IJCRR - 11(9), May, 2019
Pages: 12-17
Date of Publication: 21-May-2019
Print Article
Download XML Download PDF
Assessment of Nutritional Status of the HIV Infected Children Attending ART Centre and its Relation with Immunodeficiency - A Hospital Based Study
Author: Raghavendra N., R. G. Viveki
Category: Healthcare
Abstract:Introduction: Malnutrition is a common complication among HIV-infected children. HIV impairs the immune system, making the body vulnerable to various infections. Infections leads to malnutrition which further contributes to a weakened immune system making a vicious cycle. This leads to a rapid progression to AIDS.
Objectives: To assess the burden of malnutrition and to know its effect on immune status of HIV infected children attending Anti-Retro viral Therapy (ART) Centre.
Methodology: The study was conducted among HIV positive children aged 0-14 years, attending ART Centre of Belagavi Institute of Medical Sciences (BIMS) Hospital, Belagavi. Anthropometric measurements and CD4 counts were recorded. Anthropometric indicators were expressed in Z-scores. Three types of malnutrition were defined: acute malnutrition (WHZ/BAZ < -2 SD and HAZ ≥ -2SD), chronic malnutrition (HAZ < -2 SD and WHZ/BAZ ≥ -2 SD) and mixed malnutrition (WHZ/BAZ < -2 SD and HAZ < -2SD).
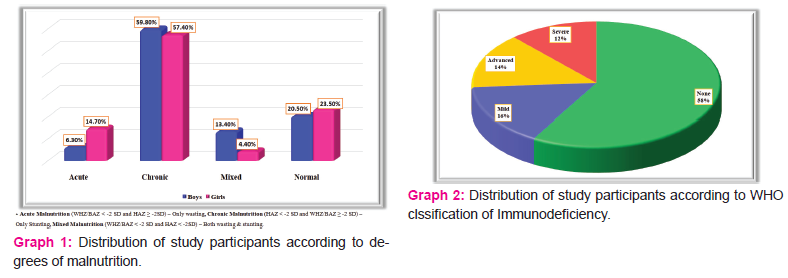
Results: The study included 180 HIV infected children (112 boys, 68 girls). The prevalence of malnutrition was 78.3%. Acute, chronic and mixed malnutrition was seen in 17 (9.4%), 106 (58.9%), 18 (10.0%) of the study participants respectively. Immunodeficiency was seen in 42% of them. The presence of malnutrition in the study participants was significantly associated with immunodeficiency.
Conclusion: There was high prevalence of malnutrition among the HIV infected children. HIV acts as an independent risk factor for malnutrition. Malnutrition should be treated and prevented to ensure optimal response to ART and reduce early mortality.
Keywords: ART, Children, CD4 count, HIV, Malnutrition
Full Text:
INTRODUCTION:
According to world health organization (WHO), by 2017 an estimated 36.9 million people were living with Human Immunodeficiency Virus(HIV) worldwide, 1.8 million People were newly infected with HIV and 9, 40,000 people died from Acquired Immune Deficiency Syndrome (AIDS) related illnesses. Children (<15yr) living with HIV accounts for an estimated 1.8 million of which 1, 80,000 children were newly infected with HIV and 1, 10,000 children died due to AIDS related illnesses.1By 2015, India has 21.17 lakh people living with HIV with adult prevalence (15-49yrs) of 0.26%. In Karnataka there were 1, 99,060 people living with HIV with adult prevalence of 0.45%. In India 1,38,456 children (<15yr) were living with HIV, with prevalence of 6.54% and 7,526 deaths due to AIDS related illnesses.2
Infants and young children who have been infected through the route of mother to child transmission (perinatal infection) have very high loads of HIV virus in their body. Furthermore, the body’s response against the HIV virus is inadequate because the immune system is still immature and developing. Thus, these children progress rapidly towards severe symptomatic disease or AIDS. HIV impairs the immune system, making the body vulnerable to various infections. In order to cope with HIV and other infections, the need for energy and other nutrients is increased. If these increased needs are not met, malnutrition sets in. Malnutrition contributes to a weakened immune system, which worsens the effect of HIV. This leads to a rapid progression to AIDS. Thus forming a vicious cycle.3 Even at the early stage of HIV when the effects may not be visible (asymptomatic phase), HIV infection has a substantial impact on the nutritionalstatus of infected people due to poor food intake as a result of poor appetite and difficulty eating, intestinalmalabsorption because of chronic diarrhea and HIV caused intestinal cell damage, metabolic changes and increased nutrient requirements related to opportunistic infections (OIs).4 HIV infected children remain nutritionally challenged due to low socio-economic status, orphan hood, food insecurity, poor dietary patterns, low maternal education and other specific health related factors. [5]Children also differ from adults as they have higher rate of viral replication hence high viral load and higher rate of CD4 cell destruction.Protein–energy /calorie malnutrition (PEM) is the commonest cause of immuno-deficiency.4 Hence this study was undertaken to assess the burden of malnutrition and its effect on immune status of HIV positive children.
