IJCRR - 10(1), January, 2018
Pages: 31-37
Date of Publication: 10-Jan-2018
Print Article
Download XML Download PDF
Comparison of Cardiovascular Risk Between Diabetic and Non - Diabetic End Stage Renal Disease (ESRD) Patients Undergoing Haemodialysis
Author: Priya K., Sangeeta K.
Category: Healthcare
Abstract:Background: This study proposes to see whether end stage renal disease (ESRD) patients undergoing haemodialysis with additional diabetes mellitus exhibit increased cardiovascular risk markers in comparison to end stage renal disease (ESRD) patients undergoing haemodialysis without diabetes mellitus.
Objectives: In this study, an attempt has been made to compare the Lipid profile and fibrinogen as inflammatory markers for assessing cardiovascular risk between diabetic and non-diabetic end stage renal disease (ESRD) patients undergoing maintenance haemodialysis.
Material and Methods: We enrolled 32 patients of both sex suffering from diabetes mellitus end stage renal disease undergoing haemodialysis and 32 non- diabetic end stage renal disease undergoing haemodialysis for this study. Results: We found that there is significant increase in the parameters like plasma fibrinogen, plasma glucose concentration, atherogenic index (TC/HDLc), serum lipid profile (TC, LDLc, TG, VLDLc) and decrease in serum HDLc in diabetic ESRD patients in comparison to non diabetic ESRD patients undergoing maintenance haemodialysis. Conclusion: We conclude that elevation in plasma fibrinogen level, serum lipid profile and atherogenic index (TC/HDLc) in diabetic ESRD patients undergoing maintenance haemodialysis which indicates higher risk of adverse cardiac events and atherosclerosis as a major cause of coronary heart disease in diabetic ESRD patients.
Keywords: Plasma Fibrinogen, Haemodialysis, Diabetes
DOI: 10.7324/IJCRR.2018.1018
Full Text:
INTRODUCTION
Diabetes mellitus is a group of metabolic diseases characterized by hyperglycaemia resulting from defects in insulin secretion, insulin action, or both. It is a chronic disease that causes serious health complications including renal (kidney) failure, heart disease, stroke and blindness. Diabetes mellitus is associated with a number of changes in thrombotic and fibrinolytic coagulation factor level or activity, which collectively increases the risk of thrombus formation. Hyperglycaemia and insulin resistance induce qualitative and quantitative changes in clotting factors, resulting in dense and compact clot structure and resistance to fibrinolysis [1]. Fibrinogen is the major coagulation protein in blood by mass, the precursor of fibrin and an important determinant of blood viscosity and platelet aggregation [2]. As a clotting factor, fibrinogen is an essential component of the blood coagulation system, being the precursor of fibrin. Fibrinogen has been identified as a major independent risk factor for cardiovascular disease. There are several mechanisms by which fibrinogen may increase cardiovascular risk. First, it binds specifically to activate platelets via glycoprotein iib/iiia, contributing to platelet aggregation. Second, increased fibrinogen levels promote fibrin formation. Third, it is a major contributor to plasma viscosity. Finally, it is an acute phase reactant that is increased in cardiovascular diseases [6]. High fibrinogen levels are associated with more compact clot structure, whereas elevated plasminogen activator inhibitor – I (PAI-I) levels impairs the fibrinolytic process. In addition to the quantitative changes, qualitative changes in clotting factors can affect the structure of the clots. High serum glucose has been shown to increase glycation of fibrinogen and clots formed from glycated fibrinogen have a more compact structure and increased resistance to lysis. A by-product of protein glycation that is glycoaldehyde induces post-translational modifications in fibrinogen, which impairs the fibrinolytic process, other post-translational modifications in fibrinogen such as oxidation, a known pathogenic process in diabetes mellitus, can also modify clot structure [1]. Diabetes mellitus is associated with an increase in low density lipoprotein cholesterol, and triglycerides, and low high density lipoprotein cholesterol levels. The alterations in the level and properties of LDL and HDL together contribute to the increased risk for Coronary artery disease (CAD) in diabetics [7]. Cardiovascular morbidity and mortality is markedly increased in diabetes mellitus with end stage renal disease (ESRD) patients undergoing haemodialysis (HD). As atherogenesis is mediated by inflammation of vessel walls and as evidence evolves that atherosclerosis and diabetes mellitus share a common inflammatory basis. Lipid profile and fibrinogen level has been compared as inflammatory markers for assessing cardiovascular risk between diabetic and nondiabetic end stage renal disease (ESRD) patients undergoing maintenance haemodialysis in this study. Atherogenic index (TC/HDLc) has also been determined and compared between control group and diabetes mellitus patients.
