IJCRR - 9(24), December, 2017
Pages: 35-39
Date of Publication: 26-Dec-2017
Print Article
Download XML Download PDF
Analysis of Haemoglobin Variants and Oxygen Affinity in Indian and Kyrgyz Population Groups
Author: Supriya Saini, Priya Gaur, Karan Pal, Alpesh K. Sharma, Praveen Vats, Akpay Sarybaev, Bhuvnesh Kumar, Shashi Bala Singh
Category: Healthcare
Abstract:Aim: The hemoglobin (Hb) variants can alter the structure and biochemical functions of Hb along with affecting physiological properties of the individual. In normal adult RBC, Hb variants that exist are HbA1, HbA2, HbS and HbF. Mutations in globin chains can change the Hb-O2 affinity which can alter the normal loading of oxygen in lungs and unloading in the tissues and also affect arterial oxygen saturation. Absence of abnormal Hbs rules out upto some extent presence of genetic or acquired facilitated oxygen affinity.
Methodology: The study was undertaken to compare haemoglobin variants using HPLC in Indians (n=10) and Kyrgyz population groups (n=10). We estimated oxygen affinity (P50) from PO2, SO2 and pH values using Lichtman equation and peripheral oxygen saturation (SpO2) using pulse oximetry at basal and upon acute HA exposure to 4111m in both the population groups.
Results: We obtained Hb fractions A1a, A1b, A1c and A2 within normal range and no HbF or HbS fractions were found in any volunteer from HPLC run. All the P50 values were well within normal range (22-28mmHg). No change in P50 was observed upon HA exposure in these two populations but Kyrgyz have been found to have a higher P50 compared to Indians at basal.
Discussion and Conclusion: Since our data rule-out the existence of abnormal Hb variant in either of the population, thus the significant decrease in SpO2 observed upon HA induction in both the groups is due to hypoxia at HA and higher P50 in Kyrgyz
compared to Indians is population specific.
Keywords: High altitude, Haemoglobin variants, Kyrgyz, P50, SpO2
DOI: 10.7324/IJCRR.2017.9247
Full Text:
Introduction
Haemoglobin (Hb) variants are structurally abnormal globin proteins and they are the mutant forms of Hb in a population and these defects are often inherited. Around 1000 Hb-variants exist and they are mostly missense or substitution mutations which may alter Hb-O2 affinity. In normal adult erythrocytes, Hb variants that exist are HbA1, HbA2, HbS (Sickle hemoglobin) and HbF (fetal haemoglobin). HbA1 (2α and 2β tetramer) is the major Hb which constitutes 95-98% of total haemoglobin. About 1.5-3.5% of all Hb molecules is constituted by HbA2 which contain 2α and 2δ tetramers. Fetal haemoglobin (HbF) constitutes ≤ 2.5% of total adult Hb (1). HbF has a slightly higher oxygen affinity then adult Hb. Greater than normal percentage of HbF in humans after 2 years of age may be due to occurrence of anemia (2). HbA0 is the non-glycated portion of HbA. HbA1a is glycated with fructose 1, 6 diphosphate and HbA1c is glycated with D-glucose at amino terminal of β-chain and is generally 6% of total Hb which may increase upto 12% in Diabetes mellitus. It’s a good indicator of long-term glycemic control. Hemoglobinopathies like thalassemia and sickle cell anaemia can be tested using High Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC), isoelectric focusing and spectroscopy and are the most commonly used routine tests to identify structurally abnormal haemoglobin variants (1, 3). HbA2 is increased in people with thalassemia. Absence of abnormal Hbs rules out upto some extent presence of genetic or acquired facilitated oxygen affinity (2, 4). Black Americans are at higher risk of sickle cell anaemia and Mediterranean ancestry individuals are at greater risk of β-thalassemia hemoglobinopathy (5). High altitude (HA) environment poses various stresses to individuals (6). Tibetan highlanders have higher oxygen affinity as part of their genetic adaptation which works as a beneficial factor to protect them from polycythemia and CMS vulnerability (2).
