IJCRR - 10(18), September, 2018
Pages: 13-17
Date of Publication: 28-Sep-2018
Print Article
Download XML Download PDF
Prevalence of Mycobacterium Tuberculosis and Multidrug Resistance Tuberculosis by Using GeneXpert MTB/ RIF System at a Tertiary Care Center in Maharashtra
Author: Kishor Ingole, Sonika Wathmore (Kamble), Sapana Mundhada
Category: Life Sciences
Abstract:Background: Despite of tuberculosis control programme and anti-tuberculosis drugs, tuberculosis (TB) and multidrug-resistant tuberculosis (MDR-TB) is a serious public health issues worldwide. Rapid laboratory detection of M. tuberculosis is needed for the early diagnosis and treatment of TB and MDR TB.Recently GeneXpert MTB/RIF system is a new molecular technique introduce for early detection of M. tuberculosis. Aim: To find out prevalence of MTB and MDR TB by using GeneXpert MTB/RIF system and also find out associated risk factor with MTB. Material and Method: Total 250 patients with suspected MDR pulmonary tuberculosis visited to TB & Chest OPD over a period of 2 years were included in study. Sputum sample was taken from each patient and tested by the GeneXpert MTB/RIF assay according to standard protocol. Result: Among 250 patients, 159 (63.6%) patients were detected as MTB positive. Out of 159 MTB patients 15 (9.43%) were detected with MDR. Maximum number of MTB was detected in patients from lower socioeconomic status. Out of 159 MTB patients, 25.15 % had showed HIV and TB coinfection. Among 15 MDR patients, 7(46.67%) were found to be defaulter,1(6.66%) due to failure & 7 (46.67%) were newly diagnose. out of 159 MTB detected patients 93 (58.49%) were cured,41 (25.79%)were died & 25 (15.72%) were still on treatment. Conclusion: Newer rapid molecular diagnostic techniques like GeneXpert will help to diagnose tuberculosis & multidrug resistant tuberculosis early so prompt treatment can be initiated for better outcome.
Keywords: Tuberculosis, GeneXpert MTB/RIF, Multidrug resistance
Full Text:
Introduction:
Mycobacterium tuberculosis (MTB) remains one of the most significant cause of morbidity worldwide, it affect up to one third of the world population. More than 9.4 million incident cases noted and almost two million people are killed each year by TB.1 Universal access to high-quality, patient-centred treatment is emphasized by WHO's Stop TB Strategy.2 Significant challenges are faced for disease control due to the emergence and spread of drug resistant Mycobacterium tuberculosis complex (MTBC) strains (multidrug resistance and extensively drug resistant).3 India is the country that bears highest burden of TB. Out of a global incidence of 9 million, World Health Organisation statistics for 2013 gives an estimated incidence figure of 2.1 million cases of TB for India. The proportion of multidrug-resistant tuberculosis (MDR TB) cases among all cases is 4.9% while in new cases and previously treated cases it is 2.9% and 15.5% respectively.4
Failure to recognize and effectively treat patients with MDR tuberculosis (Resistance to isoniazid and rifampicin, which are the 2 most effective first-line drugs for TB) and XDR TB (Resistant to isoniazid, rifampicin, any fluoroquinolone, and at least one of 3 injectable second-line drugs i.e. amikacin, kanamycin, or capreomycin) leads to increased morbidity, mortality, nosocomial outbreaks and resistance to additional antituberculosis drugs.5 However, proper identification of MDR and XDR tuberculosis can lead to an effective treatment. The gold standard technique considered for diagnosing TB is culture, but it may take 2 to 8 weeks. Another method for diagnosis is sputum smear microscopy for acid-fastbacilli (AFB) which is rapid and inexpensive, but has poor sensitivity.6, 7 In our country TB diagnosis rely on acid-fast staining and the conventional Lowenstein Jensen culture method in conjunction with assessment of patients clinical symptoms and radiographic evidence to diagnose TB.8
Rapid detection of Mycobacterium tuberculosis (MTB) is essential for diagnosis and treatment of tuberculosis because of the high risk of transmission from one person to another as well as high rate of morbidity and mortality. Presently the major problem in management of Tuberculosis is a lack of accurate and rapid diagnostic test for detection of Mycobacterium tuberculosis. In last decade Several molecular methods like line probe assays and real-time polymerase chain reaction (PCR) has been developed for rapid detection of Mycobacterium tuberculosis and drug resistance in clinical samples.7 These methods were helpful for early diagnosis and treatment of tuberculosis which in turn improving patients’ outcomes and allow taking effective public health measures.
