IJCRR - 9(16), August, 2017
Pages: 43-48
Print Article
Download XML Download PDF
Chlorpyrifos Impairs the Contraction of Uterine Smooth Muscle by Inhibiting the Secretion of Estradiol from Ovary in Rat
Author: Kamalesh Das, Kaushik Sarkar, Partha Pratim Nath, Mukti Mondal, Goutam Paul
Category: Healthcare
Abstract:Objectives: Chlorpyrifos (CPF) has been used heedlessly in India to protect crop plants from pest induced crop loss. The objective of the study was to examine the effect of CPF, a broad spectrum organophosphate pesticide, on the contraction of uterine smooth muscle in rat model.
Methodology: Two graded doses of CPF were administered orally at a dose of 5.4 mg/kg.BW /d and 8.1mg/kg.BW /d to female Charles foster rats for 30 days. The record of the movement of the uterus was obtained with isotonic transducer coupled to RMS Polyrite D. The serum levels of estradiol and progesterone were measured as per standard protocols of kits of ERBA Diagnostic Gmbh Mannheim Germany.
Results: We have observed a significant inhibition of the force and increase in frequency of the contraction of uterus in all phases of an estrous cycle dose dependently in CPF exposed groups of rats compared to control groups of rats. We have also observed significant decrease in the level of estradiol in a dose dependent manner in all test groups of rats. These results indicate that CPF impairs the contraction of the uterine smooth muscle probably by inhibiting the secretion of estradiol from ovarian follicles. Further, the oxytocin induced potentiation of the tonic tension of uterus was significantly counteracted by CPF. This result proves that CPF probably impairs the contraction of uterine smooth muscle by inhibiting the estradiol.
Conclusion: In conclusion, CPF impairs the contraction of uterine smooth muscles by inhibiting the secretion of estradiol from ovary in rat.
Keywords: Ovarian follicle, Tonic tension of uterus, Estrous cycle, Oxytocin
DOI: 10.7324/IJCRR.2017.9168
Full Text:
Introduction
In modern agriculture, agrochemicals like organophosphorous pesticide plays an important role in increasing the food grain production (Gulati, 2015). Chlorpyrifos (CPF) is a group of organophosphorous pesticide widely used in agricultural fields, food processing plants, residential pest control, paint industry and veterinary practice (Gulati, 2015). CPF has been detected considerable amount in fruits, vegetables, grains, dairy products, meat, fishes, soft drinks and also detected in cervical fluid, cord blood, breast milk and meconium (Angioni, 2011; Feei, 2008; Mathur;2003, Bedi, 2013 and Ostrea, 2006). The sources of human exposure to CPF are the food intake, inhalation and skin penetration during occupational use (Reigart, 2013). Within the human body, CPF is converted into chlorpyrifos oxon (CPO) in liver by cytochrome P450 mediated desulfuration and subsequently hydrolyzed to diethyl phosphate and 3, 5, 6- trichloro -2-pyridinol (TCPY) (Hodgson, 2008). It has been reported that CPF induces oxidative stress, inhibits the activity of AChE, promotes neurotoxicity and degeneration of dopaminergic and cholinergic neurones (Kalender, 2012; Slotkin, 2006; Whitney, 2012; Lee, 2012). CPF also exerts reproductive and developmental neurotoxicity in animals due to its endocrine disrupting function (Birnbaum, 2012; Farag, 2003; Flaskos, 2012). The reproductive effects of CPF in mammalian animals have been reported discretely. It has also been reported that CPF causes disruption of the estrous cycle rhythmicity, impairment of the growth of primordial follicles in the ovary and disruption of the of breast cell cycle through production of reactive oxygen species (oxidative stress) (Kamalesh, 2014; Ventura, 2012). But the effect of CPF on the function of uterus, one of the major female reproductive organ, has not been reported till date. It provides the habitat for implantation and growth of the fetus till maturation. Besides, it helps in the parturition of the fetus through its vigorous contractions. Histologically the wall of the uterus contains three layers from inside to outside; endometrium, myometrium and perimetrium. The myometrium of uterus is composed of visceral smooth muscle cells which are organized in circularly and longitudinally. These visceral smooth muscle cells provide rhythmic contraction of the uterus in the basal state due to their spontaneous rhythmic excitation intrinsically (Khan, 2001). The basal contraction of the uterine smooth muscle cells are regulated by oxytocin released from the posterior pituitary. Estradiol released from the developing follicle of the ovary potentiates and the progesterone released from corpus luteum inhibits the oxytocin induced contraction of uterine smooth muscle (Jackson, 1998; Fanseca, 2003). Several reproductive functions including the transport of sperms and embryo, menstruation, pregnancy and parturition will be impaired if the basal uterine contractions are changed due to alterations in the levels of oxytocin and ovarian estradiol and progesterone. Considering the toxic effects of CPF on the functions of several reproductive organs, we predict that CPF might exert harmful effects on the function of uterine smooth muscle cells. So, the objective of the present study was to examine the probable effects of CPF on the contractions of uterine smooth muscle in rat.
