IJCRR - 9(15), August, 2017
Pages: 14-20
Print Article
Download XML Download PDF
Toxicity Effect of Copper on Aquatic Macrophyte (Pistia Stratiotes L.)
Author: Rolli N.M., Hujaratti R.B., Giddanavar H.S., Mulagund G.S., Taranath TC
Category: General Sciences
Abstract:Industrial development coupled with population growth had resulted in the over exploitation of natural resources. Life support systems viz, water, air and soil are thus getting exposed to an array of pollutants, especially heavy metals released by anthropogenic activities. But tolerant species of aquatic plants are able to survive and withstand the pollution stress and serves as a pollution indicators and as tools for p1hytoremediation of heavy metals from the aquatic ecosystems. Phytoremediation is an biogeotechnological application based on \"Green liver concept\" and operates on biogeochemical cycling. The present study focuses on copper toxicity on morphology, biochemical parameters and bioaccumulation potential of Pistia. The laboratory experiments were conducted for the assay of morphological index parameter (MIP), biochemical parameters and accumulation profile of copper in the test plants at various concentrations viz, 2, 5,10, 15 and 20 ppm, at 4 days regular intervals for 12 days exposure. The test plants show visible symptoms like withering of roots, chlorosis, necrosis and lower leaves gets decayed at higher concentrations (severe at 20 ppm), however, the test plant showed normal growth at lower concentration viz, 2 and 5 ppm. The estimation of biochemical parameters viz, total chlorophyll, protein and carbohydrates of test plants showed significant increase at lower concentrations (2 and 5 ppm) of Cu. The biochemical constituents decreased with increase in exposure concentrations (10, 15 and 20 ppm) and duration. The toxic effect of sewage was directly proportional to its concentrations and exposure duration. The accumulation profile of Cu by Pistia was maximum at 4 days exposure and gradually decreases at subsequent exposure duration.
Keywords: Copper, Accumulation, Toxicity symptoms, Biochemical parameters
DOI: 10.7324/IJCRR.2017.9153
Full Text:
INTRODUCTION
Industrialization and urbanization coupled with alarming rate of population growth have resulted in the large scale pollution of aquatic ecosystems by industrial and domestic waste water discharge. Natural erosion and anthropogenic activities are greatly responsible for water pollution particularly heavy metals like Zinc (Zn), Lead (Pb), Cadmium (Cd), Copper (Cu) etc. There is likelihood of phytotoxicity both micro and macrophytes and environmental risks (de-Fillipes and Pallghy, 1994; Wei, et al., 2003). Heavy metals persisting in sediments may be slowly released into the water and become available to the organisms. Some heavy metals viz, Zn, Cu, Iron (Fe), Manganese (Mn) etc. are represented as micronutrients (Reeves and Baker, 2000) and are only toxic when taken in excess quantities (Blaylock and Huang, 2000; Campenela, 2001), but nonessential ions like Pb, Cd and Ni can inhibit various metabolic activities even in small quantities (Cerventes, et al., 2001; Dinkar, et al., 2001; Choudhary and Sharma, 2009).
The waste water emitting from source metals which could be toxic to flora and fauna. Biological treatment of waste water through aquatic macrophytes plants has great potential for its purification, which effectively accumulates the heavy metals (Brix and Schirup, 1989). Aquatic macrophytes accumulate considerable amount of toxic metals and make the environment free from the pollutants. Thus they play significant role in cleaning up of environment and make the environment free from toxic pollutants. So many aquatic plants have been successfully utilized for removing toxic metals from the aquatic environments (Satyakala and Kaiser Jamil 1992). The metal tolerance of plants may be attributed to different enzymes, stress proteins and Phytochelatins (Van-Asche and Clijsters 1990). Accumulation of metals at higher concentration causes retardation of growth biochemical activities and also generation of –SH group containing enzymes (Weckx and Clijsters 1996).
