IJCRR - 10(19), october, 2018
Pages: 14-19
Date of Publication: 10-Oct-2018
Print Article
Download XML Download PDF
Adherence to Medications in Chronic Kidney Disease: Prevalence, Predictors and Outcomes
Author: Bhupendra Verma, Amrita Singh, J. S. Bishnoi, Anil Kumar Mishra
Category: Healthcare
Abstract:Background: In India there is scarcity of studies regarding medication non-adherence in CKD (chronic kidney disease) patients and there is lack of any prospective data. Objective: To study the prevalence and predictors of medication non-adherence in patients of CKD and outcomes of nonadherence prospectively over 2 years. Material and Methods: In this multi-centric, prospective observational study a total of 510 patients were included after obtaining consent. A validated scale of medication adherence, Morisky 8-item Medication Adherence Scale (MMAS-8) was used to calculate adherence. The primary outcome of the study was all-cause mortality and secondary outcome was composite of all-cause mortality and progression of CKD or occurrence of ESRD (end-stage renal disease). Results: Longitudinal evaluation showed increase in non-adherence over time, from 58% at baseline to 82% at two years. Overall, 18% patients were taking alternative medicines. The rate of all-cause death in low adherence population was numerically double as compared to patients with high adherence (1.4vs 0.7 per 100 patient-years), though the difference was statistically non-significant. The secondary outcome in low adherence population was 5.5 per 100 patient-years compared to 9.9 per 100 patient-years in high adherence population (hazard ratio [HR] = 1.53, 95% confidence interval [CI] = 1.21-1.74). Conclusion: Non adherence to medication is very prevalent among CKD patients in India, which further increases with duration of treatment. High use of alternative medicine was seen without physician's knowledge, especially in patients on haemodialysis. Moreover, we found that low medication adherence was significantly associated with composite of mortality and disease progression.
Keywords: Haemodialysis, Morisky 8-item Medication Adherence Scale (MMAS-8), CKD progression, Death, Alternative medicine
Full Text:
Introduction
Chronic kidney disease (CKD) is a major public health problem leading to increased morbidity and mortality worldwide. CKD is defined as kidney damage (structural or functional abnormalities of the kidney) or estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) <60 mL/min/1.73m2 for 3 months or more, irrespective of cause.1 The prevalence of CKD in different parts of India has been reported from <1% to 17.2%, mostly due to non-uniform criteria of CKD.2-4 These data are comparable to data from the developed countries, where large population-based surveys have shown the prevalence to be about 12-20%.5 Diabetes (DM) and hypertension (HTN) are the major risk factors and most common co-morbidities in CKD. In India, diabetes and hypertension are responsible for up to half of the CKD cases.5 With the concomitant rise of DM, HTN and obesity in general population, the prevalence of CKD is expected to rise.
Non-adherence to medications is quite common in chronic diseases, and may be seen in over 50% of the patients.6 The major goal of treatment in CKD is slowing the rate of disease progression, together with managing its co-morbidities and complications. Non-adherence to medication is potentially harmful and can lead to increased cost of treatment over long term. Studies have shown that non-adherence in CKD caused, uncontrolled hypertension, more frequent dialysis, increase in expense of medications and hospitalisations.7 Thus, non-adherence reduces the beneficial effects of drugs and can eventually lead to CKD progression and occurrence of end-stage renal disease.8
Adherence to drug therapy can be assessed by using direct or indirect methods. Indirect methods consist of self-report, tablet refills, pill count, electronic monitoring, and Morisky’s method.9, 10 Studies on non-adherence have reported widely variable rates primarily due to method of assessment used. Worldwide, adherence to medication in CKD patients have been reported varying from 3% to 83%.11-14 The major predictors of the poor adherence include high cost, forgetfulness, high pill burden, complex dosing schedule, poor knowledge of disease/treatment, adverse effects, psychosocial issues, not feeling well, and taking alternative medicine among others.15-17
Adherence to medications, therefore, remains a major concern to therapy in CKD. Reasons for non-adherence can patient-related, socio-economic, disease specific, type and frequency of medications, and duration of treatment, among others. Studying the medication adherence helps in identifying the risk factors and consequent development of interventions to improve the compliance. The data of non-adherence in CKD population is scarce from the Indian subcontinent and limited by small sample sizes. Moreover there have been no prospective studies in this region. Hence, this study was carried out to systematically study the medication non-adherence within the CKD population and further assess predictors and outcomes of non-adherence.
