IJCRR - 10(3), February, 2018
Pages: 01-06
Date of Publication: 01-Feb-2018
Print Article
Download XML Download PDF
Prevalence and Factors Influencing Depression in Patients with Stroke Attending a Tertiary Care Teaching
Hospital, a Cross Sectional Study
Author: Shaik Afsar Pasha, Pavan Kumar TV, Chaitanya CH
Category: Healthcare
Abstract:Background: Stroke is a major public health problem contributing to significant morbidity and mortality across the globe. In spite of many reviews documenting a strong association between stroke and depression, it is the most ignored aspect in many developing countries including India, due to paucity of studies on the subject. Hence the current study was conducted with an objective of assessing the prevalence of depression among the stroke patients and factors influencing it in a tertiary care teaching hospital
Materials & Methods: This cross sectional study was conducted in the department of Neurology and the department of Psychiatry in NRI General Hospital. The study had included 56 eligible stroke patients and evaluated them for depression using DSM-IV TR Diagnostic criteria and Hamilton Depression Rating Scale (HAM-D).
Results: The prevalence of depression in study population was 46.4%, out of which 21.4% had minor depression and 25% had major depression. The demographic factors which have shown increased risk of depression were female gender, primary school educational status, middle socioeconomic class and living in an extended nuclear family or joint family. But none of the associations had shown statistical significance. The disease related factors associated with increased risk of stroke were presence of aphasia, severe limitation of and presence of stressful life event. Out of these only severe limitation of ADL has shown statistically significant association.
Conclusions: The prevalence of depression is very high in patients affected by stroke. The major factors which were associated with increased risk of depression were female gender, presence of aphasia, severe limitation of ADL and presence of stressful life events.
Keywords: Depression, Stroke, Aphasia, Stressful life events
DOI: 10.7324/IJCRR.2017.1031
Full Text:
Stroke is a major public health problem accounting for 5.5 million deaths worldwide annually, with 44 million disability- adjusted life-years lost.1 A systematic review of 56 population based studies found a 42% decrease in stroke incidence in high income countries while in low income countries, the stroke incidence more than doubled in recent years.2 Stroke is one of the leading causes of death and disability in India. Currently, the stroke incidence in India is much higher than Western industrialized countries. The reported age adjusted
prevalence rate of stroke ranges from, 84 to 262 per 100,000 among rural population. It ranges from 334 to 424 per 100,000 among urban population. The incidence rate is 119-145/100,000 based on the recent population based studies”. 3-5 In India, the overall morbidity as assessed by DALYs was 795.57 per 100,000 person-years.6
Considering the devastating consequences of stroke at personal and family level, it is likely that stroke may have serious negative impact on psychological health of the affected person. Depression is reported to be one of the common sequelae of stroke. Recent systematic reviews have reported a pooled estimate of depression in stroke patients to be about 33%.7Though it was presumed that left hemisphere strokes increase the risk for post-stroke depression (PSD), a recent systematic reviews did not support the hypothesis.8,9The depression in stroke patients is reported to be the strong predictor of adherence to treatment, quality of life of the affected patients.10 Hence, many of the recent studies have emphasized the importance of focusing on the psychological aspects apart from (neuro) biological factors, to achieve better
treatment outcomes and quality of life in stroke affected patients.11,12
In India, post-stroke depression is an ignored or highly under- diagnosed condition, hence poorly addressed. Studies documenting the burden and factors influencing depression can draw the attention of all relevant stakeholders including patients, their family members, health care providers at different levels. Hence there is a strong need for studies on the subject.
Objectives:
1. To assess the prevalence of depression among the stroke patients presenting to a tertiary care teaching
hospital in south India
2. To analyse factors associated with depression in the study population
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Study site: This study was conducted in the department of Neurology and the department of Psychiatry in NRI General Hospital, which is a tertiary care teaching hospital located in the state of Andhra Pradesh, South India.
Study population: The study population included all the adult patients diagnosed with ischemic stroke by clinical examination and confirmed by appropriate imaging (CT scan/ MRI Brain) and were attending follow up visits in neurology OPD 3 to 12 months after stroke
Sample size and sampling method: A group of 56 eligible and consenting participants were included in the study sequentially by convenient sampling.
