IJCRR - 8(14), July, 2016
Pages: 09-13
Date of Publication: 21-Jul-2016
Print Article
Download XML Download PDF
HIGH RATES OF ANTIBIOTIC DRUG RESISTANCE AMONG GRAM-NEGATIVE BACILLI IN LOWER RESPIRATORY TRACT INFECTIONS IN NORTH INDIA
Author: Sheetal Verma, V. Prakash, K. N. Prasad, T. N. Dhol
Category: Healthcare
Abstract:Introduction: Lower respiratory tract infection is a common cause of morbidity and mortality among individuals of all age groups in developing countries. It is caused by wide variety of infectious agents like viruses, bacteria, fungus and parasites. The role of drug resistant bacteria is of most important concern nowadays with fewer antibiotic options available.
Methods: A prospective observational study was conducted in an apex referral hospital among patients of all age groups with symptoms of lower respiratory tract infection (LRTI) for a period of 6 months. The samples included respiratory specimens such as sputum, endotracheal (ET) aspirate and brochoalveolar lavage (BAL). The samples were investigated for bacterial agents by microscopy, culture and anti-microbial susceptibility testing was performed.
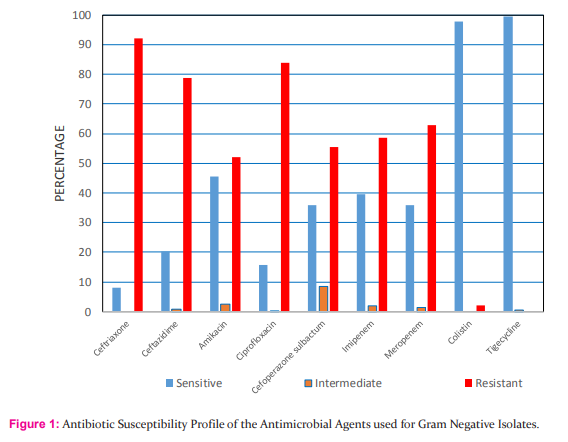
Results: A total of 525 Gram-negative pathogens were isolated from sputum, ET aspirate and BAL fluid specimens during the study period. In 456/525(87%) cases the infection was mono-microbial in nature and in rest 13% cases the infection was polymicrobial type. The gram negative isolates showed high levels of antibiotic resistance to third generation cephalosporins such as ceftriaxone and ceftazidime which were around 92.1% and 78.9% resistant respectively. The resistance to carbapenems was also high. The maximum susceptibility shown by the isolates was for colistin and tigecycline. Mortality was seen in 13% patients with LRTI.
Conclusion: Most of the gram negative isolates obtained from the LRTI samples showed high levels of drug resistance to common antibiotics and showed susceptibility to only high end antibiotics. The findings of the study emphasizes the urgent need for routine surveillance and formulation of antibiotic policies in the hospitals to reduce mortality and morbidity..
Keywords: Gram-negative, Antibiotic, Resistance
Full Text:
INTRODUCTION
Lower respiratory tract infections (LRTI) are one of the commonest diseases among all the age groups which cause high rates of mortality and morbidity worldwide especially in the developing countries like India. LRTI affects the air passages, including the nasal passages, the bronchi and the lungs1 . LRTI includes range of infections from acute infections, such as pneumonia, pleural effusion, pyopneumothorax, bronchitis to chronic conditions such as asthma, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) and tuberculosis. The situation has become even worse with the rising trends of multi-drug resistance (MDR) in gram negative bacterial infections. Various investigators have advised on judicious use of antibiotics must be done by the clinicians, pharmacist and others who are incorporated in drug delivery system so that a check on the emergence of pathogens acquiring drug resistance to various antibiotics having a role in critical condition or emergency2 . The etiological agents of LRTI is diverse in nature. Viruses, bacteria, fungus and parasites all have been implicated as causative agents of the LRTI. Among bacteria Gram-positive bacteria such as Staphylococcus aureus, Streptococcus pneumonia, and Gram-negative bacteria such as Haemophilus influenzae, Pseudomonas, Acinetobacter, and Kleb siella pneumoniae have been implicated as causative agents of LRTI3 . The studies have reported that morbidity and mortality due to LRTI can be due to various factors including characteristics of the population at risk, standard of the health-care facilities available, immunosuppressive drugs, inappropriate antibiotic therapy, distribution of causative agents and prevalence of antimicrobial resistance4 . With knowledge of local pathogen prevalence and antibiogram the physician can implement the initial empirical antimicrobial therapy which is more promising as per epidemiological data and has greater chances of decreasing the risk of death and morbidities 5 6. There is paucity of information on the profile of antimicrobial agents among LRTI in our settings. Therefore the present prospective observational study was conducted with the aims to study the etiological agents’ distribution causing LRTI and the emergence of resistance among the antimicrobial agents used for treatment of gram negative infections.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
