IJCRR - 3(5), May, 2011
Pages: 64-72
Print Article
Download XML Download PDF
BIOACCUMULATION OF MERCURY AND CHROMIUM IN A FRESHWATER FISH CLARIAS BATRACHUS
Author: Mary Josephine Rani A, John Milton MC, Uthiralingam M , Azhaguraj R
Category: General Sciences
Abstract:In the present study Clarias batrachus was exposed to sublethal concentrations (~10% of 96 h-
LC50) of mercury (0.080ppm) and chromium (10.2ppm) were investigated for 28 days under
laboratory conditions. The concentrations of these metals in the various organs were detected
through Inductively Coupled Plasma\?Atomic Emission Spectrometer (ICP-AES). The
concentration of mercury was high in brain (656.82ppb) followed by gills (287.63ppb), liver
(229.64ppb), kidney (176.44ppb) and muscles (49.21ppb) where as in the fishes exposed to
chromium, the concentration was high in gills (315.21ppb) followed by liver (241.4ppb), kidney
(187.96ppb), brain (128.29ppb) and muscles (51.3ppb).The ability of mercury and chromium as
toxicants was proved in the present study as the concentrations was found to be high in brain and
gills respectively.
Keywords: Clarias batrachus, heavy metals, ICP-AES
Full Text:
INTRODUCTION
Over the last few decades, there has been growing interest in determining heavy metal levels in the aquatic environment and attention was drawn to the measurement of contamination levels in public food supplies, particularly fish. Metals are nonbiodegradable and are considered as major environmental pollutants causing cytotoxic, mutagenic and carcinogenic effects in animals (Kamaruzzaman, et al., 2010). Heavy metal contamination may have devastating effects on the ecological balance of the recipient environment and a diversity of aquatic organisms (Farombi, et al., 2007). Mercury, the black listed element by environmentalists, is released into the environment by several sources, such as mining and fossil fuel combustion, thermal power project, by the use of fungicides, bactericides and pharmaceuticals (Khangarot, 2003). A great deal of research concerning the effects of mercury on terrestrial and aquatic biota has demonstrated the potential risk that it represents because of its toxicity, accumulation and its tendency to biomagnify and also because of its properties like mobility and transformation in the environment, and its presence in humans (Francisco, 2004). Mercury in the organic form is the most toxic as it passes the blood brain barrier owing to its lipid solubility (Farhana et al., 2005). These heavy metal ions can exert their toxic effect through the gills, liver, kidney and brain (Velma et al., 2009). Chromium is widely used in industries, like leather tanning, electroplating, paint and pigment manufacturing, textile and fertilizers (Cervantes et al., 2001). Hexavalent chromium a heavy and poisonous ion is widely used, in manufacturing of steel as an electroplated coating for corrosion prevention; as a mordant in the textile industries; as an anticorrosive agent in the tanning industry, as catalyst for the manufacture of pigments and paints; in fungicides and wood preservatives and in anodization of aluminum in the aircraft industry ( Velma et al ., 2009).The hexavalent form is considered as the toxic form of chromium because it readily crosses cell membrane. Inside the cell, the hexavalent form is reduced to the trivalent form which complexes with intracellular macromolecules, including genetic material, and is ultimately responsible for the toxic and mutagenic capacities of chromium . The bioaccumulation of heavy metals and their toxic effects have been reviewed by Waqar 2006; Rasmussen and Anderson, 2000. Aquatic organisms have the ability to accumulate heavy metals from various sources including sediments, soil erosion and runoff, air depositions of dust and aerosol and discharges of waste water (Labonne et al., 2001). Therefore, accumulative capacity of aquatic organisms can pose a long lasting effect on biogeochemical cycling in the ecosphere. Heavy metals can also adversely affect the growth rate in different fishes (Hayat et al., 2007). The organisms developed a protective defense against the deleterious effects of essential and inessential heavy metals and other xenobiotics that produce degenerative changes like oxidative stress in the body (Abou EL-Naga et al., 2005; Filipovic and Raspor, 2003). Clarias batrachus (Linn.) is an air-breathing catfish, C. batrachus occurs in fresh and brackish waters throughout India. It is highly valued as a table fish throughout the Indian subcontinent and is preferred for culture even in muddy and shallow waters (Debnath and Surajit, 2009). The present study was carried out for a period of 28 days to determine the bioaccumulation of mercury and chromium in the various organs of Clarias batrachus.