IJCRR - 2(11), November, 2010
Pages: 14-26
Print Article
Download XML Download PDF
1,3,4-THIADIAZOLE AS ANTIINFLAMMATORY AGENT:A REVIEW
Author: Mehnaz Kamal, Ashok K Shakya, Talha Jawaid
Category: Healthcare
Abstract:1,3,4-Thiadiazole nucleus exhibited remarkable pharmacological activities. Literature indicates that compounds having 1,3,4-Thiadiazole nucleus have wide range of pharmacological activities that include antibacterial, antifungal, antitubercular, antiviral, antileishmanial, anti-inflammatory, analgesic, CNS depressant, anticonvulsant, anticancer, antioxidant, antidiabetic, molluscicidal, antihypertensive, diuretic. The present review provides a broad view of the anti-inflammatory activity possessed by compounds having a 1,3,4-Thiadiazole nucleus.
Keywords: Review; 1, 3, 4-Thiadiazole; Chemistry; anti-inflammatory Activity
Full Text:
Introduction
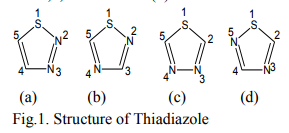
One of the main objectives of organic and medicinal chemistry is the design, synthesis and production of molecules having value as human therapeutic agents. During the past decade, combinatorial chemistry has provided access to chemical libraries based on privileged structures [1], with heterocyclic structures receiving special attention as they belong to a class of compounds with proven utility in medicinal chemistry [2]. There are numerous biologically active molecules with five membered rings, containing three hetero atoms. Thiadiazole is an important scaffold known to be associated with several biological activities (Fig.1.).
Chemistry of 1,3,4-Thiadiazole