Understanding the Hb variants is useful in diagnosing hemoglobinopathies which can alter Hb function at high altitude and further affect HA adaptation in humans (5). The Hb variants can alter the structure and biochemical functions of Hb along with affecting physiological properties of the individual (7). Mutations that increase the Hb-O2 affinity basically activate erythropoeitic drive. Mutations that reduce Hb-O2 affinity leads to high deoxy-Hb levels (3), thus altering haemoglobin oxygen saturation. P50 is the oxygen partial pressure at which Hb is 50% saturated with oxygen (8). An abnormal Hb can alter P50 and arterial oxygen saturation. Occurrence of haemoglobin variants causes problems in oxygen delivery which may lead to altered P50 (2). This genetic effect may be population specific. We present here two different population groups, compared their Hb variants, P50 and peripheral oxygen saturation (SpO2) values to understand Hb-oxygen affinity, which may help in understanding HA adaptation.
Material and Methods
Blood collection and P50 estimation:
The study conformed to the ethical guidelines of the institute (Defence Institute of Physiology and Allied Sciences, Delhi) and is in accordance to 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards. After obtaining informed written consent, whole blood collected from 20 healthy male volunteers (10 Indian and 10 Kyrgyz) matched for age and height of age group 19 to 30 years. Blood was collected from an anticubital vein after approximately 12 hours of fasting at basal (Bishkek, Kyrgyzstan) and upon acute exposure to high altitude (Day3) at 4111 m. Measurements of pH, oxygen partial pressure (PO2), saturation of oxygen (SO2) were made from fresh blood using blood gas analyser (iSTAT systems, Abbott, USA). P50 calculation was done using following equation (9):
P50 =Log pO2 (7.4) = log pO2 (observed) - [0.5 (7.40-pH (observed)]
1/k = antilog (2.7 log pO2 (7.4) × [(100 - SO2 (observed) ÷SO2 (observed)]
Estimated P50 value = antilog [(log 1 / k) ÷ 2.7] (at pH=7.4, Temperature=37°C)
Peripheral oxygen saturation (SpO2) Measurement:
Saturation of peripheral oxygen was measured using finger pulse oximeter (Nonin Medical Inc. USA). It specifically measures percentage of oxygenated haemoglobin compared to total haemoglobin in blood giving an estimate of arterial oxygen saturation.
Hemolysate preparation:
Blood was centrifuged for 15min, at 3000 rpm, 4°C and supernatant was separated. Remaining packed cell volume of blood was washed three times with chilled isotonic potassium chloride (KCl) (1.15%), centrifuged (15 min, 3000 rpm, 4°C) and supernatant was removed each time to collect washed packed cells. 0.5 ml of these washed packed cells were lysed with 0.5 ml of saline (0.7% sodium chloride) and added 0.3 ml of carbon tetrachloride (HPLC grade). Centrifuged (3000 rpm, 30 min, 4ºC) and remove supernatant (hemolysate) and stored at -80°C until further analysis.
Quantification of Haemoglobin variant:
Sample preparation: Stored hemolysate was thawed and diluted in a ratio of 1:300 in a 1.5 ml sample vial with diluent solution provided with the HPLC system (D-10TM Dual Program HbA2/F/A1c diluent/calibrator set reference no. 220-0218)
Calibrator and Control: Calibrator and control were diluted as per manufacturer’s instructions. A1c and A2/F high and low controls run was performed to check the values followed by calibrator run. Two Calibrators (high and low) of HbA2/ F/ A1C were used. Calibration and control run was performed once in every 24 hours on the instrument.
