IJCRR - 10(15), August, 2018
Pages: 20-25
Date of Publication: 16-Aug-2018
Print Article
Download XML Download PDF
Fine Needle Aspiration Cytology [FNAC] \? Review Article
Author: Sachin B. Ingle, Chitra R. Hinge (Ingle)
Category: Healthcare
Abstract:FNAC (Fine Needle Aspiration Cytology) as we know it today dates back to around 1950. FNAC being easy, safe, cost effective should be preferred as first line diagnostic method by all clinicians. Before any surgical intervention, FNAC reports direct surgeon about what treatment modality to be used. Surgical pathology has its own confirmatory role post- operatively but importance of FNAC is also well known by all clinicians. Therefore, there has to be a setting of dedicated FNAC clinic in the department of pathology. With the help of imaging modalities, FNAC has evolved as more accurate and specific method, while the use of ancillary techniques makes even this easy procedure as highly useful for diagnosis and prognosis of various lesions.
Keywords: FNAC, Preoperative, Diagnostic test
Full Text:
The Origins of FNAC /Historical Aspects
In mid –nineteenth century, Kun [1] (1847) and Lebert[2] (1851) and Menetrier[3] (1886) used needles to obtain cells and tissue fragments to diagnose malignant tumours. Kun described this technique as “new instrument for diagnosis of tumours”.
Leyden [4] (1883) employed the same method to isolate pneumonic microorganisms. Grieg and Gray who in 1904 diagnosed trypanosomiasis in cervical lymph node aspirates from patients with sleeping sickness in Uganda. Their findings were reported by a captain Bruce in a British Medical Journal memorandum in 1904.
In the mid -1920s there were attempts in New York and Chicago to employ large needle aspiration for a variety of sites ranging through lymph nodes, prostate and breast.
In the UK in 1927, Dudgeon and Patrick [5] suggested the needling of tumours as a means of rapid microscopic diagnosis.
Interest in the procedure was resurrected by Europeans in mid 1950s. It was in Europe that “FNAC” as the technique was usually called began to flourish in 1950s and1960s.
Soderstrom [6] and Franzen [7] in Sweden, Lopes Cardazo [8, 9] in Holland, Zajdela [8] in France and others became major proponents, studying thousands of cases each year.
FNAC soon established its place as a diagnostic routine to be used by team of pathologists and clinicians.
History of FNAC has been very well documented by Grunze and Spriggs,[10] and Naylor [11].
FNAC as an important clinical TOOL
FNAC is a simple, inexpensive, easily performed outpatient procedure which can provide a rapid diagnosis. It has been widely used in Europe for decades, mainly in Scandinavian countries [12-15] .
A technique which is safe, rapid, relatively pain free, cost effective and accurate is always a clinician’s first choice and this is what FNAC is about .
It is eminently suitable as first line investigation for almost all superficial palpable swellings as well as many deep seated lesions. FNAC was initially conceived as a means to confirm a clinical suspicion of local recurrence or metastasis of known cancer without subjecting the patient to further surgical intervention.
FNAC is a time tested simple office procedure having a high degree of diagnostic accuracy and precision. The specificity and sensitivity of diagnostic precision lie in range of 60% and 80% respectively.
The acceptance both by surgeons and pathologists itself speaks of the tale of comfort which it allows.
The art of medicine is practiced within a community of caregivers who are perched on innumerable speciality branches and these braches intersect each other at various times.
Clinical consultations help to acquaint cytopathologist about probable diagnoses possible for any lesion. Often a major surgical biopsy can be avoided by performing a needle aspiration instead.
FNAC SURPRISES THE SURGEON MANY TIMES
Surgeons are always impressed by the help of FNAC to make diagnoses which affect treatment of patient in a wide manner. Many tumours being diagnosed high grade on FNAC make the surgeon to go for chemotherapy before surgical intervention.
Such a simple technique and so many wonders.
Benefits of FNAC are innumerable.
Cost effective
-
It has lower risk than surgical biopsy.
-
It is readily repeatable and useful for multifocal lesions.