Hence, this study proposes to see whether end stage renal disease (ESRD) patients undergoing haemodialysis with additional diabetes mellitus exhibit increased cardiovascular risk markers in comparison to end stage renal (ESRD) patients undergoing haemodialysis without diabetes mellitus.
EXPERIMENTAL SECTION
Study Design and Subjects: This study was conducted in the Department of Biochemistry Teerthanker Mahaveer Medical College and Research Centre and Dialysis unit of Teerthanker Mahaveer Hospital, Moradabad, U.P, and India. The investigation was conducted on 32 patients of both sex suffering from diabetes mellitus end stage renal disease undergoing haemodialysis and 32 non-diabetic end stage renal disease undergoing haemodialysis. Inclusion criteria: Patients undergoing maintenance HD for atleast one year. Exclusion criteria: Patients with any infective diseases such as AIDS, Hepatitis B and Hepatitis C, and treatment with cholesterol lowering drugs, tissue plasminogen activator (tPA), anticoagulant therapy , pregnant women, and postmenopausal state conditions (which can alter the plasma fibrinogen and serum lipid profile level ) were excluded from the study. Sample collection: Blood samples were collected from an anticubital vein between 8 and 9 AM after an overnight fast from all subjects and dispensed into following vials for various biochemical tests:
1. Fluoride oxalate vial for fasting plasma glucose estimation.
2. Plain vial for Total cholesterol, Total triglycerides and High density lipoprotein cholesterol.
3. Vial containing 3.8% tri sodium citrate for fibrinogen estimation.
Analysis of Sample:
• Estimation of Plasma fibrinogen level by KjeldahlNesslerization method.
• Estimation of fasting blood sugar (FBS) level by GOD-POD method (Glucose oxidase and peroxidase).
• Estimation of serum Cholesterol by end point CHODPAP method.
• Estimation of serum triglycerides by end point GPOTRINDER method.
• Estimation of serum HDLc by end point TRINDER reaction.
Calculation
• VLDLc = [TG/5]
• LDLc = [Total Cholesterol] - [HDLc] - [(TG/5)] (Friedewald equation)
• Atherogenic index = [TC/HDLc]
Statistical analysis
Mean ± SD were calculated for all the parameters analyzed and were compared by Student’s t-test (2 tailed) using SPSS. P-values considered significant were as follows:- P <0.05 – As significant P <0.001 – As highly significant

DISCUSSION
In the present study, the comparison of lipid profile and plasma fibrinogen level as inflammatory markers for assessing cardiovascular risk between 32 diabetic and 32 non diabetic ESRD patients undergoing maintenance haemodialysis was done. In this study, atherogenic index (TC/HDLc) had also been determined and compared between control group and diabetes mellitus ESRD patients.