Materials and Methods
Chemicals and reagents
All the reagents used this study were of analytical grade. Sodium chloride (NaCl), Potassium chloride (KCl), Calcium chloride (cacl2), Sodium bicarbonate (NaHCO3), Magnesium chloride (MgCl2), Sodium dihydrogen phosphate (NaH2PO4), and Glucose were procured from E. Merck, India. Chlorpyrifos (CPF) was purchased from Devidayal (sales) Limited, Mumbai, India.
Oxytocin was purchased from E. Merck, India.
Animals
Adult female Charles foster rats aged 16-18 weeks and weighing 120-160gm were selected for the experiment. The animals were matched with age and by body weight across the treatment groups at the start of the experiment. Rats were housed in polypropylene coated plastic cage containing paddy husk bedding. Polypropylene cages contained female Charles foster rats, were kept in the animal house and maintained at an average temperature of 27• ± 1• C with 12:12h light and dark cycle (light on around 8-9 A.M).
Ethical approval
The rats were kept in the Molecular Neurotoxicology laboratory, Department of Physiology, University of Kalyani and were maintained as per recommendation of the animal ethical committee of University of Kalyani in accordance with the national guidelines.
Experimental setup
Animals showing normal and regular estrous cycle (4 to 5 days) for at least three consecutive times were selected for the study. After 10 days of acclimatization, the rats were distributed to three groups. The rats of the first group were received standard laboratory diet and were designated as control group. The rats of the second and third groups were received 5.4mg/BW/d and 8.1 mg/BW/d chlorpyrifos for 30 days duration and were termed as treated groups. After completion of treatment, rats were sacrificed by cervical dislocation and blood was collected for the determination of estradiol and progesterone. For study of uterine movement, rat was sacrificed and abdomen was immediately opened and the uterine segment of 4 cm was removed by transverse incision. Estrous cycle study (Bancroft, 2002) was performed to identify the specific phase on the day of experiment.
Uterine motility study
Devices: Glass jar Bath
A glass water bath of about 750 mL capacity fitted into a metal stand in which a fixed heater was located to maintain the temperature as required. An inner glass tube (Organ bath) of 40 mL capacity passed through the bottom of the stand and was connected by a T-shaped glass tube. Preparation of rat’s uterus
The mature female Charles foster rats at different phases of estrous cycle (i.e. proestrus, estrus, metestrus and diestrus) were used where vaginal lavage was performed for detection of the stages of sex cycle of the animals. Animals after being examined were sacrificed and the uterus was dissected out and luminal content was gently flushed out. Uterine horn was suspended in the organ bath containing warm oxygenated (95% O2 and 5% CO2) physiological salt solution (Nacl 8.0g/l, KCl 0.20g/l, CaCl2 0.2g/l, MgCl2 0.1 g/l, NaHCO3 1.0 g/l, NaH2PO4 0.05 g/l, Glucose 1 g/l, PH 7.4) at 37±0.5•C. One part of each uterine strip was connected with glass hook placed at the bottom of the organ bath and another part was attached to the isotonic transducer using metal thread.
Recording of uterine motility using RMS Polyrite D and Isotonic transducer
The uterine movement was achieved with isotonic transducer (IT-2245) coupled with RMS Polyrite D, Software (RMS, INDIA).
Hormonal study
Levels of serum 17-β estradiol (E2) and progesterone (P4) were estimated by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) methods using kits of ERBA Diagnostic GmbH Mannheim Germany.
Statistical analysis
Uterine activity was characterized by episode of uterine contractions separated by periods of silence. All the data were expressed as mean± SEM of the value of each experimental group. Force of contraction was measured in terms of amplitude, frequency and duration. Statistical comparisons between the values obtained in control and in treated rats were carried out by using a Student’s t test for paired group. The number of the uterine preparation used in each experiment is indicated by the alphabet ‘n’ in the result. P value <0.05 is considered as statistically significant.