In the present study, lower respiratory specimens included sputum, endotracheal aspirate and broncho-alveolar lavage fluid (BAL) were collected from patients of all age groups during the period of six months. The samples were collected from patients with clinical suspicion of LRTIs which included fever, presence of purulent sputum on expectoration or positive pulmonary findings on physical examination or radiological findings. The adequate amount of sample was collected in sterile, clean and leak-proof universal container and then transported to the microbiology laboratory within 2 hours of collection. The samples when received in the laboratory were processed immediately without any delay for gram staining, culture and susceptibility testing. The sputum samples which on gram staining showed less than 25 leucocytes and fewer than 10 squamous epithelial cells per field read under oil immersion objective (x100) were rejected for further processing and considered as inadequate and heavily contaminated with oropharyngeal flora containing saliva. The processing was done in BSL-2 taking all aseptic precautions. After direct gram staining was performed the samples were plated on Blood agar, Chocolate agar and MacConkey agar. The plates after inoculation were incubated at 37°C for 18-24 hours. The morphological, physiological, and biochemical features of the bacterial isolates were determined according to Mackie and McCartney7 . Antimicrobial susceptibility testing were performed on significant bacterial isolates using the Kirby-Bauer disk diffusion method, following the recommendations of the Clinical and Laboratory Standard Institute (CLSI, 2015)8 . Mueller Hinton agar (MHA) was prepared with addition of 5% sheep blood. A 0.5 McFarland turbidity standard equivalent bacteria suspension for inoculation was prepared and inoculated. Antibiotic disks (Hi-Media) were applied and the plate was incubated at 37°C for 18-24 hours. The following antibiotics were used: Ceftriaxone (30µg), Ceftazidime (30µg), Amikacin (30 µg), Ciprofloxacin (5 µg), Imipenem (10 µg), Meropenem (10µg), Cefoperazone sulbactum (75 µg +30 µg), Colistin (10 µg) and Tigecycline (15 µg).The strains of E. coli ATCC 25922, P. aeruginosa ATCC 27853 and K. pneumoniae ATCC 700603 were used for assessing quality control. Only one sample from each patient was included in final analysis.
Statistical Analysis
The Statistical Package for Social Science (SPSS) version 18.0 software was used for the descriptive statistical analysis of the data of the sample population. The frequencies and percentages were calculated for variables under study.
RESULTS
A total of 525 gram negative isolates were obtained from sputum, ET aspirate and BAL specimens received in microbiology laboratory during the study period of 6 months. 456/492(92.6%) patients had only monomicrobial infection 36/492 (7.4%) had mixed and polymicrobial infection with more than one type of gram negative bacteria recovered from the sample. It was found that Acinetobacter baumanii 28.1% (148/525) was most common isolate found in the study followed by Klebsiella pneumonia 24.8%(130/525) and Escherichia coli was found in about 17.1% (90/525) cases. The gram negative pathogens isolated from patients with LRTI is shown in Table-I. The majority of isolates were found to be resistant to the third generation cephalosporins like ceftriaxone and ceftazidime. 78.9% of the isolates were resistant to ceftazidime and 92.1% isolates were resistant to the ceftriaxone. Only 45.4% of the gram negative isolates were found to be sensitive to the amikacin. The carbapenem drugs imipenem and meropenem also showed high level of drug resistance 58.6% and 62.9% respectively. Around 84% of isolates were resistant to ciprofloxacin. The only two drugs which showed high sensitivity to the isolates were colistin (97.8%) and tigecycline (99.6%). The susceptibility profile of all the antimicrobial agents is shown in Fig.1. On follow-up it was found that mortality was around 13% and 47 patients (9.5%) had left against medical advice and 77.4% patient were discharged after improvement.