A. Plasma fibrinogen level determination in diabetic and non diabetic ESRD patients undergoing maintenance haemodialysis:
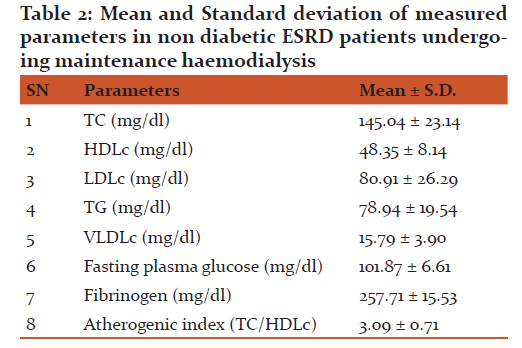
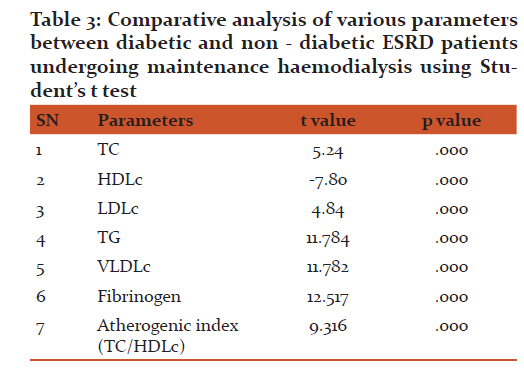
The comparison between the plasma fibrinogen levels of diabetic ESRD patients with (mean ± S.D 510.81 ± 113.32 mg/ dl) was found to be significantly higher than non diabetic (mean ± S.D 257.71 ± 15.53 mg/dl) ESRD patients undergoing haemodialysis (P< 0.001). In Gothenburg study plasma fibrinogen was an independent risk factor for MI and stroke on univariate analysis. On multivariate analysis, plasma fibrinogen was still statistically significant risk for stroke [62]. In the Framingham Study, the risk of developing cardiovascular disease was significantly related to plasma fibrinogen levels [70]. The influence of plasma fibrinogen on cardiovascular risk was much more pronounced in younger men. The impact of plasma fibrinogen levels on cardiovascular disease was comparable with the major risk factors, such as blood pressure, haematocrit, adiposity, cigarette smoking and diabetes; and was still an independent predictor of coronary artery disease on multivariate analysis) [63]. Acevedo M et al found that patients with CAD tended to have higher fibrinogen levels than those without the disease. The role of fibrinogen concentration in the development of complications in diabetics was also suggested by Wilhelmsen et al, as a risk factor for stroke and myocardial infarction. Fibrinogen may increase cardiovascular risk in several ways. It plays an important role in platelet aggregation, plasma viscosity, and fibrin formation. It is an acute phase reactant that is increased in inflammatory states and thus, its high level could simply be a reflection of underlying arterial plaque formation [64]. High plasma fibrinogen levels may cause a hypercoagulable state, platelet aggregation, and important rheological alterations. Red blood cell aggregation and disaggregation shear stress are profoundly altered by the level of fibrinogen. Enhanced red blood cell agreeability leads to increased blood viscosity, which in turn might induce a further slowing of the circulation, which may play a key role in the extent of arterial damage. Fibrinogen and fibrin not only play a key role in coagulation but are also involved in cellular interactions, wound healing, and neoplasia. High plasma fibrinogen levels are associated with an increased risk of cardiovascular disease in healthy as much as in high-risk individuals. In this study, it has been found that CAD occurs frequently in haemodialysis patients, with an even higher prevalence in diabetic patients in comparison to non diabetic ESRD patients undergoing haemodialysis.
