranged from 2.66% - 25.21% (table 2). It was observed that baking weight loss is very low in the case of control 2 cookies and maximum in the case of GTC-C. There was a significant difference (p≤0.05) in the values of baking weight loss for different GTC and control cookies samples. The changes in baking weight loss are represented in Figure 3.
Chemical analysis
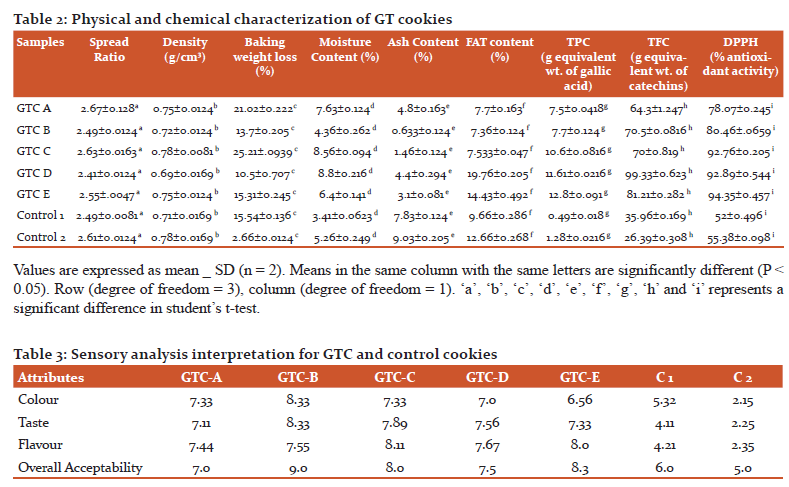
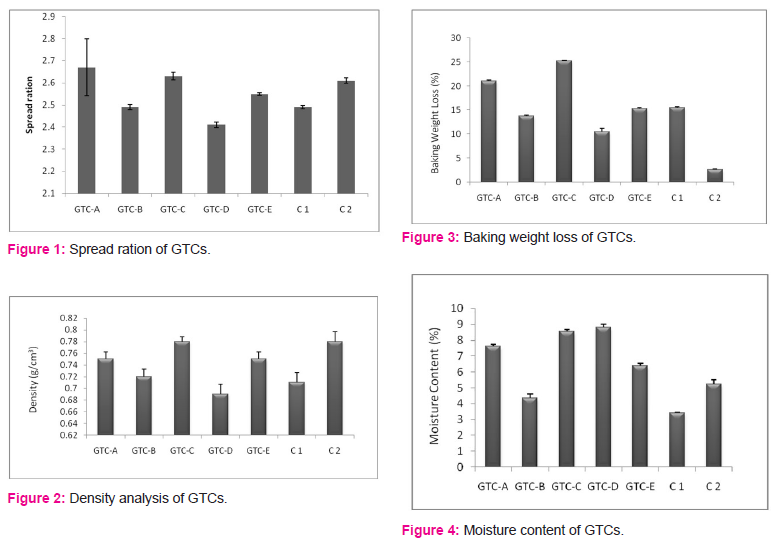
The moisture content of the GTC and control cookies varies from 3.41% to 8.8% (Table 2). There was a significant difference (p≤0.05) in the values of moisture content for different GTC and control cookies samples. The changes in moisture content are represented in Figure 4.The value of ash content varies from 0.633% to 9.03% (table 2) for different GTC and control cookies samples. The variations in ash content are represented in Figure 5, which was at 5% (p≤0.05) level of significance.
The value of fat content decreases from 7.36% to 19.76% (Table 2). The variations in fat content are represented in Figure 6 which was at 5% (p≤0.05) level of significance.