Thiadiazole is a five membered heterocyclic compound. It contains two nitrogen atoms and one sulphur atom as hetero atoms. Thiadiazole may be of 1,2,3- thiadiazoles (a) ; 1,2,4- thiadiazole (b) ; 1,3,4-thiadiazole (c) and 1,3,5-thiadiazole (d).
Anti-inflammatory properties:
Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) are an inhomogeneous family of pharmacologically active compounds used in the treatment of acute and chronic inflammation, pain, and fever. The inhibition of prostaglandin E2 (PGE2) and nitric oxide (NO) production has been proposed as a potential therapy for different inflammatory disorders. Large amounts of NO may lead to tissue damage. In inflammatory diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis, excessive NO production by activated macrophages has been observed. Therefore, it would be interesting to develop potent and selective inhibitors of NO for potential therapeutic use.
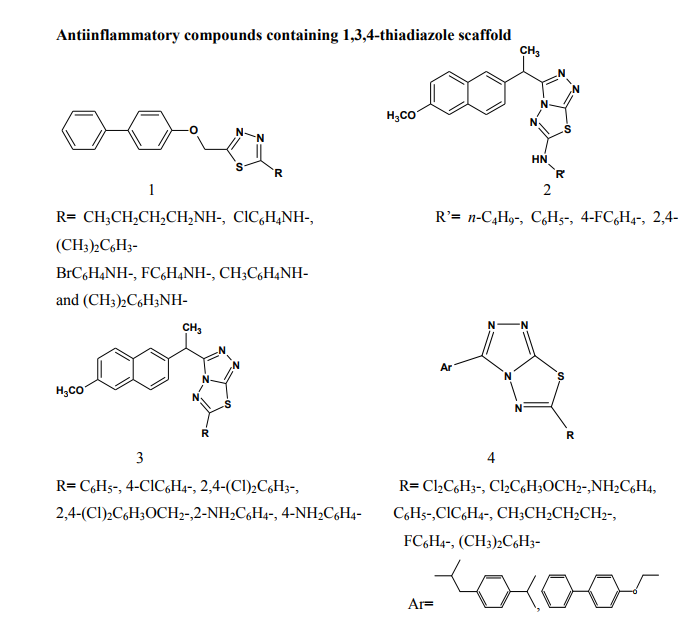
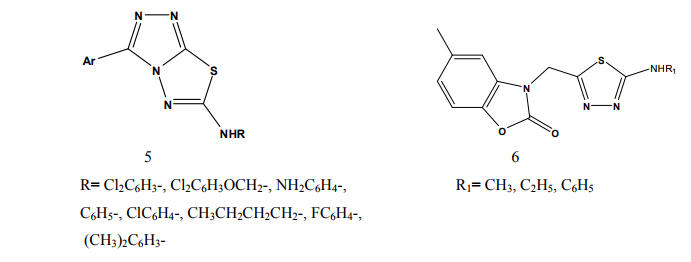
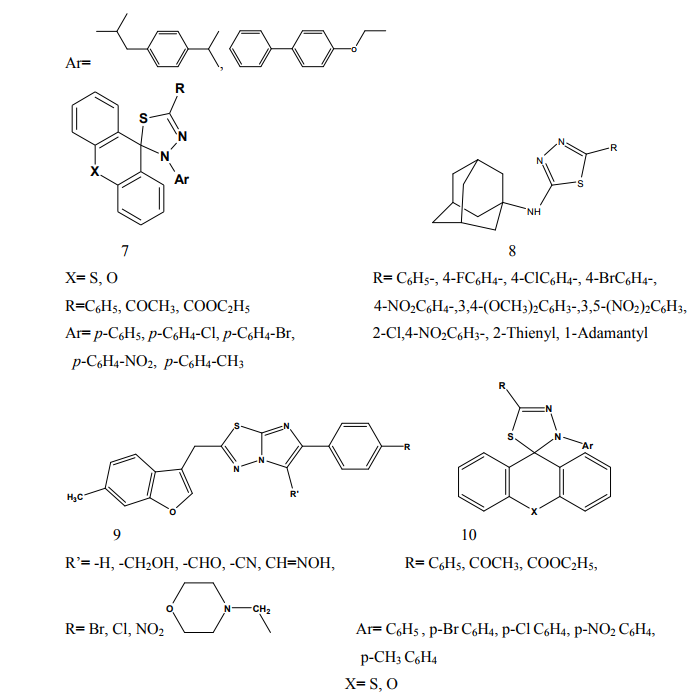
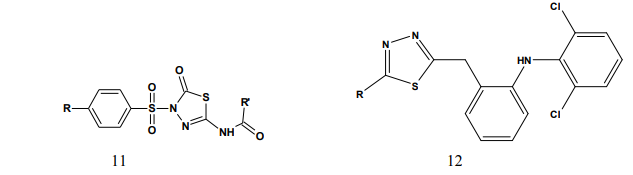
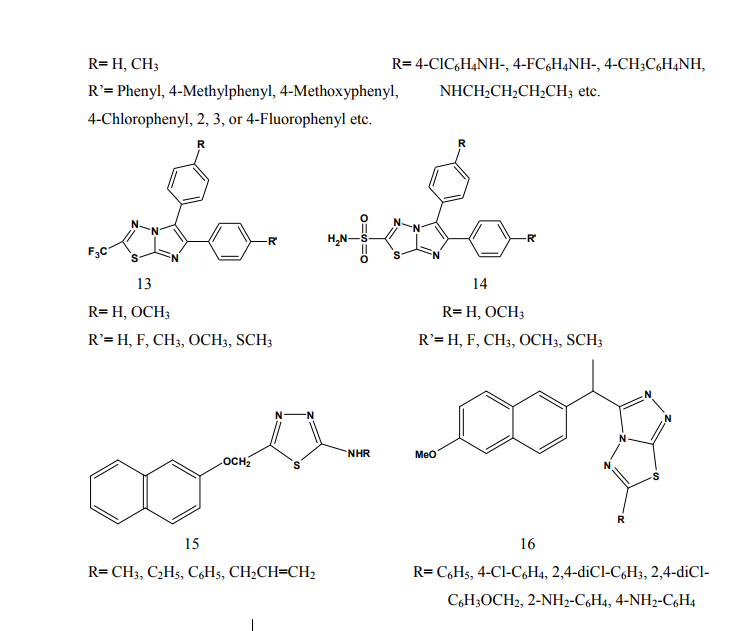
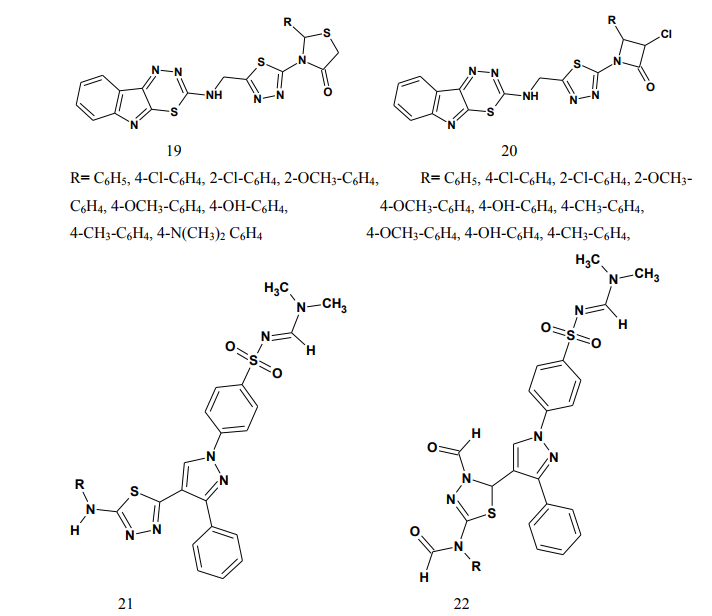
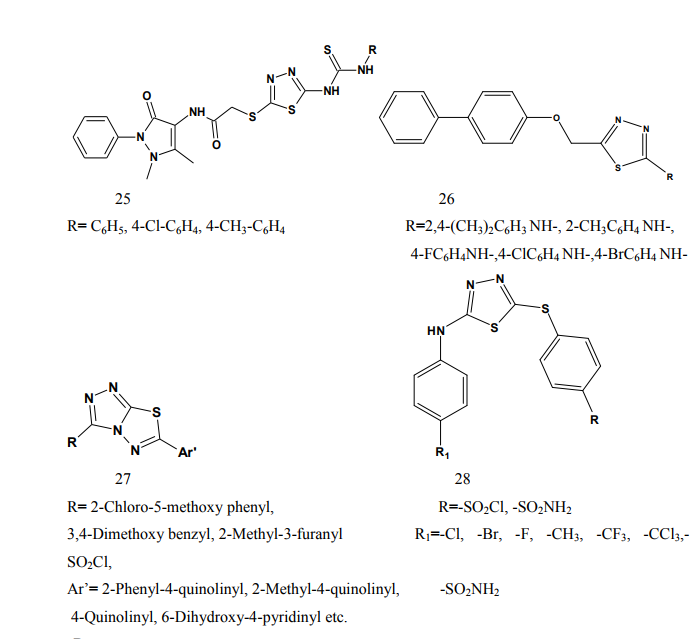
Kumar et al.(2008) synthesized a series of 1,3,4-thiadiazole derivatives of biphenyl-4-yloxy acetic acid (1) in order to obtain new compounds with potential anti-inflammatory activity, analgesic activity and lower ulcerogenic potential. All compounds were evaluated for their anti-inflammatory activity by the carrageenan induced rat paw edema test method. The compounds possessing potent antiinflammatory activity were further tested for their analgesic, ulcerogenic