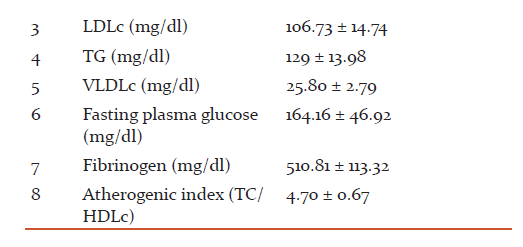
B. Serum lipid profile determination in diabetic and non diabetic ESRD patients undergoing maintenance haemodialysis:
The comparison between serum TC of diabetic with (mean ± S.D 168.88 ± 11.23 mg/dl ), serum LDLc (mean ± S.D 106.73 ± 14.74 mg/dl) , serum TG (mean ± S.D 129 ± 13.98 mg/dl) and serum VLDLc (mean ± S.D 25.80 ± 2.79 mg/ dl) was found to be significantly higher than serum TC of non diabetic ESRD patients with (mean ± S.D 145.04 ± 23.14 mg/dl), serum LDLc (mean ± S.D 80.91 ± 26.29 mg/ dl), serum TG (mean ± S.D 78.94 ± 19.54 mg/dl) and serum VLDLc (mean ± S.D 15.79 ± 3.90 mg/dl) undergoing maintenance haemodialysis (P < 0.001). Gerstein HC, Mann JF, Yi Q, Zinman B, Dinneen SF, Hoogwerf B, Halle JP, Young J, Rashkow A, Joyce C, Nawaz S, Yusuf S: HOPE Study showed that the mild renal insufficiency confers a risk for cardiovascular events even higher than that observed in patients with a coronary heart disease and a normal renal function. Although several factors may explain this association between renal and cardiovascular disease, there is growing evidence that hyperlipidemia contributes not only to cardiovascular disease but also to renal disease progression. Samuelsson et al. demonstrated a strong correlation between triglyceride-rich apoB-containing lipoproteins and the rate of progression in non-diabetic patients with chronic kidney disease. In Vaziri ND study: progressive renal failure especially that associated with proteinuria is accompanied by abnormalities of lipoprotein transport. Typically, the dyslipidemia is reflected predominantly in increased serum levels of triglycerides with high levels of VLDL, apoB and pre-β HDL, and low levels of HDL and of apoA. Cholesterol levels may be very high in proteinuric patients [52]. Chronic renal disease is accompanied by characteristic abnormalities of lipid metabolism, which may appear as a consequence of nephrotic syndrome or renal insufficiency and are reflected in an elevated plasma lipid levels. Experimental and clinical studies have suggested a correlation between the progression of renal disease and dyslipidemia. High cholesterol and triglyceride plasma levels have been demonstrated to be independent risk factors for progression of renal disease in humans. The underlying pathophysiologic mechanisms for the relationship between lipid levels and progression of renal disease are not yet fully understood, although there are data that oxidative stress and insulin resistance may mediate the lipid-induced renal damage [50]. In this study, it has been found that serum HDLc of diabetic ESRD patients with (mean S.D 36.25 ± 3.24 mg/dl) was found to be significantly less than non diabetic (mean ± S.D 48.35 ± 8.14 mg/dl) ESRD patients undergoing maintenance haemodialysis. Muntner et al. showed that people with low HDL cholesterol and hypertriglyceridemia at baseline have a higher risk for having a loss of renal function. In Kontush A, Chapman MJ study moreover, HDL serves as a potent endogenous inhibitor of inflammation, platelet adhesion and LDL oxidation, because of a number of HDL associated apolipoproteins (mainly apolipoprotein AI) and enzymes (paroxonase-1, platelet-activating factor acetylhydrolase and lecithin-cholesterol acyltransferase (LCAT) [66]. Despres JP, Lemieux I, Dagenais GR, Cantin B, Lamarche B. studies have demonstrated that HDL cholesterol is a negative risk factor for atheroscerosis. Attman PO, Samuelsson O, Alaupovic P studied that diabetic ESRD patients have, generally, reduced plasma HDL-cholesterol levels compared to non diabetic ESRD patients . Vaziri ND, Deng G, Liang K and Guarnieri GF, Moracchiello M, Campanacci L, et al. have been shown that patients with impaired renal function usually exhibit decreased levels of apolipoproteins AI and AII (the main protein constituents of HDL) , diminished activity of LCAT (the enzyme responsible for the esterification of free cholesterol in HDL particles), as well as increased activity of cholesteryl ester transfer protein (CETP) that facilitates the transfer of cholesterol esters from HDL to triglyceride-rich lipoproteins thus reducing the serum concentrations of HDL-cholesterol [53].