DISCUSSION
The current study conducted in a referral centre shows that the gram negative isolates were the predominant pathogens in patients with LRTI. The predominance of Acinetobacter baumanii (28.1%), followed by Klebsiella pneumoniae (24.8%) and Escherichia coli in (17.1%) cases. Pseudomonas aeruginosa (12.7%), Pseudomonas sp. (10.6%) and Acinetobacter lwofii (2.3%) were also found in significant number of patients with LRTI. This is in contrast to other studies which have shown Pseudomonas sp9 ., Klebsiella pneumoniae5 , Haemophilus influenzae10 as common isolates obtained in such patients. In a multicentric study conducted in 366 patients gram negative etiological agents isolated were Haemophilus influenzae (78), Pseudomonas aeruginosa (46), Pseudomonas species (14) and Klebsiella pneumoniae in 21 patients9 . In another similar study conducted among 200 patients in India it was found that the gram negative pathogens causing LRTI, in decreasing order, were Klebsiella pneumoniae (36.79%), Pseudomonas aeruginosa (11.92%), Escherichia coli (5.7%) and Proteus mirabilis (2.59%) which is similar to our settings11.It is interesting to find that the Acinetobacter baumanii was the most coomon isolate which is quite different to the other such studies. The prevalence of pathogenic agents varies across the different geographical regions12. Therefore there is need to upgrade the knowledge of the etiological bacterial agents which are causative pathogens in patients with lower respiratory tract infections in a given population so that the trends of bacterial profile can be monitored and this will guide in the empirical drug of choice in a given population and guide antibiotic policy of local region. This will be extremely beneficial for the patients of high risk area and will curtail down the morbidity and mortality in such defined populations. So advantage of the monitoring will be beneficial both for therapeutic and epidemiological purposes. As per the World Health Organization (WHO) there are high proportions of antibiotic resistance in bacteria that cause common infections especially pneumonia infections in all regions of the world13. These patients with LRTI infections caused by drug-resistant gram negative bacteria are generally at increased risk of poor prognosis and death and also responsible for the economic losses14. The rise of antimicrobial resistance is of utmost importance in Gram-negative bacteria because we have very few antibiotics for this particular pathogen group15. In the present study the rates of resistance of common antibiotics used for respiratory infections showed high level of resistance. The ceftazidime was resistant in 78.9%, ceftriaxone (92.1%), amikacin (52.1%) and ciprofloxacin (84%) cases. In a similar study conducted among 227 patients it was found that most of the bacterial isolates were susceptible to gentamicin (80.9%), meropenem (75%), ceftazidime (62.5%), cefotaxime (57.9%) and ceftriazone (57.9%) 16.In our study we report even higher burden of resistance than previously reported. In the recent years several investigators across the globe have reported increase in the antibiotic drug resistant strains and this appears mostly due to several factors like prolonged and inappropriate use of invasive devices and antibiotics17. The other factors like high risk sophisticated procedures, immune-suppression and insufficient application of standard and isolation precautions also are attributed to emerging resistance18.There is also confusion among the clinicians over the aetiology of lower respiratory tract infections when treating patients when they face limited diagnostic facilities options especially in resource setting conditions. Limited data forces them to use combined therapy for long duration which further worsens the situation and increases the chances of emergence of more drug resistant strains. The first line drugs which were cheap become ineffective and patients are put on high end costly drugs which cause economical loss for the patients19. Thus this study gives a guide to physician about gram negative etiological agents and antibiotic resistance profile of antimicrobial agents especially in hospitals which have no antibiotic policy.
CONCLUSION
The recent years have witnessed the increase in the multidrug resistant strains across the globe especially in the setting of the nosocomial and hospital acquired infections. It leads to increased mortality, prolonged hospital stay, treatment failure, spread of drug resistant strains in the community, selection pressure, threat of pre-antibiotic era and increased burden on the health costs. The emergence of drug resistance is usually multifactorial in nature and affects the patients and the hospital or other health care facility. The rise is mostly attributed to the inappropriate use of antibiotics, understaffing, overcrowding, poor health infrastructure, antibiotic abuse in animals and absence of the local and national guidelines and policies. The increase in MDR isolates from respiratory tract infections is alarming and must be treated with the results based upon the antibiotic susceptibility pattern of the organisms isolated. There is also the need to differentiate the pathogens and colonizers before starting the treatment to prevent further emergence of the MDR strains and it can be done with correlation of the clinical and laboratory parameters.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENT
Authors acknowledge the immense help received from the scholars whose articles are cited and included in references of this manuscript. The authors are also grateful to authors / editors / publishers of all those articles, journals and books from where the literature for this article has been reviewed and discussed.