In the present investigation Pistia stratiotes, a common aquatic macrophyte is used to study the effect of different concentrations of copper on morphology, biochemical constituents and accumulation profile of Cu from the experimental pond under laboratory conditions
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Pistia stratiotes, a free floating aquatic plant from unpolluted water bodies is maintained in cement pots (1 m diameter ) under natural conditions at a temperature 28-300C. About 20 g of young healthy Pistia is acclimatized for two weeks in Arnon and Hoagland nutrient solution maintaining pH between 7.1-7.4. The concentrations of Cu in the polluted water are in the range of 02, 05, 10, 15 and 20 mg/l and tap water as a control. Morphological Index parameters (MIP) viz, root length, leaf length and breadth were observed for 12 days at interval of 4 days. Photographs of Pistia treated with different concentrations of copper were taken by using Canon’s Power Shot G2 digital camera. For the further study the plants were harvested at the end of 4, 8 and 12 days exposure and are thoroughly washed with distilled water and used for the estimation of total chlorophyll, protein and carbohydrate and also for morphological observations. Plants harvested after 48 hrs were dried at 800C for 2 days for metal extraction.
The fresh plant sample of 1g is macerated in 100 ml of 80% (v/v) chilled acetone by using pestle and mortar. The centrifuged and supernatant was used for the estimation of total chlorophyll by standard method (Arnon, 1949) using 652 nm against the solvent (80% acetone as a blank). The protein was estimated by Lowry’s method (Lowry et al., 1951) using Bovine Serum Albumin (BSA) as a standard, using 660 nm and carbohydrates by phenol sulphuric acid method (Dubois et al., 1956) using glucose as standard at 490 nm. Morphological characters were identified with the help of photographs, using Canon’s Power Shot G2-digital camera.
The estimation of metal Cu in the test plant was carried out by using standard method (Allen et al., 1974). The dried and powdered 1 g plant material was digested by using mixed acid digestion method in Gerhardt digestion unit. The digested samples were diluted with double distilled water and filtered through Whatman filter paper No-44. The estimation of Cu was done by AAS (GBC 932 Plus Austrelia) with air acetylene oxidizing flame and metal hollow cathode lamp at 217.00 nm wavelength. Working standards (SISCOP-Chem-Bombay Lab) were used for the calibration of instrument.
Statistical analysis: Data are presented as mean values ± SE from two independent experiments with three replicates each. Data were subjected to Two - way ANOVA to know significance between concentrations and between exposure duration for the accumulation of heavy metal (Cu). Further, Dunet’s test is also applied for multiple comparisons between control and other concentrations. Two – way ANOVA test is also extended to know the significance between concentration and duration for biochemical parameters.
RESULTS
The experiments were conducted with the following parameters:
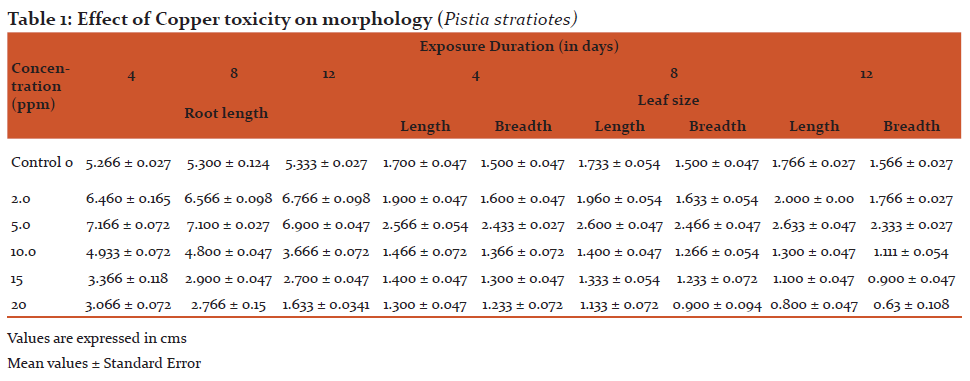
- Effect of Copper toxicity on morphology:
The test plant showed luxuriant growth and slight increase in the laminal length and breadth at 5 ppm concentration. The 5 ppm Cu found to promote length by 6.900cm (± 0.047) in comparison to control, 5.33cm (± 0.027) and laminal length 2.63 cm (± 0.047) and breadth, 2.33 cm (± 0.027) when compared to control (laminal length, 1.766 cm ± 0.027 and breadth 1.56cm ± 0.027) respectively during 12 days exposure. However, at 20 ppm Cu, severely inhibit the root length by 1.63 cm (± 0.034) in comparison to control 5.33 cm (± 0.027) and laminal length, 0.80 cm (± 0.047) and breadth, 0.63 cm (± 0.108), when compared to control (laminal length, 1.76 cm ± 0.027 and breadth 1.566 cm ± 0.027) respectively during 12 days exposure (Table 1). MCA test also represented maximum deviation at higher concentration compared to control.