GeneXpert mycobacterium tuberculosis (MTB)/rifampicin (RIF) is a new cartridge based, automated and rapid molecular diagnostic device that performs sample processing and hemi-nested real-time PCR analysis in a single, hands-free step for identifying Mycobacterium tuberculosis and rapid detection of rifampicin(RIF) resistance in sputum samples.8 The present study aimed to find out prevalence of MTB and MDR TB by using GeneXpert MTB/RIF system(CB NATT) at tertiary care center, Maharashtra and also find out associated risk factor with it.
Material and method
This cross-sectional study was done at a tertiary care center after Institutional Ethics Committee approval over a period of two year from January 2014 to December 2015. Total 250 patients with suspected MDR pulmonary tuberculosis visited to TB & Chest OPD were included. At least two sputum specimens taken from each patient for bacteriological examination.
Exclusion criteria: 1.Patients with extra pulmonary tuberculosis.
2. Non complaint patients.
GeneXpert MTB/RIF assay.10, 11
Sputum sample was taken from patient and tested by the GeneXpert MTB/RIF assay. Using a sterile pipette, briefly 2.0 ml of GeneXpert MTB/RIF sample reagent was added to 1.0mlof sputum specimen. The closed specimen container was agitated twice manually during 15min at room temperature and then 2ml of the inactivated material was transferred to the test cartridge. GeneXpert MTB/RIF (CBNAAT) is a rapid cartridge based nucleic acid amplification technique based on principle of Real time PCR gives result within 2 hours with sensitivity and specificity of 90.6% & 94.3% respectively. It is highly effective for diagnosis of tuberculosis and rifampin-resistant strains even in smear-negative sample.
Statistical analysis:
Data was entered in MS-Excel, corrected for typographic errors. For qualitative data (binomial and orderly data) chi-square test used and analyzed by using SPSS V. 16 software and quantitative data expressed in proportion or percent using MS Excel (MS office 10). Graphical presentation of the result was done using MS-Excel. The p- value of < 0.05 was considered significant.
Result:
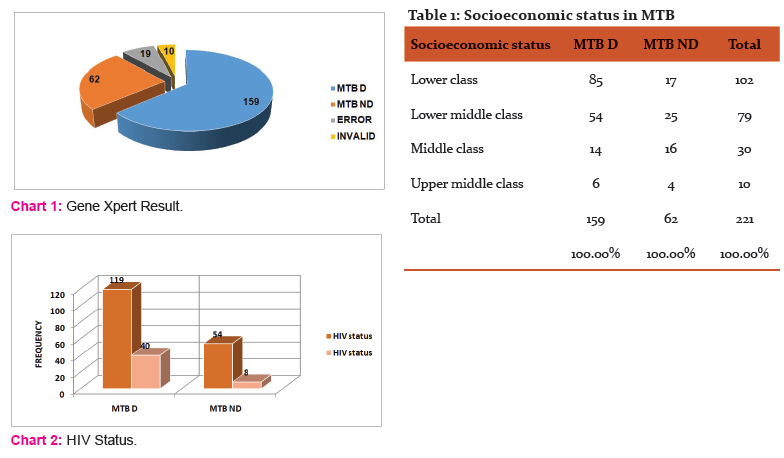
Among 250 patients, 159 (63.6%) patients were detected as MTB positive while in 62 (24.8%) MTB was not detected, 19 (7.6%) were error& 10 (4%) were invalid. (Chart no 1) Among 159 MTB patients 15 (9.43%) were MDR detected. Among MTB detected patient mean age was 36.47 years and M: F ratio was 2.7:1(117 were male & 42 were female).
Maximum number of MTB was detected in patients from lower socioeconomic status which was statistically significant.(P value =0.001) (Table no 2)when different risk factor associated with MTB were studied, we observed that among MTB patients,45 (28.30%) were smoker &114 (71.69%) were nonsmoker(P value=0.026) as well as 49 (30.81%) were alcoholic &110 (69.18%) were nonalcoholic.(P value= 0.08) when checked for MTB and HIV co-existence we found that out of 159 MTB detected patients, 40 (25.15%)were HIV positive &119 (74.84%) were negative. (P value =0.03) (Chart no 2) Out of 159 MTB detected patients, 18 (11.32 %) having family history of contact with MTB positive patient. In present study we checked for association of different illness in MTB positive (159) patients, it was found that 4 (2.51%) were diabetic&155 (97.48%) were nondiabetic (P value= 0.39) and 5 (3.14%) were suffering from renal diseases &154 (96.85%) were not.(P value= 0.06).