Dirican M, Akca R, Sarandol E, Dilek K and Liberopoulos EN, Papavasiliou E, Miltiadous GA, et al. studied that in addition to their reduced efficiency as cholesterol acceptors, HDL particles from individuals with impaired renal function have less effective antioxidative and anti-inflammatory function. This impairment can, at least in part, be attributed to the reduction in the activities of HDL-associated enzymes, such as paraoxonase (an enzyme that inhibits the LDL oxidation). Attman PO, Samuelsson O, Johansson AC, Moberly JB, Alaupovic P studied that hemodialysis procedure may also have a contributory role in the reduced HDL cholesterol levels of dialysis patients. Thus, in dialysis patients the type of membrane and dialysate used in HD procedure may influence the HDL-cholesterol levels. Blankestijn PJ, Vos PF, Rabelink TJ, van Rijn HJ, Jansen H, Koomans HA have been shown that the use of high-flux instead of low flux membranes is associated with an increase in apolipoprotein AI and HDL-cholesterol values. Jung K, Scheifler A, Schulze BD, Scholz M has shown that, the type of dialysate may also significantly affect the serum levels of lipoproteins in HD patients. Indeed, it has been shown that the use of bicarbonate dialysate may result in higher HDL-cholesterol concentrations than the use of acetate dialysate. The main function of HDL is the transport of surplus cholesterol from the arterial wall to the liver for excretion. This process, which is commonly called ‘reverse cholesterol transport’, is critical for cellular cholesterol homeostasis and protection against atherosclerosis [66].
C. Atherogenic index determination in diabetic and non diabetic ESRD patients undergoing maintenance haemodialysis:
Framingham’s study had suggested that as the TC/HDLc (atherogenic index or cardiac risk ratio) increases, so there is increased risk of coronary heart disease (CHD) [65, 66]. In this study, it has been found that, this ratio was significantly (p < 0.001) elevated in diabetic ESRD patients, as compared to non diabetic ESRD patients undergoing maintenance haemodialysis which indicates higher risk of adverse cardiac and renal events in diabetic ESRD patients. These parameters may thus be used for analyzing the risk of atherosclerosis in ESRD patients.
CONCLUSION
Thus, it can be concluded that plasma fibrinogen, lipid profile and atherogenic index are known risk factors for atherosclerosis in the general population. Fibrinogen concentration and lipid profile is significantly elevated in diabetic ESRD patients undergoing maintenance haemodialysis [68, 69]. Increase in lipid profile causes platelet adhesion and lipid oxidation and increase in plasma fibrinogen levels promote hypercoagulability. Both in combination have synergistic effect to accelerate the rate of atherosclerosis. Identification of high risk patients permits the focusing of treatment to optimize efforts to reduce mortality.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
The authors wish to thank the technical staff of Biochemistry department who assisted in performing the analysis. The study has been permitted by the research and ethical committee of Teertanker Mahaveer Medical College & Research Centre, Moradabad. The authors acknowledge the immense help received from the scholars whose articles are cited and included in references of this manuscript. We are also grateful to authors / editors / publishers of all those articles, journals and books from where the literature for this article has been reviewed and discussed.
LIST OF ABBREVIATIONS
CAD Coronary artery disease
CHD Coronary heart disease
CHOD Cholesterol oxidase
ESRD End Stage Renal Disease
GPO Glycerol phosphate oxidase
DAP Dihydroxy acetone phosphate
HD Haemodialysis
PAI-1 Plasminogen activator inhibitor-1
tPA Tissue plasminogen activator
GOD Glucose Oxidase
POD Peroxidase
FBS Fasting Blood Sugar
References:
-
SH Alzahrani and RAgul Ajjan. Coaation and fibrinolysis in diabetes. Diabetes and Vascular Disease Research 2010; 7(4) 260 –73.
-
DR Kafle and P Shrestha. Study of fibrinogen in patients with diabetes mellitus. Nepal Med Coll J 2010; 12(1): 34-7.
-
Doolittle RF, Spraggon G, Everse SJ. Three-dimensional structural studies on fragments of fibrinogen and fibrin. Curr Opin Struct Biol 1998; 8:792–8.
-
Herrick S, Blanc-Brude O, Gray A, Laurent G. Fibrinogen. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 1999; 31:741–6.
-
Haidaris PJ, Francis CW, Sporn LA, Arvan DS, Collichio FA, Marder VJ. Megakaryocyte and hepatocyte origins of human fibrinogen biosynthesis exhibit hepatocyte-specific expression of gamma chain-variant polypeptides. Blood 1989; 74:743–50.