MATERIALS & METHODS:
This Hospital based observational study was conducted among HIV positive children aged 0-14 years of age who were on Anti-Retro viral Therapy (ART) attending ART Centre of Belagavi Institute of Medical Sciences (BIMS) Hospital, Belagavi for a period of 12months from January 2015 to December 2015.
SELECTION CRITERIA:
(a) Inclusion Criteria:
(b) Exclusion criteria:
Sample size was estimated by considering the prevalence of malnutrition among HIV infected children.6 Calculated sample size was 154. However, the present study included 180 individuals. Children attending ART Centre of BIMS Hospital, Belagavi who fulfilled selection criteria were studied. Each child had a unique ART number. Hence repetition was avoided and every child was studied only once during the study period.
After obtaining consent, data was collected from parents or guardians of study participants by using a structured, pre-validated, questionnaire. Information regarding Socio-demographic profile (date of birth, religion, education, monthly income, and parental history), immunization history, and disease (HIV) related history was collected. Anthropometric measurements like height and weight of the child was taken. Immunological profile (Recent CD4 count) of the child was collected from case records of ART Centre.
To define malnutrition, several anthropometric indicators were used according to WHO definitions: Height-for-Age, for children up to 19 years, Weight-for-Height for children < 5 years and Body Mass Index (BMI)-for-Age for children ≥ 5 years, and Weight-for-age, for children < 10 years. These indicators are standardized using Z-scores, which quantify how many Standard Deviations (SDs) child’s weight and height is from the median value of a child of the same age and sex, in a reference population. For this analysis, we used the 2006 WHO growth charts for children <5, and the 2007 WHO growth charts for children ≥ 5.7 Each indicator allows to define three types of malnutrition: wasting when Weight-for-Height Z score (WHZ) or BMI-for-Age Z-score (BAZ) <-2 SD, stunting when Height-for-Age Z-score (HAZ) < -2 SD, and underweight when Weight-for-Age Z-score (WAZ) < -2 SD. A child is defined as moderately malnourished if the Z score is between -3 and -2 SD, and severely malnourished if the Z-score < -3 SD. For those children who knew exact date of birth, Z-scores were calculated using WHO Anthro Software (version 3.2.2, January 2011) and WHO Anthro Plus. In this study, we combined these indicators to define three categories of malnutrition: (1) acute malnutrition defined by WHZ or BAZ<-2 SD and HAZ≥ -2 SD; (2) chronic malnutrition defined by WHZ/BAZ ≥ -2 SD and HAZ< -2 SD, and (3) mixed malnutrition as WHZ/ BAZ < -2 SD and HAZ < -2 SD. WAZ was not used here. [6]
WHO Immunological classification8 was used to categorize immune status of the study participants. CD4+ count >500 was considered to be normal. Those with CD4+ count 350-499, 200-349, <200 or <15% were categorized to have mild, moderate and severe immunodeficiency respectively.