Material and methods
This was a prospective, observational study carried out in medicine and nephrology departments of a tertiary care hospital. The study was carried out over a period of 2 years from august 2016 to July 2018. Consecutive patients with CKD as defined by Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes (KDIGO) and aged ≥18 years were included in the study.1 All patients were included irrespective CKD stage and whether or not undergoing dialysis. Written informed consent was obtained from all the participants. The study was performed in accordance with good medical and laboratory practices and the ethical guidelines of the Declaration of Helsinki. A total of 510 patients were included in the study.
8-point Morisky Medication Adherence Scale (MMAS-8) was used to assess adherence to medication. This scale consists of seven items with binary response and one item with Likert scale response. Cumulative score based on 8 items were used to obtain final adherence score ranging from 0 to 8. Adherence was defined accordingly as low (score 0-5), medium (score 6-7) and high (score 8). MMAS-8 scale had been validated in studies with good reliability and predictive value.18 Additionally, patients were interrogated to identify the specific reason(s) for non-adherence and specific drug(s) for non-adherence.
The follow up duration was of two years. The primary outcome of the study was all-cause mortality and secondary outcome was composite of all-cause mortality and progression of CKD or occurrence of ESRD (end-stage renal disease). CKD progression was defined as 50% decline in eGFR from baseline.
2.8. Statistical analysis
Categorical variables are expressed as number and percentage of patients. Continuous data are reported as mean ± SD. Cox proportional hazard regression analyses were used to estimate hazard ratios for predefined primary and secondary outcomes. A 2-sided P value of less than 0.05 was considered statistically significant. The data were analyzed using GraphPad Prism 7, version 7.04 (GraphPad Software, Inc.).
Results
A total of 510 CKD patients were enrolled in the study. Over the follow up of 2 years, 32 patients died and 12 patients were lost to follow up. Mean age of the patients was 53.9 years and 61% were male. Hypertension (42%) was the most common co-morbidity followed by anaemia (36.8%) and obesity (28.8%). ≥1+ grade proteinuria was seen in 2/3rd of the patients. Around 20% patients were on hemodialysis. More than 90% patients were buying medicines on their own with an average pill burden of 7.2±1.2 (Table 1).
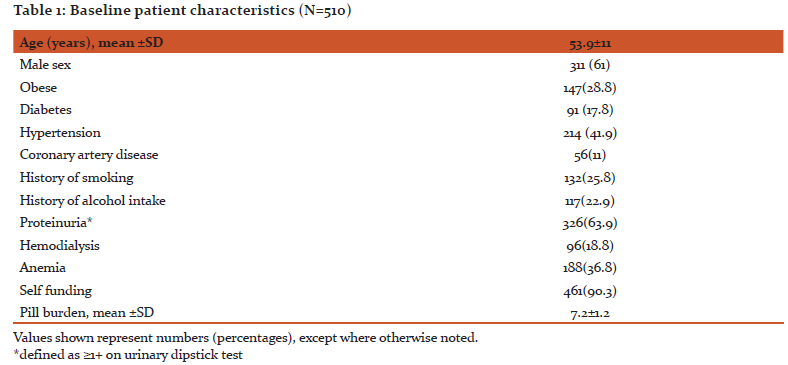
Adherence was defined accordingly as low (score 0-5), medium (score 6-7) and high (score 8) on the basis of MMAS-8 score. In our study, low adherence was seen in 26% of total CKD patients and medium adherence in 56%. Overall, only 18% of the participants showed ‘high’ medication adherence. Moreover, 58% of the patients were non-adherent to the medications at baseline, which gradually increased to 82% at 2 year follow up (Figure 1).
