IJCRR - 12(14), July, 2020
Pages: 17-22
Date of Publication: 22-Jul-2020
Print Article
Download XML Download PDF
Clinical Profile and Laboratory Investigations of Acute Dyspnea Patients: A Hospital Based Study
Author: Kiran Kumar K V
Category: Healthcare
Abstract:Background: Dyspnea is a common symptom in hospitalized adult patients and is among the most serious, as it is often a harbinger of severe pathology. Prevalence of dyspnea varies among clinical settings and patient subgroups; in the community 3% to 25%, outpatient clinics 3.7%, emergency rooms 2.7%, and at hospital admissions 15% to 25%. The study of clinical and laboratory profiles of dyspnea patients is essential for a community practice.
Objectives:
1. To study the clinical profile of acute dyspnea patients
2. To evaluate the underlying etiopathology of acute dyspnea
Materials and Methods: This observational study was be conducted at K.V.G. Medical College & Hospital, Sullia on 150 subjects from March 2016 \? Dec 2016.
Result: In the present study, 43 patients had fever, 132 patients had cough, 127 patients had sputum, 11 patients had Hemoptysis, 52 patients had PND, 34 patients had chest pain and 8 patients had syncope as a presentational symptom. Mean heart rate was 111.38/min, SBP was 135.36 mmHg, DBP was 88.85 mmHg, Respiratory rate was 29.48/min. Sp02 was 88.91. Analysis of ECG showed, 24 patients (16.00%) had LVH,29 patients (19.33%) had ST Elevation, 12 patients (8.00%) had T wave inversion, 12 patients (8.00%) had LAD, 34 patients (22.67%) had RAD, 6 patients (4.00%) had CHB, 4 patients (4.00%) had LBBB,17 patients (11.33%) had RBBB. 48 patients (32%) had cardiomegaly, 23 patients (15.33%) had pleural effusion,18 patients (12 %) had consolidation. Patients diagnosed with DKA had mean Ph of 7.11, Pco2 of 21.1 mmHg, and HCO3 of 9.62 mEq/Lit. When compared, patients diagnosed with Acute exacerbation of COPD and Asthma had mean pH of 7.21, Pco2 of 60.83 mmHg, and HCO3 of 24.7 mm/l. 30 patients (20.00%) were diagnosed with Acute exacerbation of COPD, 14 patients (9.33%) were diagnosed with Acute exacerbation of Asthma, 22 patients (14.67%) were diagnosed with Pneumonia, 3 patients (2.00%)were diagnosed with Pulmonary embolism, 11 patients (7.33%) were diagnosed with Pleural effusion, 6 patients (4.00%) were diagnosed with Pneumothorax, 24 patients (16.00%) were diagnosed with Acute on chronic CCF, 31 patients (20.67%) were diagnosed with MI with CCF,4 patients (2.67%)were diagnosed with DKA, 2 patients each (1.33%) were diagnosed with Uremic encephalopathy and Hepatic encephalopathy each, 1 patient. (1.33%) was diagnosed with psychogenic dyspnea. Acute exacerbation of COPD had mortality of 11.76%, Acute exacerbation of Asthma had a mortality of 13.33%, Pneumonia had a mortality of 13.64%, Pulmonary embolism had a mortality of 33.33%, Pleural effusion had a mortality of 16.67%, Pneumothorax had a mortality of 50%, Acute on chronic CCF had a mortality of 25.00%, MI with CCF had a mortality of 28.13 %, DKA had a mortality of 25.00%. Overall mortality was 20.67%.
Conclusion: The study concluded that Pneumothorax had the highest mortality (50%) followed by pulmonary embolism (33.33%) and MI with CCF (28.13%). Uremic encephalopathy, Hepatic encephalopathy and psychogenic dyspnea had the least mortality.