Quantitative analysis
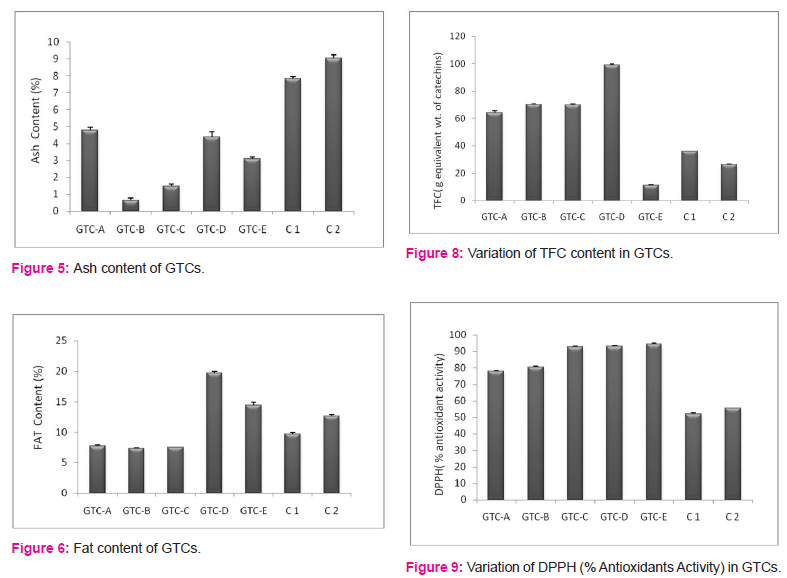
The study showed high polyphenolic and flavonoid contents in cookies with an increased concentration of green tea (Figure 7 and Figure 8). The quantitative evaluation revealed a significant difference in TPC, TFC, and antioxidant activity of GTC with the varying concentration of green tea (Table 2). In comparison to the control cookies, the TPC in GT cookies was recorded in between 64.3±1.247 and 99.33±0.62 g equivalent weight of gallic acid. The TFC was evaluated ranging from 7.5±0.41 and 12.8±0.091 g equivalent weight of catechins. The antioxidant activity was analyzed using DPPH free radical scavenging assay. The percentage of antioxidant activity was revealed between 78.07±0.245% and 94.35±0.457% (Figure 9).
The study demonstrated that out of five different GT cookies, GTC-C, GTC-D, and GTC-E demonstrated high antioxidant activity with considerable high phenolic and flavonoid content.
Sensory analysis:
The study represents the sensory ratings of GTC, and control cookies for all selected sensory attributes i.e., colour, taste, flavour, and overall acceptability. In the control cookies, (sample C1 and C2) the averaged score for colour, taste, flavour, and overall acceptability average score was 6.0 and 5.0 which is lower than GTC-A, GTC-B, GTC-C, GTC-D, and GTC-E (table 3). For control samples, C1 and C2 the averaged score for colour, taste, and flavour are also very low in comparison to GTC. Among the five GTC’s, GTC-B gained the highest score (9.0) for overall acceptability (Table 3). The least average sensory scores were recorded to the GTC-A followed by GTC- D. The overall sensory result is represented by the radar chart (Figure 10). It was inferred that among all the green tea enriched cookies, and control cookies, GTC-B was most liked by all panel members and thus could be considered to be the best cookies with promising acceptability among the consumers.
DISCUSSION:
In the present study, we evaluated the nutritional and health potential of green tea consisting of pearl millet cookies considering p<0.05 level of significance. Pearl millet is an important source of iron, zinc, and micronutrients which is a low-cost substitute for wheat or maize24. Rich in multi-vitamins and proteins, cookies prepared with pearl millet is an excellent source of energy27.
Green tea is known for its abundant free radical scavenging activity28 as the role of antioxidants in minimizing the oxidative stress in various disease conditions like diabetes, cataract, inflammatory conditions, AIDS, and mutagenic effects of reactive oxygen species are already known29. In our study, we found significantly higher DPPH free radical scavenging activity in all GTC. There is a strong correlation between antioxidant activity and TPC/TFC. With an increasing concentration of green tea, there was an increase in the TPC, and TFC of cookies25,26.
Although, the study revealed a significant difference in the antioxidant potential, the sensory profile of all the prepared cookies demonstrated that cookies with higher green tea content were less liked by the panel members. The variation in sensory ratings of different GTC could be attributed to the presence of a varying concentration of polyphenols in subsequent cookie products which resulted in distinctive sensory properties of GTC30, 31, 32. The control cookies without green tea were found less acceptable in terms of its taste, and flavour in comparison to the other GTC.
