IJCRR - 8(12), June, 2016
Pages: 01-05
Date of Publication: 20-Jun-2016
Print Article
Download XML Download PDF
DEPRESSION AMONG OLD AGE IN URBAN SLUMS
Author: Pranay Jadav, Rhythm Panchani
Category: Healthcare
Abstract:Aim: Present study was carried out to assess the prevalence and factors associated with depression among old age living in urban slums. Methodology: A cross sectional community based study was done in field practice area of urban health training center of a Medical Institute. A total of 150 participant of age 60 or more had been interviewed by house to house survey. Depression was measured by Geriatric Depression scale (GDS)-15. Results: Overall prevalence of depression among old age in urban slums was 30.7%. Prevalence among female was 33.82% and among male was 28.04%. Conclusion: Depression among geriatric population was significantly associated with illiteracy, living alone, chronic morbidity and poly-pharmacy.
Keywords: Depression, Old age, Urban slums
Full Text:
INTRODUCTION
Ageing is a natural process which begins with conception and ends with death; this progressive state is associated with physical, social, psychological spheres.1 According to Geriatric literature, those above 60 years of age are considered to be ‘old’ and belonging to the elderly segment of the population.2 As a result of improved medical facilities and awareness there is decline in mortality and increased life expectancy leading to progressive increase in proportion of elderly people.1,3Moreover this vigorous growth in their numbers in the total population in recent years is termed as “graying of the world”.4 The UN defines a country as ‘ageing’ where the population of people over 60 years reaches 7%. Indian population is expected to reach 12.6% in 2025. The Indian aged population is currently the second largest in the world.3 The elderly people are matured and experienced persons of any community. Their experience, wisdom and foresight can be useful for development and progress; they are valuable asset for any nation.5 Geriatric psychiatry has emerged in early part of nineteenth century with the differentiation of senile dementia, atherosclerotic dementia and presenile psychosis. High geriatric population leads to high geriatric psychiatric problems.6 ‘Depression’ is not a specific term for a single diagnostic condition. It mainly consists of Major Depression Disorder (MDD), dysthymia and Minor Depression. This silent disorder can be characterized by loneliness, grief, change in sleeping pattern, alteration in appetite, feeling of hopelessness and sometimes suicidal tendencies. It can occur in any age, but the most vulnerable age group is geriatric population.1 As per the disability adjusted living years(DALYs) rankings, by 2020 unipolar major depression disorder will become the second leading cause of morbidity in forms of global disease burden.3 As the age advances, there is a progressive decline in the normal functioning of the body; which leads to several deteriorating conditions like impaired vision and hearing ability, poor mobility, loss of control over several functions and cognitive impairment. This is making their lives miserable apart from those diseases affecting the other systems of the body. Eventually this leads to chronic states like ischemic heart disease, diabetes mellitus, hypertension and cancer and if person in this stage does not get enough care and attention, he/she would be mentally broken.3
There is a misconception regarding depression that it is due to aging and so it cannot be treated. But, if it is left untreated it can lead to clinical and social implications in old age. Although treatment of depression is as effective for older patients as for younger adults, the condition is often under-recognized and under-treated. According to WHO data, proportionately more geriatric people commit suicide than any other age groups, and most have major depression. Older people who attempt suicide are more likely to die than younger people, while in those who survive, prognosis is worse for older adults.7 Hence depression is an important health challenge especially in developing countries. However in most of the countries the allocation of total health expenditures to mental health budgets is shockingly less than 1%. In a country like India with second largest aged population in the world, this matter is of great concern.8 The magnitudes of depression varies in different studies from 10% to 55%.6,9 Community based studies in India have found a prevalence of depression from 6% to 50%.10,11 From a national public health point of view it is utterly important to document the distribution and characteristics of the depressive symptomology in the older populations in Gujarat2 . There is a paucity of studies regarding geriatric depression here. So, this study will further explore the magnitude and factors affecting depression in old age. It has been observed that age, gender and illiteracy were significantly associated with the cognitive impairment while only age and illiteracy were significantly associated with depression. Cognitive impairment and Depression both were also significantly associated with each other. But they have found no significant association between co factors affecting this disorder. Death of a spouse renders them vulnerable to mental stress. Indeed, widowhood has been found to be strongly associated with depression in several instances. The