Keywords: Pneumonia, Clinical profile, PFT, LRTI, Dyspnea
Full Text:
INTRODUCTION
Dyspnea is the clinical term for breathlessness or shortness of breath. Dyspnoea is taken from the Greek word ‘‘dys’’ meaning painful, difficult, or disordered and ‘‘pnoea’’ meaning breathing1. The experience derives from the interactions among multiple physiological, psychological, social, and environmental factors, and may induce secondary physiological and behavioral responses” as defined by the Consensus statement of the American Thoracic Society2.
Dyspnea is one of the common symptoms in admitted patients. It is a subjective experience that may not be always consistent with physical examination. Patients describe their sensations using a variety of terms such as shortness of breath, chest tightness, increased effort of breathing, suffocation, and air hunger3.
Dyspnea is the main complaint about 75% of the ambulance service. The prevalence of dyspnea has varied greatly across geographies. The variation is attributed to differences in the distribution of concurrent factors of dyspnea such as aging, gender, and smoking. Dyspnea is extremely common with advancing disease, and at late stages is present in 90-95% of those with COPD, 60-80% of those with CHF and 10-70% of those with cancer, whilst also being common in end-stage kidney disease and most severe in primary lung cancers, affecting 90% 4.
Prevalence of dyspnea varies among clinical settings and patient subgroups; in the community 3% to 25%, outpatient clinics 3.7%, emergency rooms 2.7%, and at hospital admissions 15% to 25%. Population-based studies have shown a prevalence of 9 to 13% for mild to moderate dyspnea among community-residing adults, 15% to 18% among community-residing adults aged 40 years or older, and 25 to 37% of adults aged 70 years and older5.
AIMS AND OBJECTIVES
MATERIALS AND METHODS
This observational study was being conducted at K.V.G. Medical College & Hospital, Sullia STUDY DESIGN:
Observational descriptive study
STUDY SITE:
Emergency ward and ICU, Department of General Medicine, K.V.G. Medical College & Hospital, Sullia
DURATION OF STUDY:
March 2016 – Dec 2016
SAMPLE SIZE:
150
INCLUSION CRITERIA:
-
Patients aged 18 years or more
-
Dyspnea of < 1week in patients of both sex with age>18 with any one of the following:
-
Respiratory rate >22
-
SpO2 less than 96% in breathing room air
-
Patients giving informed consent to participate in the study
EXCLUSION CRITERIA:
-
Patients aged less than 18 years
-
Patients with dyspnea of >1 week
-
Patients admitted in the hospital who expired in less than 4 hours for whom there was no time period for laboratory evaluation.
STUDY PROCEDURE:
A detailed history of the patient will be taken and through clinical examination will be done.
Routine investigations –
-
Haemoglobin percentage
-
Total count
-
Differential count
-
Random blood sugar
-
Blood urea
-
Serum creatinine
-
Urine routine
-
Liver function test
-
SpO2 monitoring
Special investigations –
-
PCXR
-
ECG
-
Cardiac enzymes
-
ABG
-
BNP
-
D-dimer
-
Peak flow
-
Negative inspiratory force/forced vital capacity
-
Pulmonary function testing
-
Chest CT/ VQ scan/ HRCT
-
Echocardiography
DISCUSSION
The present study was conducted from March 2016 to Dec 2016 with the objective to study the clinical profile of acute dyspnea patients and to evaluate the underlying etiopathology of acute dyspnea at K.V.G. Medical College & Hospital, Sullia.
Demography
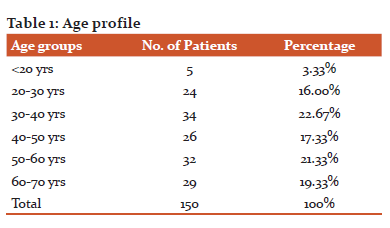
There were 5 patients within 20 years, 24 patients between 20-30 years, 34 patients between 30-40 years, 26 patients between 40-50 years, 32 patients between 50-60 years, 29 patients between 60-70 years. There were 78 male patients and 72 female patients. The mean age of patients was 61.4 years.