Among 221 patients in our study we found that 23 (10.40%) were defaulter, 11 (4.49%) were due to treatment failure &1 (0.45%) was due to relapse & 178 (80.54 %) were newly diagnose cases. Out of 15 MDR patients, 7(46.67%) were found to be defaulter, 1(6.66%) due to failure & 7 (46.67%) were newly diagnose which was found to be statistically significant (P value=0.003). In present study, out of 159 MTB detected patients 93 (58.49%) were cured, 41 (25.79%) died& 25 (15.72%) were still on treatment. While among MDR patients, 1 (6.67%) patient was cured, 6 (40%) died &8 (53.33%) were still on treatment.
Discussion:
In present study we examined total 250 patients satisfying the criteria for WHO recommending TB testing on Gene Xpert MTB/RIF system.12) Due to error & invalid results we excluded 29 samples and total 221 patients were studied further in final analysis. In our study we found the prevalence of MTB was 63.6% by using GeneXpert MTB/RIF system, similar observation noted in other study by Kumar M et al.13 Early detection of drug resistance in tuberculosis is essential to reduce morbidity and mortality associated with it. In present study we observed that prevalence of MDRTB was 9.43 %. Other studies by Chakroborty et al14 and Khalil et al15 observed similar result in their studies.
Among MTB detected patient mean age was 36.47 years and M: F ratio was 2.7:1(117 were male & 42 were female). Various reasons has been suggested to explain the gender imbalance in MTB patients. Social behavior among men, difference between male and female susceptibility to TB and less access to health care for women in many developing countries, and therefore unreported TB cases.16,17 Various studies showed that patients age, gender and race have no correlation with occurrence of drug-resistant tuberculosis.18,19 similar results were observed in our study.
Early detection of drug resistant & assessment of various factors that may increase the likelihood of drug resistant in tuberculosis is important. For that reason we had studied the patient’s sociodemographic profile, lifestyle, habitat &their illnesses in present study. Studies by Lonnroth et al 20& Muniyandi M et al21 had observed that people with lower socioeconomic status having more risk for development of tuberculosis. Similar finding were observed in our study also which was statistically significant. (P<0.05) People with low socioeconomic status were exposed to crowded and less ventilated places, malnutrition, indoor air pollution etc. which increases their risk for TB.
Bates and colleagues22, in their meta-analysis of 24 studies reported that there was clear evidence that smoking remained a major risk factor for TB infection and disease. In our study we also found statistically significant association between smoking & development of TB. Smoking leads to impaired clearance of mucosal secretion, reduced phagocytic ability of alveolar macrophage, and decrease in the immune response and/or CD4 + lymphopenia due to the nicotine in the cigarettes which would increase susceptibility to pulmonary tuberculosis.23,24 In different studies Alcohol was recognized as a strong risk factor for TB disease,25most probable reason behind that was alteration in immune response specifically alteration in signal molecule for production of cytokine.26 In present study alcoholism was not showed statistically significant association with tuberculosis. It may be because of small sample size & many patients denied for taking alcohol consumption.
Various studies concluded that HIV infection not only increases the chances of reactivation of latent TB infection but also increases the rapid progression following primary infection or reinfection with TB.27, 28 Similarresult was noted in present study which was statistically significant. (P<0.05) In our study we had not found any significant association between family history of contact & TB .This may be due to small sample size or patient didn’t aware about their close contact in past. Gillani et al29 also noted similar finding in his study. Presence of Diabetes mellitus and renal diseases increases risk for development of TB infection, as they directly impairs the innate and adaptive immune responses, thereby accelerating the proliferation of TB.30,31 In contrast to this we had not found any association between patients having diabetes mellitus & renal diseases with TB. The reason behind it may be a small sample size in our study.