absence of a caregiver was deduced to be a possible risk factor for depression. However, we did not find any significant association with depression in our study. One possible reason for this finding could be that we did not ask the number of caregivers or who the caregiver was. There was a higher rate of depression in literates, mainly because of a higher life expectancy amongst them. There were no significant differences which could be attributed to gender.12-13 Since, the Indian version of WHO (five) Well-being Index (1998 version) showed a good Internal and external validity and reliability for identifying depressive disorders in elderly population, this could be considered a useful instrument for identifying elderly subjects with depression in Indian community. Studies have shown that the validity of self-reported depression questionnaires may be influenced by somatic symptoms such as chronic pain. The purpose of this study was to compare the validity of two self-reported questionnaires, the Taiwanese Depression Questionnaire (TDQ) and the Beck Depression Inventory (BDI), for screening depression in patients with chronic pain. Thus, results suggest that the TDQ is superior to the BDI in detecting depression in patients with chronic pain in Taiwan.14-15 Present study was carried out to assess the prevalence and factors associated with depression in Geriatric population (≥60 years) living in urban slums.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Study setting: The study was done in the field practice slum area of urban health training center. As per census 2011 there were 7047 households in the slum areas including 19.92% of total population in Gandhinagar Municipal Corporation. Out of which 627 households were covered by urban health training center of GMERS Medical College, Gandhinagar Study type: Cross sectional Study participants: Geriatric people -person having age ≥60 years. Exclusion criteria: Persons who were Comatose, with preexisting mental or psychiatric illness, who could not hear and/or speak and Non-cooperative were excluded from the study. Sample size and Sampling technique:A sample size of 150 was obtained using the hypothesis testing method and based on following assumptions: 95% confidence intervals, 39.04% prevalence of depression in geriatric population from previous study in Surat city of Gujarat state13 and 10% margin of error. The calculated minimum sample was inflated by 10% to account for anticipated subject non response. Geriatric participants were acquired purposively by house to house survey in the field practice slum area of urban health training center. Measurement tools: There was a face to face interview in form of pre designed structured questionnaires. Questionnaire comprised of two parts: First part was of socio-demographic questionnaire and second part was of Geriatric Depression Scale- short Form (GDS-15). Socio-demographic details included information regarding name, age, gender, marital status, education, occupation, monthly total family income, family type, self-reported comorbidities etc. For the assessment of the Depression, Geriatric Depression Scale-15 (GDS-15), prepared by Sheikh et al., (1986)16 was used. It is easy to administer and needed no prior psychiatric knowledge. Hindi version2 and Guajarati version12 were also applied successfully in previous studies. Total score is 15. Cut-off score for GDS-15 is 5. Score > 5 was suggestive of Depression. Score of 5 to 8 suggested mild depression, 9 to 11 suggested moderate depression and 12 to 15 was considered as severe depression Data collection: After approval from Institutional Ethical Committee, data collection was carried out. House to house survey was done to find the study participants. After acquiring the study participants, the details regarding the study viz. purpose of the study, method of the study were explained in the vernacular language to each subject and head of the family. Participant’s information sheet was provided to each and every participants. Written consent was taken from the each subject with assuring that their name will not be disclosed other than the persons concern with the study. As far as possible privacy was maintained while conducting interview. Questionnaire was filled by personal interview. Questionnaire consistedof two parts. First part contained socio demographic details Second part of questionnaires had Gujarati translation of Geriatric depression Score- short form (GDS15). Study variables: Age, gender, marital status, occupation, education, source of income, involvement in recreational and spiritual activities, intake of alcohol, smoking habits, other existing morbidities, poly-pharmacy were predictor variables. Outcome variable was in form of geriatric Depression Score. A score > 5 was considered as depression. Score of 5 to 8 suggested mild depression, 9 to 11 suggested moderate depression and 12 to 15 was considered as severe depression Statistical methods: Data were entered in Microsoft excel 2007 and they were analyzed through Epi info 7. For continuous variables range, mean and standard deviation were calculated and for categorical variables proportion and percentage were obtained. To know the association between dependent and independent variable chi-square or z-test was applied accordingly. Odds ration with 95 % confidence interval was calculated. A value of p less than 0.05 was considered as statistically significant.