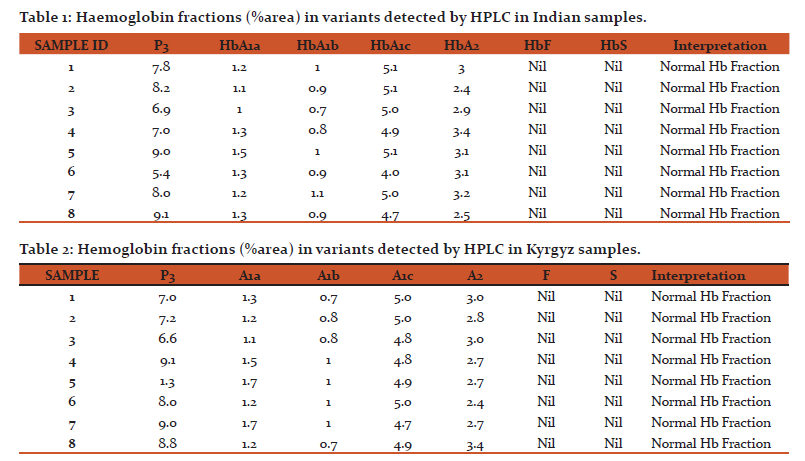
HPLC Run: Prepared hemolysate samples were run on the HPLC system (Bio-Rad Variant II D-10) using D-10 Dual HbA2/F/A1C program and area % of HbA1a, HbA1b, HbA1c, HbA2 and P3 were assessed. Samples were also assessed for presence of HbF and HbS peak. Baseline characteristics and peak shape of HbA1c, HbA2 were analysed from chromatogram and recorded. Presence of any other variant or unknown peak was analysed from chromatogram.
Statistical Analysis: Graph pad Prism 6 was used for statistical analysis and graph construction. Student t-test was done for determining p-values. P-values less than 0.05 were considered significant. Values are mean±SEM.
Results:
Initially samples were screened for P3 peak values. Samples with P3 value less than 10 and total area between 10,0000 and 40,0000 were taken for further interpretation (Fig 1). The fractions HbA1a and HbA1b peak %area in Indian volunteers ranged from 1 to 1.5 and 0.7 to 1.1 respectively (Table 1). In case of Kyrgyz these peak %areas were in the range of 1.1 to 1.7 for HbA1a and 0.7 to 1 for HbA1b fraction (Table 2). These peak areas are within normal limit in all the volunteers of both the population groups. HbA0 is the non-glycated portion of the haemoglobin and occupies the maximum area on the chromatogram.
HbA1c values more than 6% of total area represents an Hb variant condition and is an indicator of poor diabetic control. In all 16 samples, none of the volunteer had such results. The data ranged from 4.7 to 5.1 representing no abnormality. Thalassemic hemoglobinopathies causes anemia and poses serious health problems in society (5). Thalassemia trait could alter the haemoglobin oxygen affinity which would change the high altitude response in man. In both the sample groups HbA2 values are normal and thus none of the volunteers possess the thalassemia trait. HbF and HbS are well known for causing hemoglobinopathies which alter the haemoglobin structure and function and can cause changes in affinity of oxygen to haemoglobin. None of the samples showed any HbF or HbS peak in the HPLC run. These results represent a normal haemoglobin fraction.
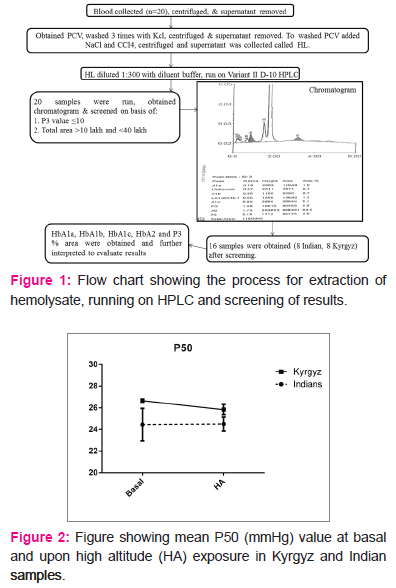
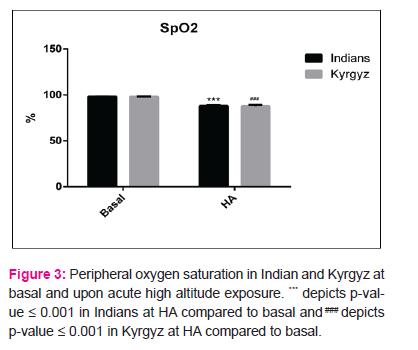
We also calculated the pressure at which 50% haemoglobin is saturated with oxygen (P50) from venous blood. A high P50 represents low oxygen affinity and vice-versa (10). The p50 values both at basal (24.4±1.5mmHg in Indians, 26.6±.15mmHg in Kyrgyz) and after induction to HA (24.5±0.64mmHg in Indians, 25.8±0.48mmHg in Kyrgyz) were well within permissible range. There was no change in P50 values upon HA exposure in any of the population group (Fig 2), but Kyrgyz had a higher mean P50 value at baseline compared to Indians. SpO2 reduced significantly in both the population groups upon HA exposure. In Indians, value decreased from 98.1±0.1% at basal to 88.1±0.94% at day 3. In Kyrgyz, value decreased from 98.1±0.18% at basal to 87.78±1.5% at day 3 (Fig 3).