The most common reason for non-adherence was the high cost of medicine (72%) followed by forgetfulness (70%), complex dosing schedule (65%), high pill burden (61%) and long term nature of treatment (59%). Poor knowledge of the disease and medicines was seen in half of the patients. 18% of them skipped doses since they felt well and thought that medicine was no more required. Overall, 18% patients were taking alternative medicines (table 2). Considering only the patients on dialysis, 32% were taking some form of alternative medicine, most common being ayurvedic (48%).
The most frequently prescribed medicines were anti-hypertensives (37%), followed by diuretics (31%) and hematopoietics (30%). Non-adherence was highest for phosphate binders and erythropoietin injections, which further increased on follow up. High cost and injectable nature was cited by patients as reasons. Highest levels of adherence were seen with anti-hypertensives and OHA both at baseline and follow up. At 2 yrs follow up, 11% patients were non-adherent to ≥5 drugs and 4% were not taking any of the medicines regularly as prescribed.
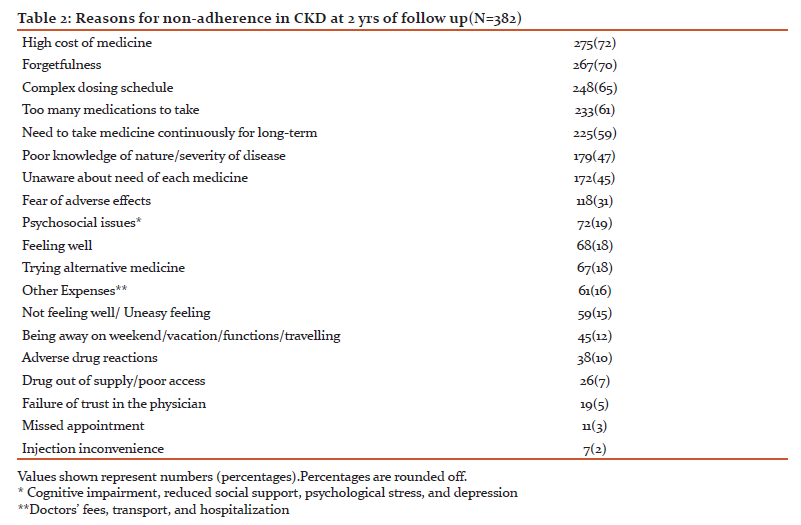
The all-cause mortality over 2 year follow up was 32. The rate of all-cause death in low adherence population was numerically double as compared to patients with high adherence (1.4vs 0.7 per 100 patient-years), though the difference was statistically non-significant. The progression to CKD or occurrence of ESRD occurred in 204 patients. The secondary outcome in low adherence population was 5.5 per 100 patient-years compared to 9.9 per 100 patient-years in high adherence population (hazard ratio [HR] = 1.53, 95% confidence interval [CI] = 1.21-1.74) (Figure 2).
Discussion
Medication non-adherence is a major problem especially in developing countries leading to increase in the disease burden, disease progression and decreases the quality of life.19 Assessment of medication adherence helps in identifying the risk factors and consequent development of interventions to improve the compliance. The present study was carried out due to scarcity of such evidence in CKD patients from India. To best of our knowledge this is the largest prospective study on medication adherence in CKD patients from India. Prospective evaluation over two years showed significant increase in non-adherence from 58% at baseline to 82%. Overall, 18% patients were taking alternative medicines. The secondary outcome, composite of all-cause mortality and progression of CKD or occurrence of ESRD, in low adherence population was significantly higher than high adherence population.