Results
Effects of CPF on the basal contraction of uterine smooth muscle
To examine the effect of CPF on the basal contraction of uterine smooth muscle, the effects of CPF on the contraction of uterus ex vivo of CPF exposed groups of rats in proestrus, estrus, metestrus and diestrus phases of an estrous cycle have been studied. In our study, we have observed a significant inhibition of the force and increase in frequency of the contraction of uterus in all phases (i.e. proestrus, estrus, metestrus and diestrus) of an estrous cycle dose dependently in CPF exposed groups of rats compared to control groups of rats (Table 1and Figure 2).
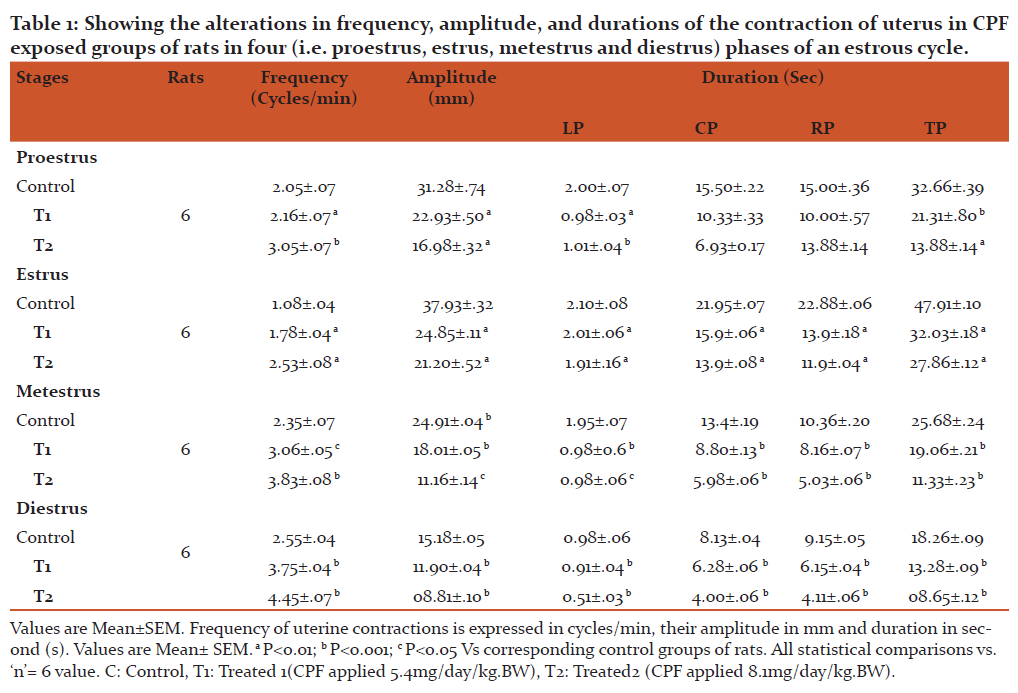
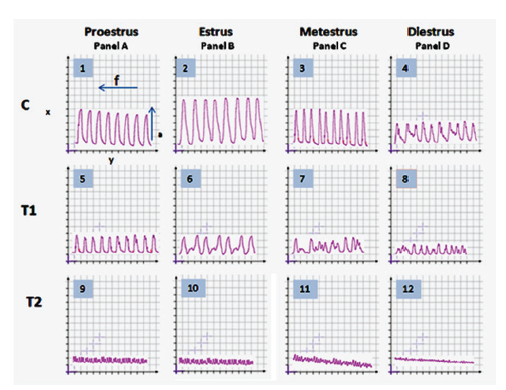
Figure 2: Representative records showing the effects of CPF on the contraction of uterus recorded ex vivo in proestrus[Panel A ( Tracing 1,5,9)], estrus [Panel B (Tracing 2,6,10)], metestrus[Panel C (Tracing 3,7,11)] and diestrus [Panel D (Tracing 4,8,12)], phases of an estrous cycle in CPF exposed groups of rats. C indicates control. T1 indicates the record of the effect of 1st dose of CPF (5.4mg/ /kg.BW/ day) on the contraction of uterus and T2 indicates the record of the effect of 2nd dose of CPF ((8.1mg/ /kg.BW day)) on the contraction of uterus. Small Square in the abscissa (x-axis) indicates 5 mm and Small Square in the ordinate (y-axis) indicate 40 sec.