-
Minimal physical and psychological discomfort for the patient.
-
Rapid reporting and bedside diagnosis of neoplastic, hyperplastic and inflammatory masses.
-
Active participation of patient in treatment planning and provides opportunity for fuller preoperative counselling.
-
Elimination of a two stage procedure
-
Therapeutic procedure for evacuation of cystic lesions.
-
Allows cases to be prioritized when there is a waiting time for surgery
-
Permits the diagnosis of some benign conditions for which there is no need for surgery
-
It is a rapid means of confirmation and recurrence of previously treated malignancy without surgery.
Technique of FNAC (Fig1)
Success of FNAC depends to a high degree on perfecting the technique of sampling and preparation of samples. Palpation skills learnt through practice and experience, judiciously complemented by radiological image guidance when appropriate are essential to obtain representative samples.
Choice of needles, the use or not of aspiration and the manipulation of needle within the target relative to type of tissue decide the adequacy of sample.
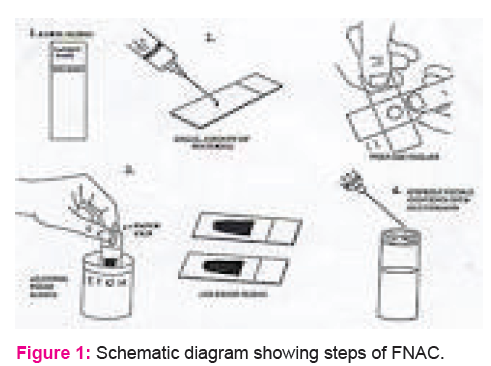
Finally, correct smearing, fixation and staining of samples is critical to assure optimal preservation and presentation of cells.
Specific staining defines and highlights specific features of aspirate smears. Comparisons between two commonly used methods are
-
Air drying followed by a Romanowsky type stain such as MGG.
-
Alcohol fixation followed by H and E staining.
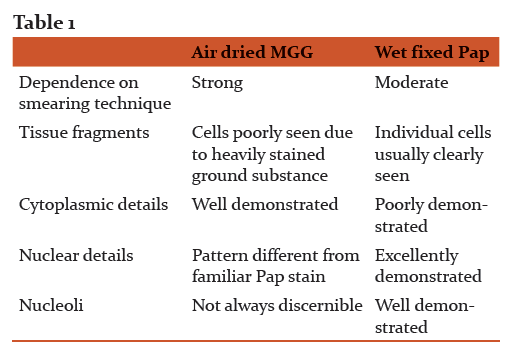
Usually, pathologists trained in gynaecological cytology prefer alcohol fixed –Pap stained smears while those trained in haematology choose air dried MGG stained smears.
Utility of special stains in diagnosing lesions
-
PAS /diastase or alcian blue for mucins - mucins can help in diagnosing mucin producing tumours of many anatomic sites (breast, gastrointestinal site, pancreas, ovary ) and sometimes can be completely devoid of cells (e.g. pseudomyxomaperitonei or pure mucinous carcinoma), yielding a false negative diagnosis.
-
Prussian blue for Iron in hemosiderin containing lesions.
-
Masson Fontana for melanin in melanoma
-
Grimelius for argyrophilic granules
-
Congo red for amyloid
-
PAS for glycogen –extracellular glycogen production is appreciated in tumours like Ewing’s sarcoma, rhabdomyosarcoma , and glycogen rich clear cell tumours).
-
Oil red O for fat
-
Fouchet’s reagent counterstained with Sirius red for bile pigments
-
Microorganisms identified by Gram, PAS, ZN or Gomori silver stain.
Pitfalls or drawbacks of morphological diagnosis
As every other technique in this world, FNAC also has some complications and limitations. These have been enlisted below:
-
Instances of serious complications have been reported in relation to different sites and organs, such as major haemorrhage, septicaemia, vasovagal reaction, seeding of tumour, bile peritonitis, acute pancreatitis, pneumothorax etc[16].