Statistical analysis was done using Microsoft excel sheet 2007 and SPSS version 22. The categorical data was expressed in terms of rates, ratios and percentages while continuous data was expressed as mean ± standard deviation. Chi square test was used to test the association between different qualitative variables. At 95% CI a probability value (p value) of ≤ 0.05 was considered as statistically significant.
Ethical Clearance:
The study was approved from Institutional Ethics Committee BIMS, Belagavi. Permission to conduct the study was obtained from head of the institute and Nodal Officer and Medical Officer of Anti-Retroviral Therapy (ART) Centre of Belagavi Institute of Medical Sciences (BIMS) Hospital, Belagavi.
RESULTS:
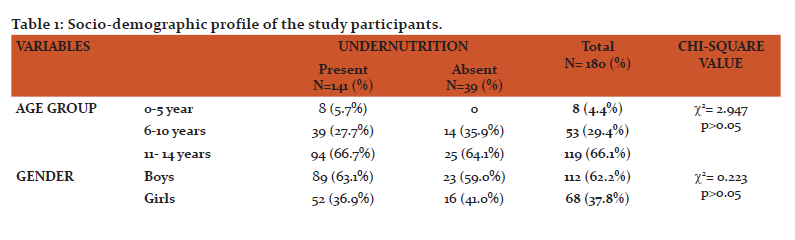
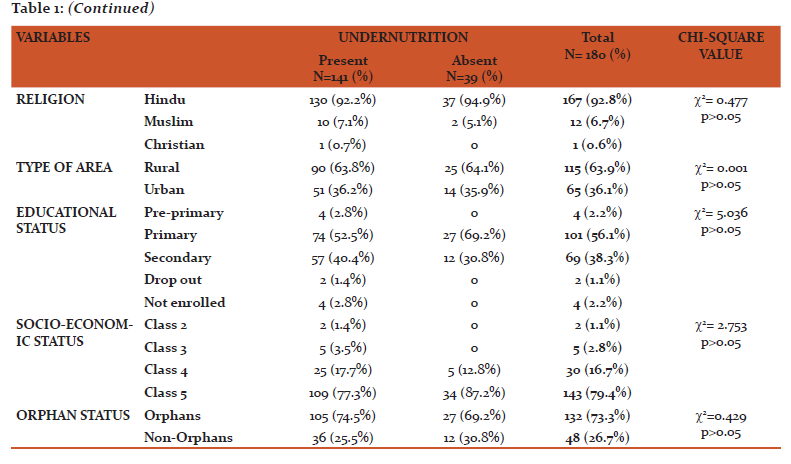
This present study included 180 HIV infected children of which boys were 112 (62.2%) and girls were 68 (37.8%) with boys to Girls ratio of 1.65:1. The study participants were of the age group 0-14 years. The mean age (in years) of study participants was 11.11± 2.87 SD. Table 1 describes the socio-demographic profile of the study participants. In this study, majority of the study participants 167 (92.7%) were Hindu’s. More than half of the study participants 115(63.9%) belonged to rural area. More than half of them 101 (56.1%) were doing primary education. More than 3/4th of study participants 143 (79.4%) belonged to class 5 socioeconomic status according to modified BG Prasad classification. Prevalence of orphan hood was 73.3% (132).