CONCLUSION:
The present study demonstrated the health benefits of green tea and pearl millet cookies based on their nutritional value and other sensory analysis. It was observed that replacing regular ingredients of cookies like refined flour, refined sugar with healthy alternatives such as green tea, pearl millet, oats, and jaggery powder exhibited improved nutritional properties and the likeliness of the cookies. Moreover, the study suggests that the incorporation of green tea enhances polyphenolic and flavonoid contents of the cookies; hence the green tea enriched cookies could be a promising and healthy source of rich antioxidants.
ACKNOWLEDGMENT: We would like to thanks the Department of Biotechnology and the Department of Life Sciences, Graphic Era (Deemed to be University) for providing all the technical facilities.
ABBREVIATIONS:
A.A.C.C-American Association of Cereal Chemists
AOAC- Association of Official Agricultural Chemists
DPPH- 2, 2-diphenyl-1-picrylhydrazyl
EGCG- Epigallocatechin gallate
FCR- Folin–Ciocalteu reagent
GAE- Galic acid equivalent
GTC- Green tea cookies
O.D- Optical density
TFC- Total Flavonoid content
TPC- Total Phenolic content
CONFLICT OF INTEREST: Authors declare no conflict of interest.

References:
-
Rosiek A, Maciejewska FM, Leksowski K, Rosiek-Kryszewska A and Leksowski L. Effect of Television on Obesity and Excess of Weight and Consequences of Health. Int J Environ Res Pub Health 2015; 12: 9408-9426.
-
Boobier WJ, Baker JS, Davies B. Development of a healthy biscuit: an alternative approach to biscuit manufacture. Nutrition J 2006; 5(7): 1-7.
-
Kulthe AA, Pawar VD, Kotecha PM, Chavan UD, Bansode VV. Development of high protein and low-calorie cookies. J Food Sci Technol 2014; 51(1):153-157.
-
Global Bakery Products Industry Outlook to 2025 - Growing Demand for RTE Foods Boost Demand for Wafer Biscuits. May 01, 2020. Research and Markets. Global news wire.
-
Kohli D, Kumar A, Kumar S, Upadhaya S. Waste Utilization of Amla Pomace and Germinated Finger Millets for Value Addition of Biscuits. Curr Res Nutr Food Sci 2019; 7(1): 272-279.
-
Kaur KD, Jha A, Sabikhi L, Singh AK. Significance of coarse cereals in health and nutrition: a review. J Food Sci Technol 2014; 51(8):1429-1441.
-
Anand J, Choudhary S, Rai, N. Lantana C, Enhances antibacterial potency of antibiotics and exerts synergistic inhibitory effect against pathogenic bacterial species. Orient Pharm Exp Med 2018; 18: 381–389.
-
Ikbal A, Roy S, Pat K. Health benefits of green tea: A mini-review. J Entomol Zoo Studies 2020; 8(1): 1424-1430.
-
Hsu E, Parthasarathy S. Anti-inflammatory and Antioxidant Effects of Sesame Oil on Atherosclerosis: A Descriptive Literature Review. Cureu. 2017; 9(7):1438.
-
Lamdande AG, Khabeer ST, Kulathooran R, Dasappa I. Effect of replacement of sugar with jaggery on pasting properties of wheat flour, physico-sensory and storage characteristics of muffins. J Food Sci Technol 2018; 55(8): 3144-3153.
-
Kumar A, Tomer V Kaur, A. et al. Millets: A solution to agrarian and nutritional challenges. Agric Food Secur 2018; 7: 31.
-
Chandrasekara A, Shahidi F. Bioaccessibility and antioxidant potential of millet grain phenolics as affected by simulated in vitro digestion and microbial fermentation. J Funct Food 2012; 4: 226-237.
-
Tiwari PK, Sahu RK, Sandey KK, Tiwari RK. Importance of Oats in Human Diet: A Review. Bull. Env. Pharmacol. Life Sci 2017; 7(1): 125-130.