and antioxidant activities. Some compounds showed significant reduction in rat paw edema induced by carrageenan treatment. These compounds showed significant analgesic effect and at an equimolar oral doses relative to flurbiprofen were also found to be non-gastrotoxic in rats [3]. Amir et al.(2007) synthesized some 6- substituted-1,2,4-triazolo[3,4-b]-1,3,4- thiadiazole derivatives (2-3). The compounds were pharmacologically evaluated for their anti-inflammatory and analgesic potentials by known experimental models. Several of these showed significant activity. Very low ulcerogenic index was observed for potent compounds [4]. Amir et al.(2007) prepared several 3,6- disubstituted-1,2,4-triazolo-[3,4-b]- 1,3,4-thiadiazoles (4-5). These compounds were investigated for their anti-inflammatory, analgesic, ulcerogenic, lipid peroxidation, antibacterial and antifungal activities. Some of the synthesized compounds showed potent anti-inflammatory activity along with minimal ulcerogenic effect and lipid peroxidation, compared to those of ibuprofen and flurbiprofen. Some of the tested compounds also showed moderate antimicrobial activity against tested bacterial and fungal strains [5]. Goksen et al.(2007) synthesized 1,3,4- thiadiazoles containing 5-methyl-2- benzoxazolinones (6). Most of the compounds were exhibiting high activity in analgesic-anti-inflammatory field [6]. Hafez et al.(2008) synthesized novel spiro-thioxanthene-9',2- [1,3,4]thiadiazoles and spiro-xanthene- 9',2-[1,3,4]thiadiazoles (7). The newly synthesized compounds were tested for anti-inflammatory and analgesic activities comparable to ibuprofen.