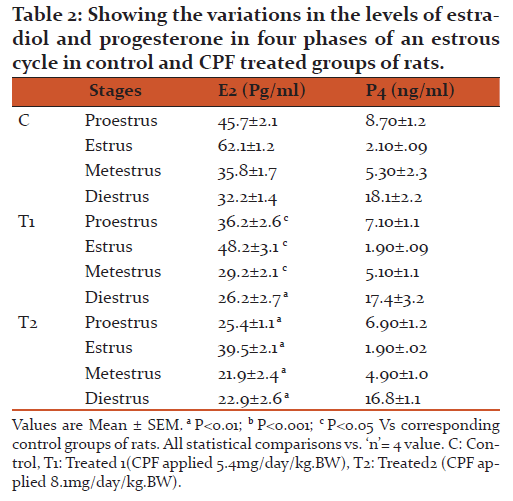
Effects of CPF on the levels of serum estradiol and progesterone in CPF exposed groups of rats.
We have found a significant decrease in the level of estradiol in a dose dependent manner and insignificant decrease in the levels of progesterone in all doses tested in CPF exposed groups of rats (Table 2).
Effect of oxytocin on the contraction of uterine smooth muscle pre incubated with CPF.
The oxytocin induced potentiation of the force and frequency of the contraction of uterus was significantly antagonized when the oxytocin is applied in CPF pre incubated uterus (Figure: 3 and Figure 4).
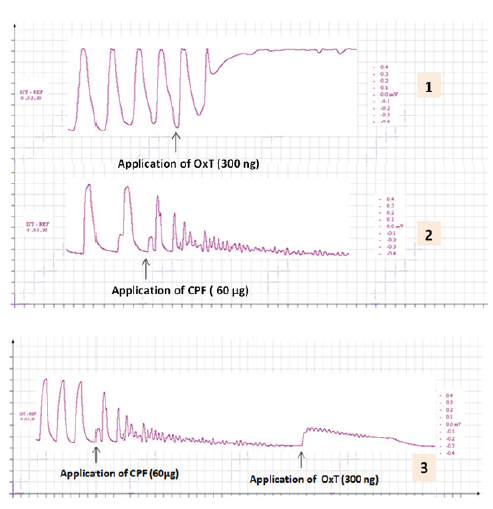
Figure 3: The representative records showing the effect of oxytocin (300 ng) on the contraction of uterus pre incubated with CPF. Tracing1 showing the effect of oxytocin on the contraction of uterus; Tracing 2 showing effect of CPF (60 µg) on contraction of uterus; and Tracing 3 showing the effect of oxytocin (300 ng) on the contraction of CPF pre incubated (60 µg) uterus. Small square in the abscissa (x-axis) indicate 5 mm & Small square in the ordinate (y - axis) indicate 40 sec.
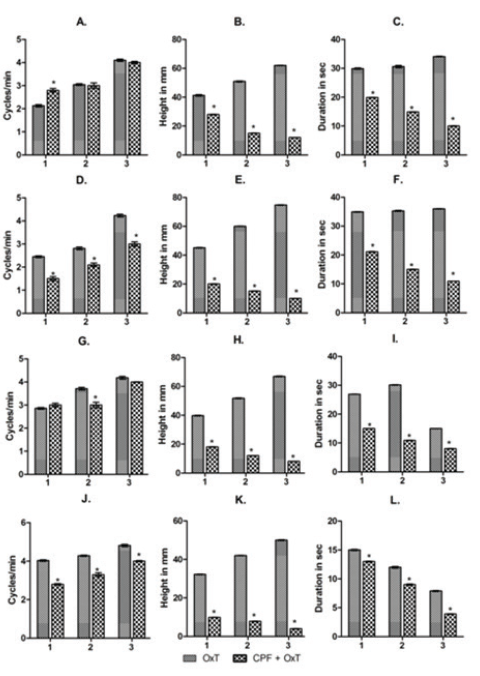
Figure 4: Bardiagrams showing the changes in frequency (A, D, G and J), amplitude (B, E, H and K) and durations (C, F, I and L) of the contraction of uterus ex vivo acute experiment in response to the application of oxytocin in CPF pre incubated uterine preparations. 1,2 and 3 indicates the changes in frequency, amplitude and duration in response to the application of 3 graded dose of Oxytocin (OxT) and chlorpyrifos (CPF) [1: OxT(3 ng) and CPF (20 µg) + OxT (3 ng))], 2: OxT(30 ng) and CPF (40 µg) + OxT (30 ng))], 3: OxT(300 ng) and CPF (60 µg) + OxT (300 ng))]. A-C: Proestrus, D-F: Estrus, G-I: Metestrus and J-L: Diestrus. The values are represented as Mean± SEM. * P<0.001 Vs Control (here oxytocin induced contraction).