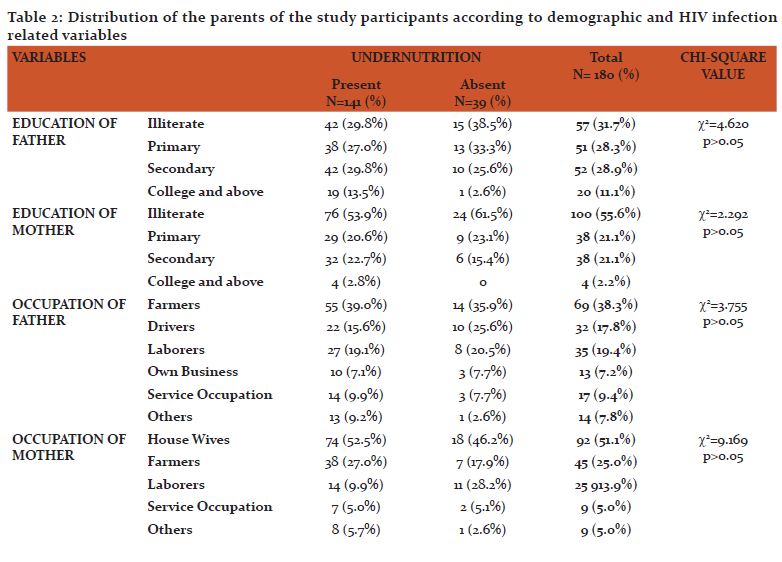
Table 2 describes the demographic and HIV infection related parameters of the parents of the study participants. Majority of the fathers i.e., 57 (31.7%) and mothers 100 (55.6%) of the study participants were illiterates. Majority of the fathers 69 (38.3%) were farmers by occupation followed by drivers 32 (17.8%) and laborers 35 (19.4%). Half of the mothers 92 (51.1%) were house wives by occupation followed by farmers 45 (25.0%) and laborers 25 (13.9%) etc. Only 70% of the fathers HIV status was known, of which 117 (65.0%) were positive and 9 (5.0%) of them were negative. Whereas 85% of the mothers HIV status was known, of which 148 (82.2%) of them were positive and 5 (2.8%) of them were negative. Among HIV positives, 42 (23.3%) of the fathers and 107 (59.4%) of the mothers were on ART.
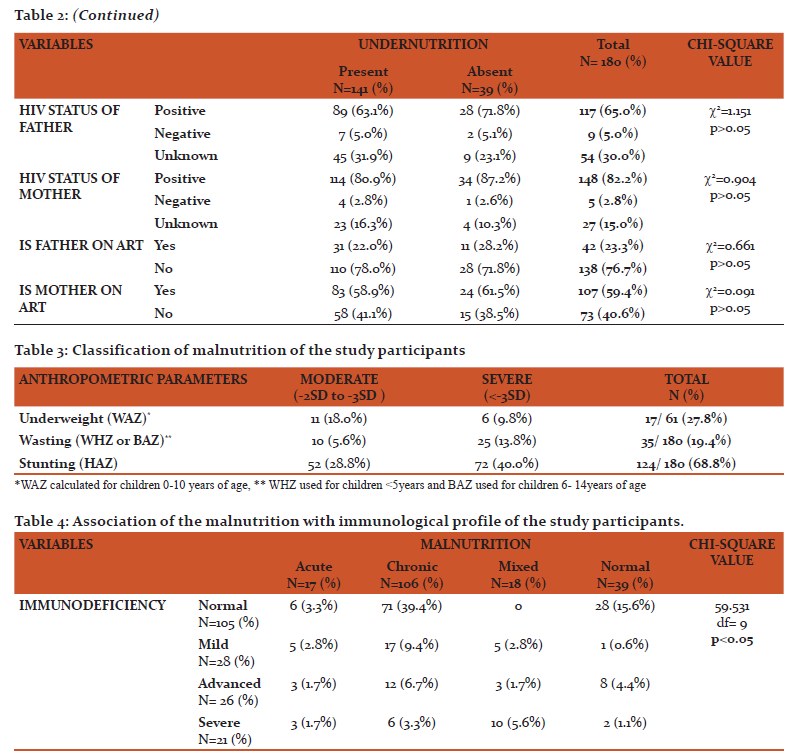
The prevalence of malnutrition in this study was 78.4%. Under nutrition was more common in boys 89 (63.1%) than girls 52 (36.9%). Among children aged 0-10years old, underweight was seen in 17 (27.8%) of them. Among children aged 0-14 years old, wasting was seen in 35 (19.4%) and stunting was seen in 124 (68.8%) of them as shown in table 3. Acute, chronic and mixed malnutrition was seen in 17 (9.4%), 106 (58.9%), 18 (10.0%) of the study participants respectively as shown in graph 1. The mean CD4 count of the study participants was 735.1±532.2 cells/mm3. According to WHO immunological classification, 105 (58.3%) of the study participants did not have immunodeficiency. Whereas 28 (15.6%) of them had mild, 26 (14.4%) of them had advanced and 21 (11.7%) of them had severe immunodeficiency as shown in graph 2. There was significant association between malnutrition and presence of immunodeficiency among stud participants as mentioned in table 4.