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Healthy living specimens of Clarias batrachus were procured, from Bharath Fish Seed India, Poondi, Thiruvallur district, Tamilnadu. C. batrachus measuring 9.5+ 0.5cm in length and weighing 5 + 0.5 gram were used in the experiment. The fishes were acclimatized to the laboratory conditions for 20 days prior to experiment in a glass aquarium (40 x 40 x 100 cm) filled with dechlorinated water. Water quality characteristics were determined. The mean values for the test water qualities were as follows, temperature 27.5±1.5C°, pH 7.5±0.03, dissolved oxygen 6.4±0.2mg/l, alkalinity 250±2.8mg/l as calcium carbonate(CaCo3), total hardness 456±3.5mg/l. Stock solutions of mercuric chloride and potassium dichromate were prepared by dissolving analytical grade mercuric chloride (HgCl2 from Merck) and potassiumdichromate (K2Cr2O7·7H2O from Merck) respectively in double distilled water. Acute toxicity test was conducted in accordance with standard methods (APHA, 1995). Sublethal or safe level concentrations were derived from 96 hours Lethal Concentration 50 (LC50) as per the procedure described by Finney (1971). The 96h LC50 were selected as sublethal concentrations for mercury (0.080ppm), chromium (10.2ppm) and ten fishes of same size were exposed to each concentration with three replicates for a period of 28 days. A control batch corresponding to each test group was simultaneously maintained. The experiments were repeated five times for each test concentrations. To maintain a constant toxic concentration in the media, the water medium with appropriate concentration of heavy metal was changed every day. Fish were fed with commercial pelleted diets ad libitum. After 28 days the gills, liver, kidney, brain and muscle tissues of control and treated C. batrachus were dissected and dried, the samples were processed for acid digestion by using perchloric acid and nitric acid in the ratio1:3. The digested tissue samples were made up to 25 ml and 1 ml of the sample was introduced into Inductively Coupled Plasma–Atomic Emission Spectrometer (ICP-AES) (ISA JOBIN YVON 24 MODEL). The obtained data were tabulated in order to get bioaccumulation in ppb levels (Topping, 1973).
RESULTS
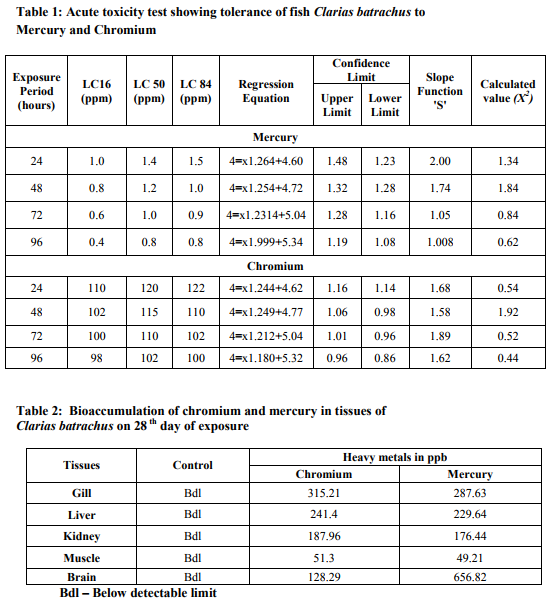
The median lethal concentration (LC50) of mercury to Clarias batrachus for 24, 48, 72 and 96 hours of exposure are 1.4 ppm, 1.2 ppm, 1.0 ppm and 0.8 ppm respectively (Table 1). The LC50 value of chromium to C. batrachus for 24, 48, 72 and 96 hours of exposure are 120 ppm, 115 ppm, 110 ppm and 102 ppm respectively (Table 1). Increase in exposure period results in decreased LC50 values. The sublethal concentrations (~10% of 96 h-LC50) of mercury (0.080ppm), (~10% of 96 h-LC50) chromium (10.2ppm) were treated to C. batrachus for 28 days. Table 2 and figure 1 summarise the bioaccumulation of mercury and chromium in ppb levels in the various organs of control and treated Clarias batrachus. It is evident from the table that both mercury and chromium are consumed by the fish from the surrounding medium and accumulated in the various organs. In the mercury treated tissues of C. batrachus, the bioaccumulation was significantly higher in the brain (656.82 ppb) and lower in the muscles (49.21 ppb). The levels of mercury accumulation in the gills, liver and kidney were 287.63 ppb, 229.64 ppb and 176.44ppb respectively. The bioaccumulation of mercury in the tissues followed the order: Brain> Gills > Liver > Kidney > muscle. Bioaccumulation of chromium was significantly high in the gills (315.21.ppb) and low in the muscle (51.30 ppb). The levels of chromium accumulation in the liver, kidney and brain were 241.4 ppb, 187.96ppb and 128.29ppb respectively .The bioaccumulation of chromium in the tissues followed the order: Gills > Liver > Kidney > Brain > muscle.