Discussion
The uterine smooth muscle cells organized circularly and longitudinally in the myometrium of uterus provide the basal contraction of uterus needed for the several basic female reproductive functions viz. transport of sperm and embryo, implantation of the embryo and parturition of the mature fetus. The above female reproductive functions will be impaired if the pattern or force and frequency of the contractions are changed due to toxicity caused by CPF within the smooth muscle cells. The aim of the study was to examine the effect of CPF on the contraction of uterine smooth muscle in rat. In this study we found a significant inhibition of the force and increase in frequency of the contraction of uterus in all phases (i.e. proestrus, estrus, metestrus and diestrus) of an estrous cycle dose dependently in CPF exposed groups of rats compared to control groups of rats (Figure 2 and Table 1). This result indicates that CPF alters the contraction of the uterine smooth muscle probably by inhibiting the facilitatory action of oxytocin released from posterior pituitary for maintaining basal contraction of uterus during different phases of an estrous cycle. The inhibiting action of CPF on oxytocin might be due to direct inhibitory action of CPF on oxytocin in uterine smooth muscle cells and/or inhibiting the secretion of estradiol from ovary. Because estradiol normally promotes the sensitivity of oxytocin in oxytocin induced promotion of contraction of uterine smooth muscle probably by increasing and/ or promoting the receptor expression of oxytocin and α adrenergic signaling which modulate membrane Ca++ channels (Jackson, 1998; Fanseca, 2003). It has also been reported that progesterone inhibits the oxytocin sensitization in uterine smooth muscle cells. To examine the involvement of estradiol and progesterone in CPF induced inhibition of the contraction of uterine smooth muscle, the serum levels of estradiol and progesterone in CPF exposed groups of rats have been determined. We observed significant decrease in the level of estradiol and insignificant increase in the level of progesterone in a dose dependent manner in all test groups of rats. This result suggests that CPF probably inhibits the contraction of uterine smooth muscle by inhibiting the secretion of estradiol from the ovarian follicular cells. From the results, we hypothesize that CPF inhibits the contraction of uterine smooth muscle probably by decreasing the estradiol sensitivity to the action of oxytocin. In support of our hypothesis, we have examined the effect of oxytocin in different doses on the contraction of uterus ex-vivo in CPF pre incubated uterine preparations. We have observed significant counteraction in the oxytocin induced potentiation of the tonic tension of the uterine muscle in CPF pre incubated uterine preparation in single dose acute experiment (Figure 3 and Figure 4).
This result supports the hypothesis that CPF might inhibit the contraction of uterine smooth muscle probably by decreasing the estradiol sensitivity to oxytocin action. Considering the entire results we may conclude that CPF depresses the female reproductive functions probably by impairing the function of uterus. The CPF induced impairment in the function of uterus might be due to inhibition of the contraction of uterus due to CPF induced inhibition of the secretion estradiol from ovary in rat.
Conclusion
Chlorpyrifos (CPF) impairs the female reproductive functions by depressing the motor function of uterus and endocrine function of ovary. CPF induced depression of the function of uterus might be due to inhibition of the estradiol dependent contraction of uterine smooth muscle. The results obtained in rat model may be extrapolated in human females who have been suffering from infertility due to long term CPF exposure.
Acknowledgement
Financial support of PRG of Professor Goutam Paul, Professor, Department of physiology, University of Kalyani is gratefully acknowledged to carry out this study. Authors acknowledge the immense help received from the scholars whose articles are cited and included in references of this manuscript. The authors are also grateful to authors/editors/ publishers of all those articles, journals and books from where the literature for this article has been reviewed and discussed.
Conflict of interest: None
Source of Funding: PRG from Dr. Goutam Paul, Professor, Department of Physiology, University of Kalyani, Kalyani, West Bengal-741235, India.