Data collection tools:
DSM-IV TR Diagnostic criteria was followed to screen for Depression. Hamilton Depression Rating Scale (HAM-D) was used to assess the severity of depression in the study group. Lawton scale of Instrumental Activities of Daily Living (IADL) was applied to assess the degree of physical impairment. Mini Mental Status Examination (MMSE) was applied to assess cognitive impairment. Presumptive Stressful Life Event Scale (PSLES) was administered to find the role of stressful life events in post stroke depression.
Inclusion Criteria:
1. All adult patients with the diagnosis of Ischemic stroke made by a neurologist both clinically and with
CT/ MRI scan belonging to both genders
2. Conscious and cooperative and accompanied by at least one informant.
3. The stroke should be of first episode.
Exclusion Criteria:
1. Patients with past history of psychiatric illness.
2. Patients with neuro radiological evidence of hemorrhage.
3. Patients with duration of less than 3 months and more than 12 months from the stroke episode.
4. Patients who could not communicate or severely aphasic.
Study procedure: After obtaining informed consent, special proforma was prepared for collecting the socio-demographic profile. This consisted of socio demo graphic data, history of present illness, history of past medical and psychiatric illness and detailed neurological examination, CT scan and other important investigations. Patients meeting the criteria for depressive disorder due to general medical condition based on
DSM-IV TR criteria were administered the following tools. This study had cleared the institutional ethical committee requirements.
Statistical Methods
IBM SPSS statistical software version 21 was used for statistical analysis. Socio demographic variables like age and gender, religion, education, occupation, socioeconomic status, type of family etc. were taken as explanatory parameters. Presence of depression as assessed by HAM depression score was considered as primary outcome. Descriptive analysis of all the explanatory and outcome parameters was done. All the categorical variables were presented in frequencies and percentages. The numerical variables presented
in means and standard deviations. The association between various explanatory variables and depression was assessed by univariate binary logistic regression in the first step. Unadjusted odds ratios along with 95% CI were presented. Variables showing statistically significant association in univariate analysis were included in the multivariate binary logistic regression analysis, to identify the independent predictors of depression. IBM SPSS statistical software version 21 was used for statistical analysis.13
RESULTS
A total of 56 stroke patients, who satisfied inclusion criteria were included in the study. Following Table 1 illustrates the distribution of sociodemographic parameters in the study population.
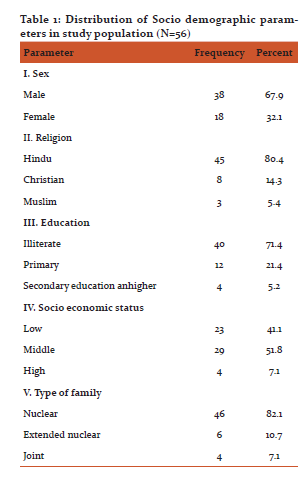
Out of total 56 participants, 38 (67.9%) were males. Hindus constituted 80.4% of participants and the proportion of Christians and Muslims was 14.3% and 5.4% respectively. Majority (71.4%) were illiterates and 21.4% completed primary education and only 5.2% completed secondary education and higher. Four (7.1%) belonged to high socio economic status. The proportion of low and middle socio economic status people was 41.1% and 51.8% respectively. Forty six (82.1%) of them belonged to nuclear family, 6 (10.7%) belonged to extended nuclear family and 4 (7.1%) belonged to joint family.