Jeon et al 32, showed that inadequate treatment had contributed to the high prevalence of MDR and XDR-TB. Our study showed similar results with a statistically significant association between defaulter and treatment failure with MDR TB. Among the tuberculosis patients 58.49% got cured, 25.79% died & 15.72% were still on treatment while among multidrug resistant tuberculosis patients 6.67% were cured, 40% died & 53.33 % were still on treatment. Study showed that there was higher percentage of death & extension of duration of treatment among MDR patients compared to tuberculosis patients.
Conclusion-
Management of TB & multidrug resistant TB has remained a persistent public health problem as it has high morbidity & mortality. As there is significant association of TB with risk factors like socioeconomic status, smoking & HIV. There is need of intervention to reduce smoking, HIV incidence & need to improve patient socioeconomic status for prevention of tuberculosis. As there is highly significant association of MDR TB in patients with history of default, failure & relapse. We need to find out the causes of these factors & early intervention should be instituted to reduce the default, failure and relapse cases. Newer rapid molecular diagnostic techniques like GeneXpert will help to diagnose tuberculosis & multidrug resistant tuberculosis early so prompt treatment can be initiated for better outcome.
Acknowledgement:
Authors acknowledge the immense help received from the scholars whose articles are cited and included in references of this manuscript. The authors are also grateful to authors / editors / publishers of all those articles, journals and books from where the literature for this article has been reviewed and discussed.
Source of Funding : None
Conflict of interest : None
References:
-
World Health Organization. Global Tuberculosis Report 2015, Geneva: WHO, WHO/HTM/TB/2015.22
-
The global plan to stop TB, 2006-2015. Geneva, World Health Organization, (WHO/HTM/STB/2006.35) (2006).
-
WHO. 2010. Multidrug and extensively drug-resistant TB (M/XDR-TB): 2010 global report on surveillance and response. WHO/HTM/TB/2010.3. World Health Organization, Geneva, Switzerland.
-
Tuberculosis Service. 2009. Tuberculosis report in Turkey. Ministry of Health, Ankara, Turkey.
-
Extensively Drug-Resistant Tuberculosis (XDR TB). Centers for Disease Control and Prevention
-
Farmer, P., J. Bayona, M. Becerra, J. Furin, C. Henry, H. Hiatt, J. Y. Kim, C. Mitnick, E. Nardell, and S. Shin. 1998. The dilemma of MDR-TB in the global era. Int. J. Tuberc. Lung Dis. 2:869-876.
-
Zeka AN, Tasbakan S and Cavusoglu C. Evaluation of the GeneXpert MTB/RI Fassay for rapid diagnosis of tuberculosis and detection of rifampin resistance in pulmonary and extrapulmonary specimens. J Clin Microbiol 2011; 49: 4138–4141.
-
8. Xia H and Zhao YL. The application prospect of Xpert MTB/RIF in China. The Journal of Practical Medicine 2013; 29:3799–3800.
-
Blakemore R, Story E, Helb D, et al. Evaluation of the analytical performance of the Xpert MTB/RIF assay. J Clin Microbiol 2010; 48: 2495–2501.
-
GeneXpert Dx System Operator Manual. Cepheid Inc., Sunnyvale, CA, USA (2011).
-
Bodmer T and Stro¨ hle A. Diagnosing Pulmonary Tuberculosis with the Xpert MTB/RIF Test. J Vis Exp 2012; 62: e3547.
-
WHO. Roadmap for rolling out Xpert MTB/RIF for rapid diagnosis of TB and MDR-TB. December 6, 2010. Accessed May 4, 2011.
-
Kumar M, Datta A, Kumar H.A study on prevalence of rifampicin resistance by Gene Xpert with clinico-radiological correlation in previously treated pulmonary tuberculosis patients. Int J Res Med. 2016; 5(2); 52-56.
-
Chakraborty, S., Chakraborty, A., Talukder, T., Mukherjee, M. and Chatterjee, T. Prevalenceof Mycobacterium tuberculosis Strains Isolated from Both Pulmonary and Extra Pulmonary Samples and Their Resistance to Rifampicin: A Study from Kolkata and Surrounding Suburbs. Journal of Tuberculosis Research, 4, 61-71.
-
Khalil KF, Butt T. Diagnostic Yield of Bronchoalveolar Lavage Gene Xpert in Smear-Negative and Sputum-Scarce Pulmonary Tuberculosis Journal of the College of Physicians and Surgeons Pakistan 2015, Vol. 25 (2): 115-118
-
Karim F, Islam MA, Chowdhury AM, Johansson E, Diwan VK. Gender differences in delays in diagnosis and treatment of tuberculosis. Health Policy Plan. 2007;22(5):329–334.