- Effect of Copper toxicity on biochemical parameters:
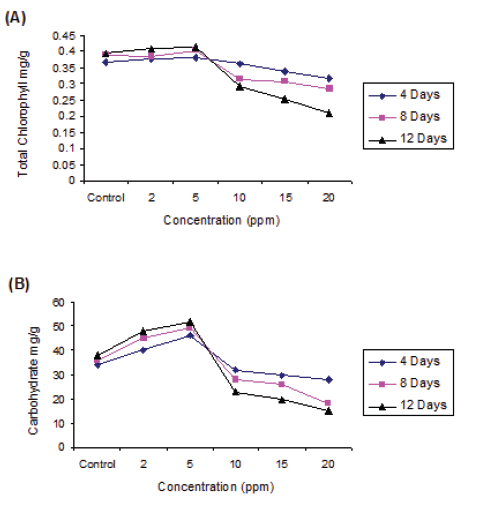
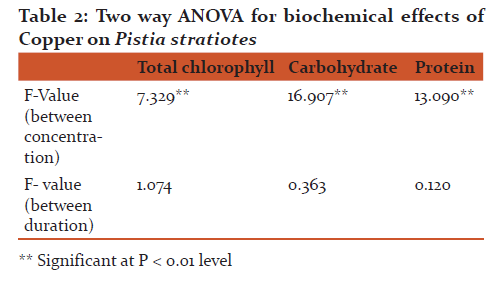
The chlorophyll content was very sensitive to copper toxicity. The results found that Cu at 5 ppm found to augment chlorophyll synthesis and was directly proportional to concentration and exposure duration. The chlorophyll content increased by 3.81% ( 0.381 mg/gm), 4.10% (0.406mg/gm) and 4.79% (0.415mg/gm) respectively at 4, 8 and 12 days exposure compared to control pond. However, the higher concentration of copper found to inhibit the chlorophyll synthesis. The inhibition at 20 ppm Cu by 13.35% (0.318mg/gm), 27.7% (0.284mg/gm) and 46.71% (0.211mg/gm) (significant at p > 0.95) at 4, 8 and 12 days exposure respectively compared to control. Two-way ANOVA represents biochemical toxicity to the test plant, concentrations were significant at p > 0.01 level but duration is not significant (Fig. 1).
The increase in the carbohydrate content of Pistia at 5 ppm Cu by 23.06% (32.0 mg/g), 35.71% (38.0 mg/g) and 36.66% (41.0 mg/g) respectively during 4, 8 and 12 days exposure duration. The severity of inhibition of carbohydrate synthesis was noticed at 20.0 ppm by 46.15% (14.0 mg/g), 57.14% (12.0 mg/g) and 68.75% (10.0 mg/g) respectively at 4, 8 and 12 days exposure in comparison to control (fig.).
The protein synthesis at 5 ppm Cu was promotive irrespective exposure duration. However, the protein content decreased at subsequent higher concentration and inhibition was directly proportional to the duration of exposure. The 5 ppm Cu promoted protein synthesis by 8.06% (6.7 mg/g), 18.75% (7.6 mg/g) and 19.11 (8.1 mg/g) respectively at 4, 8 and 12 days exposure duration. The reduction in protein content was observed with progressive increase in Cu concentration. The inhibition of protein content increase viz, 11.36% (3.9 mg/g), 32.60% and (3.1 mg/g) and 43.75% (2.7 mg/g) was respectively at 4, 8 and 12 days exposure in comparison to respective control (Fig. 1)
Application of two-way ANOVA, it is found that the biochemical responses of test plant species with respect to concentrations were significant at p < 0.01 level. However, exposure duration was not statistically significant (Table 2).