Source of Funding: Nil
Conflict of interest: Nil
References:
1. Vijay S, Dalela G. Prevalence of LRTI in Patients Presenting with Productive Cough and Their Antibiotic Resistance Pattern. Journal of Clinical and Diagnostic Research. 2016;10(1):DC09- DC12
2. Khan S, Priti S, Ankit S. Bacteria Etiological Agents Causing Lower Respiratory Tract Infections and Their Resistance Patterns. Iranian biomedical journal. 2015;19(4):240
3. Kumari HBV, Nagarathna S, Chandramuki A. Antimicrobial resistance pattern [5] among aerobic gram-negative bacilli of lower respiratory tract illness in the community. Thorax. 2007;56:109-14.
4. Idelevich EA, Lanckohr C, Horn D, Wieler LH, Becker K. Antibiotika-resistente Erreger in Deutschland. Bundesgesundheitsblatt-Gesundheitsforschung-Gesundheitsschutz. 2016;59(1):113- 23.
5. Vishwanath S, Chawla K, Gopinathan A. Multidrug resistant Gram-negative bacilli in lower respiratory tract infections. Iranian journal of microbiology. 2013;5(4):323.
6. Gagneja D, Goel N, Aggarwal R, Chaudhary U. Changing trend of antimicrobial resistance among gram-negative bacilli isolated from lower respiratory tract of ICU patients: A 5-year study. Indian Journal of Critical Care Medicine. 2011 Jul 1;15(3):164.
7. Collee JG, Fraser AG, Marmion BP, Simmons A. Practical medical microbiology. Practical medical microbiology. Fourteenth edition.1996.
8. Jorgensen JH, Turnidge JD. Susceptibility Test Methods: Dilution and Disk Diffusion Methods. 2015:1253-1273.
9. Manyahi et al. BMC Research Notes 2014, 7:500 http://www. biomedcentral.com/1756-0500/7/500
10. Goto H, Takeda H, Kawai S, Watanabe S, Okazaki M, Shimada K, Nakano K, et al. Susceptibilities of bacteria isolated from patients with lower respiratory infectious diseases to antibiotics. Jpn J Antibiot. 2008;61(4):209-40.
11. Vijay S, Dalela G. Prevalence of LRTI in Patients Presenting with Productive Cough and Their Antibiotic Resistance Pattern. Journal of Clinical and Diagnostic Research. 2016;10(1): DC09- DC12
12. Egbe CA, Ndiokwere C and Omoregie R. Microbiology of lower respiratory tract infections in Benin City, Nigeria. Malays. J. Med. Sci. 2011;18(2): 27-31.
13. World Health Organization. http://www.who.int/mediacentre/ factsheets/fs194/en/
14. Poulikakos P, Tansarli GS, Falagas ME. Combination antibiotic treatment versus monotherapy for multidrug-resistant, extensively drug-resistant, and pandrug-resistant Acinetobacter infections: a systematic review. European Journal of Clinical Microbiology and Infectious Diseases. 2014;33(10):1675-85.
15. Boucher HW, Talbot GH, Bradley JS, Edwards JE, Gilbert D, Rice LB, Scheld M, Spellberg B, Bartlett J. Bad bugs, no drugs: no ESKAPE! An update from the Infectious Diseases Society of America. Clinical Infectious Diseases. 2009;48(1):1-2.
16. Shah SN, Ullah B, Basit A, Begum A, Tabassum A, Zafar S, Saleha S. Prevalence and susceptibility patterns of bacteria causing respiratory tract infections in North Waziristan, Pakistan. Pakistan journal of pharmaceutical sciences. 2016;29(2 Suppl):701-6.
17. Tacconelli E, Cataldo MA, Dancer SJ, Angelis G, Falcone M, Frank U, Kahlmeter G, Pan A, Petrosillo N, Rodríguez-Baño J, Singh N. ESCMID guidelines for the management of the infection control measures to reduce transmission of multidrug-resistant Gram-negative bacteria in hospitalized patients. Clinical Microbiology and Infection. 2014;20(s1):1-55.
18. Spellberg B, Bartlett JG, Gilbert DN. The future of antibiotics and resistance. New England Journal of Medicine. 2013;368(4):299- 302.
19. Worthington RJ, Melander C. Combination approaches to combat multidrug-resistant bacteria. Trends in biotechnology. 2013;31(3):177-84.

|






 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License