IJCRR - 8(13), July, 2016
Pages: 12-16
Print Article
Download XML Download PDF
ITEM ANALYSIS OF MCQS - MYTHS AND REALITIES WHEN APPLYING THEM AS AN ASSESSMENT TOOL FOR MEDICAL STUDENTS
Author: Priya S. Patil, Manisha R. Dhobale , Nitin R. Mudiraj
Category: Healthcare
Abstract:Multiple choice questions [MCQs'] form one of the tools for evaluation of medical graduates. The widespread use of MCQs' raises the question of their validity and authenticity. The present study was focused on MCQ validation with an attempt to highlight the importance of item analysis and discuss the myths and realities of MCQs'. Aim: The aim was to perform Item analysis while probing into myths and realities of MCQ as an assessment tool for first year medical students. A total of hundred students underwent MCQ test as part of their first periodic assessment.
Methodology: A total of hundred students underwent MCQ test as part of their first periodic assessment. A pre-validated MCQ test was given to students and a post-validation was done through item analysis. The indices were calculated using Microsoft excel and various indices compared.
Results: Inspite of using a well-designed MCQ test validated by senior faculty and colleagues, after item analysis the difficulty index of 65 % items and discrimination index of 75 % items was in the acceptable range. The distractor efficacy showed that 9 out of 120 distractors needed revision.
Conclusions: Item analysis must be routinely implemented to validate MCQs'. The myths like shortfalls of MCQ framing, only four options in clinical setting or cueing effect are duly considered and the realities like strict and elaborate protocol for MCQ construction, stimulating critical and lateral thinking of students should be implemented. An integrated approach can help to achieve an ideal assessment tool for the benefit of students.
Keywords: MCQ validation, Difficulty index, Discrimination index
Full Text:
INTRODUCTION
Evaluation is an important tool that guides student learning. Multiple choice questions form one of the tools for evaluation and are currently being widely used for assessment of medical graduates.1 Multiple choice questions are particularly useful to assess a large body of material for many students. A multiple-choice question (MCQ) consists of a stem with a question line at its end or underneath it, followed by a number of options. One of the options is correct or best response known as the key, while the others are described as distractors.1 Constructing a valid and effective MCQ is difficult task and needs a different approach. The methodical development of MCQ banks can be an asset which can lead to reliable assessment of students.2 Current widespread use of MCQs’ raises the issue regarding their validity and authenticity.3 Review of literature highlights different views regarding use of MCQ or combined approach of MCQ and free response essay type questions for better assessment of medical graduates. Considering the above issues the present study was focused on MCQ validation through item analysis. The importance of item analysis and the myths and realities concerned with MCQ as an assessment tool for medical students are discussed further.
MATERIAL AND METHODS
The study was conducted in the Department of Anatomy as a part of First Periodic Examination. Hundred First-year MBBS students were voluntarily involved in the study. They were given the MCQ test comprising of forty [40] questions with single best response. The MCQs’ were constructed to assess various levels of knowledge according to Bloom’s Taxonomy.Pre-validation of the MCQs’ was done by the Head of Department and other colleagues in the department. There was no negative marking and the time allotted was forty minutes. Evaluation was done out of forty marks and students were grouped as low, moderate and high achievers. Post validation of the MCQs’ was done by item analysis.4 The scores of all the students were arranged in such a way that there was order of merit.The students were divided into three groups according to their marks. Those students who belonged to the first group were considered as high achievers H [n=30] and those in the third group as low achievers L[n=30]. Each item was analyzed for the following;
• Difficulty Index or Facility value or p value was calculated using the formula p = H + L / N ×100, Where H= number of students answering the item correctly in the high achieving group L= number of students answering the item correctly in the low achieving group1 N= Total number of students in the two groups (including non-responders) Items having p value between 30 – 70% are considered as acceptable, among which items with p value between 50-60% are ideal while items with p value less than 30% (too difficult) and more than 70% (too easy) are not acceptable and need modification.1
• Discrimination index (DI) or d value was calculated using the formula d= H-L× 2/N Where the symbols H, L and N represent the same values as mentioned above. The DI or d value is a measure of the item to discriminate between students of higher and lower abilities and ranges between 0 and 1. In general‘d’ values between 0.20 and 0.35 is considered as good. Items having DI values more than 0.35 are considered to be excellent and those with less than 0.20 are considered poor.