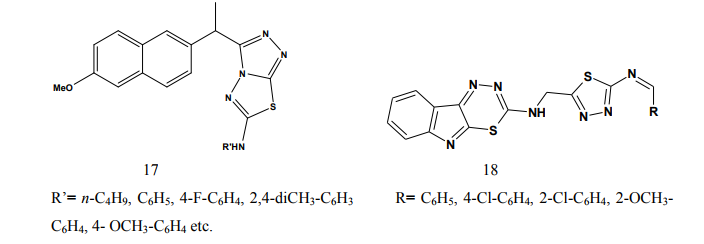
Some of the compounds showed significant activity compared to standard drug [7]. Kadi et al.(2007) synthesized novel 2- (1-adamantyl)-5-substituted-1,3,4- oxadiazoles and 2-(1 adamantylamino)- 5-substituted-1,3,4-thiadiazoles (8). The in vivo anti-inflammatory activity of the synthesized compounds was determined using the carrageenin-induced paw edema method in rats. The oxadiazole derivatives produced good dosedependent anti-inflammatory activity [8]. Jadhav et al.(2008) synthesized a series of 6-substituted and 5,6-disubstituted 2- (6-methyl-benzofuran-3-ylmethyl)- imidazo[2,1-b][1,3,4]thiadiazoles (9). The new compounds have been tested for their in vivo analgesic, antiinflammatory activities. Qualitative SAR studies indicate that the chloro substitution in the imidazole ring and introduction of formyl group at C-5 position of the imidazole ring increased the anti-inflammatory and analgesic activity [9]. Hafez et al.(2008) synthesized novel spiro-thioxanthene-9',2- [1,3,4]thiadiazoles and spiro-xanthene- 9',2-[1,3,4]thiadiazoles (10). Some of the newly synthesized compounds were tested for anti-inflammatory and analgesic activities comparable to ibuprofen. Most of the compounds showed significant activity compared to standard drug [10]. Schenone et al.(2006) synthesized two series of N-[5-oxo-4-(arylsulfonyl)-4,5- dihydro-1,3,4-thiadiazol-2-yl]-amides (11) and tested in vivo for their analgesic and anti-inflammatory activities. All the new compounds possess good antalgic action in the acetic acid writhing test and some terms of the series showed also fair antiinflammatory activity in the carrageenan rat paw edema test [11]. Amir and Kumar(2004) synthesized new 1,3,4-thiadiazoles derived from 2- [(2,6-dichloroanilino) phenyl] acetic acid (12). These compounds were tested in vivo for their anti-inflammatory activity. Some compounds showed very good anti-inflammatory activity in the carrageenin induced rat paw edema test, with significant analgesic activity in the acetic acid induced writhing test together with negligible ulcerogenic action. The compounds, which showed less ulcerogenic action, also showed reduced malondialdehyde content (MDA), which is one of the byproduct of lipid peroxidation [12]. Gadad et al.(2008) synthesized a series of 2-trifluoromethyl/sulfonamido-5,6- diarylsubstituted imidazo[2,1-b]-1,3,4- thiadiazole derivatives (13-14). The selected compounds were evaluated for their preliminary in vitro cyclooxygenase inhibitory activity against COX-2 and COX-1 enzymes using colorimetric method. The compounds tested showed selective inhibitory activity toward COX-2 (80.6-49.4%) over COX-1 (30.6-8.6). These compounds also exhibited significant anti-inflammatory activity (70.09-42.32%), which is comparable to that of celecoxib in the carrageenaninduced rat paw edema method [13]. Palaska et al.(2002) synthesized 2-(2- naphthyloxymethyl)-5-substituted amino-1,3,4-thiadiazole derivatives (15) and evaluated as orally active antiinflammatory agents with reduced sideeffects. The anti-inflammatory and ulcerogenic activities of the compounds were compared with naproxen, indomethacin and phenylbutazone. In carrageenan-induced foot pad edema assay some compounds showed an interesting anti-inflammatory activity. Side effects of the compounds were examined on gastric mucosa, liver and stomach and none of the compounds showed significant side effects compared with reference nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) [14]. Amir et al.