IJCRR - 10(20), october, 2018
Pages: 15-19
Date of Publication: 26-Oct-2018
Print Article
Download XML Download PDF
Role of Candida in Catheter Associated Urinary Tract Infection
Author: Swati Sahai, Amit Kumar
Category: Healthcare
Abstract:Background: UTI in hospitalised patients due to Candida spp. is becoming increasingly common in ICU setting. There is always a dilemma as to differentiate colonisation from true infection and whether to treat candiduria or not. The choice of antifungal is also controversial due to low urinary concentration of many antifungal drugs.
Objective: This study was conducted to assess the significance of Candida spp. as the causative agent of symptomatic CAUTI in medical ICU patients and perform microbiological characterisation of Candida and their antifungal susceptibility pattern.
Methods: A total of 100 patients admitted in medical ICU and put on Foley's catheter were included in the study and followed up for the development of symptomatic CAUTI. The urine samples from the catheter were collected on day 1 and then on day 3,5,7,10,14 and every weekly till the patient was discharged, expired, catheter removed or developed bacteriuria or candiduria. The samples positive for Candida spp. were identified and processed as per standard guidelines.
Results: In this study, it was found that 23% (6/26) of the symptomatic CAUTI was caused by Candida spp. Candida species comprised 15% of the causative organisms. Among the candida species, non-albicans Candida spp. contributed to 83.3% of the isolates and only 16.7% of isolates were Candida albicans. All Candida isolates were sensitive to fluconazole, voriconazole, amphotericin B and itraconazole.
Conclusion: Symptomatic catheter associated urinary tract infection with Candida spp. is becoming increasingly common. Among Candida spp., non-albicans Candida is emerging as the predominant pathogen causing CAUTI.
Keywords: Candida, Candiduria, Catheter associated urinary tract infection, Nosocomial, Intensive Care Unit
Full Text:
INTRODUCTION
Catheter associated urinary tract infection (CAUTI) is the most common hospital acquired infection which accounts for more than 80% of nosocomial urinary tract infections (UTIs)[1]. The risk factors associated with CAUTI in adults mainly include intensive care unit (ICU) admission, broad-spectrum antibiotics, diabetes mellitus, increased age, and female sex.[2,3] The microorganisms causing CAUTI range from Gram negative bacteria to Gram positive cocci to Candida. UTI in hospitalised patients due to Candida spp. is becoming increasingly common in ICU setting[27]. There is always a dilemma as to differentiate colonisation from true infection and whether to treat candiduria or not[28]. Symptomatic CAUTI is considered when symptoms / signs consistent with UTI exists along with candiduria in a catheterized patient [2]. The signs and symptoms either are localized to the urinary tract or can include otherwise unexplained systemic manifestations, such as fever[2]. The accepted threshold for bacteriuria/candiduria varies from 103colony forming units per millilitre (cfu/mL) to 105 cfu/mL[2]. The choice of antifungals is also controversial due to low urinary concentration of many antifungal drugs[28]. This study was conducted to assess the significance of Candida spp. as the causative agent of symptomatic CAUTI in medical ICU patients and perform microbiological characterisation of Candida and their antifungal susceptibility pattern.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Approval of the Institutional Ethics Committee was obtained before starting the study. Informed written consent was taken from all the patients included in the study. This was a cross-sectional study conducted at the Institute of Microbiology, Madras Medical College in association with Medical ICU, Rajiv Gandhi Government General Hospital, Chennai. It was of one year duration from October 2014 to September 2015 which included a total of 100 patients admitted to medical ICU. Those who were 18 years and above and put on Foley’s catheter were included in the study. The exclusion criteria included patients less than 18 years of age, those catheterised prior to admission in ICU, those confirmed to have UTI on 1st day and whose Foley’s catheter was removed or who were discharged before the 3rd day of catheterisation.
Data were collected from the patients using a preformed structured questionnaire. Physical examination findings and details of clinical diagnosis was also noted. Daily examination of the patients were done to look for any evidence of urinary tract infection. The patients were followed till they developed bacteriuria/candiduria or discharged, expired or catheter was removed. Patients who were shifted to different ward were followed for up to 48 hrs for the developments of symptoms of CAUTI [3].
Urine specimens were collected aseptically from the Foley’s catheter, approximately (minimum) 3ml of urine was taken as a sample in a flat bottomed universal container. The samples were taken to laboratory within 1 hour of collection. Day 1 sample was taken to rule out prior presence of UTI. The samples were repeated on 3rd, 5th, 7th, 10th, 14th day and then every weekly until catheter removal, or patient developed bacteriuria, or until discharge/death of the patient [1,3].
The patients were diagnosed as symptomatic CAUTI as per Centre for disease Control (CDC) guidelines January, 2014 which included the development of UTI caused by Candida spp., with a culture of ≥103 CFU/ml on a specimen collected at least 48 hrs after hospital admission and a previous Candida spp.-negative culture [2].