• Distractor Effectiveness (DE) or Functionality of the distractors was calculated by observing how many students used the distractor in an item. If less than 5% of students used the option other than the key then that distractor is said to be a non- functional distractor [NFD]. On the basis of number of NFDs in an item, DE ranges from 0 to 100%. If an item contains three or two or one or nil NFDs then DE would be 0, 33.3%, 66.6% and 100% respectively.6
RESULTS
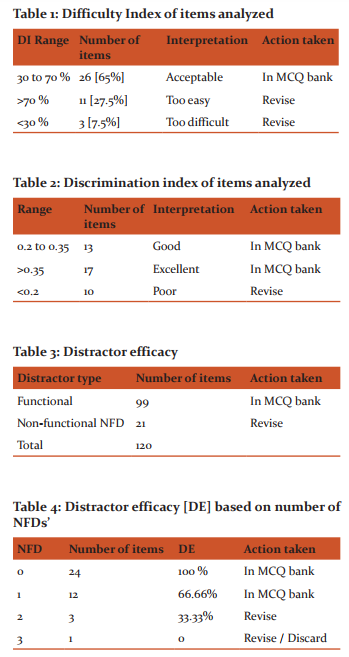
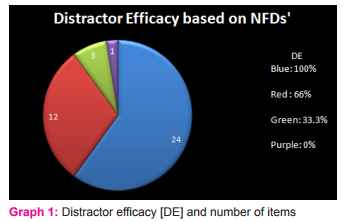
1] Difficulty Index of items analyzed After individually analyzing the items it was observed that the difficulty index (p value) of 26 items that means 65 % were acceptable. 11 items were too easy and 3 were too difficult hence 14 itemsthat means 35 %could be used after modification. [Table 1] 2] Discrimination index of items analyzed The discrimination index of 30 items [75 %] was acceptable but 10 items [25 %] need revision due to poor index. [Table 2] 3] Distractor efficacy [DE] based on number of NFDs’ As per tables 3, 4 and Graph 1, distractor efficacy was 100% in 24(60%) itemsand was 66.66% in 12(30%) items. So these questions can be added to the MCQ bank. In 3 items distractor efficacy was 33.33% hence their distractors should be modified and in 1 item having distractor efficacy 0%, its distractors should be either changed or the question should be discarded. Hence out of 120 distractors 9 needrevision. It was observed that higher the Difficulty Index, lower was the difficulty of the question. The Difficulty Index and Discrimination Indexwere often reciprocally related. Questions having a high p value (easier questions) discriminate poorly; while those with a low p value were good discriminators.