-
Neyrolles O, Quintana-Murci L. Sexual inequality in tuberculosis. PLoS Med. 2009;6(12):e1000199. doi: 10.1371/journal.pmed.1000199
-
Melzer M, Gupta N, Petersen I, Cook S, Hall B. Previous treatment in predicting drug-resistant tuberculosis in an area bordering East London, UK. International Journal of Infectious Diseases 2010; 14:e717–e722.
-
Kim HR, Hwang SS, Kim EC, et al. Risk Factor for Multidrug-Resistant Bacterial Infection among Patients with Tuberculosis. Journal of Hospital Infection 2010; xxx: 1-4.
-
Lönnroth k , Jaramillo E, Williams B.G, Dye C, Raviglione M. “Drivers of tuberculosis epidemics: the role of risk factors and social determinants,” Social Science and Medicine, vol. 68, no. 12, pp. 2240–2246, 2009.
-
Muniyandi M, Ramachandran R, P. Gopi P.G. et al., “The prevalence of tuberculosis in different economic strata: a community survey from South India,” International Journal of Tuberculosis and Lung Disease, vol. 11, no. 9, pp. 1042–1045, 2007.
-
Bates M.N., Khalakdina A, Pai M, Chang L, Lessa F, Smith K.R. “Risk of tuberculosis from exposure to tobacco smoke: a systematic review and meta-analysis,” Archives of Internal Medicine, vol. 167, no. 4, pp. 335–342, 2007.
-
Sopori M. “Effects of cigarette smoke on the immune system,” Nature Reviews Immunology, vol. 2, no. 5, pp. 372–377, 2002.
-
H. Wang, M. Yu, M. Ochani et al., “Nicotinic acetylcholine receptor α7 subunit is an essential regulator of inflammation,” Nature, vol. 421, no. 6921, pp. 384–388, 2003.
-
K. Lönnroth, B. G. Williams, S. Stadlin, E. Jaramillo, and C. Dye, “Alcohol use as a risk factor for tuberculosis-a systematic review,” BMC Public Health, vol. 8, article 289, 2008.
-
A. Fok, Y. Numata, M. Schulzer, and M. J. FitzGerald, “Risk factors for clustering of tuberculosis cases: a systematic review of population-based molecular epidemiology studies,” International Journal of Tuberculosis and Lung Disease, vol. 12, no. 5, pp. 480–492, 2008.
-
H. C. Bucher, L. E. Griffith, G. H. Guyatt et al., “Isoniazid prophylaxis for tuberculosis in HIV infection: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials,” AIDS, vol. 13, no. 4, pp. 501–507, 1999.
-
P. A. Selwyn, D. Hartel, V. A. Lewis et al., “A prospective study of the risk of tuberculosis among intravenous drug users with human immunodeficiency virus infection,” The New England Journal of Medicine, vol. 320, no. 9, pp. 545–550, 1989.
-
Gillani et al. Study on drug-resistant tuberculosis and tuberculosis treatment on patients with drug resistant tuberculosis in chest clinic outpatient department Int J Pharm Pharm Sci, 2012:Vol 4, Issue 2, 733-37.
-
B. Alisjahbana, R. Van Crevel, E. Sahiratmadja, M. den Heijer, A. Maya, E. Istriana, et al., “Diabetes mellitus is strongly associated with tuberculosis in Indonesia,” The International Journal of Tuberculosis and Lung Disease, vol. 10, no. 6, pp. 696–700, 2006.
-
M. Delamaire, D. Maugendre, M. Moreno, M. C. Le Goff, H. Allannic, and B. Genetet, “Impaired leucocyte functions in diabetic patients,” Diabetic Medicine, vol. 14, no. 1, pp. 29–34, 1997.
Jeon DS, Shin DO, Park SK, Seo JE, Seo HS, Cho YS, Lee JY, Kim DY, Kong SJ, Kim YS, Shim TS. Treatment Outcome and Mortality among Patients with Multidrug-resistant Tuberculosis in Tuberculosis Hospitals of the Public Sector. Journal of Korean Medical Science 2011;26: 33-41.
|






 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License