DISCUSSION:
This present study included HIV infected children of age 0-14years old. Of which, more than half of them 66.2% were of 11-14years of age group. Similar finding was seen in a study by Meenal Gupta et.al.9 The mean age (in years) of study participants was 11.11± 2.87 SD. Which was slightly high compared to other studies10,11. Boys to Girls ratio was 1.65:1 which was similar to other studies.5,12-14 More than half of the study participants (63.9%) belonged to rural area. This was the same as seen in a study done in Punjab9 and several other studies.5,14 More than 3/4th of study participants (79.4%) belonged to class V socioeconomic status, whereas several other studies4,5,13 showed that majority of them were in Class IV. The prevalence of orphan-hood was 73.3%, which was very high compared to studies conducted in Nigeria (36.4%)15 and North India (39.15%).11
The prevalence of under nutrition was 78.3%. Nearly same result was seen in a study done in Nigeria.15 Whereas this was very high compared to studies done in Cotonou (27.1%)[16] and Central and West Africa (42%).6 More than half of the study participants (58.9%) had chronic malnutrition followed by mixed malnutrition (10.0%) and acute malnutrition (9.4%). Similar findings were seen in studies conducted in Central and West Africa6 and in India.17 Majority of the children had stunting (68.8%) followed by underweight (27.8%) and wasting (19.4%). Similar results were seen in several studies.5,15
Majority of the study participants had mild immunodeficiency (15.6%) followed by advanced (14.4%) and severe immunodeficiency (11.7%). Similar result was seen in many studies.4,18,16 Whereas in few other studies6,19 majority of the study participants had severe immunodeficiency. The mean CD4 count of the study participants was 735.1±532.2 cells/mm3. Similar result was seen in few studies done in North India20 and Bengaluru.21
CONCLUSION AND LIMITATIONS:
There was high prevalence of malnutrition among the HIV infected children. HIV acts as an independent risk factor for malnutrition. Malnutrition should be targeted to ensure optimal response to ART and reduce early mortality.
ACKNOLEDGEMENTS: The authors would like to thank the Director, Dr. S.T. Kalsad for granting permission to do the study, Dr. A B Halappanavar and Mrs. SunandaHalki (statistician) for their guidance and support.Authors acknowledge the immense help received from the scholars whose articles are cited and included in references of this manuscript. The authors are also grateful to authors / editors / publishers of all those articles, journals and books from where the literature for this article has been reviewed and discussed.
References:
-
WHO: Summary of the global HIV epidemic. Available at: http://www.who.int/hiv/data/2017_summary-global-hiv-epidemic.png?ua=1. Retrieved on: 12/08/2018
-
India HIV estimations 2015. Technical report. NACO & NIMS ICMR, Ministry of Health & Family Welfare. Gov`t of India. Available at: http://www.naco.gov.in/sites/default/files/India%20HIV%20Estimations%202015.pdf Retrieved on: 12/08/2018.
-
Nutrition Guidelines for HIV-Exposed and Infected Children (0-14 Years Of Age) NACO. Ministry of Health & Family Welfare. Gov`t of India. Available at: http://www.naco.gov.in/sites/default/files/Paedia%20Nutrition%20national%20guidelines%20NACO.pdf Retrieved on: 02/08/18
-
Dundigalla C, Chidugulla SK, Ashwani N, Divya BP, Dundigalla P. Study of Prevalence Of Malnutrition In HIV Positive Children and Its Correlation With Cd4 Count. IOSR J of Denl and Med Sci. 2015; 14(12):50-57.