In the study by Shrestha et al., the mean age of patients was 63.8 years with a minimum of twenty-two and a maximum of eighty-four years. Sixty patients were female and forty were male. Anne Maree Kelly et al. found that elderly patient was represented in higher proportion compared to the younger population.
The finding that most patients are older (more than 60% aged > 60 years) is not surprising as the chronic conditions associated with dyspnea including COPD, heart failure, and acute coronary syndrome become more common with age. However, patients with DKA present with type 1 Diabetes mellitus and hence present in younger age.
Symptomology
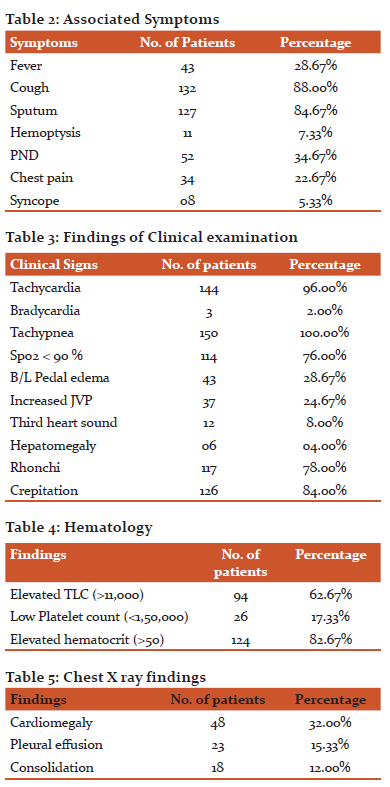
In the present study, 43 patients had fever, 132 patients had cough, 127 patients had sputum, 11 patients had Hemoptysis, 52 patients had PND, 34 patients had chest pain, and 8 patients had syncope as presentational symptom. The mean heart rate was 111.38/min, SBP was 135.36 mmHg, DBP was 88.85 mm Hg, Respiratory rate was 29.48/min. Sp02 was 88.91.
Anne Maree Kelly et al. observed that Bilateral crepitations were present in 31.5% of patients, Wheeze present in 20.4% patients, Localized rhonchi/bronchial breathing present in 3.7%, Widespread rhonchi present in 6 % of patients presenting with acute dyspnea 6.
Various studies have predicted PND has low sensitivity (<30%) but 75% specificity to diagnose heart disease7. PND and orthopnea though share a close relationship in terms of pathophysiology, they are temporally separated in most patients. Hence, the absence of PND can rule out the probability of a CCF 8,9.
Persistent Tachycardia is one of the earliest signs of acute pulmonary embolism and data from the present study substantiate it. Published Case series across the globe observed that tachycardia as a regularly associated sign of pulmonary embolism. When combined with observation of low Pa02 (< 60 mmHg), the sensitivity of the diagnosis of pulmonary embolism increases. Observations from our studies support this finding.
ECG Findings
An ECG with ST-segment changes constitutes strong evidence supporting the diagnosis of cardiac ischemia. However, clinicians must remember that neither normal biomarkers nor a non-diagnostic ECG can rule out cardiac disease in the ED. The initial ECG is normal in approximately 20 percent of patients subsequently diagnosed with myocardial infarction, and only 33 percent of initial ECGs are diagnostic. The ECG may also reveal signs of pulmonary embolism (PE) (right heart strain), pericardial effusion (diffuse low voltage, electrical alternans), and other disease processes. However, the sensitivity and specificity of the ECG for PE is limited. It is helpful to compare the ECG with prior studies.
Despite the availability of newer diagnostic tests such as radionuclide imaging and echocardiography, the ECG remains of prime importance in the evaluation of patients with suspected ischemic heart disease. Multiple studies using animal models have documented the link between ventricular repolarization and depolarization of body surface ECG tracing with transmembrane electrical recordings, which have given rise to a pathophysiological basis and explanation of ECG changes, under different clinical conditions. Although most of the ECG abnormalities detected in patients in the emergency department or CCU are caused by primary cardiac diseases, ECG changes do not invariably imply cardiac diseases.