DISCUSSION
Metals cannot be metabolized and therefore have the potency to accumulate in the body, leading to chronic effects. The only way in which the metals can be eliminated is by excretion. The rate and pathway of excretion vary greatly from one metal to another and between different tissues (Goyer, 1992).
According to Ferard et al. (1983) aquatic organisms take up heavy metals and concentrate in amounts considerably higher than found in the environment. Measurement of metals in aquatic environment is an important monitoring tool to assess the extent of pollution of the aquatic biotopes (Kumar and Mahadevan, 1995). The field of heavy metal detection by ICP-AES in the industrial waste and soilsediment is still very much in the stage of development (Shrivastava and Chaudhary, 2000). ICP-AES determination of metals is of high sensitivity and accuracy with low matrix effect and simple operation. Mercury in the aquatic ecosystem and its bioaccumulation as methylmercury at higher trophic levels are strongly influenced by the uptake of bioavailable forms of mercury by bacteria enhanced levels of mercury have since been found in fish (Nsikak et al., 2007). Mercury has the potential to bioaccumulate in food chains; the representative selection of an indicator species for a specified ecosystem appears to be a crucial step for reliable interpretation, particularly in long-term studies (Dusek, 2005). Increasing accumulation of mercury in tissues over the lifetime of examined fish can be regarded as an indication of contamination (Rincon et al., 1993; Niimi and Kissoon, 1994; Mueller and Serdar, 2002) and age-related changes then represent a crucial variability component in biomonitoring studies. The accumulation of mercury in the tissues of Clarias batrachus followed the order: Brain > Gill > Liver > Kidney > Muscle. As per the observations made, the accumulation of mercury occurs considerably on 28th day of exposure and significant accumulation takes place in the brain (Table 3 and Figure 1). A possible explanation could be that mercury has a high affinity for the sulfhydryl methyl group compound (Carty and Malone, 1979). Takeuchi (1982) suggested that methylmercury affects the nerve cells during the intermediate or late period of animal fetal life. The present study showed a pronounced change in the brain than in liver and kidney on the 28th day of exposure to mercury. Highest accumulation of mercury in the brain was observed when compared to the liver and kidney. This is because the high affinity of the neurosecretory cells of brain and its strong binding affinity towards mercury. Mercury can easily cross over the blood-brain-barrier system (Smith et al., 1987). Nsikak (2007) indicated in his finding that the accumulation of mercury was significantly higher in liver tissues of Pomadasys jubelini and Oreochromis nilotica. The present observation determined a low molecular bioaccumulation of mercury in the kidneys on the 28th day of exposure to the toxicant. This could be attributed to the low activity and functioning of the kidney in the C. batrachus. The slow blood flow into the renal tissue may lead to less accumulation of mercury in the kidney of the fish (Spitzer, 1985). At the lowest mercury concentration, the metal content was similar in gills, liver and kidneys and they were all statistically different from muscle (Antonia et al., 2003). Romeo et al. (1999) showed that mercury concentrations in edible muscles of pelagic fish species are lower than those of benthic fish species. It is generally accepted that muscle is not an organ in which metals accumulate. Similar results were reported from a number of fish species showing that muscle is not an active tissue in accumulating heavy metals (Karadede and unlu, 2000; Kargin and Erdem, 1991). Chromium is dangerous as it can accumulate in many organisms. The hexavalent chromium behaves toxicologically in a manner quite different from most heavy metal because hexavalent chromium can readily penetrate gill membranes passively and concentrate at high levels in various organs and tissues and can manifest its toxic action