DISCUSSION
Good teaching is more a giving of right questions than a giving of right answers - Joseph Alberts The selection of an appropriate assessment method for students’ performances remains a daunting task for the teachers. In an attempt to change and upgrade the existing assessment tools MCQs’ are introduced at various levels and are used rampantly for regular assessments as well as important career deciding entrance examinations. A large number of educational research studies have demonstrated poor validity of MCQ’s. Barrows and Tamblyn in their book on Problem Based Learning mention, multiple choice and true/false questions under the heading “reliable evaluation tools with questionable validity”. 5 Item analysis is truly the assessment of the assessment tool itself.1 Post examination analysis of the MCQs helps to assess the quality of individual test items and test as a whole. Poor items can be modified or removed from the question bank. It also helps the teachers to identify the subject content which lacks understanding and need greater emphasis and clarity, by improving or changing the method- ology of teaching. In spite of validating the MCQ items by seniors and colleagues in the current study post validation systematic item analysis showed lacunae. The difficulty index was acceptable in only 65 % items while the discrimination index was acceptable in 75 % items. The distractor effectiveness also reflected need for revision in 9 out of 120 total distractors. Similar results were seen in different studies conducted for item analysis of MCQ. 6 They reveal that though item analysis was traditionally considered as tedious and time consuming task, the use of software applications such as Microsoft Excel has made it relatively easy and effective way to calculate various indices and test the validity of the items.7 Item analysis thus gives an insight and opportunity to revise and improve the MCQ and develop a valid question bank.1 MCQ- Myths and Realities There are many opinions and views of teachers as well as students regarding MCQ assessment and assessment in the form of short essay questions.8 This has led to the following discussion on the myths and realities about MCQs’. • MCQ as guess items assess only factual knowledge: One of the myth we frequently come across regarding MCQs’ is that they are multiple guess items3,6 which are useful to assess only factual recall of knowledge and higher orders of cognitive skills cannot be assessed. However the reality is MCQs’ can be framed and well validated in order to assess higher domains of Bloom’s taxonomy. Developing a good bank of valid and reliable multiple-choicetest items targeting higher cognitive abilities while conformingto item construction guidelines presents a big challenge to theitem developer.2 Yet in reality a dilemma remains during assessment because MCQs’ give four options to the students. Hence we cannot know exactly whether a particular question was answered by rapid retrieval of overlearned content or by purposeful relating of principles.9 • The MCQs’ challenge - Another widely prevalent myth regarding use of MCQ as an assessment tool is that MCQs’ are easy to frame and less time consuming. In reality it is a challenge for the teachers to construct ideal MCQs’ such that all options present as plausible answers. The distractors should be such that they attract students who do not know the answer while who know the right answer ignore them. • Cueing effect - MCQs’ are recently used in most of the entrance examinations at various levels. This has probably led to the myth that they are the best and fast method for assessment in competitive examinations. Multiple studies show that if same group of students are assessed by MCQ and free response tests all students scored higher in objective assessment. The cueing effect of readymade options available was thought to be the major factor.3,10,11 • Integrated approach- If we consider medical professional trainingit is mandatory that more emphasis be given to academic excellence and clinical competency. The medical students should be trained to evolve as problem solvers and not wait for situations with four options. Moreover there are certain clinical scenarios where there is one and only one diagnosis or some other conditions where there are more than four differential diagnoses which cannot be dealt with in an MCQ.The above dilemmas can perhaps be solved by introducing MCQs’ as a part of student assessment in undergraduate examinations more so in pre-clinical subjects. Some of the advantages in doing so are that the MCQs’ can be assessed rapidly with the aid of computers and softwares so can be employed when large number of students are to be assessed along with fast results and less error. They can provide highly structured and clear tasks with easy, objective and reliable scoring where legibility of handwriting doesn’t matter. Such data can be compared from class to class and year to year. Such assessment with MCQs’ can also be applied to certain clinically relevant topics like Paediatrics.12Later in the medical coursewhile using MCQ as an assessment tool for students they should undergo strict protocol for their framing, validation and selection.2 They should be overweighed by free response questions13 and newer ways of assessment to enhance critical thinking of students like case based learning, early clinical exposure, clinical scenarios and problem solving can be introduced. The MCQ test in entrance examinations can be supplemented with well-designed OSCE modules to assess students’ performances.14,15 In studies conducted by various authors16,17 it was seen that most of the students had a consistent performance in both objective and theory assessment. Interestingly it was also noticed that in some cases there was no correlation between MCQ and long essay scores for either the more competent students or the students who received failing grades. Thus, students’ grades determined by an examination format that includes both testing modalities may be different than the grades obtained by using only one of the modalities.18
CONCLUSION
Item analysis enhances the quality of MCQs’ which can help create an authentic and validated MCQ bank which can also assess higher orders of cognitive skills. The myths like shortfalls of MCQ framing, only four options in clinical setting or cueing effect must be considered during the use of MCQ as an assessment tool. The realities like strict and elaborate protocol for MCQ construction, integration with well designed free response and short essay type questions, stimulating critical and lateral thinking of students should be implemented. Sucha perspectivecan help to achieve an ideal assessment tool for the benefit of students at large.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
Authors acknowledge the immense help received from the scholars whose articles are cited and included in references of this manuscript. The authors are also grateful to authors/ editors/publishers of all those articles, journals and books from where the literature for this article has been reviewed and discussed. I sincerely thank the institute as well as all the students, colleagues, office clerk and non-teaching staff for their co-operation during this study. Sources of funding: Nil Conflict of interest: Nil
References:
1. Mehta G, Mokhasi V. Item analysis of multiple choice questions- an assessment of the assessment tool. Int J Health Sci Res. 2014; 4(7):197-202.