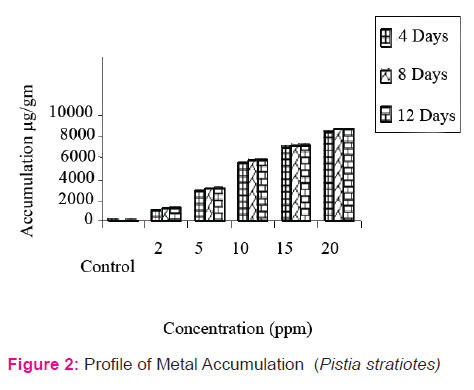
- Profile of Metal Accumulation
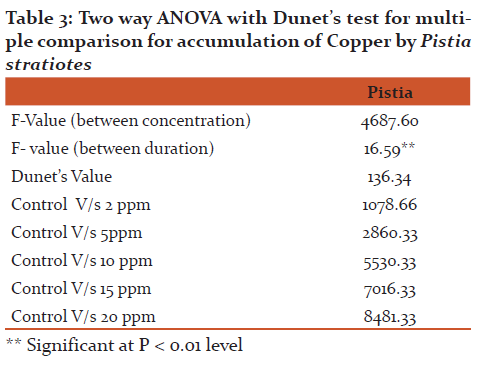
The accumulation data (Fig 2) revealed that ‘Cu’ accumulation in Pistia was directly proportional to its concentration and exposure duration. The Pistia grown in experimental pond containing 5 ppm accumulate 2812.04 µg/g, 3062.0 µg/g and 3208 µg/g and accumulation at higher concentration (20 ppm) was 8425.0µg/g, 8750.0 µg/g and 8770.0 µg/g during 4, 8 and 12 days exposure respectively. Two-way ANOVA showed that both concentration and exposure duration were significant at p < 0.01 level in test plants and further Dunet’s test was applied for the multiple comparison between control and different concentration treatments of test plant. From the statistical analysis it is clear that concentration treatments are significantly differ with control (Table 3).
DISCUSSION
- Effect of Copper toxicity on morphology Morphometric assay, is one of the quantitative tool for the assessment of toxicants, was measured by using Morphological Index Parameters (MIP). The rate of inhibition of growth in the root and leaf was directly proportional to the concentrations of copper. The test plant show luxurieant growth and slight increase in the laminal length and breadth at 5 ppm concentration. However, at higher concentration (20 ppm) severely inhibit the root length, laminal length and breadth. Similar observations were made by Garg et al.(1994) in Limnathemum cristastum at 1 ppm concentration of Pb, Zn and Cr. Our results of toxicity symptoms of copper at higher concentrations observed were similar to Dagon and Saygideger (2011) and Kopitte et al., (2007) and also of Yongpisamshap et al., (2005) in Salvinia natanas. Two – way ANOVA states that the concentrations were significantly toxic at 5% level but duration was not significant. MCA test also represented maximum deviation at higher concentration compared to control (Table. 1).
- Effect of Copper toxicity on biochemical parameters: Copper is essential trace element required by all plants. The accumulation of copper in plants lead to biochemical changes. Total chlorophyll content, a parameter, was a sensitive to heavy metal toxicity (Gupta and Chandra, 1996). Similar observations had been reported by Dhir and Srivastava (2013) in Salvinia natanas at 10 ppm of Cu, Fe, Zn, Co and Cr. The stimulation of chlorophyll synthesis may be due to phytochelatins (PCs) which plays role in detoxification (Rolli, et al ., 2010) however, the higher concentration of Cu found to inhibit the chlorophyll synthesis. The inhibition at 20 ppm Cu by 13.35% (0.318mg/gm), 27.7% (0.284mg/gm) and 46.71% (0.211mg/gm) (significant at p > 0.95) at 4, 8 and 12 days exposure respectively compared to control. Similar observations was made by Singh et al 2011 in Hydrilla verticillata at higher concentration of Pb at 20 ppm and Cd at 0.05 ppm. This is due to decline in chlorophyll content in plants exposed to Cu due to: 1) inhibition of important enzymes associated with chlorophyll synthesis, 2) peroxidation of chloroplast membranes resulting from heavy metals induced oxidative stress, 3) formation of metal substituted chlorophyll (Patsikka, et al., 2002). Two-way ANOVA represents biochemical toxicity to the test plant, concentrations were significant at p > 0.01 level but duration is not significant. Two way ANOVA represents toxicity was at p > 0.01 level significant towards but duration was not significant.
