IJCRR - 10(7), April, 2018
Pages: 12-17
Date of Publication: 14-Apr-2018
Print Article
Download XML Download PDF
Cognitive Functions in Patients of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus with Peripheral Neuropathy, An Observational Cross Sectional Study Done in India
Author: Shubhra Bhardwaj, Sunita Mondal, Rajiv Bandhu, Debasish Chaudhury, Ekta Malik Debnath, Gaurav Swami, Madhulika Monga, Mukul Adlakha
Category: Healthcare
Abstract:Background: Peripheral neuropathy and cognitive decline both are very common in diabetics but relationship between them is yet unclear. Hence, this study aimed at assessing the cognitive functions in patients of type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) with diabetic peripheral neuropathy (DPN) and compare them with that of patients of T2DM without DPN and apparently healthy controls.
Materials and Methods: In this observational cross sectional study eligible T2DM patients were divided into two groups with DPN (25) and without DPN (25) by Nerve conduction velocity (NCV). 25 apparently healthy controls were taken. Cognitive functions were tested by using P300 event related potential.
Result: P300 latency on Pz was significantly delayed in the T2DM with DPN as compared to T2DM without DPN (p < 0.05) and controls (p < 0.01). The average latency was also significantly delayed in T2DM with DPN as compared to controls(p < 0.05).A positive correlation between duration of diagnosis of T2DM (r= 0.3339, p= 0.0178*) with P300 Latency Fz was observed.
Conclusion: Cognitive functions are impaired in T2DM with DPN. Duration of illness is positively correlated to decline of cognitive functions.
Keywords: T2DM, DPN, P300, Cognitive functions
DOI: 10.7324/IJCRR.2018.1073
Full Text:
INTRODUCTION
The term diabetes mellitus (DM) is used for a group of common metabolic disorders that share the common phenotype of hyperglycaemia1.
T2DM has assumed more importance due to its attendant long termmicro2‚3 and macro-vascular4 complications.Diabetic peripheral neuropathy (DPN) is one of the most common long term complications of DM. It is progressive and irreversible with an incidence rate of about 50% 5 .T2DM patients are also at increased risk of developing dementia and number of patients of T2DM demonstrating cognitive decline is also on the rise 6
Cognitive impairments can be detected by event related potentials using P300. Cognitive event-related evoked potentials (EREPs) are long-latency potential. P300 is an index of cognitive processing time and has been shown to be prolonged in dementia 7.
Conflicting results have been reported regarding the relationship between any association of the long term complications like DPN and cognitive decline. In some studies diabetic patients with DPN have shown a decrease in cognitive and executive functions as compared with those without DPN8‚9.
Whereas, no relationship between cognitive functions and neuropathy in diabetic patients was observed in another study10. In India, studies showing correlation between DPN and cognitive decline are scanty.
In view of these discordant findings, the fact remains unclear that whether the microvascular complications like DPN provide an early evidence of cognitive decline beyond what is observed in diabetic patients free from such complications.
Moreover, development of cognitive dysfunction has an important bearing on the management and further progression of complications in diabetes. Therefore there is a strong need for documenting any such association in T2DM patients.
OBJECTIVES:
To find out -
1. Differences in cognitive function between T2DM patients with DPN as compared to T2DMpatients without DPN.
2. Relationship between the duration of diagnosis T2DM and cognitive functions.
MATERIAL and METHODS:
This present study was an observational cross sectional study carried out in department of Physiology in association with department of Medicine, Lady Hardinge Medical College and associated Smt. Sucheta Kriplani Hospital conducted between November2014 to March2016.
The ethical clearance was obtained from the Institutional Ethics committee for Human Research. Written and informed consent was taken from all study participants. The study protocol was carried out as per declaration of Helsinki.
Inclusion criteria:
For Diabetics-Comprised of 50 new or already diagnosed cases of T2DM either gender (as per ADA criteria 11) in the age group 40 to 60 years. They were then divided into two groups based on presence or absence of DPN (as per minimal criteria given by Tesfaye et al.12
For Controls-v Apparently healthy volunteers in the age group 40 to 60 years which were age, gender, BMI, socioeconomic status (SES) 13 and educational status (ES) matched.