-
Pre-operative FNAC may cause local tissue changes which could render subsequent histological diagnosis difficult .Such changes include hematoma, infarction, capsular pseudoinvasion, reparative reactions have been reported[17]
-
Results and accuracy are highly dependent on quality of samples and smears.
-
Many pathological processes are heterogeneous and tiny sample obtained from FNAC may not be representative.
-
Some lesions are recognised on basis of specific micro architectural pattern, which may not be represented in cytological preparations
-
Small FNA sample may not allow full armamentarium of ancillary techniques to be drawn upon.
Aspiration cytology requires highly skilled and trained personnel in both aspiration and assessment .Stewart commented in 1933 that “until the pathologist has familiarized himself with the various pitfalls, errors are certain to occur” and “it must not be inferred that the diagnosis is always a simple and that no errors have been made”.
Extrinsic factors which may lead to diagnostic pitfalls are lack of or misleading clinical information, non-representative samples, contamination of samples by tissue adjacent to target lesion, artefacts due to poor processing of samples and too much reliance on and technical failure of ancillary tests.
Intrinsic factors which may lead to diagnostic pitfalls arise mainly due to deviations from general cytodiagnostic criteria which can occur in various benign and malignant tumours.
Pitfalls are an inseparable part of the practice of FNAC, but they can be minimised, if requisite diagnostic rigours are applied and care taken to correlate cytology with clinical an radiological findings. Judicious use of ancillary techniques also helps in reducing incidence of pitfalls.
Ancillary techniques
No wonder that technology is the fastest spreading tumour in pathology, but this tumour is having all gains.
Various new techniques have revolutionised FNAC since its history. The pathologist must always keep in mind to apply any of these appropriate ancillary diagnostic techniques to cytological preparations.
-
Electron microscopy –It is particularly useful in unusual lung or mediastinal lesions. Valuable information is obtained in recognizing neuroendocrine tumours, in specific diagnosis of melanoma, mesothelioma, and some carcinomas where immunocytochemistry often cannot provide such positive diagnostic features[18.19] .
-
Immunocytochemistry- It is the most important recent development in diagnostic cytology. Monoclonal antisera to various proteins and cell products are nowadays commercially available. Alcohol fixed smears are usually preferred over air dried smears. The avidin –biotin complex method is the most commonly used with both monoclonal and polyclonal primary antibodies. Diaminobenzidine is used as marker dye. Appropriate controls are crucial to achieve diagnostic accuracy[20]..The results of immunocytochemistry should be interpreted with caution in relation of conventional cytomorphology and clinical data [21]. 
-
Image analysis – there are 3 ways of image analysis
-
Morphometry-quantitative analysis of geometric features of structures such as tissues, cells, nuclei or nucleoli [22,23].
B. Object counting – quantitation of mitosis or measurement of proliferation fraction of a cell population using antibodies. It also makes it possible to quantitate apoptotic figure by TUNEL assay [24].
C. Cytometry –based on ability to detect a particular substance of interest by a specific dye and to measure the concentration of dye by assessing optical density [25].
Fluorochromes can also be used such as propidium iodide dyes [26-28].
Powerful computers also have automatic cell classification based on pattern recognition for diagnostic [29,30], prognostic [31,32] and predictive purpose [33].
Quantitation of nuclear immunostain of Estrogen and progesterone receptors [34], proliferation markers [35-37] can be done.
-
Flow cytometry
Based on fundamental work showing that DNA content , measured by UV visible light in unstained cells , double during cell cycle [38], followed by improved detection of antigens using fluorescence methods [39] and development of apparatus capable of counting [40] and sizing blood cells [41].
-
Molecular cytopathology
Application of molecular probes to cytologic samples of human malignancies has refined the diagnostic and prognostic armamentarium [42-45].
In situ hybridization – It is a newly developed and global approach to detect genetic changes in tumors.
For localization of specific nucleic acid within individual cells based on complementary binding of a nucleotide probe, labelled with non-isotopic reporter molecule, to a special target sequence of DNA or RNA [46].
Using probes to chromosome specific sequence, it is possible to detect aneuploidy in interphase nuclei [47-48] and losses, gains or amplification of chromosome regions with known prognostic value [49-50].