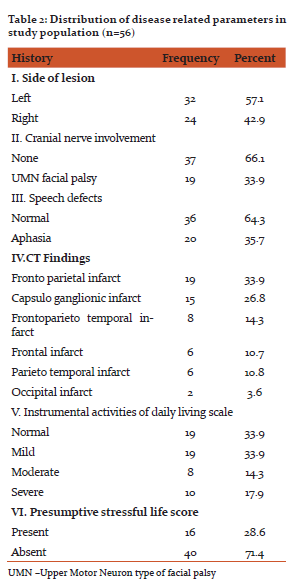
The lesion was on left side for 32 (57.1%) patients and was on right side for remaining 24 (42.9%) patients. UMN facial palsy was seen in 19 (33.9%) of patients and aphasia was seen in 20 (35.7%) of patients. The most common lesion in CT was fronto parietal infarct, which was seen in 19(33.9%) patients, followed by capsuloganglionic infarct, seen in 15 (26.8%) of patients. (Table 2) As per Lawton instrumental activities of daily living, 19 (33.9%) people were having normal scores, 19 (33.9%) had mild limitation, 8 (14.3%) had moderate limitation and 10(17.9%) had severe limitation of activities of daily living. (table 2)
The prevalence of depression in study population was 46.4%, as 26 subjects out of 56 had depression of various severities. Out of the 26, 12 (21.4%) had minor depression and 14 (25%) had major depression. (table 3)
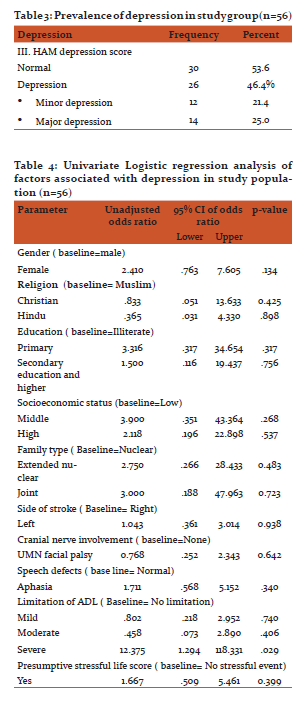
The demographic factors which have shown increased risk of depression were female gender (Odds ratio=2.410, 95% C.I. 0.763 to 7.605, P value 0.134), primary school educational status (OR=3.316, 95% CI 0.317 to 34.654, p value 0.317), middle socio-economic class. (OR=3.90, 95% CI 0.351 to 43.364, p value 0.268) and living in an extended nuclear family (OR=2.750 95% CI 0.266 to 28.433) or joint family (OR=3.0, 95% CI 0.266 to 28.433). But none of the associations had shown statistical significance. The disease related factors associated with increased risk of stroke were presence of aphasia (OR=1.711, 95% CI 0.568 to 5.152, p value=0.340), Severe limitation of ADL (OR=12.375, 95% CI 1.294 to 118.331, P value 0.029) and presence of stressful life event (OR=.667, 95% CI 0.509 to 5.461, P value 0.399). Out of these only severe limitation of ADL has shown statistically significant association.
DISCUSSION
Assessment of the epidemiology of stroke is a difficult but exciting challenge that is justified by the objectives of identifying vascular risk factors, establishment of needs for the implementation of dedicated services, and guiding and assessment of future preventive and therapeutic priorities.
As per a conservative estimate, one third of all people experience significant depressive symptoms at some time after the onset of stroke. Unfortunately, the potential of under-reporting or under-recognition of abnormal mood is common due to the inherent difficulties in assessing the mood changes among patients with neurological disabilities like dysphasia and/or dementia.7 Traditionally it has been considered that the greatest risk of depression is during the first few months of stroke onset. Conversely, Hackett et al., observed a consistency in the overall frequency of depression in their systematic review.7
In our study there were 67.9 % Male patients. Comparatively the proporion of males was 53.2% in the study by Aben et al.,14 and 55.4% in that of Carod Artal et al.,10.A 10 year follow-up study reported that though, strokes were marginally more common in males, it could be explained by confounding and that more research is needed to understand the gender disparity in stroke pathophysiology.15
Majority (71.4%) were illiterates and 21.4% completed primary education and only 5.2% completed secondary education and higher. Laborers (48.2%) and house wives (19.6%) were the most prevalent occupations, in the study group. Out of 56 participants, only 4 (7.1%) belonged to high socio economic status. The proportion of low and middle socio economic status people was 41.1% and 51.8% respectively. Forty six (82.1%) of them belonged to nuclear family, 6 (10.7%) belonged to extended nuclear family and 4 (7.1%) belonged
to joint family.
We found aphasia in 20 (35.7%) of our patients. Engelter et al.,16reported aphasia in 30% of ischemic stroke patients in a geographical defined population of 188,015. They concluded that individuals of advancing age and cardioembolism had higher risk for aphasia. Evidence also suggests that aphasia in stroke patients is associated with higher mortality 17, decreased rates of functional recovery 18,19, and reduced chances to return to work20compared with non-aphasic stroke patients .
