IJCRR - 9(18), September, 2017
Pages: 14-17
Print Article
Download XML Download PDF
Prevalence of Inducible Clindamycin Resistance of Staphylococcus aureus in Hospitalized Patients in Tertiary Care Hospital
Author: Smita S. Damke, Shahin Vishani, Ramesh P. Fule
Category: Healthcare
Abstract:Background: Methicillin resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) has emerged as one of the most common pathogen isolated from patients with very few drugs available for their treatment. Clindamycin is a good alternative optional drug for the treatment of these infections. In vitro routine testing may fail to detect such resistance. Thus it is important to detect such resistance by simple D test.
Material and Methods: 300 staphylococcal isolates where isolated from clinical samples by conventional microbiological methods. Of these 208(69.33%) were identified as Staphylococcus aureus. Methicillin resistance and inducible clindamycin resistance was detected by cefoxitin disk diffusion method and D test as per CLSI guidelines respectively.
Results: 135 (64.9%) were MRSA and 73 (35.09%) were Methicillin sensitive Staphylococcus aureus (MSSA), 45(21.63%) isolates showed inducible clindamycin resistance, 19(9.1%) showed constitutive clindamycin resistance, 112(53.84%) showed MS phenotype whereas 32(15.38%) were erythromycin sensitive. Inducible clindamycin resistance and constitutive clindamycin resistance was higher in MRSA than in MSSA (25.92%, 11.11% and 13.69%, 5.47% respectively).
Conclusion: D test should be done as routine test in all Microbiology laboratory for detection of true resistance of clindamycin among staphylococcal isolates.
Keywords: MRSA, Inducible clindamycin resistance, D test
Full Text:
Introduction
Staphylococcus aureus infections are a major cause of morbidity and mortality worldwide. The increasing prevalence of Methicillin resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) infections especially with the spread of resistant strain in the community (1,2) pose a challenge to physician in terms of the use of alternative antibiotic agents. Although clindamycin has been considered an acceptable option for patients with community acquired MRSA infections, reports on high rates of clindamycin resistant community-acquired MRSA strains are limiting its use(2).
Antimicrobial resistance in S. aureus has become an ever increasing problem among hospitalized patients, persons in long term care facilities and ambulatory outpatients. This has led to the renewed interest in the use of macrolide-licosamide streptogramin B (MLSB) to treat S. aureus infection with clindamycin being preferred agent due to its excellent pharmacokinetic properties (3). Clindamycin is frequently used to treat skin and bone infection because of its tolerability, cost, oral forms and excellent tissue penetration and the fact that it accumulates in abscesses and no renal dosing adjustment are needed(4). Good oral absorption makes it an important option in outpatient therapy as follow-up after intravenous therapy. Clindamycin is good alternative for the treatment of both methicillin resistant and susceptible staphylococcal infections (5).
However wide spread use of MLSB antibiotics has led to an increase in number of Staphylococcal strain acquiring resistance to MLSB antibiotics (6). The most common mechanism of such resistance is target site modification mediated by erm genes which can be expressed either constitutively (constitutive MLSB phenotype) or inducibly (inducible MLSBphenotype). Strains with inducible resistance to clindamycin are difficult to detect in routine laboratory as they appear erythromycin resistance and clindamycin sensitive in vitro when not placed adjacent to each other. In such cases, in vivo therapy with clindamycin may select constitutive erm mutants leading to clinical therapeutic failure.
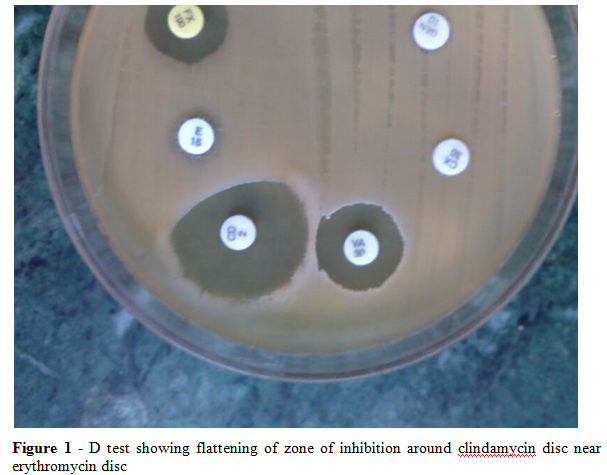
In vitro, staphylococcus aureus isolates with constitutive resistance are resistant to both erythromycin and clindamycin whereas those with inducible resistance are resistant to erythromycin but appears to be sensitive to clindamycin (iMLSB). These isolates, when used along with clindamycin, erm mutants for constitutive resistance emerge, which leads to failure in treatment(7). This resistance goes undetected by Kirby Bauer method however, it is detected by simple D test. The result is observed as a flattening zone in the area between erythromycin and clindamycin disc, in a shape of 'D' which indicates inducible clindamycin resistance.