-
James J. Stec, Halit Silbershatz, et al. Association of Fibrinogen with Cardiovascular Risk Factors and Cardiovascular Disease in the Framingham Offspring Population. Circulation. 2000; 102: 1634-8.
-
Textbook of Biochemistry for Medical Students 6th Ed. Editors: Vasudevan DM, S Sreekumari, Vaidyanathan K. Jaypee Brothers Medical Publishers (P) Ltd. 2011, 296.
-
Hogan P, Dall T, Nikolov P. Economic costs of diabetes in the US in 2002. Diabetes Care. 2003; 26:917–32.
-
Lippincott’s Illustrated Reviews: Biochemistry 4th Ed. Editors: Champe Pamela C, Harvey Richard A. Wolters Kluwer Publishers (India) Pvt. Ltd., 2008,337.
-
UK Prospective Diabetes Study (UKPDS). VIII. Study design, progress and performance. Diabetologia. 1991; 34:877–90.
-
Rahman S, Rahman T, Ismail AA, Rashid AR. Diabetes-associated macrovasculopathy: pathophysiology and pathogenesis. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2007; 9:767–80.
-
W Todd Cad. Diabetes-Related Microvascular and Macrovascular Diseases in the Physical Therapy Setting. Phys Ther. 2008 November; 88(11): 1322–35.
-
Michael Brownlee; the Pathobiology of Diabetic Complications-A Unifying Mechanism; DIABETES, VOL. 54, JUNE 2005.
-
R. G. Ahmed; The Physiological and Biochemical effects of diabetes on the balance between oxidative stress and antioxidant defense system; Medical Journal of Islamic World Academy of Sciences 2005; 15:1, 31-42.
-
Lingjie Zhao; Effects of Free Radicals in Diabetes; Free Radical and Radiation Biology Graduate Program; Department of Radiology B-180 ML; the University of Iowa.
-
John Doupis, MD, PhD1 and Aristidis Veves; Antioxidants, Diabetes, and Endothelial Dysfunction-a report; T O U C H B R I E F I N G S 2 0 0 7.
-
Haffner S.M., Coronary heart disease in patients with diabetes, N Engl J Med, 2000; 342, 1040–2.
-
Rossi R., Nuzzo A., Grimaldi T., et al., Diabetes and cardiovascular disease: a close and dangerous connection, Heart Int, 2005; 1, 18–23.
-
Jay D., Hitomi H., Griendling K.K., Oxidative stress and diabetic cardiovascular complication, Free Rad Biol Med, 2006; 40, 183–92.
-
Stratmann B and Tschoepe D. Atherogenesis and atherothrombosis--focus on diabetes mellitus. Best Pract Res Clin Endocrinol Metab 2009; 23: 291–303.
-
Williams SB, Cusco JA, Roddy MA, et al. Impaired nitric oxide-mediated vasodilation in patients with non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. J Am Coll Cardiol. 1996; 27:567–74.
-
De Vriese AS, Verbeuren TJ, Van de Voorde J, et al. Endothelial dysfunction in diabetes. Br J Pharmacol. 2000; 130:963–74.
-
Milstien S, Katusic Z. Oxidation of tetrahydrobiopterin by peroxynitrite: implications for vascular endothelial function. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1999; 263:681–4.
-
Grant PJ. Diabetes mellitus as a prothrombotic condition. J Intern Med. 2007; 262:157–72.
-
Inoguchi T, Li P, Umeda F, et al. High glucose level and free fatty acid stimulate reactive oxygen species production through protein kinase C–dependent activation of NAD(P)H oxidase in cultured vascular cells. Diabetes. 2000; 49:1939–45.
-
Linden E, Cai W, He JC, et al. Endothelial dysfunction in patients with chronic kidney disease results from advanced glycation end products (AGE)-mediated inhibition of endothelial nitric oxide synthase through RAGE activation. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2008; 3:691–8.
-
Rask-Madsen C, King GL. Mechanisms of disease: endothelial dysfunction in insulin resistance and diabetes. Nat Clin Pract Endocrinol Metab. 2007; 3:46–56.