internally as well as on the gill surface (Buhler et al. 1977). In the present study the effects of sublethal concentration of chromium on the freshwater fish C. batrachus has been investigated to elucidate the persistence of chromium induced effects during chronic long term exposure. Maximum bioaccumulation was observed in the gill followed by liver, kidney, muscle and brain after 28 days of exposure to chromium (Table 1 and Figure 1). The gills generally showed highest metal concentrations, due to their intimate contact with the environment and their importance as effectors of ionic and osmotic regulation. The degree of chromium bioaccumulation in tissues suggests that the gills take up chromium more readily. Increased bioaccumulation in the gills may be due to the constant and increased ventilatory movements of the operculum under the influence of the xenobiotics. The protective mucous plug inside the opercular chamber is quite often discharged into the medium. Such discharges of mucous plug might make the gills a more vulnerable site for accumulation (Paul and Banerjee 1997). The accumulation of chromium in gill tissue is usually associated with structural damage to the gill epithelium as well as impaired respiratory and osmoregulatory function. These effects have often been cited as the acute mechanism of metal toxicity (Burton et al., 1972). Liver is the tissue with the second highest chromium accumulation. The liver, in its role as a storage and detoxification organ, can also accumulate high levels of metals (Nussey et al., 2000). It is suggested that in the liver chromium is stored and linked to proteins and smaller peptides such as glutathione (Gauglhofer and Bianchi, 1991). According to Heath, (1987) fish excrete chromium via their feces, as shown by high levels in bile during and after the ingestion of contaminated food or contaminated water. A higher concentration of chromium was mostly recorded in the gills followed by the liver. Muscles and skin accumulated much less metal concentrations (Nussey et al., 2000). The concentrations of chromium found in the gills, liver and muscle in this study also supported by various other study (Wepener, 1997). In the present study, the lowest chromium concentrations were mainly found in the muscles. This coincides favorably with the results from other study (; Wepener, 1997). The levels of chromium accumulations in the various organs is as follows Gills > Liver > Kidney > Brain > muscle. These observations agree with results obtained in similar study by (Avenant-Oldewag and Marx 2000) for Clarias gariepinus. The present findings are in perfect harmony with the above results. Thus the transformation, mobilization transport and bioaccumulation of chromium are of fundamental environmental significance.
CONCLUSION
In this study, it was clearly shown that the mercury and chromium exposure is having a significant impact on the brain and gills of the C. batrachus. Knowledge of these 69 International Journal of Current Research and Review www.ijcrr.com Vol. 03 issue 05 May 2011 outputs made a possibility to give a better description of the variation and the pattern of metal accumulation in the various organs of C. batrachus. The scientific data discussed in this study provide a basis for understanding the potential impact, as well as for advancing our knowledge of the ecotoxicology and risk assessment of mercury and chromium.
References:
1. Abou EL-Naga EH, EL-Moselhy KM, Hamed M A. Toxicity of cadmium and copper and their effect on some biochemical parameters of marine fish Mugil seheli. Egyptian. J Aquat Res 2005; 31 (2); 60-71.
2. Antonia CE, Roberta G, Maria IT, Ambrosius JMD Luciana M. Antioxidant responses and bioaccumulation in Ictalurus melas under mercury exposure. Ecotoxic and Environ Saf, 2003; 55: 162–167.
3. APHA. Standard Methods for the Examination of water and wastewater, 19th edition, American Public Health Association, Washington DC. 1995.
4. Buhler DR, Stokes RM, Caldwell RS. Tissue accumulation and enzymatic effects of hexavalent chromium in rainbow trout Salmo gairdneri. J Fish Res Board Can 1977; 34 :9-18.