(2007) synthesized some 6- substituted-1,2,4-triazolo[3,4-b]-1,3,4- thiadiazole derivatives (16-17) by cyclisation of 4-amino-5-[1-(6- methoxy-2-naphthyl)ethyl]-3-mercapto- (4H)-1,2,4-triazole with various substituted aromatic acids and aryl/ alkyl isothiocyanates. The compounds were evaluated for their antiinflammatory and analgesic potentials by known experimental models. Several of these showed significant activity [15]. Bhati and Kumar(2008) synthesized various N-({5-[(arylmethylene)amino]- 1,3,4-thiadiazol-2-yl}methyl) [1,3,4] thiadiazino[6,5-b]indol-3-amine (18), 2- aryl-3-{5-[([1,3,4] thiadiazino[6,5- b]indol-3-ylamino)methyl]-1,3,4- thiadiazol-2-yl}-1,3-thiazolidin-4-one (19) and 3-chloro-4-aryl-1-{5- [{[1,3,4]thiadiazino[6,5-b]indol-3- ylamino]methyl]-1,3,4-thiadiazol-2- yl}azetidin-2-one (20). One compound has shown most active antiinflammatory and analgesic activities with better ulcerogenic activity than phenylbutazone, while this compound was found to be associated with lesser degree of anti-inflammatory and analgesic activities as compared to indomethacin [16]. Bekhit et al.(2008) synthesized some thiazolyl and thiadiazolyl derivatives of 1H-pyrazole (21-22). All the target compounds showed anti-inflammatory activity and three of them surpassed that of indomethacin both locally and systemically in the cotton pellet granuloma and rat paw edema bioassay.[17]. Schenone et al.(2001) synthesized two series of 3-arylsulphonyl-5-arylamino- 1,3,4-thiadiazol-2(3H)ones (23) with potential anti-inflammatory and analgesic activity. Pharmacological results revealed that all the title compounds possess good antalgic activity and fair anti-inflammatory properties [18]. Rostom et al.(2009) described the synthesis of two groups of structure hybrids comprising basically the antipyrine moiety attached to polysubstituted 2,5-disubstituted-1,3,4-
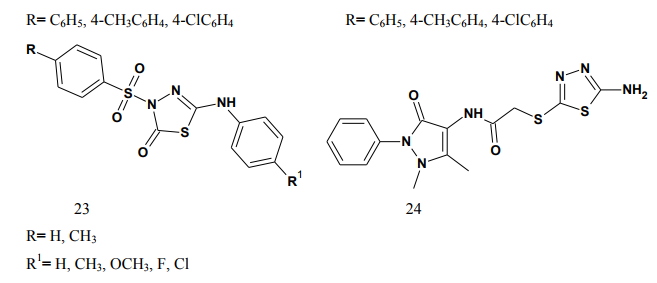
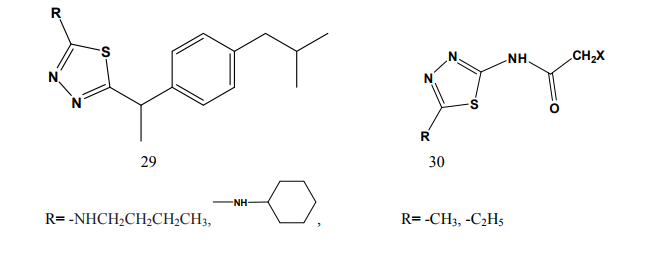
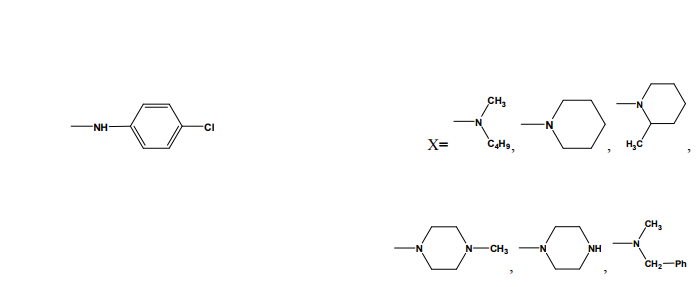
thiadiazole (24-25) through various linkages. The newly synthesized compounds were evaluated for their anti-inflammatory activity using two different screening protocols; namely, the formalin-induced paw edema and the turpentine oil-induced granuloma pouch bioassays, using diclofenac Na as a reference standard. Meanwhile, the analgesic activity of the same compounds was evaluated using the rat tail withdrawal technique. In general, compounds belonging to the thiazolylantipyrine series exhibited better biological activities than their thiadiazolyl structure variants [19]. Kumar et al.(2008) synthesized a series of 1,3,4-thiadiazole derivatives of biphenyl-4-yloxy acetic acid (26) in order to obtain new compounds with potential anti-inflammatory activity, analgesic activity and lower ulcerogenic potential. The compounds possessing potent anti-inflammatory activity were further tested for their analgesic, ulcerogenic and antioxidant activities. Out of all tested compounds, the some compounds showed significant reduction in rat paw edema induced by carrageenan treatment [20]. Mathew et al.