RESULTS
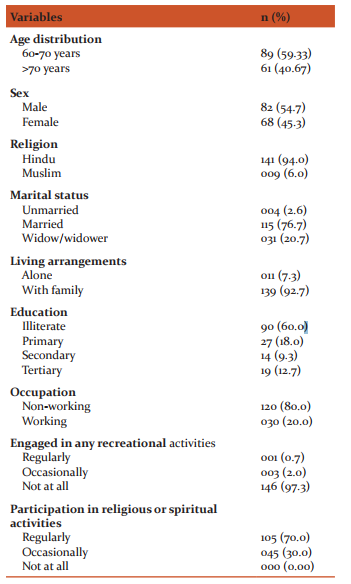
Table 1 shows that majority of the participants (59.33%) belonged to age group of the 60-70 years. Proportion of male subjects is higher (54.7%) in the old age group. Most of the subjects (94.00%) belonged to Hindu religion. Out of the total respondents 76.6% were married and 20.7% were widow/ widower. Those subjects living alone constituted 7.3% and rest 92.7% lived with their families. Overall 60% subjects were illiterate and 40% subjects were literate. Higher education was quite low in both male and female (12.7%). Moreover 80% of the subjects were not working (either retired or unemployed).Around 97 % study participants were not engaged in any form of recreational activities. It can be inferred that they ledan inactive lifestyle but 70% of subjects had a regular participation in religious and spiritual activities. (Table 1)

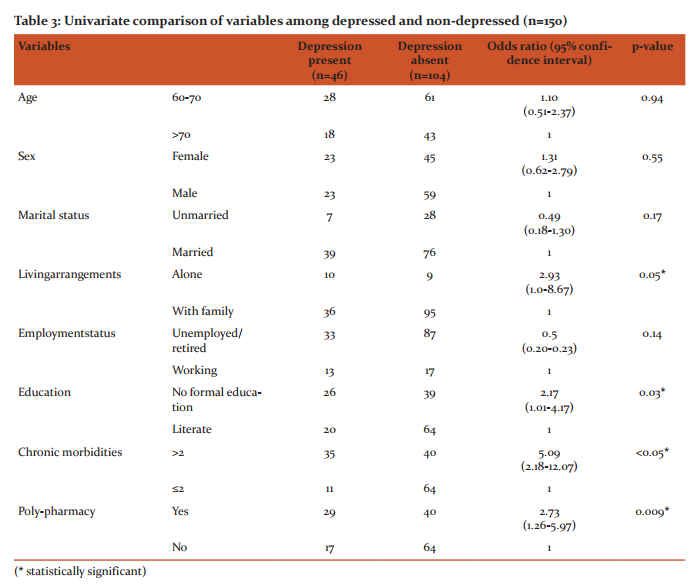
Overall prevalence of depression among the old age group is 30.7% with mean score 7.43 and standard deviation 3.08. Old age females had prevalence of 33.82% as compared to old age males having 28.04%. (Table-2) Table 3 shows univariate analysis of the factors associated with depression among the elderly participants. The association between depression and age, gender and marital status was not statistically significant. Depression was significantly higher among participants who were living alone compared to those who were living with their wives and/or children (OR=2.93, CI=1.0-8.67).Participants with no formal education were significantly more depressed as compare to literate (OR=2.17, CI=1.01-4.17).Elderly participants having more than two chronic morbidities were more depressed and association was also statistically significant (OR=5.09, CI=2.18-12.07). There was also statistically significant association between depression and poly-pharmacy OR=2.73, CI=1.26-5.97).
DISCUSSION
Present study was carried out in the urban slums of Gandhinagar city of Gujarat state. In present study prevalence of depression was 30.7% among people aged more than 60 years of age. A study done in the Surat city11 of same state showed similar prevalence of depression of 39.04% in old age which is comparable for the same region. A community based study done in Vellore-south India17 (Raj Kumar AP et al 2009) had shown prevalence of depression among elderly was 12.7%. Which is lower than the present study. Jain RK et al18 found prevalence of depression among old age was 45.9% which was assessed by geriatric depression scale which was higher than the present study. We have included participants only from urban slums. Another reason in differences in the prevalence may be due to use of different screening tools used to detect depression. In present study females had more depression as compared to males (Table 2). But the association with gender and de-pression was not statistically significant (Table-3). Findings are comparable with a previous study done by Begda A et al12 in a Vadodara city of Gujarat state showed that females had more depression than males. Other studies done in the different regions also showed higher prevalence of depression among females as compared to males.2, 19 Present study shows significant depression among the participants who were living alone (Table 3). This finding is comparable with the previous study done in Malasiya.1 In our study literacy was significantly associated with depression (Table 3). Due to illiteracy, there is unavailability of good jobs which leads to unproductive and frustrated life may lead to depression. Studies done by Ganguly et al and Jain RK et al showed similar results.2, 18. Our study proves significant relationship between chronic illness and depression (Table 3). Also, there was a significant association between poly-pharmacy and depression (Table 3). Hypertension, diabetes, age related morbidities like osteoarthritis, cataract, dental problems and may other diseases are quite common among geriatric age group. People among slums are also economically poor and some of chronic diseases require round the clock medications which they can hardly afford. So, they are physically, mentally as well as economically frustrated and this may be the reason of the depression. Other studies done by Pennix et al, Dorsey SM et al, and Tellez-Zenteno et al had also proved this fact.19, 20, 21
CONCLUSION
Prevalence of depression among geriatric age group in urban slum area was 30.7%. Prevalence among female was 33.82% and among male was 28.04%. Depression among geriatric population was significantly associated with illiteracy, living alone, chronic morbidity and poly-pharmacy. Funding: Presenting study was carried out as a short term student scholarship which was funded and supported by Indian Council of Medical Research (ICMR) Conflict of interest: None
ACKNOWLEDGEMENT
We are thankful to all study participants for their full cooperation during the study
References:
1. Sherina MS, Rampal L, Mustaqim A. The Prevalence of Depression among the Elderly in Sepang, Selangor. Med J Malaysia 2004; 59(1):45-49.
