IJCRR - 3(3), March, 2011
Pages: 59-64
Print Article
Download XML Download PDF
NUTRITIONAL COUNSELLING AND SUPPLEMENTATION: NEED OF THE HOUR IN NATIONAL TUBERCULOSIS CONTROL PROGRAMME IN INDIA
Author: Padma Shetty, Shobha Kowli
Category: Healthcare
Abstract:Background: The magnitude of malnutrition is high in India, which easily predisposes the individuals to risk of developing TB and Tuberculosis in turn further aggravates wasting. This
vicious cycle results in high morbidity and mortality. Anti TB drug causes nausea, vomiting, poor
appetite that further knocks down dietary intake considerably.
Aim: The aim of the present study is to highlight the importance of nutrition in TB patients by assessing the percentage of underweight TB patients and caloric intake using the 24 hour recall
method.
Methods and Material: The study was conducted in the urban slum area of Mumbai, covering a population of approximately 72000. Fifty consecutive TB patients who came to DOTS centre
were interviewed to assess the dietary intake. Pre-Treatment weight was compared with the
standard reference weights of Indian Council of Medical Research?s (ICMR). The caloric intake
was calculated as percentage of recommended dietary allowance (RDA) for specific age and
occupation as per ICMR standards.
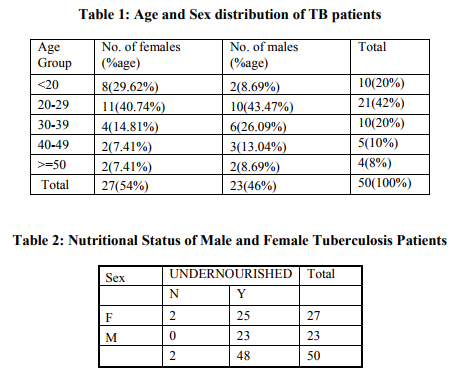
Results: Tuberculosis patients interviewed were predominantly females (54%) and in the age group of 20-29 years (42%). The mean age of the patients was 28.56 \?1.79yrs. Except for two
females, all the TB patients were underweight. The mean weight of the TB patients was 36.82
kilograms. Almost all the TB patients were consuming less than 50% of RDA.
Conclusions: Poor nutritional status predisposes the individual to tuberculosis. It is important
therefore that the health care workers while giving priority to drug compliance should not forget
to counsel on balanced diet and developing linkages with NGO?s to provide food
supplementation for filling in the dietary gap, in an effort to improve the nutritional status.
Keywords: Tuberculosis, Thinness, Energy intake, Diet
Full Text:
INTRODUCTION
Tuberculosis (TB) is a global public health problem, responsible for more than 2 million deaths each year [1]. The association between TB and malnutrition is well recognized [2] , since pre chemotherapeutic era when cod liver oil was given to TB patient to strengthen the host defense [3] . Various studies have reported that TB coexists with NUTRITIONAL COUNSELLING AND SUPPLEMENTATION: NEED OF THE HOUR IN NATIONAL TUBERCULOSIS CONTROL PROGRAMME IN INDIA Padma Shetty1 , Shobha Kowli1 1Department of Community Medicine, K. J. Somaiya Medical College, Mumbai E-mail of corresponding author: shettypadma@hotmail.com 60 International Journal of Current Research and Review www.ijcrr.com Vol. 03 issue 03 Mar 2011 malnutrition at the time of starting treatment [4, 5, and 6]. It is well known fact that TB is associated with various socio demographic factors like poverty; poor housing, economic deprivation and these are some of the factors predisposing to poor nutritional status and impaired immune system. Generally malnourished and immunological compromised patients contract TB and TB in turn causes anorexia and wasting. This vicious cycle results in high morbidity and mortality. Also deterioration of nutritional status leads to reactivation of latent TB. Anti TB drug causes nausea, vomiting, poor appetite that further knocks down dietary intake considerably. Randomized controlled trial that provided an energy-protein supplement to TB patients receiving treatment showed gains in lean mass, and greater grip strength so faster recovery[6] . The magnitude of malnutrition is widely prevalent in India, as evident by several studies that have shown low weight for age amongst under-five, and low BMI for school children, adolescents, and adults. There are several reasons for malnutrition varying from a low birth weight, inadequate caloric intake due to poor socio-economic conditions or dietary fads, occupations involving travelling or odd hours at jobs etc. According to NFHS III 39.5%, 36% and 34% of under-five children, adult women and men respectively are malnourished [7] . The Revised National TB control programme (RNTCP) using the strategy of Directly Observed Treatment Short course (DOTS) is being implemented throughout India since 2006. The RNTCP quarter I, 2010 report reveal that the case detection rate of New Smear Positive cases is > 70% and treatment success rate of > 85%. A total of 3,73,655 TB cases were registered for treatment during the first quarter 2010, of which nearly 70654 were retreatment cases. In Mumbai itself, RNTCP covers a population of 137 lakhs. The annualized TB case detection cases is 237 per lakh population for Mumbai, which means about 170 TB cases per year [8] . However the programme does not emphasis on nutritional supplementation or counselling, nor are any efforts made to discuss these aspects by the DOTS strategy. Hence the present study was conducted to highlight the need for incorporating nutrition counselling / supplementation in RNTCP programme with the objective to find out the percentage of TB patients on DOTS who are underweight and assess the nutritional intake of the TB patients through 24 hour recall method.