Exclusion criteria:
Individuals having history of neuropsychiatric illness, type 1 diabetes mellitus14, presence of any significant impairment in communication , pre diabetics 15(as per ADA criteria 11) and history or examination suggestive of any other risk factors known to cause cognitive impairment .
The minimum values of nerve conduction velocity for diagnosing peripheral neuropathy were as follows:
|
Nerve
|
Conduction Velocity
|
|
Median motor nerve 7
Median sensory nerve 7
Peroneal nerve 7
Sural nerve 16
|
54.44 m/sec
36.05m/sec
42.14m/sec
30.5m/sec
|
Study procedure
1. A detailed history taking and examination was done. For screening the CBC, LFT, KFT, serum electrolytes, blood urea, serum creatinine, chest X ray and ECG were done. Nerve conduction studies were done on all.
They were then divided into the following groups
Group I a: 25 patients of T2DM with DPN
Group I b: 25 patients of T2DM without DPN
Group II: 25 apparently healthy individuals as controls
2. Age and anthropometric measurements were recorded.
3. P 300 Recording -
Cognitive evoked potential P300 was tested by using a machine SCHWARZER TOPAS EMG neurophysiological measuring system provided by NATUS, Europe.
P300 is endogenous or event related potential (ERP) recorded in response to external stimulus or event7. P300 latency was recorded as per standard guidelines17.
Patients were asked to report with a clean and oil free scalp18 and to avoid anti-histaminics on the day of testing. The procedure was explained and it was emphasized that he/she should remain alert and still during the test7???????.
Gold cup electrodes were applied by 10-20 system for calculating sites for placement 19.Electrode impedance was kept below 10 K ohms7.
Auditory stimuli were delivered bilaterally using odd ball paradigm .Target and non target stimuli were used (that comprised 20 % and 80 of total stimuli respectively).Target stimuli (4000 Hz) were presented randomly. Non target stimuli (1000 Hz) appeared at fixed interval of time.7 Intensity of stimuli was kept at 65 dB SPL.
STATISTICAL ANALYSIS
The data was submitted for statistical evaluation using Graph Pad Prism software version 6.Mean and Standard error of mean (Mean ± SEM) of all the variables were calculated. After testing for normal Gaussian distribution, intergroup comparison was done using ANOVA and Tukey's post-hoc test was applied for multiple comparisons. Chi square test and Mann - Whitney test were applied as per requirement. Correlation was assessed using the Spearman’s correlation coefficient.
RESULTS
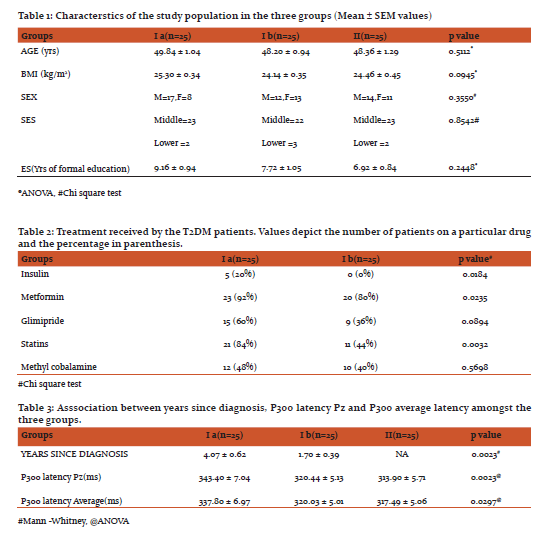
Table 1 illustrates socio-demographic characteristics of study population. They were age, BMI, WC, sex distribution, SES and ES matched.
Table 2 shows the treatments being received by the diabetics of the two groups. There was a statistically significant difference in number of patients receiving Insulin, Metformin and Statins.
Table 3 shows -P300 latency on Pz was significantly delayed in the T2DM with DPN as compared to T2DM without DPN (p < 0.05)v and controls (p < 0.01)as shown in Fig.1. The average latency is also significantly delayed in T2DM with DPN as compared to controls (p < 0.05) as shown in Fig.2.