The drug adherence in CKD patients in different studies varies from 3-83%.11-14, 20 The widely variable rates of non-adherence is mainly due non-uniformity in criteria across studies. Hence, objective and validated parameters for adherence must be used to allow reproducibility and comparability between studies. In our study we have used a validated adherence scale (MMAS-8); most frequently used in the current studies.18 Prevalence of non-adherence in the present study was 58% at baseline and increased to 82% at two years. Similar level of non-adherence was seen in a previous study using MMAS-8 scale on 150 CKD patients from India (78%).21 The most plausible explanations for high prevalence of non-adherence could be high cost of medications, lack of insurance schemes, chronic nature of disease, high pill burden, poor education and disease awareness, and poor paying capacity of the general population. The setting up of “Jan Aushadhi Kendra”, “Mohalla clinics”, promotion of generic medicines and central and state government health insurance schemes would come a long way in decreasing drug non-adherence and disease burden.
High cost of medications (72%) and need to take medicines for long durations (59%) were among the most common types of non-adherence. Cost is a crucial factor in deciding drug compliance particularly in those suffering from chronic diseases. In a study of haemodialysis patients from 12 countries, high cost was the cause on non-adherence in 3% to 29%.22 High cost has a greater impact on non-adherence in Indian studies (up to 62%).21, 23 High pill burden and complex dosing schedule were other common causes of non-adherence in this study. Prescription of ≥ 4-5 pills/day has been significantly associated with non-adherence in CKD patients.13, 24, 25 Although difficult, few measures to minimise non-adherence could be to prescribe cheaper generic medicines, reduce the amount and frequency of drugs, prescribing the drug combinations for hypertension, DM and anemia, giving priority to long-acting formulations, use of long-acting insulin when indicated, judicious use of antibiotics, multivitamins and PPIs/H2 blockers.
Fear of adverse effects of medication, lack of knowledge about necessity of individual drug, and lack of knowledge and insight about nature of disease were other important factors. Healthcare providers and allied staff can play an important role by explaining favourable risk-benefit effect of medications and further help to allay anxiety in patents. Educating and counselling patients and caregivers about the nature of disease and importance of medications would help to increase adherence. Additionally, 18% of the patients were taking alternative medicine without the knowledge of the treating physician. Similar finding has been reported by other Indian authors, for example 14% in a study by Sontakke et al.23 Considering only the patients on dialysis, 32% were taking some form of alternative medicine, most common being ayurvedic (48%). In a tertiary care hospital in India, 26% of patients on haemodialysis used alternative medicine, most commonly ayurveda (30.4%).26 Such medicines contain pharmacologically active ingredients, many of which are nephrotoxic. Unfortunately, most of the patients suffering from chronic diseases do not disclose the use of alternative and complementary medicine to the treating physician.27 Therefore, it becomes imperative for the healthcare providers to enquire about their use and properly advise patients accordingly.
Another major issue highlighted by this study is the progressive increase in non-adherence on longitudinal follow up. Early discontinuation of treatment is a major problem with long term treatment. According to studies, about half of the patients stop treatment within one year, despite having been prescribed for long term.28 In a study of 149 CKD patients, medication non-adherence was lower (17.4%) at the baseline period of the study than after 1 year of the study (26.8%).13 The non-adherence in present study at baseline was 58% which increased to 82% over a period of two years. At 2 yrs follow up, 11% patients were non-adherent to ≥5 drugs and 4% were not taking any of the medicines regularly as prescribed. Non-adherence was highest for phosphate binders and erythropoietin injections, which further increased on follow up. Highest levels of adherence were seen with anti-hypertensives and OHA (oral hypoglycaemic agent) both at baseline and follow up. This is in contrast to results of previous studies which report lower levels of adherence to anti-hypertensives.21
Studies evaluating the impact of medication non-adherence in CKD patients are sparse. Poor medication adherence has been shown to be associated with increased adverse outcomes particularly in chronic diseases like hypertension, diabetes mellitus, coronary artery disease and CKD.29 Though the individual studies failed to show increased mortality in non-adherence group, a meta-analysis by Simpson et al. in non-CKD populations revealed a significant association to be present.30 In a cross-sectional analysis of CKD patients, Hsu et al. found that patients with poor adherence were associated with the progression of CKD (adjusted OR 1.96, 95 % CI 1.02–3.76).31 In yet another study, low adherence was associates with increased with CKD progression and all-cause mortality, though statistically not significant.11 In this study, the composite of all cause death, progression of CKD or occurrence of ESRD was significantly higher in low adherence population (hazard ratio [HR] = 1.53, 95% confidence interval [CI] = 1.21-1.74).