Discussion
To the best of our knowledge, this is the first study which estimate and compare haemoglobin variants in Indians and Kyrgyz population groups. P50 was calculated using Litchman equation from PO2, SO2 and pH values of venous blood (9) .We observed no change in P50 values upon high altitude exposure in these two populations. Though the P50 values are well within normal range (22-28mmHg), but as compared to Indians, Kyrgyz had a higher mean P50 as compared to Indians representing a higher oxygen delivery. Additionally, our data rule-out the existence of abnormal Hb in either of the population group and the decrease in SpO2 observed upon HA induction is due to increase in altitude
Hb variants have been known to cause a reduction in oxygen supply to tissues (11). About 100 Hb variants are known in humans which can cause altered erythrocytosis (12). Impairment in β-globin protein production resulting in thalassemia is one of the most common hemoglobinopathy. (7). Another clinically important Hb variant is HbS (13). Mutations that alter α- or δ-globin are present at birth and mutations altering β-globin are expected few months after birth causing structurally abnormal haemoglobin (3). Thalassemia is characterised by abnormal Hb formation which can cause RBC destruction and also hinder oxygen transport (14). Hb variants can cause erythrocytosis and hemolysis in otherwise healthy individuals. Also they help in understanding RBC function. Mutations in hemoglobin fraction which leads to high Hb-O2 affinity increases hypoxic tolerance (15). Many Hb variants have modified oxygen binding site which may lead to altered Hb-O2 affinity. Mutations in globin chains can change the Hb-O2 affinity which can alter the normal loading of oxygen in lungs and unloading in the tissues (5). P3 fraction is for estimation of ‘degenerated hemoglobin’ and signifies the degraded haemoglobin in the sample (16). Normal acceptable cut off value of P3 fraction is <10% which we have used in our analysis as a stringent filter to screen out 16 samples out of 20 for further interpretation. We have obtained Hb fractions A1a, A1b, A1c and A2 within normal range using HPLC. Another clinically important Hb variant is HbS (13). The system was capable of evaluating ‘S-window’, but we have not found any HbS fraction in our study. Similarly no HbF fraction was obtained in any of the samples. These abnormal Hbs can alter P50 and peripheral oxygen saturation by changing oxygen affinity to haemoglobin. Occurrence of abnormal haemoglobin variants causes altered oxygen delivery which may lead to altered P50 and also oxygen saturation in arterial blood. In our study we have obtained P50 values within normal range which could be due to absence of any abnormal Hb variant. In a similar study on healthy volunteers, no Hb variants were detected (2). These P50 values do not change significantly upon high altitude induction in either of the population group
at day 3. The higher P50 in Kyrgyz compared to Indians results in a higher oxygen delivery to tissues in this population which is adaptive when ascending to HA and this difference in P50 is not due to occurrence of abnormal haemoglobin. This higher P50 may have aided in acclimatization of this population group at HA during initial days. Altered Hb-oxygen affinity could decrease SpO2 which can be seen in clinical conditions like HAPE (15). In our study too SpO2 decreased significantly upon HA induction in both the population groups, but absence of abnormal Hb variants rule-out such effect signifying that the decrement in peripheral oxygen saturation is due to HA hypoxia and is not genetic or acquired.
Limitation of the study that requires attention includes basically three variables. First being low sample size, second being unable to quantitate 2,3 DPG and nitric oxide in the samples and thirdly few other Hb variants including HbH, HbE and HbD (5) (3) could have been measured. But due to technical reasons these variables could not be taken into account in the present study and could be included in future analysis.
Conclusion:
It can be interpreted from this preliminary study that absence of abnormal haemoglobin variants could account for normal P50 values in both the groups. Population specific higher P50 in Kyrgyz compared to Indians is not due to abnormal haemoglobin variant. The decrease in arterial oxygen saturation upon high altitude induction is due to effect of hypoxia on both the population groups upon HA exposure and not due to any abnormal haemoglobin variant. But since sample size was limited, continuing similar investigation with larger number of samples would further clarify these results.