Direct Gram’s stain of uncentrifuged urine was done to observe for the presence of bacteria or candida. Detection of nitrites and leucocyte esterase was done on uncentrifuged urine using dipstick test. Then the urine sample was centrifuged at 3000rpm for 3-5 minutes. A wet mount of the sediment was done and the number of pus cells / high power field was counted under 40 x objective. More than 5 WBC/hpf was considered significant for diagnosing CAUTI [1,4].
The specimens were cultured by semi-quantitative method using Mac Conkey Agar and Blood Agar as culture medium. The plates were read after 24 hours of incubation for any growth[1]. Based on colony morphology on 5% sheep blood agar and no growth on Mac Conkey agar, the colonies were suspected to belong to Candida species. Gram stained smear showed Gram positive budding yeast cell with pseudohypahae. Candida was speciated based on germ tube test as Candida albicans and non-albicans Candida[5,6]. The candida species were identified on Dalmau plate culture method by the presence of hyphae, blastoconidia and chlamydospores [7,8]. Further speciation of Candida was done by sugar fermentation and sugar assimilation tests [5,6,8]. In sugar fermentation tests, 2% sugars were used which included glucose, maltose, sucrose and lactose. For sugar assimilation test, carbohydrate discs -glucose, maltose, sucrose, lactose, cellibiose, galactose, trehalose, raffinose, xylose, inositol and dulcitol were placed on the yeast nitrogen agar and incubated for 24-48 hours at 25°C. The assimilation of the particular carbohydrate by the yeast was indicated by the growth around the discs. The pattern of assimilation was noted [1].
Speciation of Candida spp. was also done using Candida Chrom Agar [5,8,9]. Candida spp. was subcultured onto Sabouraud’s Dextrose Agar and then streaked onto Chrom agar plate. This was incubated for 48 hours at 37°C and the colour and morphology of the colonies were noted.
The antifungal susceptibility test was done by disc diffusion method and minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) method [10,11]. The drugs fluconazole (25µg) and voriconazole (1µg) were tested by Kirby Bauer Disk diffusion method on supplemented Mueller Hinton Agar which contained Mueller Hinton agar supplemented with 2% glucose and 0.5 μg/ml methylene blue. MIC by microbroth dilution was done for fluconazole, itraconazole and amphotericin B.
RESULTS
In this study, among 100 patients enrolled, 26 developed symptomatic CAUTI. It was found that 23% (6/26) of the symptomatic CAUTI was caused by Candida spp. A total of 40 organisms were isolated. Majority of the organisms isolated belonged to Enterobacteriaceae (34.5%) and nonfermenters (32.5%). Candida species comprised 15% of the causative organisms.
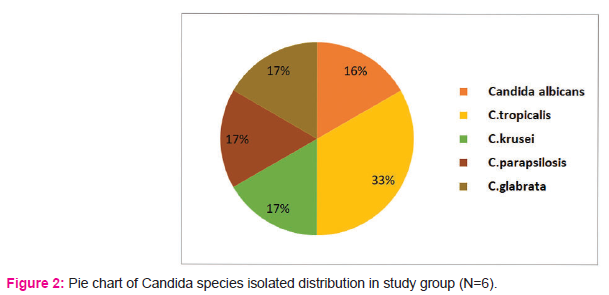
Among the candida species, non-albicans Candida spp. contributed to 83.3% of the isolates and only 16.7% of isolates were Candida albicans.
Among non-albicans Candida, 2 patients had Candida tropicalis and one patient each had Candida krusei, Candida parapsilosis and Candida glabrata isolate.
All Candida isolates were sensitive to fluconazole, voriconazole, amphotericin B and itraconazole.
DISCUSSION
Catheter associated urinary tract infection is the commonest device associated nosocomial infection. The rate of device associated infections shows variation in India. According to a study conducted by Angshuman Jana et al (2015) [12], the incidence was 31.85%. A study by Priya Datta et al (2014) [13] found the CAUTI rate as 10.75% , by Kamat et al (2009) [14] as 33.6%, and Al Jebouri et al (2006) [15] as 28.1 %. In this study, out of 100 patients, 26 patients were diagnosed to develop symptomatic CAUTI during their course of hospitalisation. Therefore, the incidence was 26% and the CAUTI rate was calculated as 25.67 per 1000 catheter days.
It is thought that candiduria is very common in hospitalised patients [16,17,18,19] and is mainly due to antibiotic usage [20]. In one of the point prevalence survey done in 228 hospitals from 29 European countries, 9.4% of nosocomial UTIs were found to be caused by Candida spp. The incidence of candiduria varies with hospital setting and is most common in ICUs [19] and among those in burn units [34]. A study conducted by N. Febre et al (1999) found Candida spp. in 18.6% of urine specimens from patients with indwelling urinary catheters in ICU. Other studies report that 11 to 30% of nosocomial UTIs are caused by Candida [22,23]. In the present study, 23% of the symptomatic CAUTI in medical ICU was caused by Candida spp. and it comprised 15% of the total causative agents.