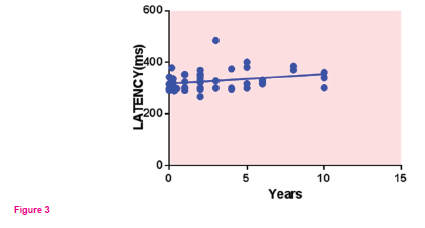
A positive correlation between years since diagnosis of T2DM(r= 0.3339, p= 0.0178*) and P300 Latency Fz was observed as shown in Fig .3.
DISCUSSION
In our study it was observed that the P300 latency on Pz is significantly higher in T2DM with DPN as compared to the T2DM without DPN and controls. The average P300 latency is also significantly higher in T2DM with DPN as compared to the controls.
These above findings suggest that cognitive functions as shown by P300 latency are delayed in diabetics with neuropathy as compared to the diabetics without neuropathy as well as controls. This is similar to study conducted by Ryan et al where they showed relationship between neuropathy and cognitive dysfunctions in diabetics9, however, this study was done in T1DM patients..In an another study conducted by Dey et al no relationship between peripheral neuropathy and cognitive functions was observed in T2DM patients10.Ryan et al hypothesized that peripheral neuropathy could be a marker for a metabolically mediated “central neuropathy” which too, may be a consequence of a long history of hyperglycaemia9.
A positive correlation of years since diagnosis of T2DM with P300 Latency Fz.(P=0.0178,r= 0.3339) was found .This suggests that as the duration of illness increases ,there is a cognitive decline. Our finding is similar to that of Ryan et al where they have observed a significant decline in cognitive functions in T1DM patients over period of time as compared to controls 20.Worall G. et al also found similar observation between duration of T2DM and cognition 21.
Thus, our study is also consistent with the work done by Perlmuter et al where they observed that peripheral neuropathy is associated with cognitive impairment T2DMpatients 8 and in contrast to other study done by Lawson et al 22 where they observed no such association.
Cognitive decline in diabetes mellitus can be due to impaired neurogenesis, changes in blood brain barrier, chronic hyperglycaemia, inflammatory mechanisms, vascular dysfunction affecting neuronal functions in brain6. Hyperglycaemia may have toxic effects on neurons in the brain through osmotic insults and oxidative stress. Chronic high glucose level leads to the enhanced formation of advanced glycation end products (AGEs) 23. AGEs couple with free radicals and create oxidative damage, which in turn leads to neuronal injury 24. AGEs also activate microglia in the CNS .Microglia can become deleterious and damage neurons 25. The metabolic disturbances that are associated with clinically apparent distal symmetric polyneuropathy like alterations in peripheral nerve Na+-K+ ATPase activity that leads to a reduction in myo-inositol and sorbitol metabolism 26 may also cause biochemical and physiological abnormalities that disrupt cell transport of various metabolities and substrates in both the peripheral and central nervous systems.
In our study, DPN and cognitive dysfunction may be present in same patient and a part of the same disease process.
CONCLUSION
In our study it can be concluded that T2DM patients with DPN have impaired cognition as substantiated by delayed P300 latency. This cognitive impairment may also progress as duration of T2DM increases.
LIMITATIONS-There are confounding factors in our study which could have affected the outcome.
1. Patients of both the diabetic groups were receiving Metformin and Statins. Metformin leads to an exacerbation of peripheral neuropathy27???????. Metformin also affects cognition 28‚29. Some studies on Statins have shown lower prevalence of vascular dementia and Alzheimer's disease 30‚31‚32 with use of Statins while others have shown an equivocal result 33???????.
2. Years since diagnosis of DM was also significantly different in both the diabetic groups.
Due to the small sample size in a tertiary care setting and the above said confounding factors, the study results cannot be generalized to all the diabetics in routine management.
RECOMMENDATIONS
It is necessary to carry out the study on a larger sample size involving multi-ethnic and multi-centric population.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENT
Authors are grateful to workers whose articles and books have been cited for reference. We are also grateful to Mr. Gaurav and his team from NATUS, Europe which provided us SCHWARZER TOPAS EMG neurophysiological measuring system along required with technical help. Authors acknowledge the immense help received from the scholars whose articles are cited and included in references of this manuscript. The authors are also grateful to authors /editors /publishers of all those articles, journals and books from where the literature for this article has been reviewed and discussed.