Thus the present study was carried out to find the prevalence of inducible clindamycin resistance of S. aureus by very simple method of detecting inducible clindamycin resistance in hospitalized patients by performing D test.
Material and methods
This study was a prospective study over a period of six months from July 2014 to December 2014 in the department of Microbiology attached to the tertiary care hospital in central India. After obtaining ethical clearance a total of 300 isolate of staphylococcus from various clinical specimen like pus, wound swabs, sputum, throat swabs, suction tips, aspirates, blood and urine were tested. Isolates were identified upto species level by conventional methods such as Gram stain, growth on mannitol salt agar, slide and tube coagulase test, DNAse test and by biochemical tests (8).
The isolates were subjected to susceptibility testing by Kirby bauer disc diffusion method on Mullier Hinton agar plate using erythromycin (15ug), clindamycin (2ug), linozolide (30ug), rifampicin (5ug), cotrimaxazole (30ug), ciprofloxacin (5ug), gentamycin (30ug), tetracycline (30ug), penicillin (10ug), nitrofurantoin (10ug) and norfloxacin (300ug)(for urinary isolates only). The results were interpreted as per CLSI guidelines. Methicillin resistance was detected by cefoxitin disc diffusion method.
To detect inducible clindamycin resistant, 15 ug erythromycin and 2ug clindamycin discs were placed on Mullier Hinton plate that had been inoculated with staphylococcal isolates. The disc were placed at a distance of 15 -20 mm edge to edge from each other. Plates were incubated overnight at 37o C. A positive D test was taken as flattening of the zone of inhibition around clindamycin disc proximal to erythromycin disc (D shaped zone of inhibition) and was defined as inducible MLSB resistance (Figure 1). Strains that were resistant to both erythromycin and clindamycin were defined as exhibiting constitutive MSLB resistant and those that were resistant to erythromycin and sensitive to clindamycin were MS phenotype.
Results
In the present prospective study, a total of 300 isolates of Staphylococcus were studied. Among these 208 (69.33%) were found to be coagulase positive Staphylococcus aureus and 92 (30.66%) were coagulase negative staphylococcus. Of 208 staphylococcus aureus isolates, 135(64.9%) were methicillin resistance staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) while 73 (35.09%) were methicillin sensitive staphylococcus aureus (MSSA).
In the present study, inducible clindamycin resistance i.e. positive D test in MRSA was found to be in 35(25.92%) isolates and 10 (13.69%) isolate showed D test positive in MSSA. Strains showing resistance to both clindamycin and erythromycin i.e. exhibiting constitutive MSLB (cMLSB) resistance were found to be 15 (11.11%) in MRSA isolates and 4 (5.47%) in MSSA. Isolates showing resistance to erythromycin and sensitivity to clindamycin, termed as MS phenotypes was found to be 70 (51.85%) in MRSA and 42 (57.83%) in MSSA(Table 1) (Figure1).Thus in the present study, higher incidence of resistance was found to be in methicillin resistance staphylococcus aureus whereas higher incidence of sensitivity was found in methicillin sensitive staphylococcus aureus.
Discussion
There is a growing concern about the rapid rise in resistance of S. aureus to antimicrobial agents (9). In India, the importance of MRSA as a problem has been recognized relatively late (10). The prevalence of MRSA varies in different parts of India and is not uniform. This variation in prevalence may be because of several factors like study design, population and geographical distribution, differential clonal expression, drug pressure in community, health care facilities available in the hospital, implementation and monitoring of infection control committee, rationale antibiotic usage which varies from hospital to hospital. MRSA is a major cause of nosocomial infection worldwide. Serious endemic and epidemic MRSA infections occur globally as infected and colonised patients in the health care settings are the reservoirs.