In most studies, C. albicans dominates and accounts for 50% to 70% of all Candida-related urinary isolates, followed by C. glabrata, and C. tropicalis, which is the third most common species [16,21]. In a large multicentre study from Spain, C. albicans was recovered in 68%, followed by C. glabrata (8%) and C. tropicalis (4%). However, various studies show a steady increase in the incidence of non-C. albicans strains producing nosocomial infections such as those conducted by De Francesco MA et al (2007) [24], Horn DL et al (2009), [25] and Xess I et al (2007) [26]. In a study conducted by Manisha Jain et al (2011) [27], non-albicans Candida spp. (71.4%) was the predominant pathogen causing CAUTI. Similar findings were seen in this study. Among Candida isolates, non-albicans Candida spp. emerged as the predominant isolate accounting for 83.3%. These included Candida tropicalis (2), C. parapsilosis (1), C. krusei (1) and C. glabrata (1).
Antifungal susceptibility in candiduric patients depends largely on the infecting strains. In this study, all Candida isolates were sensitive to fluconazole, voriconazole, amphotericin B and itraconazole.
CONCLUSION
Symptomatic catheter associated urinary tract infection with Candida spp. is becoming increasingly common. It is usually difficult to ascertain the difference between Candida colonization and infection. Diagnosis mainly depends on the symptoms of UTI along with pyuria and high colony Candida counts in the urine. Among Candida spp., non albicans Candida is emerging as the predominant pathogen causing CAUTI. Based on clinical setting, the relevance of candiduria must be determined and appropriate decision should be taken for the need of antifungal therapy. There is a need for further studies to determine regime for such patients so as to address some of the unanswered questions of when to treat, whom to treat and how long to treat.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENT
I wish to express my sincere thanks to our Dean, Dr.R.Vimala M.D., for permitting me to use the resources of this institution for my study.
I would like to thank the Director I/C & Professor, Dr. Mangala Adisesh, M.D.for her guidance and support throughout the study. My sincere thanks to Prof. Dr. Ragunanthanan, M.S., Professor, Institute of Internal Medicine, for permitting to carry out my study. I would like to thank Dr. Amit Kumar, MD(Medicine), Senior Resident, Southern Railway Headquarters Hospital, Chennai for his invaluable suggestions and continuous support throughout my study.
I owe special thanks to Dr. S. Vasanthi, M.D., Professor, Institute of Microbiology for her support, guidance in my study and for being a source of inspiration in my endeavours. I extend my whole hearted gratitude to our Assistant Professor Dr. David Agatha M.D. for her valuable guidance and immense support in my study.
I would also like to thank our professors and assistant professors for their valuable guidance in my study
I hereby express my gratitude to all the technical staff for their help throughout my study. I don’t have any conflict of interest.
I acknowledge the immense help received from the scholars whose articles are cited and included in references of this study. I am also grateful to authors/editors/publishers of all those articles, journals and books from where the literature for this article has been reviewed and discussed.


References:
-
Betty a Forbes, Alice S Weissfeld, Daniel F. Sahm. Bailey and Scott diagnostic microbiology, 13th edition 2013; 919-930.
-
Device-associated module, Cauti: January 2014: available at: http://www.cdc.gov/nhsn/pdfs/pscmanual/7psccauticurrent.pdf; 26.07.2014; 16:39
-
C. M. Poudel, g. Baniya, b. M. Pokhrel. Indwelling catheter associated urinary tract infection. Journal of institute of medicine, December, 2008; 30:3.
-
Monica Cheeseborough; district laboratory practice in tropical countries- part 2; 2nd edition; Cambridge university press, 2006; pgs 105-115
-
Jagdish Chander. Textbook of Medical Mycology, 3rd edition, Mehta publishers, 2009. Page 266-290
-
Jagdish Chander. Textbook of Medical Mycology, 3rd edition, Mehta publishers, 2009. Page 508-513
-
Fran fisher, norma b. Cook. Fundamentals of diagnostic mycology. Edition 1, saunders. 1998. pg 196-212
-
Davise H. Larone. Medically important fungi-a guide to identification. 5th edition.asm press.2011. Pgs 115-126
-
Chrom agar candida; http://www.chromagar.com/clinicalmicrobiology-chromagar-candida-focus-on-candida-species-22.html#; 22.07.2015; 11:00
-
Method for antifungal disk diffusion susceptibility testing of yeasts; approved guideline—second edition, CLSI document 2009
-
Reference method for broth dilution antifungal susceptibility testing of yeasts; approved standard—third edition, clsi document. 2008
-
Angshuman Jana, NK Pal, Arijit Majumdar, Jayeeta Mitra, Anirban Jana, Soumali Biswas, Babita Bag device-associated infection rates and median length of acquiring device-associated infection in an intensive therapeutic unit of an Indian hospital : Journal of medicine in the tropics: Year: 2015 | volume : 17 | issue : 2 | page : 97-102
-
Priya Datta, Hena Rani, Rajni Chauhan, Satinder Gombar, and Jagdish Chander. Health-care-associated infections: risk factors and epidemiology from an intensive care unit in northern India. Indian j anaesth. 2014 jan-feb; 58(1): 30–35.