Sources of financial support- Nil
Conflict of interest – Nil.

References:
- Fauci AS, Braunwald E, Kasper DL, Hauser SL, Longo DL, Jameson JL, et al., editors. Harrison's principles of internal medicine. 17th ed. New York: McGraw Hill; 2008.
- Qiu C, Cotch MF, Sigurdsson S, Garcia M, Klein R, Jonasson F, Klein BE, Eiriksdottir G, Harris TB, van Buchem MA, Gudnason V. Retinal and cerebral microvascular signs and diabetes the age, gene/environment susceptibility-reykjavik study. Diabetes. 2008 Jun 1; 57(6):1645-50.
- Yuan SY, Breslin JW, Perrin R, Gaudreault N, Guo M, Kargozaran H, Wu MH. Microvascular permeability in diabetes and insulin resistance. Microcirculation. 2007 Jan 1; 14(4-5):363-73.
- Fowler MJ. Microvascular and macrovascular complications of diabetes. Clinical diabetes. 2008 Apr 1; 26(2):77-82.
- Boulton AJ, Vinik AI, Arezzo JC, Bril V, Feldman EL, Freeman R, Malik RA, Maser RE, Sosenko JM, Ziegler D. Diabetic neuropathies a statement by the American Diabetes Association. Diabetes Care. 2005 Apr 1; 28(4):956-62.
- Umegaki H. Type 2 diabetes as a risk factor for cognitive impairment: current insights. ClinInterv Aging. 2014 Jun 1;9(9):1011-9.
- Mishra UK, Kalita J. Clinical Neurophysiology. 2nd Ed. New Delhi:Elsevier ; 2006
- Perlmuter LC, Hakami MK, Hodgson-Harrington C, Ginsberg J, Katz J, Singer DE, Nathan DM. Decreased cognitive function in aging non-insulin-dependent diabetic patients. Am J Med. 1984 Dec 31;77(6):1043-8.
- Ryan CM, Williams TM, Finegold DN, Orchard TJ. Cognitive dysfunction in adults with type 1 (insulin-dependent) diabetes mellitus of long duration: effects of recurrent hypoglycaemia and other chronic complications. Diabetologia. 1993 Apr 1; 36(4):329-34.
- Dey J, Misra A, Desai NG, Mahapatra AK, Padma MV. Cognitive function in younger type II diabetes. Diabetes Care. 1997 Jan 1; 20(1):32-5.
- American Diabetes Association. Diagnosis and classification of diabetes mellitus. Diabetes care. 2013 Jan 1; 36 (Supplement 1):S67-74.
- Tesfaye S, Boulton AJ, Dyck PJ, Freeman R, Horowitz M, Kempler P, Lauria G, Malik RA, Spallone V, Vinik A, Bernardi L. Diabetic neuropathies: update on definitions, diagnostic criteria, estimation of severity, and treatments. Diabetes care. 2010 Oct 1; 33(10):2285-93.
- Modified kuppuswamyscale:CPI guidelines:2013
- Brands AM, Biessels GJ, De Haan EH, Kappelle LJ, Kessels RP. The effects of type 1 diabetes on cognitive performance A meta-analysis. Diabetes care. 2005 Mar 1; 28(3):726-35.
- Papanas N, Vinik AI, Ziegler D. Neuropathy in prediabetes: does the clock start ticking early?.Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2011 Nov 1;7(11):682-90.
- Burke D, Skuse NF, Lethlean AK. Sensory conduction of the sural nerve in polyneuropathy. J NeurolNeurosurg Psychiatry 1974; 37:647-52.
- Picton TW, Bentin S, Berg P, Donchin E, Hillyard SA, Johnson R Jr, Miller GA, Ritter W, Ruchkin DS, Rugg MD, Taylor MJ Guidelines for using human event-related potentials to study cognition: recording standards and publication criteria.; Psychophysiology. 2000 Mar; 37(2):127-52.