Our investigation revealed that lower concentration of copper (5 ppm) promotes the carbohydrate synthesis. The carbohydrate content was increased at lower concentration of Cu, was due to detoxification free radicals by quenching / utilization by enzymatic superoxide dismutase (SOD), peroxidase (POD), catalases or glutathione reductase (Wang et al. 1997). Similarly Choudhary and Ramachandra (2005) observed stimulatory effect of carbohydrate in Nostoc muscorum at lower concentration (1.5 ppm) of Cu like other heavy metals. But the severity of inhibition of carbohydrate was noticed (Fig. 1). The heavy metals damaged the photosynthetic apparatus, in particular light harvesting complex II (Krupa, 1988) and photosynthesis I and II (Siedlecka and Krupa, 1996) and Hasan et al., (2009).
The proteins play an important role in energy metabolism. In the test plant, the lower concentration of copper enhances the protein synthesis and is directly proportion to exposure duration. However, the protein content was decreased at subsequent higher concentration and inhibition was directly proportional to the exposure duration. Many studies show that protein content of many aquatic macrophyte was increased by accumulation of Pb at lower toxicity concentration. The stimulation of protein synthesis at lower concentration of Cu (5 ppm) may be attributed to the synthesis of stress proteins. The phytochelatins (PC) and phytochelatin synthetase bind and regulate the Cu and sequesters the toxicity in the plants and thus showed metal tolerance Mohan and Hosetti, 1997; Steffens, 1997). The reduction in protein content was observed with progressive increase in Cu concentration. The inhibition of protein content increase viz, 11.36% (3.9 mg/g), 32.60% and (3.1 mg/g) and 43.75% (2.7 mg/g) was respectively at 4, 8 and 12 days exposure in comparison to respective control (fig. 1)
The proteins played an important role in energy metabolism. A decrease in protein content could be due to inactivation of protein synthesizing enzymes in the cell. The Cu induced oxidative stress by generating reactive oxygen species (ROS). These disrupted cellular homeostasis, thus, enhanced the production of ROS. These ROS reactions with proteins, lipids, nucleic acids causing membrane damage and enzyme content of macrophyte may be due to above reasons (Garg et al., 1994; Romero et al., 2007). (fig. 1)
Application of two-way ANOVA, it is found that the biochemical responses of test plant species with respect to concentrations were significant at p < 0.01 level. However, exposure duration was not statistically significant (Table 2).
- Profile of Metal Accumulation
Heavy metal pollution of a water is a major environmental concern, is increasing at (Dushenkar et al. 1995) alarming rate due to anthropogenic activities and is drawing attention and gaining paramanual importance due to its obvious impact on health through the food chain (Prasad 1997). The aquatic plants are able to accumulate heavy metals from sediment water. In the present investigation aquatic macrophyte viz, Pistia stratiotes is used in accumulation. The accumulation data (Fig 2) revealed that ‘Cu’ accumulation in Pistia was directly proportional to its concentration and exposure duration.
It was observed that the rate of accumulation is maximum at 4 days exposure irrespective of concentrations and exposure duration, however, at remaining durations it is marginal. Similar observations were made by Bendra et al., (1990) in Cladophora glomerata at the concentration of 0.1M solution of Cd. Initial increase in the accumulation might be due to the availability of increased number of binding sites for the complexation of heavy meals ions leading to the increased complexation of heavy metal ions, leading to the increased absorption, however, slow accumulation may be attributed to binding ions to the plants and establishment of equilibrium status between adsorbate and adsorbent (Rai and Kumar, 1999; Sibihi, et al., 2012).
Two-way ANOVA showed that both concentration and exposure duration were significant at p < 0.01 level in test plants and further Dunet’s test was applied for the multiple comparison between control and different concentration treatments of test plant. From the statistical analysis it is clear that concentration treatments are significantly differ with control (Table 3)
CONCLUSION
It is concluded from the findings of the present investigation, it is concluded that morphological, biochemical responses and profile of Cu accumulation by Pistia stratiotes are directly proportional to concentration of the media and exposure duration. Regular harvest of the plants at the interval of 4 days help to cleanup aquatic environment.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENT
The authors are thankful to the Principal, BLDEA’s Degree College, Jamkhandi (India), Research and Development centre, Bharthiar University, Coimbatore. Dept. of Botany, Karnatak University Dharwad for providing necessary facilities to carry out research work. Further, the author acknowledges the immense help received from the scholars whose articles are cited and included in references of this manuscript. The author is also greatful to authors / editors, publishers of all those articles, journals and books from where the literature for this article has been received and discussed.