In present study, Analysis of ECG showed, 24 patients (16.00%) had LVH,29 patients (19.33%) had ST Elevation,12 patients (8.00%) had T wave inversion, 12 patients (8.00%) had LAD, 34 patients (22.67%) had RAD,6 patients (4.00%) had CHB,4 patients (4.00%) had LBBB, 17 patients (11.33%) had RBBB. In a study of 9-year period by Malkayahalom et al., 5,400 patients were hospitalized in CCU; 1,350 were diagnosed as ST-elevation myocardial infarction (STEMI); and 4,050 patients were diagnosed as non-ST-elevation myocardial infarction (NSTEMI) 14.
In present study, ECG findings were also appreciated for pulmonary embolism and COPD ( RAD). However, S1Q3T3 pattern was not observed in the present study.
Chest Radiograph
In the present study, 48 patients (32%) had cardiomegaly, 23 patients (15.33%) had pleural effusion, and 18 patients (12%) had consolidation.
Signs of acute decompensated heart failure (ADHF) that appear on a CXR include: cardiomegaly, cephalization of blood vessels, interstitial edema, and vascular congestion. Pleural effusions may be present. Radiograph may lag behind the clinical picture and approximately 20 percent of patients admitted with ADHF have a nondiagnostic CXR. Observations from the present study showed Kerley B lines, Chest infiltrates, Cardiomegaly. However, though Lung ultrasound is more sensitive than CXR in diagnosing ADHF it was not used in the present study.
Although an infiltrate on CXR is considered the "gold standard" for diagnosing pneumonia, radiographs obtained early in the clinical course may be non-diagnostic. Volume depletion may also lead to a negative initial CXR. Recent studies have observed that contrary to past studies, the appearance of the CXR (lobar versus diffuse disease) does not accurately predict the nature of pneumonia (typical versus atypical). The present study observed non-cardiogenic infiltrates with symptoms as criteria for pneumonia.
Large lung volumes and a flattened diaphragm on CXR suggest air trapping, which occurs with COPD or asthma (10). Unilateral air trapping suggests a foreign body. Many patients with mildly or moderately severe COPD and most patients with asthma have an unremarkable CXR. However, the present study has observed hyperinflation on chest X-ray.
Arterial blood gases
In the present study, patients diagnosed with DKA had mean pH of 7.11, Pco2 of 21.1 mmHg and HCO3 of 9.62 mEq/Lit. When compared, patients diagnosed with acute exacerbation of COPD and Asthma had mean Ph of 7.21, Pco2 of 60.83 mmHg, and Hco3 of 24.7 mm/l.
In a study by Pankajseth et al. on clinical profile of DKA, mean pH was 7.13 and mean HCO3 was 12.46 mm/further, mean RBS was 535.6 mg/dl. As evident from the comparison of the present study with study by Set et al., pH and bicarbonates will be lower and Pco2 will be higher in DKA when compared to COPD patients11.
Hence, ABG is useful in the management of acute dyspnea with DKA and COPD patients which can decide upon bicarbonate infusion in DKA and Ventilator requirements in COPD patients.
Diagnosis
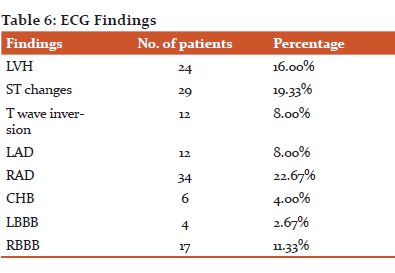
30 patients (20.00%) were diagnosed with Acute exacerbation of COPD,14 patients (9.33%) were diagnosed with Acute exacerbation of Asthma, 22 patients (14.67%) were diagnosed with Pneumonia, 3 patients (2.00%) were diagnosed with Pulmonary embolism, 11 patients (7.33%) were diagnosed with Pleural effusion, 6 patients (4.00%) were diagnosed with Pneumothorax, 24 patients (16.00%)were diagnosed with Acute on chronic CCF, 31 patients (20.67%) were diagnosed with MI with CCF, 4 patients (2.67%) were diagnosed with DKA, 2 patients each (1.33%) were diagnosed with Uremic encephalopathy and Hepatic encephalopathy each, 1 patient (1.33%) was diagnosed with psychogenic dyspnea.