In situ amplification – based on PCR this allows recovery of large amount of DNA from minute quantities of starting material [51].
Various adaptations of PCR have been developed for cytological preparations [52] such as PCR in situ hybridisation ,in situ PCR, reverse transcriptase in situ PCR[53], methylation specific PCR [54],and primed in situ synthesis [55] . The most crucial steps in optimising in situ amplifications are fixation and preparation of cells.
IMAGING METHODS FOR GUIDANCE OF ASPIRATION CYTOLOGY
Nowadays, to make FNAC more accurate and precise, imaging modalities have been used for guiding the tract of needle. Various imaging modalities used are
-
Fluoroscopy –
Uses-
-
Quick alternative for radiologist not experienced in USG guidance.
-
Is most useful in guidance for small, very mobile lesions.
-
Efficient sampling options for cortical bony lesions.
-
Ultrasound –
Only real time guidance which allows imaging in any plane and is only suitable guidance for biopsy of foetal tissues.
Some parts of body [56] such as chest wall, musculoskeletal system, through neglected in past, have undergone an increase in interest for both diagnosis and interventional studies.
-
CT scanning – localization of needle tip with in a lesion is very accurate with CT. There are very few areas of body which cannot be biopsied under CT control and extremely small lesions can be sampled.
-
MRI – its sensitivity is generally greater than that of other imaging methods, particularly useful in brain, liver and breast [57].
Conclusion –Fine needle aspiration cytology has an utmost importance in the current era of surgical practice in the preoperative stage as it guides the clinician a lot in the treatment plan and mostly clear the pathological aspects of the disease avoid untoward complications related to disease and treatment for the sake of pathological diagnosis. Many times it avoids unnecessary surgical intervention
Acknowledgement-
Dr Ingle is grateful to the past and present members of his laboratory for their contributions to his studies. He is very much thankful to his journal team of IJCRR for invaluable suggestions and guidelines throughout the publication process of the manuscript. He also wishes to express his gratitude to several investigators worldwide for their collaborations. Indeed, he is Grateful to his Chief Patron and Executive president Hon. Prof V.D. Karad and Patron Hon. Executive director Shri Ramesh Appa Karad for their constant and strong support throughout my academic journey
References:
-
Kun M. A new instrument for diagnosis of tumours. Monthly J Med Sci 1846; 7:853.
-
Lebert H. Traitepratique des maladies cancereusesetddes affections curable confondues avec le cancer. Paris:J B Bailliere;1851.
-
Menetrier P. Cancer primitive du poumon. Bull Soc Anat( Paris )1886;11:643.
-
Leyden. Ueber infectose Pneumonie. Dtsch Med Wschr 1883;9:52-4.
-
Dudgeon LS, Patrick CV.A new method for the rapid microscopical diagnosis of tumours.Br J Surg 1927;15:250-61.
-
Soderstrom N. Fine needle aspiration biopsy. Stockholm: Almqvist and Wiksell;1966.
-
Franzen S, Giertz G, Zajicek J. Cytological diagnosis of prostatic tumours
By transrectal aspiration biopsy :a preliminary report. Br J Urol 1960;32:193-6.
8. Lopes Cardazo P. Clinical cytology. Leiden :Safleu;1954.
9. Lopes Cardazo P. Atlas of clinical cytology. Leiden: 1978.
10. Grunze H, Spriggs AI. History of clinical cytology –a selection of documents .Darmstadt:E.Giebeler;1980.
11. Naylor B .The century for cytopathology. Actacytol 2000:44:709- 25.
12. Soderstrom N. Punctures of goitre for aspiration biopsy. A preliminary report. Acta Med Scand 1952;144:23-44.
13. Einhorn J, Franzen S, Thin needle biopsy in diagnosis of thyroid disease. Acta Radiol 1962;58:321-36.
14. Lowhagen T, Willens JS, Lundell G, et al. Aspiration Biopsy Cytology in diagnosis of thyroid Cancer.World J Surgery 1981;5:61-73.