The study found stroke lesions were more commonly on left hemisphere (57.1%) than right (42.9%). Similar findings (left:43% and right (37%) were found in the cohort study by Reid et al.,.15However, Cardo-Artal et al.,10 reported an equal prepondarence, while Aben et al., found higher involvment of right hemisphere (53.2%). As per Lawton instrumental activities of daily living, 14.3% had moderate limitation and 17.9% had severe limitation of activities of daily living. Evidence suggests that stroke survivors experience physical deconditioning and lead sedentary lifestyles and hence need to do exercise training (both aerobic and strength training).21Exercise training improves functional capacity, the capacity to perform activities of daily living and quality of life. It also reduces the risk for subsequent cardiovascular events. Hence physical activity goals and exercise prescription for stroke survivors need to be customized for the individual to maximize long-term adherence.21
In the current study, the prevalence of depression was 46.4%, with 21.4% cases of Minor depression and 25% Major depression. Carod-Artal et al,10found 38% of their patients belonging to depressed range, while Astrom et al.,22 reported 25% at acute stage and 31% after three months. A three year longitudinal study revealed that left anterior brain lesion, dysphasia and living were the important predictors of immediate
major depression.22
The demographic factors which have shown increased risk of depression were female gender (Odds ratio=2.410, 95% C.I. 0.763 to 7.605, P value 0.134), primary school educational status (OR=3.316, 95% CI 0.317 to 34.654, p value 0.317), middle socioeconomic class. (OR=3.90 ,95% CI 0.351 to 43.364, p value 0.268) and living in an extended nuclear family (OR=2.750 95% CI 0.266 to 28.433) or joint family (OR=3.0, 95% CI 0.266 to 28.433). But none of the associations had shown statistical significance. Females had higher proportion of depression compared to Males. Reid et al,15 highlight the rising proportion of elderly women hospitalized because of stroke. After adjusting for confounding variables, the authors found that women were more likely to have depression.
The disease related factors associated with increased risk of stroke were presence of aphasia (OR=1.711, 95% CI 0.568 to 5.152, p value=0.340), Severe limitation of ADL (OR=12.375 ,95% CI 1.294 to 118.331, P value 0.029) and presence of stressful life event (OR=.667, 95% CI 0.509 to 5.461, P value 0.399). Out of these, only severe limitation of ADL had shown statistically significant association. Many studies have reported major factors influencing depression on long term to be inability to work due to disability, dependence in activities of daily living, diminished social activity, being a housewife7, 10, 23 and cerebral atrophy.22 Usually by one year, patients with early depression recover, but those not recovered had a higher risk of developing chronic depression. 7, 24, 25 There were statistically significant differences in the proportion of people with mild and severe depression in patients with different levels of activity in Lawton instrumental scale of daily living. Even though the proportion of Major depression was higher in people with more limitation of activity, there was no clear increasing or decreasing trend observed with increasing levels of activity limitation.
On the whole, depression after stroke is influenced my multifactorial interaction of biological, psychological and social aspects and their understanding would facilitate targeted preventive strategies and more effective and comprehensive preventive programs.22, 26, 27
CONCLUSIONS
The prevalence of depression is very high in patients affected by stroke. The major factors which were associated with increased risk of depression were female gender, presence of aphasia, severe limitation of ADL and presence of stressful life event.
RECOMMENDATIONS
1. Adequate attention has to be given to depression and other psychological consequences of stroke while
managing patients with stroke.
2. There is strong need for large scale prospective studies and intervention studies to assess log term impact of depression on these patients and to provide guidance to clinicians on appropriate management.
LIMITATIONS
1. Lack of statistical significance of many of the association could be attributed to smaller sample size. This
also did not permit multivariate analysis to assess the confounding and interaction between the factors evaluated.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENT
Authors acknowledge the immense help received from the scholars whose articles are cited and included in references of this manuscript. The authors are also grateful to authors / editors / publishers of all those articles, journals and books from where the literature for this article has been reviewed and discussed.
Source of support – None.
Conflict of interest –Nil.
References:
1. Feigin VL, Roth GA, Naghavi M, Parmar P, Krishnamurthi R, Chugh S, et al. Global burden of stroke and risk factors in 188 countries, during 1990-2013: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2013. Lancet Neurol. 2016;15:913- 24.
2. Feigin VL LC, Bennett DA, Barker-Collo SL, Parag V. Worldwide stroke incidence and early case fatality reported in 56 population-based studies: a systematic review. Lancet Neurol. 2009;8:355–69.
3. Pandian JD, Sudhan P. Stroke epidemiology and stroke care services in India. Journal of stroke. 2013;15:128-34.
4. Pandian JD SV, Read SJ, Thrift AG. Poverty and stroke in India. A time to act. Stroke. 2007;38:3063–9.
5. Prasad K VD, Meenakshi. Cerebrovascular disease in South Asia - Part I: A burning problem. JRSM Cardiovasc Dis. 2012;1:20.