-
Assert R, Scherk G, Bumbure A, et al. Regulation of protein kinase C by short- term hyperglycaemia in human platelets in vivo and in vitro. Diabetologia. 2001; 44:188–95.
-
Carr ME. Diabetes mellitus: a hypercoagulable state. Journal of Diabetes Complications. 2001; 15:44–54.
-
Hansson GK, Robertson AK, Soderberg-Naucler C. Inflammation and atherosclerosis. Annu Rev Pathol. 2006; 1:297–329.
-
Williams MD, Nadler JL. Inflammatory mechanisms of diabetic complications. Curr Diab Rep. 2007; 7:242–8.
-
Beckman JA, Creager MA, Libby P. Diabetes and atherosclerosis: epidemiology, pathophysiology, and management. JAMA. 2002; 287:2570–81.
-
Suzuki LA, Poot M, Gerrity RG, Bornfeldt KE. Diabetes accelerates smooth muscle accumulation in lesions of atherosclerosis: lack of direct growth-promoting effects of high glucose levels. Diabetes. 2001; 50:851–60.
-
Reusch JE, Draznin BB. Atherosclerosis in diabetes and insulin resistance. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2007; 9:455–63.
-
Grant PJ. Inflammatory, atherothrombotic aspects of type 2 diabetes. Curr Med Res Opin 2005; 21(Suppl 1): 5–12.
-
Schwartz CJ, Valente AJ, Kelley JL, Sprague EA, Edwards EH. Thrombosis and the development of atherosclerosis: Rokitansky revisited. Semin Thromb Hemost 1988; 14: 189-95.
-
Herrick S, Blanc-Brude O, Gray A, Laurent G. Fibrinogen. Int J Biochem Cell Biol1999; 31:741–6.
-
Haidaris PJ, Francis CW, Sporn LA, Arvan DS, Collichio FA, Marder VJ. Megakaryocyte and hepatocyte origins of human fibrinogen biosynthesis exhibit hepatocyte-specific expression of gamma chain-variant polypeptides. Blood 1989; 74:743–50.
-
Meade TW, Brozovic M, Chakrabarti RR, et al. Haemostatic function and ischemic heart disease: principal results of the Northwick Park Heart Study. Lancet. 1986; 6:533–7.
-
Kannel WB, Wolf PA, Castelli WP, et al. Fibrinogen and risk for cardiovascular disease. JAMA. 1987; 258:1183–6.
-
Pieters M, van Zyl DG, Rheeder P, Jerling JC, Loots du T, van der Westhuizen FH, et al. Glycation of fibrinogen in uncontrolled diabetic patients and the effects of glycaemic control on fibrinogen glycation. Thromb Res 2007; 120: 439–46.
-
Andrades ME, Lorenzi R, Berger M, Guimaraes JA, Moreira JC and Dal Pizzol F. Glycolaldehyde induce fibrinogen post-translational modification, delay in clotting and resistance to enzymatic digestion. Chem Biol Interact 2009; 180: 478–84.
-
Henschen-Edman AH. Fibrinogen non-inherited heterogeneity and its relationship to function in health and disease. Ann N Y Acad Sci 2001; 936: 580–93.
-
Neil A, Hawkins M, Potok M, Thorogood M, Cohen D and Mann J. A prospective population-based study of microalbuminuria as a predictor of mortality in NIDDM. Diabetes Care 1993; 16: 996-1003.
-
Dotevall A, Johansson S, Wilhelmsen L. Association between fibrinogen and other risk factors for cardiovascular disease in men and women. Results from the Goteborg MONICA survey 1985. Ann Epidemiology 1994; 4: 369–74.
-
Zeinab Hegab, Stephen Gibbons. Role of advanced glycation end products in cardiovascular disease. World J Cardiol. 2012 April 26; 4(4): 90-102.
-
Williams ME. Management of diabetes in dialysis patients.Curr Diab Rep.2009 Dec; 9(6):466-72.
-
Brenner BM, Cooper ME, de Zeeuw D, et al. Effects of losartan on renal and cardiovascular outcomes in patients with type 2 diabetes and nephropathy. N Engle J Med. 2001; 345:861–9.