15. Lowhagen T, Grunberg P, lundell G, et al. Aspiration Biopsy Cytology (ABC) in nodules of thyroid gland suspected to be malignant. Surg Clin N Am 1979;59:3-18.
16. Smith EH : complications of percutaneous abdominal fine needle biopsy. Review. Radiology 1991;178:253-8.
17. Chan JKC, Tang SK ,Tsang WYW, et al .Histological changes induced by fine needle aspiration. Advances Anat Pathol 1996;3:71-90.
18. Dabbs DJ, Silverman JF. Selective use of electron microscopy in fine needle aspiration cytology. Acta Cytol 1988;32:880-4.
19. Akhtar M, Bakry M, Al –Jeaid AS, et al. Electron microscopy of fine needle aspiration biopsy specimens :a brief review. Diagn Cytopathol 1992;8:278-82.
20. Kurtycz DFI, Logrono R, Leopando M, et al. Immunocytochemistry controls using cell cultures. Diagn Cytopathol 1997;17:74- 9.
21. Holmes GF, Eisele DW, Rosenthal D.PSA immunoreactivity in a parotid oncocytoma: A diagnostic pitfall in discriminating primary parotid neoplasms from metastatic prostate cancer. Diagn Cytopathol 1998;19:221-5.
22. Baak JPA. Mannual of quantitative pathology in cancer diagnosis and prognosis.Berlin:Springer-Verlag;1991.
23. Hamilton PW , Allen DC. Quantitative clinical pathology. Oxford: Blackwell Scientific ;1995.
24. Maciorowski Z, Klijanienko J, Padoy, et al .Comparative image and flow cytometry TUNEL analysis of fine needle samples of breast carcinoma. Cytometry 2001;46:150-6.
25. Caspersson TO. History of the development of cytophotometry from 1935 to the present. Anal Quant Cytol Histol 1987;9:2-6.
26. Mikel UV. Quantitative staining techniques for image cytometry. In: Mikel
UV, editor. Advanced laboratory methods in histology and pathology. Washington DC : Armed forces institute of pathology ;1994.p.131-60.
27. Maciorowski Z, Veilleux C,Gibaud A, et al. Comparison of fixation procedures for fluorescent quantitation of DNA content using image cytometry. Cytometry 1997;26:123-9.
28. Truong K, Vielh P, Malfoy B, et al. Fluorescence based analysis of DNA
ploidy and cell proliferation within fine needle samplings of breast tumors; a new approach using automated image cytometry. Cancer 1998;84:309-16.
29. Cross SS, Bury JP, Stephenson TJ, et al. Image analysis of fine needle aspirates of breast produces useful discrimination between benign and malignant cases. Cytopathol 1997;8:265-73.
30. Teague MW, Wolberg WH, Street WN, et al. Indeterminate fine needle
aspiration of breast ;image analysis-assisted diagnosis. Cancer 1997;81:129-35.
31. Briffod M, Le Doussal V, Spyratos F. Cytologic nuclear grading of fine needlecytopunctures of breast carcinoma. Comparison with histologic nuclear grading and image cytometric data .Anal Quant Cytol Histol 1997;19:114-22.
32. Cohen C.Image cytometric analysis in pathology. Human Pathol 1996;27:482-93.
33. Briffod M, Syratos F, Hacene K, et al. Evaluation of breast carcinoma chemo sensitivity by flow cytometris DNA analysis and computer assisted image analysis. Cytomery 1992;13:250-8.
34. Auger M, Katz RL, Johnston DA, et al . Quantitation of Immunocytochemical estrogen and progesterone receptor content in fine needle aspirates of breast carcinoma using the SAMBA 4000 image analysis system. Anal Quant Cytol Histol 1993;15:274-80.
35. Bozzetti C, Nizzoli R, Camisa R, et al .Comparison between Ki-67 index and S-phase fraction on fine needle aspiration samples from breast carcinoma. Cancer 1997;81:287-92.