The strengths of this study were a prospective design, large sample size, long term follow up and use of a validated tool to assess medication adherence. However, there were few important limitations too. Though we used MMAS-8 scale, even this objective measure has significant limitations and currently there is no gold standard to assess medication adherence. In addition, several factors that may influence medication adherence including socioeconomic status, education level, third party drug administration, knowledge of disease were not assessed. Finally, the findings of this study are subject to confounding and bias that are inherent to the observational studies.
Conclusion
Non adherence to medication is very prevalent among CKD patients in India, which further increases with duration of treatment. High use of alternative medicine was seen without physician’s knowledge, especially in patients on haemodialysis. Health care professionals have a crucial role to play in removing most of the barriers to adherence. Implementation of measures to provide free or subsidized medicines needs to be seriously considered especially in Indian context. Furthermore, we found that low medication adherence was significantly associated with composite of mortality and disease progression. Combined with previous studies this suggests that medication non-adherence may represent a modifiable risk factor for CKD progression. Further large and prospective studies are required to assess and devise effective interventions to improve medication adherence in the CKD population.
Acknowledgements
Authors acknowledge the immense help received from the scholars whose articles are cited and included in references of this manuscript. The authors are also grateful to authors / editors / publishers of all those articles, journals and books from where the literature for this article has been reviewed and discussed.
Source of Funding
None disclosed by authors
Conflict of interest
None
References:
-
KDIGO, CKD Work Group. KDIGO 2012 clinical practice guideline for the evaluation, prevention and management of chronic kidney disease-mineral and bone disorder. Kidney Int. 2013; 3:1–150.
-
Agarwal SK, Dash SC, Irshad M, et al. Prevalence of chronic renal failure in adults in Delhi, India. Nephrol Dial Transplant.2005; 20: 1638-1642.
-
Varma P.P. Prevalence of chronic kidney disease in India—where are we heading? Indian J Nephrol.2015; 25:133–135.
-
Singh AK, Farag YM, Mittal BV, et al. Epidemiology and risk factors of chronic kidney disease in India - results from the SEEK (Screening and Early Evaluation of Kidney Disease) study. BMC Nephrol. 2013; 14:114.
-
Rajapurkar MM, John GT, Kirpalani AL, et al. What do we know about chronic kidney disease in India: first report of the Indian CKD registry. BMC Nephrol.2012; 13: 10.
-
World Health Organization Adherence to long-term therapies: evidence for action. World Health Organization, Geneva, Switzerland (2003).
-
Manley HJ, Wang S, Nissenson AR. Denver, Colorado, November: 2010. Medication Non-adherence Predicts Hospitalization Rate and Healthcare Costs in Hemodialysis Patients. Renal Week 2010 American Society of Nephrology 43rd Annual Meeting.
-
Cedillo-Couvert EA, Ricardo AC, Chen J. Self-reported Medication Adherence and CKD Progression. Kidney Int Rep. 2018; 3(3):645-651.
-
Lindberg M, Lindberg P. Overcoming obstacles for adherence to phosphate binding medication in dialysis patients: A qualitative study. Pharm World Sci. 2008; 30:571–6.
-
Lars Osterberg, M.D., and Terrence Blaschke, M.D. Drug therapy adherence to Medication. N Engl J Med 2005; 353; 5:487-497.
-
Chiu YW, Teitelbaum I, Misra M, et al. Pill burden, adherence, hyperphosphatemia, and quality of life in maintenance dialysis patients. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2006; 4: 1089-1096.
-
Neri L, Martini A, Andreucci VE, et al. Regimen complexity and prescription adherence in dialysis patients. Am J Nephrol.2011; 34: 71-76.