-
Hasslacher C, Ritz E, Wahl P, Michael C. Similar risks of nephropathy in patients with type I or type II diabetes mellitus. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 1989; 4:859–63.
-
Roberto Trevisan, Alessandro R. Dodesini, Giuseppe Lepore. Lipids and Renal Disease. JASN April 2006; vol. 17 no. 4 suppl 2 145-7.
-
Sammuelsson O, Attman P, Knight-Gibson C, Larsonn R, Mulec H, and Weiss L, Alaupovic P: Complex apolipoprotein B-containing lipoprotein particles are associated with a higher rate of progression of human chronic renal insufficiency. J Am Soc Nephrol 1998; 9: 1482 –8.
-
Vaziri ND: Molecular mechanisms of lipid disorders in nephrotic syndrome. Kidney Int 2003; 63: 1964 –76.
-
Vaziri ND, Liang K, and Park JS: Acquired lecithin: Cholesterol acyltransferase (LCAT) deficiency in nephrotic syndrome. Am J Physiol 2001; 49: F823 –F9.
-
Chait A, Heinecke JW: Lipoprotein modification: Cellular mechanisms. Current Opin Lipidol 1994; 5: 363 –70.
-
Wheeler DC, Chana RS: Interaction between lipoproteins, glomerular cells and matrix. Miner Electrolyte Metab 1993; 19: 149 –64.
-
Reaven GM: Role of insulin resistance in human disease. Diabetes 1988; 37: 1595 –607.
-
Medical Laboratory Science Theory and Practice 7th Ed. Editors: Ochei. J, Kolhatkar. A, Haemostasis and fibrinolysis, Assay of coagulation factors fibrinogen. Tata McGraw Hill, 2008, 347.
-
Allain C.C., Poon L. S., Chan C.S.G., Richmond W. and Fu P., Cli. Chem 1974; 20(470).
-
McGowan MW, et al. Cli Chem 1983; 29; 538.
-
Williams, P., et al. High density lipoprotein and coronary risk factor, Lancet, 1969; 1; 72.
-
Trinder, P. Ann. Clin.BioChem. 1969; 6(24).
-
Wilhelmsen L, Svardsudd K, Korsan-Bengtsen K, Larsson B, Welin L, Tibblin G. Fibrinogen as a risk factor for stroke and MI. N Engl J Med 1984; 311:501–5.
-
Kannel WB, Wolf PA, Castelli WP, D’Agostino RB. Fibrinogen and risk of cardiovascular disease. The Framingham Study. JAMA 1987; 258:1183–6.
-
Berk BC, Weintraub WS, Alexander RW. Elevation of C-reactive protein in “active” coronary artery disease. Am J Cardiol. 1990; 65:168–72.
-
Castelli W.P, Abbott R.D, Mc Namara P.M, Summary estimates of cholesterol used to predict coronary heart disease. Circulation, 1983 67(4):730-734.
-
Sangeeta K, et al, Glycosylated Haemoglobin in Non- Diabetic End-Stage Renal Disease Patients Undergoing Haemodialysis. Journal of Clinical and Diagnostic Research 2010 October; 4:3191-5.
-
Vasilis Tsimihodimos, Zoi Mitrogianni. Dyslipidemia Associated with Chronic Kidney Disease. Open Cardiovasc Med J. 2011; 5: 41–8.
-
Wilhelmsen L, Svardsudd K, Korsan-Bengtsen K, et al. Fibrinogen as a risk factor for stroke and myocardial infarction. N Eng L J Med. 1984 Aug 23. 311(8):501-5.
-
Go A.S, Chertow G M, Fan D et al. Chronic kidney disease and the risks of death, cardiovascular events, and hospitalization. N Engl J Med. 2004 Sep 23. 351(13): 1296-305.
-
Meade T W, Mellows S, Brozovic M et al. Homeostatic function and ischaemic heart disease: Principal results of the Northwick Park Heart study. Lancet 1986; 2:537-7.
|






 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License