36. Katz RL, Wojcik EM, EI-Naggar AK, et al .Proliferation markers in non hodgkins lymphoma :a comparative study between cytophotometric quantitation of Ki-67 and flow cytometric proliferation index on fine needle aspirates. Anal Quant CytolHistol 1993;15:179-86.
37. Oud PS, Bauwens A, Nauwelaers FA. Multiparameter absorption measurements in automated microscopy: simultaneous quantitative determination of DNA and nuclear antigen. Acta Cytol 1997;41:188-96.
38. Caspersson TO, Schultz J. Nucleic acid metabolism of chromosomes in relation to gene reproduction. Nature 1938;142:294-7.
39. Coons AH, Kaplan MH. Localization of antigens in tissue cells II. Improvements in a method for the detection of antigen by means of Fluorescent antibody. J Exp Med 1950;91:1-4.
40. Crosland –Taylor PJ. A device for counting small particles suspended in a fluid through a tube. Nature 1953;171:37-8.
41. Coulter WH. High speed automatic blood cell counter and cells size analyser. Proc Natl Electronics Conf 1956;12:1034-42.
42. Krishnamurthy S, Applications of molecular techniques to fine needle aspiration biopsy .Cancer 2007;11:106-22.
43.Schmitt F, Loghatto-Filho A, Valent A, et al. Molecular techniques in cytopathology practice .J ClinPathol 2008;61:258-67.
44. Chevillard S, Pouillart P, Beldjord C, et al . Sequential assessment of multidrug resistance phenotype and measurement of S phase fraction as predictive markers of breast cancer response to neoadjuvant chemotherapy. Cancer 1996;77:292-300.
45. Chevillard S, Lebeau J, Pouillart P, et al .Biological and clinical significance of concurrent p53 gene alterations, MDR1 gene expression , and S phase fraction analysis in breast cancer patients treated with primary chemotherapy or radiotherapy. Clin Cancer Res 1997;3:2471-8.
46. Mc Nicol A M, Farquharson MA. In: situ hybridization and its diagnostic applications in pathology. J Pathol 1997; 182:250-61.
47. Sauer T, Beraki K, Jebsen PW, et al. Ploidy analysis by in situ hybridization of interphase cell nuclei in fine needle aspirates from breast carcinomas: correlation with cytologic grading. Diagncytopath 1997;17:267-71.
48. Truong K, Guilly MN, Gerbault-Seureau M, et al. Quantitative FISH by image cytometry for detection of chromosome 1 imbalances in breast cancer: A novel approach analysing chromosome rearrangements within interphase nuclei. Lab Invest 1998; 78:1607-13.
49. Wolman S. Applications of fluorescence in situ hybridisation in cytopathology. Cancer 1997;81:193-7.
50. Klijanienko J, Couturier J, Galut M, et al. Detection and quantitation by FISH and image analysis of HER -2 /neu gene amplification in breast cancer fine needle aspirates .Cancer 1999;87:312-8.
51. O’Leary JJ, Engels K, Dada MA. The polymerase chain reaction in pathology. J Clin Pathol 1997;50:805-10.
52. Tisserand P, Fouquet C, Marck V, et al. Thin prep –processed fine needle samples of breast are effective material for RNA and DNA based molecular diagnosis .Cancer 2003;99:223-32.
53. Gazagne A, Claret E, Wijdenes J, et al. A fluorospot assay to detect single T lymphocytes simultaneously producing multiple cytokines
54. Pu RT, Laitala LE, Alli PM, et al. Methylation profiling of benign and malignant breast lesions and its application to cytopathology. Mod Pathol 2003;16:1095-101.
55. O’Leary JJ, Landers RJ, Chetty R. In: situ amplification in cytological preparations. Cytopathology 1997;8:148-60.
56. HoLM, Thomas J, Fine SA, et al. Usefulness of sonographic guidance during percutaneous biopsy of mesenteric masses. AJR 2003;180:1563-6.
57. Morris EA, Liberman L, Bllon DJ, et al. MR of occult breast carcinoma in a high risk population. AJR 2003;181:619-26.
|






 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License