-
Meydani M. Potential health benefits of avenanthramides of oats. Nutr Rev 2009; 67(12):731-735.
-
Mahalaxmi BK and Hemalatha S. Standardization and Nutritional Characteristics of Organic Jaggery Millet Cookies. Int J Pure App Biosci 2019; 7(3): 383-390.
-
Pathak N, Rai AK, Kumari R, Bhat KV. Value addition in sesame: A perspective on bioactive components for enhancing utility and profitability. Pharmacogn Rev 2014; 8(16):147-155.
-
Lattime JM, Haub MD. Effects of Dietary Fiber and Its Components on Metabolic Health Nutr 2010; 2(12): 1266–1289.
-
Approved methods of American Association of Cereal Chemists (10th ed.). Published by American Association of Cereal Chemists, Ins. Saint Paul, Minnesota, 2000, USA.
-
Tanska M, Roszkowska B, Czaplicki S, Borowska EJ, Bojarska J, D?browska A. Effect of Fruit Pomace Addition on Shortbread Cookies to Improve Their Physical and Nutritional Values. Plant Foods Hum Nutr 2016; 71: 307–313.
-
Talpur MA, Changying J, Chandio FA, Junejo SA, Mari IA. Application of oven drying method on moisture content of ungrounded and grounded (long and short) rice for storage. J Stored Prod Postharvest Res 2011; 2(12): 245 - 247.
-
AOAC International. Official methods of analysis, 18th edn, 2005; Current through revision 2, 2007 (Online). AOAC International, Gaithersburg, MD.
-
Anand J, Upadhayaya B, Rawat P, Rai N. Biochemical characterization and pharmacognostic evaluation of purified catechins in green tea (Camellia sinensis) cultivars of India. 3 Biotech 2015; 5 (3): 285- 294.
-
Pereira EA, Roncatti R, Todescatto C, Beux S, Marchi JF, Daltoe MLM. Acceptance of Santo Giorno cheese typical of the Southwestern region of Parana, Brazil. Ciencia Rural Santa Maria 2017; 47: (04) e20160418.
-
Krishnan R, Meera MS. Pearl millet minerals: effect of processing on bioaccessibility. J Food Sci Technol 2018; 55(9): 3362-3372.
-
Rai KN, Gowda CLL, Reddy BVS, Sehgal S. Adaptation and potential uses of sorghum and pearl millet in alternative and health foods. Comp Rev Food Sci Food Safety 2008; (7): 340–352.
-
Lorenzo JM, Munekata PES. Phenolic compounds of green tea: Health benefits and technological application in food. Asian Pacific J Trop Biomed 2016; 6 (8): 709-719.
-
Neeraj, Pramod J, Singh S, Singh J. Role of free radicals and antioxidants in human health and disease. Int J Curr Res Rev 2013; 5 (19):14-22.
-
Ahmad M, Baba WN, A Wani T, et al. Effect of green tea powder on thermal, rheological & functional properties of wheat flour and physical, nutraceutical & sensory analysis of cookies. J Food Sci Technol 2015; 52(9): 5799-5807.
-
Zhao CN, Tang GY, Cao SY, et al. Phenolic Profiles and Antioxidant Activities of 30 Tea Infusions from Green, Black, Oolong, White, Yellow and Dark Teas. Antioxidants (Basel) 2019; 8(7): 215.
-
Atoui AK, Mansouri A, Boskou G, Kefalas P. Tea and herbal infusions: Their antioxidant activity and phenolic profile. Food Chem 2005; (89): 27–36.
-
Zhang YT, Li Q, Xing H, Lu XF, Zhao LS, Qu KK, Bi KS. Evaluation of the antioxidant activity of ten compounds in different tea samples using an on-line HPLC-DPPH assay. Food Res Int 2013; (53): 847–856.
32. Zhang C, Suen CL, Yang C, Quek SY. Antioxidant capacity and major polyphenol composition of teas as affected by geographical location, plantation elevation and leaf grade. Food Chem 2018; 244:109-119.
|






 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License