SUBJECTS AND METHODS
Study settings: The city of Mumbai, called financial capital of India spreads over an area of 437.71 sq. km and is a merger of 7 islands in city area and 4 islands in suburbs. The population of Mumbai is about 1.19 crores with a population density of 27209/sq. km. The city accounts for 1.2% of the Indian population and 12% of the Maharashtra population [9] . The city of Mumbai is divided into wards for administrative purpose. Each of the wards has several health posts, dispensary, maternity home, post-partum centres and hospitals of BMC to cater to the needs of the community. Apart from the government and the municipal infrastructure there are several private practitioners, private hospitals and charitable trusts catering to the health needs of the Mumbaikars. Health posts are amongst many of the functional DOT centres.
The study was conducted in the urban slum area of Mumbai, Chembur Naka, which falls under the Jurisdiction of the Ramabai health post of M/W ward of the Municipal Corporation of Greater Mumbai (MCGM).The study area has a population of approximately 72000, with an estimated household of 14,400.
MATERIAL AND METHOD
Fifty consecutive TB patients who came to DOTS centre were selected irrespective of their status of TB and treatment and were interviewed using a structured questionnaire. The interviewer collected data on demographic profile, last 24 hr dietary intake and nutritional advice received by them during course of treatment. Other data like sputum results, type of TB, treatment category etc. was recorded from the TB treatment card. Pre-Treatment weight recorded on the TB treatment card was compared with the weight which is used for calculating ICMR recommended dietary intake. Using the 24 hour dietary recall method, dietary intake was expressed in kilocalories (Kcal) per day. It was further calculated as percentage of recommended dietary intake for specific age and occupation as per ICMR standard [10] .
RESULTS The TB patients interviewed were mostly in the age group of 20-29 years (42%). Eight of the TB patients were adolescents and two were below the age of 10 years. Four patients were aged 50 years and above. The mean age of the patients was 28.56 ±1.79yrs. The study population was predominantly females (54%), and amongst the adolescent TB patients again there wasdisproportionately higher percentage of females (87.5%) as compared to males (Table 1). The preponderance of females was also found in the age group of 20-29 years. In the age group of 30 and above, the number of male patients was higher than females. Only 5 of the 50 TB patients were extrapulmonary of which two was abdominal TB, two lymph node TB and one ileo-caecal TB. Twenty of the TB patients were sputum positive TB. 14% of the TB patients reported of a family member having suffered from TB in the past or has reported a death due to TB. 20% of the patients also gave a past history of TB. Except for two females in the age group of 20-24 years, all the TB patients were underweight as per the ICMR standards. The mean weight of the TB patients was 36.82 with Standard error of 1.34 (Table 2).
The dietary assessment using the 24 hour recall method revealed that the patient?s were consuming less than 50% of their daily caloric intake. The reasons for poor dietary consumption was not only due to socioeconomic conditions but also due to loss of appetite, likes and dislikes for different food items, irregular working hours, nonavailability of home -made food etc.. Many patients were scared to eat because of nausea and vomiting, which further affected the drug compliance.