References:
Allen, S.E., Grimshaw, H.M., Parkinson, J.A.and Quarmby, C. 1974. Chemical analysis of ecological materials. Blackwell Scientific Publications, Oxford.
Arnon, D.I. 1949. Copper enzymes in isolated chloroplast Polyphenol Oxidase in Beta vulgaris. Plant Physiol, 24: 1-15.
Bendra, M., Mc Hardy, Jennifer, J. and George. 1990. Bioaccumulation and toxicity of zinc in the Green alga, Clodophora glomerata. Environmental Pollution. 66: 55-66.
Blaylock, M.J., Haung, J.W. 2000. Phytoremediation of toxic metals using plants to clean up the environment (Eds : 1 Raskin and B D Ensley) John wiley and sons Inc 53-70.
Brar, M.S., Mahli, S.S., Singh, A.P., Arora, C.L.and Gill, K.S. 2000. Sewer water irrigation effects on some potentially toxic trace elements in soil and potato plants in Northwestern India. Can. J. Soil. Sci. 80: 465-471.
Cervanates, C., Campos-Garcia, J., Devars, S., Gutierrez-Corona, F., Loza-Tavera, H., Torres-Guzman, J.C. and Moreno-Sanchez, R. 2001. Interactions of Cr with microorganisms and plants. FEMS. Microbial. Rev. 25: 335-347.
Chaudhary, S., Yogesh Kumar, S. 2009. Interactive studies of potassium and copper with cadmium on seed germination and early seeding growth in maize (Zea mays L.). J. Environ. Biol. 30: 427-432.
Choudhary, M.P. and Ramachandra. 2005. Toxicity assessments of heavy metals with Nostoc muscorum L. Journal of Environmental Biology. 26(1):129-134.
de Filippis, L.F, Pallaghy, C.K. 1994. Heavy metals: Sources and biological effects. In: Rai, L.C., Gaur, J. P. and Soedar, C. J. (eds) Algae and water pollution. E. Schweizerbart’she Verlagsbuchhandlung. Stuttgart, 31-77.
Dhir, B. and Srivastava, S. 2013. Heavy metal tolerance in metal hyperaccumulator plant, Salvinia natans. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 90: 720-724.
Dinakar, N., Nagajyothi, P.C., Suresh, S., Dhamodharam, T. and Suresh, C. 2009. Cadmium induced changes on proline, antioxidant enzymes, nitrate and nitrite reductases in Arachis hypogaea L. J. Environ. Biol. 30: 289-294.
Dogan, M., Saygideger, S.D. and Colak, U. 2009. Effect of lead toxicity on aquatic macrophyte Elodea Canadensis Michx. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 83: 249-254.
Dubois, M., Gilles, K.A., Hamilton, J.K., Rebers, P.A. and Smith, F. 1956. Colorimetric method for determination of sugars and related substances. Annul. Chem. 28: 350-356.
Dushenkov, V., Kumar, P.B.A.N., Motto, H. and Raskin, I. 1995. Rhizofiltration the use of plant to remove heavy metals from aqueous streams. Environ. Sci. Tech. 29:1239-1245.
Garg, P., Chandra, P. and Devi, S. 1994. Cr (VI) induced morphological changes in Limnanthemum cristatum Griseb: A possible biondicator. Phytomorphology. 44(3 and 4): 201-206.
Gupta, M., and Chandra, P. 1996. Response of Cd to Ceratophyllum demersum L. A rootless submerged plant. Waste management. 16:335-337.
Hasan, S.A., Fariduddin, Q., Ali, B., Hayat, S. and Ahmad, A. 2009. Cd: Toxicity and tolerance in plants. J. Environ. Biol. 30(2): 165-174.
Koppitte, P.M., Asher, C.J., Koppitte, R.A. and Menzies, N.W. 2007. Toxic effects of Pb2+ on growth of cowpea (Vigna unguiculata). Environ Pollut 150: 280-287.