Acknowledgement: Authors acknowledge the immense help received from scholars whose articles are cited and included in references of this manuscript. The authors are also grateful to authors/editors/publishers of all those articles, journals and books from where the literature for this article has been reviewed and discussed. The authors are thankful to the troops of India and Kyrgyzstan for participating in the study and to Dr. R K Gupta for helping with HPLC study.
Ethical statement: The study conformed to the ethical guidelines of the institute (Defence Institute of Physiology and Allied Sciences, Delhi) and is in accordance to 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Conflict of interest: Authors declare no conflict of interest
Source of Funding: The project is funded by Defence RandD Organization, Delhi
References:
1. Colah RB, Surve R, Sawant P, D'Souza E, Italia K, Phanasgaonkar S, et al. HPLC studies in hemoglobinopathies. Indian journal of pediatrics. 2007;74(7):657-62.
2. Tashi T, Feng T, Koul P, Amaru R, Hussey D, Lorenzo FR, et al. High altitude genetic adaptation in Tibetans: no role of increased hemoglobin-oxygen affinity. Blood cells, molecules and diseases. 2014;53(1-2):27-9.
3. Thom CS, Dickson CF, Gell DA, Weiss MJ. Hemoglobin variants: biochemical properties and clinical correlates. Cold Spring Harbor perspectives in medicine. 2013;3(3):a011858.
4. Huber FL, Latshang TD, Goede JS, Bloch KE. Does venous blood gas analysis provide accurate estimates of hemoglobin oxygen affinity? Annals of hematology. 2013;92(4):517-21.
5. Lorey FW, Arnopp J, Cunningham GC. Distribution of hemoglobinopathy variants by ethnicity in a multiethnic state. Genetic epidemiology. 1996;13(5):501-12.
6. Beall CM. Andean, Tibetan, and Ethiopian patterns of adaptation to high-altitude hypoxia. Integrative and comparative biology. 2006;46(1):18-24.
7. Forget BG, Bunn HF. Classification of the disorders of hemoglobin. Cold Spring Harbor perspectives in medicine. 2013;3(2):a011684.
8. Morgan TJ. The Significance of the P50. In: Vincent J-L, editor. Yearbook of Intensive Care and Emergency Medicine 1999. Yearbook of Intensive Care and Emergency Medicine. 1999: Springer Berlin Heidelberg; 1999. p. 433-47.
9. Lichtman MA, Murphy MS, Adamson JW. Detection of mutant hemoglobins with altered affinity for oxygen. A simplified technique. Annals of internal medicine. 1976;84(5):517-20.
10. Winslow RM, Monge CC, Statham NJ, Gibson CG, Charache S, Whittembury J, et al. Variability of oxygen affinity of blood: human subjects native to high altitude. J Appl Physiol Respir Environ Exerc Physiol. 1981;51(6):1411-6.
11. Percy MJ, Butt NN, Crotty GM, Drummond MW, Harrison C, Jones GL, et al. Identification of high oxygen affinity hemoglobin variants in the investigation of patients with erythrocytosis. Haematologica. 2009;94(9):1321-2.
12. Wajcman H, Galacteros F. Hemoglobins with high oxygen affinity leading to erythrocytosis. New variants and new concepts. Hemoglobin. 2005;29(2):91-106.
13. Cao A, Kan YW. The prevention of thalassemia. Cold Spring Harbor perspectives in medicine. 2013;3(2):a011775.
14. Weatherall DJ, Clegg JB. Inherited haemoglobin disorders: an increasing global health problem. Bulletin of the World Health Organization. 2001;79(8):704-12.
15. Soree P, Gupta RK, Singh K, Desiraju K, Agrawal A, Vats P, et al. Raised HIF1alpha during normoxia in high altitude pulmonary edema susceptible non-mountaineers. Scientific reports. 2016;6:26468.
16. Gupta M, Thalquotra M, Rao P. P3 Fraction: Effect on HbA1c Values by HPLC. Journal of clinical and diagnostic research : JCDR. 2016;10(9):BC12-BC4.
|






 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License