5. Burton DT, Jones AH, Cairns J. Acute zinc toxicity to rainbow trout (Salmo gairdneri): Confirmation of the hypothesis that death is related to tissue hypoxia. J Fish. Res Bd Can 1972; 29:1463-1456.
6. Carty AJ, Malone SF. The chemistry of mercury in biological systems. In: The biogeochemistry of mercury in the environment. Nrigau, J.O. (editors.), Elsevier/North Holland Biomedical Press, Amsterdam.1979; p. 433 - 379.
7. Cervantes C, Campos Garcia J, Devars S, Gutierrez-Corona F, Loza-Tavera H, Torres-Guzman JC, Monreno Sanchez, R. Interactions of chromium with microorganisms and plants. FEMS Microbiol Rev., 2001; 25: 335–47.
8. Debnath Surajit. Traditional Consumption of Magur (Clarias batrachus) an Air Breathing Catfish among the Population of North Eastern India is Rationalized by Its Blood Lipid Parameters CHEMFERENCE, Annual Research Symposium, IIT Madras 22 - 23rd August, 2009. Available at SSRN: http://ssrn.com/abstract=1401145.
9. Dusek L, Svobodova Z, Janoušková D, Vykusová B, Jarkovský J, Šmíd R and Pavliš P. Bioaccumulation of mercury in muscle tissue of fish in the Elbe River (Czech Republic): multispecies monitoring study 1991–1996. Ecotoxi and Environl Safe, 2005; 61:256–267.
10. Farhana, Zahir., Shamim, J. Rizwi., Soghra, K. Haqb, Rizwan H. Khanb. Low dose mercury toxicity and human health. Envirol Toxico and Pharma 2005; 20: 351–360.
11. Farombi EO, Adelowo OA, Ajimoko YR. Biomarkers of oxidative stress and heavy metal levels as indicators of environmental pollution in African Cat fish Clarias gariepinus from Nigeria Ogun river. Int J Environ Res Public Health 2007;. 4 (2), 158-165.
12. Ferard JF, Jouany JM, Truhaut R, and Vasseur P. Accumulation of cadmium in a freshwater food chain experimental model. Ecotoxico Environ Safe, 1983;7: 43-52.
13. Filipovic, V, Raspor B. Metallothionein and metal levels in cytosol of liver, kidney and brain in relation to growth parameters of Mullus surmuletus and Liza aurata. From the eastern Adriatic Sea. Water Res., 2003; 37 (13), 3253-3262.
14. Finney DJ. Probit analysis third edition Cambridge University Press, London and New York. 1971.
15. Francisco J, Picado Pavón. Mercury in the environment and the gold mining activity in the St Domingo district, 71 International Journal of Current Research and Review www.ijcrr.com Vol. 03 issue 05 May 2011 Chontales-Nicaragua. Introductory paper no. 2004; 157.
16. Gauglhofer J, Bianchi V.Chromium. In: Merian E (edited.) Metals and their compounds in the environment. Occurrence, analysis and biological relevance. VCH Publishers Inc New York, USA.1991. P 853-878.
17. Goyer RA. Toxic effects of metals. In: Amdur MO, Doull J, and Waarren, CD, Casarett and Doull‘s (edited.) toxicology. The basic science of poisons. Pergamon Press.1992 p 623 - 680.
18. Hayat S, Javed M, Razzaq S. Growth performance of metal stressed major carps viz. Catla catla, Labeo rohita and Cirrhina mrigala reared under semiintensive culture system. Pak Vet J 2007; 7: 8-12.
19. Heath AG, Water Pollution and Fish Physiology. CRC Press Inc, Boca Ranton, Florida, USA 1987; p.245. 20. Kamaruzzaman BY, Akbar B, Jalal KCA, Shahbudin S. Accumulation of metals in the gills of Tilapia ngerlings (Oreochromis niloticus) from in vitro toxicology study. J Fish Aquat Sci 2010; 5: 503-509.
21. Karadede H, Unlu E. Concentrations of some heavy metals in water, sediment and fish species from the Atatürk dam lake (Euphrates), Turkey. Chemosphere 2000; 41: 1371-1376.