References:
-
Angioni A, Dedola F, Garau A, Sarais G, Cabras P, Caboni P. Chlorpyrifos residues levels in fruits and vegetables after field treatment. J Environ Sci Health 2011; 46(6):544-9.
-
Bancroft JD and Gamble M. Theory and practice of histological techniques, Edinburgh Churchill Livingstone Pub. 2002; 5:172-75.
-
Bedi JS, Gill JP, Aulakh RS, Kaur P, Sharma A, Pooni PA. Pesticide residues in human breast milk: risk assessment for infants from Punjab, India. Sci Total Envioron 2013; 463-464:720-6.
-
Birnbaum L. Environmental chemicals: evaluating low-dose effects. Health Perspect. 2012; 120 (4): 143-
-
-
Fanseca Da EB, Bittar RE, Carvalho MH, Zugaib M. Prophylactic administration of progesterone by vaginal suppository to reduce the incidence of spontaneous preterm birth in women at increased risk: A randomized placebo-controlled double-blind study. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2003; 188:419-24.
-
Farag AT, Okazy AM, Aswed AF. Developmental toxicity study of Chlorpyrifos in rats. Reprod Toxicol. 2003; 17(2): 203-8.
-
-
Feei S, Hui-Shan C. Monitoring of pesticide Chlorpyrifos residue in farmed fish: Investigation of possible sources. Chemosphere 2008; 71(10):1866-69.
-
Flaskos J. The developmental neurotoxicity of organophosphorous insecticides: A direct role for the oxon metabolites. Toxicol Lett. 2012; 209 (1):86-3.
-
Gulati K, Thakur S, Jindal T. Chlorpyrifos toxicology and persistence in environment: An Indian perspective. 2015; 2(7): 1-6.
-
Hodgson E, Rose RL. Metabolic interactions of agrochemicals in humans. Pest Mang Sci 2008; 64(6): 617-21.
-
Jackson M, Dudley DJ. Endocrine assay to predict preterm delivery. Clin Perinat. 1998; 4:837-57.
-
Kalender Y, Kaya S, Durak D, Uzun FG, Demir F. Protective effect of catechin and quercetin on antioxidant status, lipid peroxidation and testis histoarchitecture induced by Chlorpyrifos in male rats. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol 2012; 33(2): 141-48.
-
Kamalesh D, Kaushik S, Panchali T, Partha PN and Goutam P. Chlorpyrifos suppresses female reproductive function in rat. Int J Pharm Bio Sci. 2014; 5(1): 810-18.
-
Khan RN, Matharoo-Ball B, Arulkumaron S and Ashford MLJ. Potassium channels in the human myometrium. Exp Physiol. 2001; 86:255-64.
-
Lee JE, Park JH, Shin IC, Koh HC. Reactive Oxygen Species regulated mitochondria-mediated apoptosis in PC 12 cells exposed to Chlorpyrifos. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2012; 263(2):148-62.
-
Mathur HB, Johnson S, Kumar A. Analysis of pesticide residue in soft drinks. Centre for science and environment. 2003 New Delhi. http:www.cscindia.org/content/analysis pesticide residue soft drinks.
-
Ostrea EM Jr., Bielawski DM, Posecion NC Jr. Meconium analysis to detect fetal exposure to neurotoxicants. Arch Dis Child 2006; 91(8):628-29.
-
Reigart JR, Roberts JR, Recognition and Management of pesticide poisonings. Sixth edition, U.S Environment Protection Agency, Washington, DC 20460, 2013; http://www.epa.gov/oppfeady /safety/healthcare/handbook/handbook.htm.
-
Slotkin TA, Levin ED, Seidler FJ. Comparative developmental neurotoxicity of organophosphate insecticides effects on brain development are separable from systematic toxicity. Environ Health Perspect. 2006; 114 (5): 746-51.
-
Ventura C, Nunez M, Miret N, Lamas DM, Randi A, Venturino A, Rivera E, Cocca C. Differential mechanisms of action are involved in Chlorpyrifos effects in estrogen- dependent or independent breast cancer cells exposed to low or high concentration of pesticide. Toxicol Lett. 2012; 213(2): 184-193.
-
Whitney KD, Seidler FJ, Slotkin TA. Developmental neurotoxicity of Chlorpyrifos: Cellular mechanism. Toxicol Appl Phamacol. 2012; 134 (10):53-62.
|






 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License