- Ray K, Chatterjee A, Panjwani U, Kumar S, Sahu S, Ghosh S, Thakur L, Anand JP. Modafinil improves event related potentials P300 and contingent negative variation after 24h sleep deprivation. Life sciences. 2012 Aug 21; 91(3):94-9.
- Klem GH, Lüders HO, Jasper HH, Elger C. The ten-twenty electrode system of the International Federation. ElectroencephalogrClinNeurophysiol. 1999; 52(3).
- Ryan CM, Geckle MO, Orchard TJ. Cognitive efficiency declines over time in adults with type 1 diabetes: effects of micro-and macrovascular complications. Diabetologia. 2003 Jul 1;; 46(7):940-8.
- Worall G, Moulton N, Briffet E: Effect of type II diabetes on cognitive function. J FamPract 1993; 36:639-643.
- Lawson J, Williams Erdahl D, Monga T, Bird C, Donald M, Surridge D, Letemendia F: Neuropsychological function in diabetic patients with neuropathy. Br J Psychiatry. 1984; 145:263-68.
- Yamagishi S, Ueda S, Okuda S. Food-derived advanced glycation end products (AGEs): a novel therapeutic target for various disorders. Curr Pharm Des. 2007; 13(27):2832–2836.
- Valente T, Gella A, Fernàndez-Busquets X, Unzeta M, Durany N. Immunohistochemical analysis of human brain suggests pathological synergism of Alzheimer's disease and diabetes mellitus. Neurobiol Dis. 2010;37(1):67–76.
- Block ML, Zecca L, Hong JS. Microglia-mediated neurotoxicity: uncovering the molecular mechanisms. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2007;.8(1):57–69.
- Greene DA, Lattimer S, Ulbrecht J, Carroll P. Glucose-induced alterations in nerve metabolism: current perspective on the pathogenesis of diabetic neuropathy and future directions for research and therapy. Diabetes Care. 1985 May 1; 8(3):290-9.
- Wile DJ, Toth C. Association of metformin, elevated homocysteine, and methylmalonic acid levels and clinically worsened diabetic peripheral neuropathy. Diabetes care. 2010 Jan 1;33(1):156-61.
- Chen Y, Zhou K, Wang R, Liu Y, Kwak YD, Ma T, Thompson RC, Zhao Y, Smith L, Gasparini L, Luo Z. Antidiabetic drug metformin (GlucophageR) increases biogenesis of Alzheimer's amyloid peptides via up-regulating BACE1 transcription. ProcNatlAcad Sci. 2009 Mar 10;106(10):3907-12.
- Moore EM, Mander AG, Ames D, Kotowicz MA, Carne RP, Brodaty H, Woodward M, Boundy K, Ellis KA, Bush AI, Faux NG. Increased risk of cognitive impairment in patients with diabetes is associated with metformin. Diabetes care. 2013 Oct 1;36(10):2981-7.
- Hajjar I, Schumpert J, Hirth V, Wieland D, Eleazer GP. The impact of the use of statins on the prevalence of dementia and the progression of cognitive impairment. J Gerontol A BiolSci Med Sci. 2002 Jul 1;;57(7):M414-8.
- Sparks DL, Sabbagh MN, Connor DJ, Lopez J, Launer LJ, Browne P, Wasser D, Johnson-Traver S, Lochhead J, Ziolwolski C. Atorvastatin for the treatment of mild to moderate Alzheimer disease: preliminary results. Arch Neurol. 2005 May 1; 62(5):753-7.
- Fassbender K, Simons M, Bergmann C, Stroick M, Lütjohann D, Keller P, Runz H, Kühl S, Bertsch T, Von Bergmann K, Hennerici M. Simvastatin strongly reduces levels of Alzheimer's disease β-amyloid peptides Aβ42 and Aβ40 in vitro and in vivo. ProcNatlAcad Sci. 2001 May 8; 98(10):5856-61.
- Carlsson CM, Nondahl DM, Klein BE, McBride PE, Sager MA, Schubert CR, Klein R, Cruickshanks KJ. Increased atherogenic lipoproteins are associated with cognitive impairment: effects of statins and subclinical atherosclerosis. Alzheimer Dis AssocDisord . 2009; 23(1):11.









 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License