22. Kargin F, Erdem C. Accumulation of copper in liver, spleen, stomach, intestine, gill and muscle of Cyprinus carpio. Doga Tr J of Zool 1991; 15: 306-314.
23. Khangarot BS, Mercury-Induced Morphological Changes in the Respiratory Surface of an Asian Freshwater Catfish, Saccobranchus fossilis. Bul Environ Contam Toxicol 2003; 70; 0705-0712.
24. Kumar V, Mahadevan A. Heavy metal pollution at Tuticorin coast. Pollut Resea, 1995; 14: 227-232.
25. Labonne M, DB, Othman JM, Luck. Lead isotopes in muscels as tracers of metal sources and water movements in a Lagoon (Thau Basin, S. France). Chem. Geol., 2001; 181-191.
26. Mueller KW, Serdar, DM. Total mercury concentrations among fish and crayfish inhabiting different trophic levels in Lake Whatcom, Washington. J Freshwater Ecol. 2002; 17: 621–633.
27. Niimi AJ, Kissoon GP. Evaluation of the critical body burden concept based on inorganic and organic mercury toxicity in rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) Arch. Environ Conta. Toxicol, 1994; 26: 169–178.
28. Nsikak UB, Joseph PE, Akan BW, David EB. Mercury accumulation in fishes from tropical aquatic ecosystems in the Niger Delta, Nigeria. Curre scien 2007; 92: 6.
29. Nussey GJ, Van Vuren JH, Du Preez HH. Bioaccumulation of chromium, manganese, nickel and lead in the tissues of the moggel, Labeo umbratus (Cyprinidae), from Witbank Dam, Mpumalanga.Water SA. 2000; 26: 2.
30. Paul VI, Barerjee TK. Histopathological changes induced by ambient ammonia (ammonium sulphate) on the opercular linings of the live fish Heteropneustes fossilis (Bloch). Dis. Aquat Org 1997; 28:151- 161.
31. Rasmussen AD, Anderson O. Effects on cadmium exposure on volume regulation in the lugworm, Arenicola 72 International Journal of Current Research and Review www.ijcrr.com Vol. 03 issue 05 May 2011 marina. Aquat Toxicol. 2000; 48:151- 164.
32. Rincon F, Zurera G, Moreno R, Amaro-Lopez M. Importance of eating habits and sample size in the estimation of environmental mercury contamination using biological indicators. Environ Monit Assess 1993; 27:193–200.
33. Romeo M, Siau Y, Sidoumou Z, Gnassia-Barelli, M. Heavy metal distribution in different fish species from the Mauritania coast. Sci Total Environ 1999; 232:169–175.
34. Shrivastava VS, Chaudhary GR. Hazardous heavy metal in and around MIDC Jalgaon by inductively Coupled Plasma Atomic Emission Spectrophotometer. Ind. J.Environ.and Ecoplann 2000; 3:707-709.
35. Smith QR, Momma S, Aoyagi M, Rapoport SI. Kinetics of neutral aminoacid transport across the bloodbrain barrier. J. Neuro chem 1987; 49: 1651-1658.
36. Spitzer A. The developing kidney and the process of growth. In: Seldin, DW and Giebish, G. (edited ) The kidney, physiology and pathophysiology, Raven Press, New York,1985.
37. Takeuchi T. Pathology of Minamata disease with special reference to its pathogeneis. Acta Pathol J, 1982; 32 (1): 73 - 99.
38. Topping G. Heavy metals from Scottish water. Aquacul 1973; 1: 379- 384.
39. Velma V, Vutukuru SS, Paul B, Tchounwou. Ecotoxicology of Hexavalent Chromium in Freshwater Fish A Critical Review. Rev Environ Health. 2009; 24(2): 129–145.
40. Waqar A. Levels of selected heavy metals in Tuna fish. Arab JSci Eng 2006; 31 (1A), 89–92.
41. Wepener V. Metal ecotoxicology of the Olifants River in the Kruger National Park and the effect there of on Fish Haematology. (Ph.D. Thesis), Rand Afr Univ.; South Africa 1997.
|






 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License