Krupa, Z. 1988. Cadmium induced changes in the composition and structure of the light-harvesting complex Ii in radish cotyledons. Physiol. Plant. 73: 518-524.
Lowry, O.H., Rosebrough, N.J., Randall, R.J. and Farr, A. 1951. Protein determination by the folin phenol reagent. J. Biol. Chem. 193: 265-275.
Mohan, B.S. and Hosatti, B.B. 1997. Potential phytotoxicity of Pb and Cd to Lemna minor grown in sewage stabilization ponds. Environmental pollution. 98:233-238.
Patsikka, E., Kairavuo, M., Seren, F., Aro, E.M. and Tyystjavi. 2002. Excess copper predisposes photosystem II to Photoinhibition in vivo by outcompeting iron and causing decrease in leaf chlorophyll. Plant Physiol 129: 1359-1367.
Prasad, M.N.V. 1997. Trace metal In: Plant ecophyscology (Ed. Prasad, M.N.V.) John Wiley and Son. New York. 207-249.
Rai, A.K. and Kumar, S. 1999. Removal of Cr (VI) by low cost dust adsorbants. Applied Microbiol. Biotechno. 39:661-667.
Reeves, R.D. and Baker, A.J.M. 2000. Metal accumulating plants, In: Phytoremediation of toxic metals: Using plant to clean up the environment. (Ed. I. Raskin and B.D. Ensely). John Wiley and sons, Inc, Torento, Canada. 193-229.
Rolli, N.M., Suvarnakhandi, S.S., Mulagund, G.S., Ratageri, R.H. and Taranath, T.C. 2010. Biochemical responses and accumulation of cadmium in Spirodela polyrhiza. J. Environ Biol 31: 529-532.
Romero-Puertas, M.C., Corpas, F.J., Rodriguez-Seranno, M., Gornez, M., and Dei Rio, L.A. 2007. Differential expression regulation of antioxidative enzymes by cadmium in pea plants. J Plant Physiol 164: 1346-1357.
Satyakala, G. and Jamil, K. 1992. Cr-induced biochemical changes in Eichhornea crassipes (Mart) Solms and Pistia stratiotes L. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 48: 921-928.
Sibihi, K., Cherifi, O., Agarwal, A., Oudra, B. and Aziz, F. 2012. Accumulation of toxicological effects of cadmium, copper and zinc on the growth and photosynthesis of the fresh water diatom Planothidium lanceolatum (Brebison) Lange-Bertalot; A laboratory study. J Mater Environ Sci 3: 497-506.
Siedlecka, A.and Krupa, Z. 1996. Interaction between cadmium and iron and effects on photosynthetic capacity of primary leaves of Phaseolus vulgaris. Plant. Physiol. Biochem. 34: 833-841.
Singh, A., Kumar, C.S. and Agarwal, A. 2011. Phytotoxicity of Cadmium and Lead in Hydrilla verticillata (L.F) Royle. Journal of Physiology 3: 01-04.
Steffens, J.C. 1997. The heavy metal binding peptides of plants, Ann. Rev. Plant Physiol. Plant mol. Biol. 41: 553-575.
Van Assche, F. and Clijsters, H. 1990. Effects of metals on enzyme activity in plants, Plant. Cell Environ. 13: 195-206.
Wang, W. and Lewis, M.A. 1997. Metal accumulation by aquatic macrophytes In: Plants for environmental studies (Eds: W. Wang, J.W. Gorsuch and J.S. Hugkes). CRC Press, New York. 367-416.
Weckx, J. and Clijsters, H. 1996. Oxidative damage and deference mechanisms in primary leaves of Phaseolus vulgaris. Physiol. Plant. 96: 506-512.
Wei, L., Donat, J.R., Fones, G. and Ahner, B.A. 2003. Interactions between Cd, Cu, and Zn influence particulate phytochelatin concentrations in marine phytoplankton: laboratory results and preliminary field data. Environ. Sci. Technol. 37: 3609-3618.
Yongpisanphop, J., Chue, M.K. and Porethitiyook, P. 2005. Toxicity and accumulation of Lead and Chromium in Hydrocotyle umbellate, Journal of Environmental Biology. 26(1):79-89.
|






 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License