DISCUSSION
Nutritional status determines normal health and functioning of all body system including immune system which is responsible for various infectious diseases. General malnutrition compromises cell mediated immunity leading to TB. Though nutrition has proven importance, the Revised National Tuberculosis Control Programme, does not emphasise nor focus on the nutrition of the TB patients. 96% of the TB patients were undernourished. A study in Malawi and Ghana found that 57% and 51% of the TB patients admitted to the district hospital were having less than 18.5 kg/m2 . [11,12] A study in Ajmer in India, found that 75% of the patients had low BMI. [13] Dietary intake was less than 50% of RDA in all the patients in the present study which was almost similar to the findings of the study conducted in Ajmer [13] . Dietary intakes was very low due to poor appetite, likes and dislikes for different food items, irregular working hours, non-availability of home -made food , nausea, vomiting, side effects of anti TB drugs etc. Though TB treatment improves the nutritional status, it is limited to gain in fat mass. Thus even a balanced diet is inadequate to support lean body mass repletion. A majority of the patients (94%) reported that they did not receive nutritional counseling. Since the focus is only on ensuring drug compliance, health workers are counseling on regular intake of drugs and no effort was made to assess the dietary intake and explore reasons for poor weight gain. Nobody can deny the role of a balanced diet even in normal healthy individuals. Therefore, it is all the more relevant to have a proper diet for a sick person whose rate of metabolism is high and wasting is pronounced. Though no special emphasis on diet is required in the modern management of a TB patient whose general health condition is satisfactory and who is able to take his usual diet, but drugs alone cannot help a patient if his general health condition is poor and is unable to take a proper diet. While giving priority to drugs, we must not forget the importance of a basic, balanced diet in the management of TB.
In conclusion it may be said that proper drugs, diet, improved living conditions and health awareness all play vital roles in handling the problem of TB. Some recommendations that we want to suggest are Nutritional assessment for determination of nutritional status at time of registration of patient. Nutritional counseling/education on symptom management and improved dietary intake during/after TB treatment. Food supplementation to fill in the dietary gap.
References:
1. Christopher Dye, DPhil; Suzanne Scheele, MS; Paul Dolin, DPhil; Vikram Pathania, MBA; Mario C. Raviglione, MD; Global Burden of Tuberculosis : Estimated Incidence, Prevalence, and Mortality by Country ; JAMA. 1999;282:677-686
2. Macallan D. Malnutrition in tuberculosis. Diagnostic Microbiology and Infectious Diseases. 1999; 34:153–157.
3. Goldberg G. Clinical Tuberculosis 1946:E3-E45 F. A. Davis Philadelphia, PA.
4. Van Lettow M, Kumwenda JJ, Harries AD, et al. Malnutrition and the severity of lung disease in adults with pulmonary tuberculosis in Malawi. Int J Tuberc Lung Dis. Feb 2004; 8(2):211-217.
5. Harries AD, Nkhoma WA, Thompson PJ, Nyangulu DS, Wirima JJ. Nutritional status in Malawian patients with pulmonary tuberculosis and response to 63 International Journal of Current Research and Review www.ijcrr.com Vol. 03 issue 03 Mar 2011 chemotherapy. Eur J Clin Nutr. May 1988; 42(5):445-450.
6. Paton NI, Chua YK, Earnest A, Chee CB. Randomized controlled trial of nutritional supplementation in patients with newly diagnosed tuberculosis and wasting. Am J Clin Nutr. Aug 2004; 80(2):460-465.
7. Nutrition and Anaemia, http://www.nfhsindia.org/chapters.html, website accessed on 25/01/2011.
8. RNTCP Performance report, Quarter 1, 2010 , Central TB Division, Directorate General of Health Services, Ministry of Health and Family Welfare, Nirman Bhavan, New Delhi 110108 http://www.tbcindia.org. Accessed on 10/11/2010.
9. Aamchi Mumbai, http://mcgm.gov.in/irj/ portal/anonymous?NavigationTarget= navurl://c4b79f15e55f98176905a7c2c7d 910ee accessed on 10/11/2010.
10. ICMR (1990), recommended dietary intakes for Indians, New Delhi.
11. Zachariah R, Spielmann M.P., Harries A.D. and Salaniponi M.L.; Moderate to severe malnutrition in patients with tuberculosis is a risk factor associated with early death. Transactions of the Royal society of Tropical Medicine and Hygiene (2002) 96, 291-294
12. Evaluation of Nutritional Status of New Tuberculosis Patients at the EffiaNkwanta Regional Hospital, Ghana Med J. 2008 March; 42(1): 22–28.
13. Rakesh C. Gupta, Mayank Vats, Pramod Dadhich, Neeraj Gupta, Mukesh Taylor and Vinita Singh, Nutritional status of young pulmonary tuberculosis patient at tertiary care teaching hospital, Chest, / 124 / 4 / OCTOBER, 2003 SUPPLEMENT , 209S.
|






 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License