(2007) synthesized several 3,6-disubstituted-1,2,4- triazolo[3,4-b]-1,3,4-thiadiazole and their dihydro analogues (27). Antiinflammatory and analgesic activity screening indicated that some of the tested compounds showed good and some showed moderate antiinflammatory and analgesic activities [21]. Sharma et al.(2008) synthesized a new series of cyclooxygenase-2 inhibitors with 2-amino- -5-sulfanyl-1,3,4-thiadiazole (28) as the central scaffold unit. Some compounds exhibited significant biological activity [22]. Amir and Kumar(2007) synthesized various 1,3,4-thiadiazoles derivatives of ibuprofen (29). The cyclized derivatives were screened for their antiinflammatory activity by the carrageenan induced rat paw edema method and showed 50 to 86% inhibition, whereas the standard drug ibuprofen showed 92% inhibition at the same oral dose [23]. Mishra et al.(1992) synthesized new Nsubstituted acetyl derivetives of 2- amino-5-alkyl-1,3,4-thiadiazoles (30) and evaluated for anti-inflammatory activity. Some of the compounds showed anti-inflammatory activity [24].



References:
1. Horton DA, Bourne GT, Smyth ML. Chem. Rev. 2003; 103: 893.
2. (a) Thompson LA, Ellman JA. Chem. Rev. 1996; 96: 555; (b) Fruchtel JS, Jung G, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 1996; 35:17; (c) Nefzi A, Ostresh JM, Houghten RA. Chem. Rev. 1997; 97: 449; (d) Frazen RG. J. Comb. Chem. 2000; 2: 195.
3. Kumar H, Javed SA, Khan SA, Amir M. Synthesis and pharmacological evaluation of condensed heterocyclic 6- substituted-1,2,4-triazolo[3,4-b]-1,3,4- thiadiazole derivatives of naproxen. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2008; xx: 1-11.
4. Amir M, Kumar H, Javed SA. Synthesis and pharmacological evaluation of condensed heterocyclic 6-substituted- 1,2,4-triazolo[3,4-b]-1,3,4-thiadiazole derivatives of naproxen. Bioorg. and Med. Chem. Lett. 2007; 17: 4504-4508.
5. Amir M, Kumar H, Javed SA. Condensed bridgehead nitrogen heterocyclic system: Synthesis and pharmacological activities of 1,2,4-triazolo-[3,4-b]-1,3,4-thiadiazole derivatives of ibuprofen and biphenyl-4- yloxy acetic acid. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2007; xx: 1-11.
6. Goksen US, Kelekci NG, Goktas O, Koysal Y, K?l?c E, Is?k S, Aktay G, Zalp MO. 1-Acylthiosemicarbazides, 1,2,4-triazole-5(4H)-thiones, 1,3,4-thiadiazoles and hydrazones containing 5- methyl-2-benzoxazolinones: Synthesis, analgesic-anti-inflammatory and antimicrobial activities. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2007; 15: 5738-5751.
7. Hafez HN, Hegab MI, Ahmed-Farag IS, El-Gazzar ABA. A facile regioselective synthesis of novel spiro-thioxanthene and spiro-xanthene-9',2-[1,3,4]thiadiazole derivatives as potential analgesic and anti-inflammatory agents. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2008; 18: 4538-4543.
8. Kadi AA, El-Brollosy NR, Al-Deeb OA, Habib EE, Ibrahim TM, El-Emam AA. Synthesis, antimicrobial, and antiinflammatory activities of novel 2-(1- adamantyl)-5-substituted-1,3,4- oxadiazoles and 2-(1-adamantylamino)-5- substituted-1,3,4-thiadiazoles. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2007; 42: 235-242.
9. Jadhav VB, Kulkarni MV, Rasal VP, Biradar SS, Vinay MD. Synthesis and anti-inflammatory evaluation of methylene bridged benzofuranyl imidazo[2,1-b][1,3,4]thiadiazoles. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2008; 43: 1721-1729.