-
Ambey R, Sahu S, Sharma A, Gupta R, Goyal B. Assessment of Nutritional Status of HIV Positive Children in Antiretroviral Therapy Center: A Study from Central India. Int J of Pediatr Res and Pract. 2015; 1(1):7-11.
-
Jesson J, Masson D, Adonon A, Tran C, Habarugira C, Zio R et.al. Prevalence of malnutrition among HIV-infected children in Central and West-African HIV-care programmes supported by the Growing up Programme in 2011: A cross-sectional study. BMC Infectious Dis. 2015; 15(216):1-12.
-
Kishore J. National Health Programs of India, National Policies and Legislations related to Health. 11th ed. Century Publications. 2014: 289-343.
-
WHO case definitions of HIV for surveillance and revised clinical staging and immunological classification of HIV-related disease in adults and children. WHO 2007. Available at: http://www.who.int/hiv/pub/guidelines/HIVstaging150307.pdf Retrieved on: 16/08/18
-
Gupta M, K.J.P.S. Puri1, Singh K, Malhotra S. The road less travelled: A social and demographic profile of HIV- infected children accessing care at tertiary care centre in North India. Egyptian Dermatology Online Journal. 2013; 9(4):1-10.
-
Madiba S, Mokwena K. Profile and HIV diagnosis disclosure status of children enrolled in a pediatric antiretroviral program in Gauteng province, South Africa. Southeast Asian J Trop Med Pub Health. 2013; 44(6):1010-1020.
-
Chauhan RC, Singh N. Socio-demographic profile of HIV infected children accessing care at pediatric clinic of a tertiary level hospital in North India. Int J ContempPediatr. 2014; 1(1):20-23.
-
S. Rajasekaran, L. Jeyaseelan, K. Raja, N. Ravichandran. Demographic & clinical profile of HIV infected children accessing care at Tambaram, Chennai, India. Indian J Med Res. 2009; 129:42-49.
-
Bhattacharya M, Rajeshwari K, Saxena R. Demographic and Clinical Features of Orphans and Nonorphans at a Pediatric HIV Centre in North India. Ind J Ped. 2010; 77:627-631.
-
Solunke VN, Kamble MB, Suryawanshi AR, Saple P, Tiwari MM, Bhete SB et.al, Clinical Profile and Prevalence of Opportunistic Infection in HIV Patients Attending Pediatric Department. Int Med J. 2014; 1(2):69-74.
-
Oladokun R, Brown B, Aiyetan P, Ayodele O, Osinusi K. Comparison of socio-demographic and clinical characteristics of orphans and non-orphans among HIV-positive children in Ibadan, Nigeria. Int J Inf Dis. 2009; 13:462-468.
-
Adedemy JD, Zohoun L, Alihonou F, d'Almeida M, Couringa Y, Agossou J et.al. Screening for malnutrition and nutritional care in HIV-infected children followed up in the pediatric unit of CNHU-HKM in Cotonou. MaternPediatrNutr. 2016; 2(2):1-7.
-
Rakholia R, Bano M, Rawat V. Malnutrition among HIV- infected Children by Anthropometric Measures in Poor Outreach Area of a Developing Country and its Relationship with CD4 Counts. Int J Pediatr. 2016; 4(4):1643-1654.
-
Gomber S, Kaushik JS, Chandra J, Anand R. Profile of HIV infected children from Delhi and their response to antiretroviral treatment. Indian Pediatrics. 2011; 48:703-707.
-
Agarwal D, Chakravarty J, Sundar S, Gupta V, Bhatia BD. Correlation between Clinical Features and Degree of Immunosuppression in HIV Infected Children. Indian Pediatrics. 2008; 45(17): 140-143.
-
Lodha R, Upadhyay A, Kapoor V, Kabra SK. Clinical Profile and Natural History of Children with HIV Infection. Ind J of Ped. 2006; 73: 201-204.
-
Sanjeeva GN, Sukanya V, Govindaraj M, Shivananda. Clinical profile, treatment response, and outcome of HIV-TB co-infected children. Pediatric Infectious Dis. 2013(5):3-8.
|






 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License