Emergence of MRSA has left us with very little therapeutic options to treat staphylococcal infections. In the present study, a total of 300 staphylococcal isolate, the prevalence of S. aureus was found to be 208 (69.33%) isolates were coagulase positive and out of this 135(64.9%) were MRSA and 73(35.09%) were MSSA. Similar results were found by Borge et al (11) and Dar et al(12) having the prevalence rate of MRSA as 65% and 54.85% respectively.
The determination of antimicrobial susceptibility of a clinical isolate is often crucial for optimal antimicrobial therapy of infected patients. This is particularly important considering the increase of resistance and the emergence of multidrug resistant organisms. There are only few options available for treatment of MSSA and MRSA infections, with clindamycin being one of the good alternatives(5). However, clindamycin resistance can develop in staphylococcal isolates with inducible phenotype, and from such isolates, spontaneous constitutively resistant mutants have arisen both in vitro testing and in vivo during clindamycin therapy(13).
In the present study, of the total coagulase positive staphylococcal isolates inducible clindamycin resistance was found to be 45 (21.63%), of this 35 (25.92%) were from MRSA and 10(13.69%) from MSSA. The study report by Dardichandran Kaur(14), Gadepalliet(6), Pal et al(15) and Lt. Col. Mahima Lall(16) showed prevalence of inducible clindamycin resistance as 21.12%, 21%, 24.63% and 20.3% respectively. The study by Deotale et al(3)reported 27.6% iMLSB in MRSA, whereas Yilmaz et al(13) found inducible resistance of 24.4%in MRSA and 14.8% in MSSA; Gadepalli et al(6) showed it to be 30% in MRSA and 10% in MSSA, while Mohamed Rahabar et al(17) reported 22.6% in MRSA and 4% in MSSA. In another study Schreckenberger et al(18) and Levin et al(19) showed higher percentage of inducible resistance in MSSA as compared to MRSA, 7-12% in MRSA and 19-20% in MSSA; 12.5% MRSA and 68% MSSA respectively.
In our study, constitutive resistance was observed to be 19(9.1%) isolates, in which 15 (11.11%) from MRSA and 4 (5.47%) from MSSA. Other studies reporting constitutive MLSB differ in their prevalence as Sireesha et al(20) reported 10% and Deotale et al (3) reported 3.6%. Results near about similar to our study were observed in the studies by Gurdale Yilmaz et al(13) showed 14.8%; Ciraj et al (21)15.3% and Sireeshaet al (20) 18%.
Prabhu K et al (22) observed that percentage of inducible resistance and constitutive resistance were higher in MRSA as compared to MSSA which is in concordance with our present study.
Conclusion
The true sensitivity to clindamycin can only be judge after performing the D test on erythromycin resistant isolates. The use of D test in routine laboratory will help us in advising the clinicians regarding the use of clindamycin in superficial skin and soft tissue infections, as clindamycin should not be used for clindamycin induced resistant staphylococcus i.e. D test positive while it can be the drug of choice in case of D test negative isolates. Thus microbiological laboratories should report Saureus isolates exhibiting inducible MLSB as clindamycin resistant.
Acknowledgment: Authors acknowledge the immense help received from the scholars whose articles are cited and included in references of this manuscript. The authors are also grateful to authors / editors / publishers of all those articles, journals and books from where the literature for this article has been reviewed and discussed.
Source of Funding / Support: Nil
Conflict of Interest: Nil
Table 1: Distribution of resistance pattern of S. aureus
|
|
iMLSB
|
cMLSB
|
MS phenotype
|
Erythromycin sensitive
|
|
MRSA (n=135)
|
35(25.92%)
|
15 (11.11%)
|
70 (51.85%)
|
15(11.11%)
|
|
MSSA(n= 73)
|
10 (13.69%)
|
4 (5.47%)
|
42 (57.83%)
|
17(23.28%)
|
|
Total (n=208)
|
45(21.63%)
|
19(9.1%)
|
112(53.84%)
|
32(15.38%)
|
(MRSA-methicillin resistant staphylococcus aureus; MSSA- methicillin sensitive staphylococcus aureus; iMLSB- inducible macrolide-licosamide streptogramin B; cMLSB - constitutive macrolide-licosamide streptogramin B)
References:
- Gorak EJ, Yamada SM, Brown JD. Community-acquired methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in hospitalized adults and children without known risk factors. Clin Infect Dis 1999; 29: 797-800.
- Daum RS. Clinical practice. Skin and soft-tissue infections caused by methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. N Engl J Med 2007; 357: 380-90.