2. Sadaf S, Khan S, Ali SK. Tips for Developing a Valid and Reliable Bank of Multiple Choice Questions (MCQs). Educ Health 2012; 25:195-7.
3. Srivastava A, Dhar A, Aggarwal CS. Why MCQ? Indian J Surg 2004; 66:246-8.
4. Bloom, B., Englehart, M. Furst, E., Hill, W., and Krathwohl, D. (1956). Taxonomy of educational objectives: The classification of educational goals. Handbook I: Cognitive domain. New York, Toronto: Longmans, Green.
5. Barrows HS, Tamblyn RM. Problem based learning: An approach to medical education. Springer Publishing Company New York 1980.
6. Poulomi Mukherjee, Saibendu Kumar Lahiri. Analysis of Multiple Choice Questions (MCQs): Item and Test Statistics from an assessment in a medical college of Kolkata, West Bengal IOSRJDMS, Volume 2015; 14(12): 47–52.
7. Parag Chavda, Shobha Misra, Bithika Duttaroy. Item Analysis of MCQs’ South East AsianJourn al of Medical Education.2015; Vol. 9 (1):66-68.
8. Agu, A. U., Esom, E. A., Nto, J. N., Anyanwu, G. E., Ezugworie, J. O., Adiri, C. O. and Ozoemena, F. N. Students preference for various types of assessments in anatomy examination. International Journal of Development Research, 2014; Vol. 4 [7]:1377- 1379.
9. Elstein AS. Beyond multiple-choice questions and essays: The need for a new way to assess clinical competence. AcadMed 1993;68:244-9.
10. Baig M, Ali SK, Ali S, Huda N. Evaluation of Multiple Choice and Short Essay Question items in Basic Medical Sciences. Pak J MedSci 2014;30(1):3-6.
11. Walke YSC, Kamat AS, Bhounsule SA. A retrospective comparative study of multiple choice questions versus short answer questions as assessment tool in evaluating the performance of the students in medical pharmacology. Int J Basic Clin Pharmacol. 2014; 3(6): 1020-1023.
12. Duff, Jonathan P., et al. “Development and validation of a multiple choice examination assessing cognitive and behavioural knowledge of pediatric resuscitation: A report from the EXPRESS pediatric research collaborative.”Resuscitation 84.3 (2013): 365-368.
13. Newble DI and Jaeger K (1983). The assessment and examinations on the learning medical students. Medical Education; 17:165-171.
14. Gajjar S, Sharma R, Kumar P, Rana M. Item and test analysis to identify quality Multiple Choice Questions (MCQs) from an assessment of medical students of Ahmadabad, Gujarat. Indian journal of Community Medicine 2014;39:17-20.
15. Walubo A, Burch V, Parmar P, Raidoo D, Cassimjee M, Onia R, et al. A model for selecting assessment methods for evaluating medical students in African medical schools. Acad Med. 2003;78(9):899-906.
16. Singh, T. and Anshu (2012) Principles of Assessment in Medical Education, New Delhi: Jaypee Brothers Medical Publishers.
17. Anbar M. Comparing assessments of students’ knowledge by computerized open-ended and multiple-choice tests. Acad Med. 1991;66(7):420-2.
18. Khan MZ, Aljarallah BM. MEQs and MCQ as a tool for assessing the cognitive skills of undergraduate medical students. Int J Heal Sci.2011;5(1):45-50.
|






 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License