6. Banerjee TK DS, Ray BK, Ghosal M, Hazra A, Chaudhuri A, et al. Disease burden of stroke in Kolkata, India: Derivation of disability-adjusted life years by a direct method. Neuroepidemiology. 2013;41:88–93.
7. Hackett ML, Yapa C, Parag V, Anderson CS. Frequency of depression after stroke: a systematic review of observational studies. Stroke. 2005;36:1330-40.
8. Carson AJ MS, Allen K, Lawrie SM, Dennis M, House A, Sharpe M. Depression after stroke and lesion location: a systematic review. Lancet. 2000;356:122–6.
9. Singh A HN, Black SE. The importance of lesion location in post stroke depression: a critical review. Can J Psychiatry. 1998;43:921–7.
10. Carod-Artal EJ, González JL, de Seijas EV. Quality of Life Among Stroke Survivors Evaluated 1 Year After Stroke. Stroke. 2000;31:2995-3000.
11. Kumar S. Sobering news about post-stroke depression. The lancet Psychiatry. 2017;4:2-3.
12. Hesdorffer DC. Comorbidity between neurological illness and psychiatric disorders. CNS spectrums. 2016;21:230-8.
13. Spss I. IBM SPSS statistics version 21. Boston, Mass: International Business Machines Corp. 2012:126.
14. Aben I DJ, Louseberg R, Vershey F, Wojciechowski F, Honig A, MRCPsych. Personality and Vulnerability to Depression in Stroke Patients. A 1-Year Prospective Follow-Up Study. Stroke. 2002;33:2391-5.
15. Reid JM, Dai D, Gubitz GJ, Kapral MK, Christian C, Phillips SJ. Gender differences in stroke examined in a 10-year cohort of patients admitted to a Canadian teaching hospital. Stroke. 2008;39:1090-5.
16. Engelter ST, Gostynski M, Papa S, Frei M, Born C, Ajdacic- Gross V, et al. Epidemiology of aphasia attributable to first ischemic stroke: incidence, severity, fluency, etiology, and thrombolysis. Stroke. 2006;37:1379-84.
17. Laska AC HA, Murray V, Kahan T, Von Arbin M Aphasia in acute stroke and relation to outcome J Intern Med. 2001;249:413–22.
18. Tilling K SJ, Rudd AG. . A new method for predicting recovery after stroke. Stroke. 2001;32:2867–73.
19. Paolucci S AG, Pratesi L, Traballesi M, Lubich S, Grasso MG. Functional outcome in stroke inpatient rehabilitation: predicting no, low and high response patients. Cerebrovascular diseases (Basel, Switzerland). 1998;8:228–34.
20. Black-Schaffer RM OJ. Return to work after stroke: development of a predictive model. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 1990;71:285–90.
21. Billinger SA, Arena R, Bernhardt J, Eng JJ, Franklin BA, Johnson CM, et al. Physical activity and exercise recommendations for stroke survivors: a statement for healthcare professionals from the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association. Stroke. 2014;45:2532-53.
22. Astrom M AR, Asplund K. Major Depressionin StrokePatients. A 3-Year Longitudinal Study. Stroke. 1993;24:976-82.
23. Gabaldon L, Fuentes B, Frank-Garcia A, Diez-Tejedor E. Poststroke depression: importance of its detection and treatment. Cerebrovascular diseases (Basel, Switzerland). 2007;24 Suppl 1:181-8.
24. Gaete JM, Bogousslavsky J. Post-stroke depression. Expert review of neurotherapeutics. 2008;8:75-92.
25. Gainotti G, Antonucci G, Marra C, Paolucci S. Relation between depression after stroke, antidepressant therapy, and functional recovery. Journal of neurology, neurosurgery, and psychiatry. 2001;71:258-61.
26. Politi P, Sciarini P, Lusignani GS, Micieli G. [Depression and stroke: an up-to-date review]. Epidemiologia e psichiatria sociale. 2006;15:284-94.
27. Paolucci S, Gandolfo C, Provinciali L, Torta R, Toso V. The Italian multicenter observational study on post-stroke depression (DESTRO). Journal of neurology. 2006;253:556-62.
|






 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License