2. Ganguli M, Dube S, Johnston JM, Pandav R, Chandra V, Dodge HH. Depressive symptoms, cognitive impairment and functional impairment in a rural elderly population in India: a Hindi version of the geriatric depression scale (GDS-H).Int J Geriatr Psychiatry1999; 14(10):807-20.
3. Dasgupta A, Ray D, Roy S, Sarkar T, Ghosal A, Das A, Pal J. Depression among the Geriatric Population is a Matter of Concern: A Community Based Study in a Rural Area of West Bengal. Nepal Journal of Epidemiology 2013; 3(4): 282-287.
4. Seby K, Chaudhari S, Chakraborty R. Prevalence of Psychiatric and physical morbidity in an urban geriatric population. Indian Journal of psychiatry 2011; 53(2):121-27.
5. Singh C, Mathur JS, Mishra VN, Singh JB, Garg BS, Kumar A. IJCM 1995; 20(1-4):24-27
6. Tipple P, Sharma SN, Shrivastave AS. Psychiatric morbidity in geriatric people. Indian j Psychiatry 2006;48:88-94
7. Manthorpe J, Iliffe S. Suicide in later life: public health and practitioner perspectives. Int J Geriatr Psychiatry2010; 25:1230- 8.
8. Shah A, Herbert R, Lewis S, Mahendran R, Platt J, Bhattacharyya B. Screening for depression among acutely ill geriatric in patients with a short geriatric depression scale.Age and Ageing1997;26:217-221
9. Chou K L, Chi I. Prevalence and correlates of depression in Chinese oldest-old. International Journal of Geriatric Psychiatry 2005:41–50.
10. Khattri JB, Nepal MK. Study of depression among geriatric population in Nepal. Nepal Med Coll J 2006;8(4):220-3
11. Jariwala V, Bansal RK, Patel S, Tamakuwala B.A study of depression among aged in Surat city. National Journal of Community Medicine 2010; 1(1):47-49
12. Begda A, Kantharia SL. Screening of Cognitive Impairment and Depression in Elderly Patients.Indian Journal of Gerontology 2006;20( 4): 347-58
13. Vishal J, Bansal RK, Patel S, Tamakuwala B.A study of depression among aged in surat city. National Journal of Community Medicine 2010; 1(1):47-49.
14. Barua, A, Kar, N. Screening for depression in elderly Indian population. Indian journal of psychiatry 2010;52(2):150-53
15. Lee, Y, Lin, P. Y, Hsu, S. T, Cing-Chi, Y, Yang, L. C, Wen, J. K. Comparing the use of the Taiwanese Depression Questionnaire and Beck Depression Inventory for screening depression in patients with chronic pain. Chang Gung Med J 2008; 31(4):369- 377.
16. Sheikh JI, Yesavage JA. Geriatric Depression Scale (GDS) - Recent evidence and development of a shorter version. Clinical Gerontologis 1986; 5: 165-173.
17. Rajkumar AP, Thangadurai P, Senthilkumar P, Gayathri K, Prince M, Jacob KS. Nature, prevalence and factors associated with depression among the elderly in a rural south Indian community. International Psychogeriatric 2009; 21:2, 372–378
18. Jain RK, Aras RY. Depression in geriatric population in urban slums of Mumbai. Indian J Public Health. 2007; 51(2):112-3.
19. Pennix BWJH, Geerlings SW, Deeg DJH, van et al. Minor and Major Depression and The Risk of Death in older Persons. Arch Gen Psychiat 1999; 56:889-895
20. Dorsey SM, Rodriguez HD, Brathwaite D. Are things really so different? A research finding of satisfaction, illness and depression in rural South African elderly. ABNF J 2002; 13: 41-4.
21. Tellez-Zenteno JF, Cardiel MH. Risk factors and associated with depression in patients with type 2 diabetis mellitus. Arch. Med. Res.2002; 33: 53-60.
|






 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License