-
Magacho EJ, Ribeiro LC, Chaoubah A, et al. Adherence to drug therapy in kidney disease. Braz J Med Biol Res.2011; 44: 258-262.
-
Schmitt KE, Edie CF, Laflam P, et al. Adherence to antihypertensive agents and blood pressure control in chronic kidney disease. Am J Nephrol.2010; 32: 541-548
-
Ammassari A, Trotta MP, Murri R, et al. Correlates and predictors of adherence to highly active antiretroviral therapy: overview of published literature. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr. 2002; 3: S123-S127.
-
Lacey J, Cate H, Broadway DC. Barriers to adherence with glaucoma medications: A qualitative research study. Eye. 2009; 23:924–32.
-
Laws MB, Wilson IB, Bowser DM, Kerr SE. Taking antiretroviral therapy for HIV infection: Learning from patients’ stories. J Gen Intern Med. 2000; 15:848–58.
-
Morisky DE, Ang A, Krousel-Wood M, et al. Predictive validity of a medication adherence measure in an outpatient setting. Clin Hypertens. 2008; 10(5):348-54.
-
Burkhart PV, Sabate E. Adherence to long-term therapies: evidence for action. J Nurs Scholarsh.2003; 35: 207.
-
Schmid H, Hartmann B, Schiffl H. Adherence to prescribed oral medication in adult patients undergoing chronic hemodialysis: A critical review of the literature. Eur J Med Res. 2009; 14:185–90.
-
Ahlawat R, Tiwari P, Cruz SD. Prevalence and Predictors of Medication Non-Adherence in Patients of Chronic Kidney Disease: Evidence from A Cross Sectional Study. J Pharma Care Health Sys. 2016; 3: 152.
-
Hirth RA, Greer SL, Albert JM, et al. Out-of-pocket spending and medication adherence among dialysis patients in twelve countries. Health Aff. 2008; 27:89–102.
-
Sontakke S, Budania R, Bajait C, et al. Evaluation of adherence to therapy in patients of chronic kidney disease. Indian J Pharmacol. 2015;47(6):668
-
Moreira L, Fernandes P, Monte S, et al. Medication Compliance in Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease. J Bras Nefrol. 2008; 30: 113-119.
-
Shrivastava PS, Shrivastava SR, S MM. A community-based study to assess the treatment adherence and its determinants among hypertensive patients residing in a rural area of Kancheepuram district, Tamil Nadu. Int J Med Sci Public Health. 2017; 6(9): 1386-1393.
-
Arjuna Rao AS, Phaneendra D, Pavani CD, et al. Usage of complementary and alternative medicine among patients with chronic kidney disease on maintenance hemodialysis. J Pharm Bioallied Sci. 2016;8:52–57.
-
Tangkiatkumjai M, Boardman H, Praditpornsilpa K, Walker DM. Prevalence of herbal and dietary supplement usage in Thai outpatients with chronic kidney disease: A cross-sectional survey. BMC Complement Altern Med. 2013; 13:153.
-
Vrijens B, Vincze G, Kristanto P, Urquhart J, Burnier M. Adherence to prescribed antihypertensive drug treatments: longitudinal study of electronically compiled dosing histories. BMJ. 2008; 336: 1114-1117.
-
M. Tangkiatkumjai, D.M. Walker, K. Praditpornsilpa, et al. Association between medication adherence and clinical outcomes in patients with chronic kidney disease: a prospective cohort study. Clin Exp Nephrol. 2017; 21(3):504-512.
-
S.H. Simpson, D.T. Eurich, S.R. Majumdar, et al. A meta-analysis of the association between adherence to drug therapy and mortality. BMJ. 2006; 333(7557):15.
-
K.L. Hsu, J.C. Fink, J.S. Ginsberg, et al. Self-reported medication adherence and adverse patient safety events in CKD. Am J Kidney Dis. 2015; 66(4): 621–629.
|






 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License