10. Hafez HN, Hegab MI, Ahmed-Farag IS, El-Gazzar AB. A facile regioselective synthesis of novel spiro-thioxanthene and spiro-xanthene-9',2- [1,3,4]thiadiazole derivatives as potential analgesic and antiinflammatory agents. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2008; xxx: xxx-xxx.
11. Schenone S, Brullo C, Bruno O, Bondavalli F, Ranise A, Filippelli W, Rinaldi B, Capuano A, Falcone G. New 1,3,4-thiadiazole derivatives endowed with analgesic and anti-inflammatory activities. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2006; 14: 1698-1705.
12. Amir M, Shikha K. Synthesis and antiinflammatory, analgesic, ulcerogenicand lipid peroxidation activities of some new 2-[(2,6-dichloroanilino) phenyl]acetic acid derivatives. Eur. J. Med. Chemistry 2004; 39: 535-545.
13. Gadad AK, Palkar MB, Anand K, Noolvi MN, Boreddy TS, Wagwade J. Synthesis and biological evaluation of 2- trifluoromethyl/sulfonamido-5,6-diaryl substituted imidazo[2,1-b]-1,3,4- thiadiazoles: A novel class of cyclooxygenase-2 inhibitors. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2008; 16: 276-283.
14. Palaska E, Sahin G, Kelicen P, Durlu NT, Altinok G. Synthesis and antiinflammatory activity of 1- acylthiosemicarbazides, 1,3,4- oxadiazoles, 1,3,4-thiadiazoles and 1,2,4-triazole-3-thiones. Il Farmaco 2002; 57: 101-107.
15. Amir M, Kumar H, Javed SA. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2007; 17: 4504-4508.
16. Bhati SK, Kumar A. Synthesis of new substituted azetidinoyl and thiazolidinoyl-1,3,4-thiadiazino (6,5-b) indoles as promising anti-inflammatory agents. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2008; 43: 2323-2330.
17. Bekhit AA, Ashour HMA, Abdel Ghany YS, Bekhit AA, Baraka A. Synthesis and biological evaluation of some thiazolyl and thiadiazolyl derivatives of 1H-pyrazole as antiinflammatory antimicrobial agents. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2008; 43: 456-463.
18. Schenone S, Bruno O, Ranise A, Bondavalli F, Filippelli W, Falcone G, Giordano L, Vitelli MR. 3- Arylsulphonyl-5-arylamino-1,3,4- thiadiazol-2(3H)ones as Antiinflammatory and Analgesic Agents. Bioorg. and Med. Chemistry 2001; 9: 2149-2153.
19. Rostom SAF, El-Ashmawy IM, Razik HA, Badr MH, Ashour HMA. Design and synthesis of some thiazolyl and thiadiazolyl derivatives of antipyrine as potential non-acidic anti-inflammatory, analgesic and antimicrobial agents. Bioorg. and Med. Chemistry 2009; 17: 882-895.
20. Kumar H, Javed SA, Khan SA, Amir M. 1,3,4-Oxadiazole/thiadiazole and 1,2,4- triazole derivatives of biphenyl-4-yloxy acetic acid: Synthesis and preliminary evaluation of biological properties. Eur. J. Med. Chemistry 2008; 43: 2688-2698.
21. Mathew V, Keshavayya J, Vaidya VP, Giles D. Studies on synthesis and pharmacological activities of 3,6- disubstituted-1,2,4-triazolo[3,4-b]-1,3,4- thiadiazoles and their dihydro analogues. Eur. J. Med. Chemistry 2007; 42: 823- 840.
22. Sharma R, Sainy J, Chaturvedi SC. 2- Amino-5-sulfanyl-1,3,4-thiadiazoles: A new series of selective cyclooxygenase- 2 inhibitors. Acta Pharm. 2008; 58: 317- 326.
23. Amir M, Kumar S. Synthesis and evaluation of anti-inflammatory, analgesic, ulcerogenic and lipid peroxidation properties of ibuprofen derivatives. Acta Pharm. 2007; 57: 31- 45.
24. Shakya AK, Patnaik GK, Mishra P. Synthesis and Biological evaluation of 2-[substituted acetyl]amino-5-alkyl- 1,3,4-thiadiazoles. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 1992; 27: 67-71.
|






 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License