- Deotale V, Mendiratta DK, Raut U, Narang P (2010) Inducible clindamycin resistance in Staphylococcus aureus isolated from clinical samples. Indian J Med Microbiol 28:124-126
- Kasten MJ (1999) Clindamycin, metronidazole, and chloramphenicol. Mayo Clin Proc 74:825-833
- Fiebelkorn KR, Crawford SA, McElmeel ML, Jorgensen JH. Practical disc diffusion method for detection of inducible clindamycin resistance in Staphylococcus aureus and coagulase negative Staphylococci. J Clin Microbiol 2003;41:4740-4.
- Gadepalli R, Dhawan B, Mohanty S, Kapil A, Das BK,Chaudhry R. Inducible clindamycin resistance in clinical isolates of Staphylococcus aureus. Indian J Med Res 2006;123:571-3.
- Mukesh Patel, Ken B. Waites, Stephen A. Moser, Gretchen A. Cloud and Craig J. Hoesley, 2006. Prevalence of Inducible Clindamycin Resistance among Community- and Hospital- Associated Staphylococcus aureus isolates: J Clin Microbiol.44( 7), 2481-2484.
- Kloos WE, Banerman TL. Staphylococcus and Micrococcus, Chapter 22. In: Manual of clinical microbiology. 7th ed. Murray PR, Baron EJ, Pfaller MA, Tenover FC, Yolken RH, editors. Washington DC: ASM Press; 1999. p. 264-82.
- Mulla S, Patel M, Shah L, Vaghela G. Study of antibiotic sensitivity pattern of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Indian J Critical Care Medicine. 2007;11(2):99-101.
- Rajaduraipandi K, Mani KR, Panneerselvam K, M, Bhaskar M, Manikandan P. Prevalence and antimicrobial susceptibility pattern of methicillin resistant Staphylococcus aureus: a multicentre study. Indian J Med Microbiol 2006;24:34-8.
- Borg M, Scicluna E, De Kraker M, Van de Sande-Bruinsma N, Tiemersma E, Gur D et al (2006) Antibiotic resistance in the southeastern Mediterrenean-preliminary results from the AR medical project. European surveillance 11(7):639
- Dar JA, Thoker MA, Khan JA, Ali A, Khan MA, Rizwan M et al (2006) Molecular epidemiology of clinical and carrier strains of methicillin resistant Staphylococcus aureus in the hospital settings of north India. Ann Clin Microbiol Antimicrobial 5(1):22
- Yilmaz G, Aydin K, Iskender S, Caylan R, Koksal I. Detection and prevalence of inducible clindamycin resistance in staphylococci. J Med Microbiol 2007;56:342-5.
- Dardi CK, Khare AS. Inducible clindamycin resistance in staphylococcus aureus in a tertiary care rural hospital. I Jou
- Pal N, Sharma B, Sharma R, Vyas L. Detection of inducible clindamycin resistance among Staphylococcal isolates from different clinical specimens in western India. J Postgrad Med 2010;56:182-5.
- Lt Col Mahima L, Brig Sahni AK. Prevalence of inducible clindamycin resistance in staphylococcus aureus isolated from clinical samples. Med J Armed forces India 2014;70:43
- Rahabar M, Hajia M. Inducible clindamycin resistance in Staphylococcus aureus: A cross sectional report. Pak J Biol Sci 2007;10:189-92.
- Schreckenberger PC, Ilendo E, Ristow KL. Incidence of constitutive and inducible clindamycin resistance in Staphylococcus aureus and coagulase-negative staphylococci in a community and a tertiary care hospital. J Clin Microbiol 2004;42:2777-9.
- Levin TP, Suh B, Axelrod P, Truant AL, Fekete T. Potential clindamycin Resistance in clindamycin-susceptible, erythromycin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus: Report of a clinical failure. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 2005;49:1222-4.
- Sireesha P, Setty CR. Detection of various types of resistance patterns and their correlation with minimal inhibitory concentrations against clindamycin among methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus isolates. Indian J Med Microbiol 2012;30:165-9.
- Ciraj AM, Vinod P, Sreejith G, Rajani K. Inducible clindamycin resistance among clinical isolates of staphylococci. Indian J Pathol Microbiol 2009;52:49-5.
- Prabhu K, Rao S, Rao V. Inducible clindamycin resistance in Staphylococcus aureus isolated from clinical samples. J Lab Physicians 2011;3:25-7.







 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License