In a study by Shrestha et al., 52.9 % pneumonia and 47.1 % were heart failure. Other associated medical conditions were bronchial asthma, hypothyroidism, interstitial lung disease, and tuberculosis12.
Anne Maree Kelly et al. observed that the most common diagnoses were lower respiratory tract infection (20.2%), heart failure (14.9%), chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (13.6%), and asthma (12.7%). In the EURODEM pilot study by S. Laribi, 22% had a cardiac cause and 15% had both cardiac and respiratory components.
In a study by Gottikonda et al., patients with ADHF constituted 43%, and patients having both cardiac and non-cardiac cause of dyspnea constituted 28% mostly with a diagnosis of ischemic cardiomyopathy (ICMP) with chronic kidney disease (CKD), COPD, or interstitial lung disease (ILD) with RV failure, and ADHF with pneumonia. The remaining patients had other causes like ARDS (7%), COPD (4%), acute pulmonary embolism (7%), acute pneumonia (4%), volume overload (4%), and massive pleural effusion (3%)13.
The present study observed that 53.19 % of CCF patients had LV systolic dysfunction and 40.43% of CCF patients had LV diastolic dysfunction. Heart failure was earlier understood as pump failure or left ventricular (LV) systolic dysfunction, but several studies found that several patients admitted with heart failure had a normal systolic function and were labeled as heart failure patients with normal LV systolic function, later on, defined as a separate entity as Diastolic heart failure (DHF). Differentiating LVSD from LVDD helps in the management of diuretics and Inotropes. In earlier studies, DHF was presumed to account for approximately one-third of all patients with heart failure, but over the last two decades, these perspectives have changed substantially with an increase in the prevalence of DHF to almost half of all heart failure cases. Observation from the present study supports the findings of previous studies18,40.
Mortality
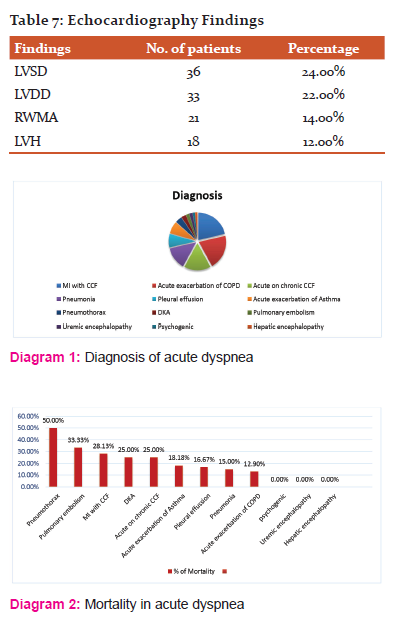
Acute exacerbation of COPD had a mortality of 11.76%, Acute exacerbation of Asthama had a mortality of 13.33%, Pneumonia had a mortality of 13.64%, Pulmonary embolism had a mortality of 33.33%, Pleural effusion had a mortality of 16.67%, Pneumothorax had mortality of 50%, Acute on chronic CCF had a mortality of 25.00%, MI with CCF had a mortality of 28.13 %, DKA had a mortality of 25.00%. Overall mortality was 20.67%.
Spontaneous pneumothorax is regarded as a common and benign clinical entity; however, it can be life-threatening if it progresses to tension pneumothorax. As evident in the present study, Tension Pneumothorax presents with the highest risk of mortality. A study by Saiphoklang et al. observed that Causes of pneumothorax were pulmonary tuberculosis (55.9%), chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (41.2%), and pneumonia (23.5%). The mortality rate was 12%14.
Myocardial infarction itself has a mortality of 20-25%. However, when complicated by CCF, mortality rate doubles. In a study by Zorbozan et al., they observed that the presence of CCF increases the mortality rate significantly. The present study showed 28.13% of mortality among patients of MI with CCF 15,16.