-
Kamat U S, Ferreira A, Amonkar D, Motghare D, Kulkarni M S. Epidemiology of Hospital Acquired Urinary Tract Infections in a Medical College Hospital in Goa. Indian j urol 2009; 25:76–80.
-
Al-Jebouri, O.A.H. 2006. The relationship between urinary caliculi types and urinary tract infections among patients in Tikrit District. M. Sc. Thesis, college of medicine, tikrit university, tikrit.
-
Alvarez-Lerma, F., J. Nolla-Salas, C. Leon, M. Palomar, R. Jorda, N. Carrasco, and F. Bobillo. 2003. Candiduria in critically ill patients admitted to intensive care medical units. Intensive Care Med. 29:1069-1076. [PubMed]
-
Kauffman, C. A., J. A. Vazquez, J. D. Sobel, H. A. Gallis, D. S. McKinsey, A. W. Karchmer, A. M. Sugar, P. K. Sharkey, G. J. Wise, R. Mangi, A. Mosher, J. Y. Lee, and W. E. Dismukes. 2000. Prospective multicenter surveillance study of funguria in hospitalized patients. The National Institute for Allergy and Infectious Diseases (NIAID) Mycoses Study Group. Clin. Infect. Dis. 30:14-18. [PubMed]
-
Richards, M. J., J. R. Edwards, D. H. Culver, and R. P. Gaynes. 2000. Nosocomial infections in combined medical-surgical intensive care units in the United States. Infect. Control Hosp. Epidemiol. 21:510-515. [PubMed]
-
Schaberg, D. R., D. H. Culver, and R. P. Gaynes. 1991. Major trends in the microbial etiology of nosocomial infection. Am. J. Med. 91:72S-75S. [PubMed]
-
Weinberger, M., S. Sweet, L. Leibovici, S. D. Pitlik, and Z. Samra. 2003. Correlation between candiduria and departmental antibiotic use. J. Hosp. Infect. 53:183-186. [PubMed]
-
Bougnoux, M. E., G. Kac, P. Aegerter, C. d'Enfert, and J. Y. Fagon. 2008. Candidemia and candiduria in critically ill patients admitted to intensive care units in France: incidence, molecular diversity, management and outcome. Intensive Care Med. 34:292-299. [PubMed]
-
Lundstrom, T., and J. Sobel. 2001. Nosocomial Candiduria: a review. Clin. Infect. Dis. 32:1602-1607. [PubMed]
-
Richards, M. J., J. R. Edwards, D. H. Culver, and R. P. Gaynes. 2000. Nosocomial infections in combined medical-surgical intensive care units in the United States. Infect. Control Hosp. Epidemiol. 21:510-515. [PubMed]
-
De Francesco, M. A., G. Ravizzola, L. Peroni, R. Negrini, and N. Manca. 2007. Urinary tract infections in Brescia, Italy: etiology of uropathogens and antimicrobial resistance of common uropathogens. Med. Sci. Monit. 13:BR136-BR144. [PubMed]
-
Horn, D. L., D. Neofytos, E. J. Anaissie, J. A. Fishman, W. J. Steinbach, A. J. Olyaei, K. A. Marr, M. A. Pfaller, C. H. Chang, and K. M. Webster. 2009. Epidemiology and outcomes of candidemia in 2019 patients: data from the prospective antifungal therapy alliance registry. Clin. Infect. Dis. 48:1695-1703. [PubMed]
-
Xess, I., N. Jain, F. Hasan, P. Mandal, and U. Banerjee. 2007. Epidemiology of candidemia in a tertiary care centre of north India: 5-year study. Infection 35:256-259. [PubMed]
-
Jain M1, Dogra V, Mishra B, Thakur A, Loomba PS, Bhargava A. Candiduria in catheterized intensive care unit patients: emerging microbiological trends. Indian J Pathol Microbiol. 2011 Jul-Sep;54(3):552-5. doi: 10.4103/0377-4929.85091.
-
Bukhary Zakeya Abdulbaqi ; Candiduria: A Review of Clinical Significance and Management: Year : 2008 | Volume: 19 | Issue Number: 3 | Page: 350-360
|






 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License