The present study found that dyspnea is a common reason for presentation to ED and that these patients make up approximately 10% of ward admissions and 20% of ICU admissions making them a high consumer of acute healthcare resources.
CONCLUSION:
The study concluded that Pneumothorax had the highest mortality (50%) followed by pulmonary embolism (33.33%) and MI with CCF (28.13%). Uremic encephalopathy, Hepatic encephalopathy, and Psychogenic dyspnea had the least mortality.
Acknowledgement:
Authors acknowledge the immense help received from the scholars whose articles are cited and included in references of this manuscript. The authors are also grateful to authors / editors / publishers of all those articles, journals and books from where the literature for this article has been reviewed and discussed.
Conflict of Interest: None
Source of Funding: Self
Ethical clearance: Cleared
Informed consent : taken
References:
-
Yernault JC. Dyspnea in the elderly: a clinical approach to diagnosis. Drugs Aging 2016;18:177–87.
-
Rao AB, Gray D. Breathlessness in hospitalized adult patients. Postgrad Med J 2017;79:681-85.
-
Eagan TM, Bakke PS, Eide GE, Gulsvik A. Incidence of asthma and respiratory symptoms by sex, age and smoking in a community study. EurRespir J. 2016;19:599-605.
-
Weingart SD, Levitan RM. Preoxygenation and prevention of desaturation during emergency airway management. Ann Emerg Med. 2012 Mar;59(3):165–175. e161.
-
Walls RM, editor. Manual of Emergency Airway Management. Second ed. Lippincott Williams and Wilkens; Philadelphia: 2014.
-
Currow DC, Clark K, Mitchell GK, Johnson MJ, Abernethy AP. Prospectively Collected Characteristics of Adult Patients, Their Consultations and Outcomes as They Report Breathlessness When Presenting to General Practice in Australia. PLoS One. 2019;8(9):e74814.
-
Frese T, Sobeck C, Herrmann K, Sandholzer H. Dyspnea as the reason for encounter in general practice. J Clin Med Res. 2019;3(5):239–46.
-
Parshall MB. Adult emergency visits for chronic cardiorespiratory disease: does dyspnea matter? Nurs Res. 2016;48(2):62–70.
-
Ekstrom MP, Abernethy AP, Currow DC. The management of chronic breathlessness in patients with advanced and terminal illness. BMJ. 2015;349:g7617.
-
Nishimura K, Izumi T, Tsukino M, Oga T. Dyspnea is a better predictor of 5-year survival than airway obstruction in patients with COPD. CHEST J. 2002;121(5):1434–40.
-
Baker K, Barsamian J, Leone D, Donovan BC, Williams D, Carnevale K, et al. Routine dyspnea assessment on unit admission. Am J Nurs. 2018;113(11):42.
-
Vital FM, Saconato H, Ladeira MT, et al. Non-invasive positive pressure ventilation (CPAP or bilevel NPPV) for cardiogenic pulmonary edema. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018;(3):CD005351.
-
Silvers SM, Howell JM, Kosowsky JM, Rokos IC, Jagoda AS. Clinical policy: Critical issues in the evaluation and management of adult patients presenting to the emergency department with acute heart failure syndromes. Ann Emerg Med. 2017 May;49(5):627–669.
-
Zorbozan, Dharmarajan K, Strait KM, Lagu T, et al. Acute decompensated heart failure is routinely treated as a cardiopulmonary syndrome. Plo Sone. 2018;8(10):e78222.
-
Lichtenstein DA, Mezière GA. Relevance of lung ultrasound in the diagnosis of acute respiratory failure: the BLUE protocol. Chest. 2018;134(1):117–125.
-
Remes J, Miettinen H, Reunanen A, Pyörälä K. Validity of clinical diagnosis of heart failure in primary health care. Eur Heart J. 1991;12:315–321.
|






 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License