IJCRR - 3(9), September, 2011
Pages: 21-32
Print Article
Download XML Download PDF
STUDY OF DIABETES MELLITUS, COMORBIDITY DEPRESSION AND QUALITY OF LIFE
Author: Sivaji.M, Indumathi.S
Category: Healthcare
Abstract:Aim: To examine the intriguing relationship between quality of life and depression in diabetes mellitus Objectives: a) To estimate the prevalence of clinical depression in patients with type II diabetes mellitus, b) predictive factors associated with depression in patients with type II diabetes mellitus,c) quality of life of the depressed diabetic compared with the non-depressed diabetic. Materials and Methods: The study population consists of patients attending the Medical OPD Kilpauk Medical College and Psychiatric OPD Madras Medical College, Chennai. A total of 185 patients were screened for the study of which 100 patients were included in this study. The control group consists of relatives and care givers accompanying the patients. A total of 105 were screened of which 50 were included in this study as control .Assessment Instruments such as socio demographic profile sheet, disease measures, Backs depression inventory, Ferrans and Power diabetic quality of life index III \? 1985 were used. Results: Depressive episode as per the criteria diagnosis was present in 18% of patients with diabetes. Elevation in depressive symptoms on the BDI scales were significantly more common and were present in 36% of patients with diabetes (p < 0.00). Among the variables patient's marital status and occupation were found to be highly significant predictors of depression in diabetes mellitus. Poor glycaemic control , family level of stress family history diabetes ,family harmony were found to be significant predictors of depression. Conclusion: The study hypothesised that prevalence of depression is more in diabetics compared to the non-diabetic group. The study established the fact that the odds and prevalence of depression is double in diabetics than in the non diabetic control group. The psychosocial factors play important role in the etiology of depression in individuals with diabetes.This study has identified the prevalence and the independent factors that are associated in depression in individuals with diabetes.
Keywords: Depression, Diabetes Mellitus, Beck‘s Depression Inventory, Psychological factors, Ferrans and power diabetic quality of life.
Full Text:
INTROCDUTION
Diabetes is a chronic condition that has reached epidemic proportions and depression is quite prevalent in patients with diabetes due to psychological distress, restricted physical activity and inability to fulfill role obligations. The reported prevalence of depression among patients with diabetes varies considerably due to differences in study design and study population. In patients with type I diabetes the prevalence of depression is probably about 30% to 40%( 1) and the prevalence of depression on cross sectional analysis appears to be about 20% (2).The patients with diabetes having an episode of major depression at some point in their lifetime appears to be about 33.1% (3). Among 3,481 patients studied of which 1897 patients revealed with major depressive disorder had more risk of developing type II diabetes (4). Younger people tend to have higher prevalence rate than do older people. Women had higher rate of depression especially those who were unmarried and with lower education. The patients who had diabetes with depression had significantly higher levels of HbA1c than who were not depressed (5). There is an established association between depression and poor glycemic control. The prevalence of depression was 28% in women compared with 18% in men(6) .There is a stronger relationship between depression and glycemic control in women compared with men and suggested that the reasons for this may be a more profound effect on women's self care behaviour (6). Depression may have an adverse effect on the HPA axis and on compliance with diabetes treatment (5). There is some speculation that serotonin dysfunction may be a factor in both depression and lack of glycemic control( 4). The younger age, female sex, previous psychiatric illness and demographic variables such as social insecurity are some of the important associations for depression to occur in any physical disease (7). The hypotheses includes: 1) depression is found in increased frequency in patients with type II diabetes, 2)the socio demographic factors disease indicators and occurrence of depression in type II diabetics are significantly correlated, 3) the quality of life in depressed diabetic individuals is poorer than non - depressed diabetic group.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
The study population consists of patients attending the Medical OPD Kilpauk Medical College and Psychiatric OPD Madras Medical College, Chennai. A total of 185 patients were screened for the study of which 100 patients were included in this study. The control group consists of relatives and care givers accompanying the patients. A total of 105 were screened of which 50 were included in this study as control. The inclusion criteria are those patients diagnosed with type II diabetes by the ADA criteria, aged above 18 years came with medical records, patients on regular follow up for the past 6 months and informed consent. The exclusion criteria are those patients with type 1 diabetes diagnosed by the ADA criteria, presence of other chronic medical conditions like hypertension, asthma, tuberculosis, cancer, past (or) present H/o psychiatric illness - even not fulfilling the diagnostic criteria, family H/o psychiatric illness, history of substance abuse, patients with a history of diabetic ketoacidosis in the recent 6 months and any history of hospital admission in recent 3 months.
Design of Study
Subjects were taken from the out patients department. Subjects who fulfilled the inclusion criteria were included in the study group. Informed consent was obtained from the patients. A detailed history which included present and past medical, psychiatric illness, drug abuse details was taken. Thorough MSE was done to assess the presence of any psychiatric illness. A detailed physical examination was done to exclude any physical illness. Patients medical records were reviewed to got a detailed knowledge of the present or past medical illness, drugs taken, and whether the patients is on any medication other than that for diabetics. Details of referrals to other specialty department like neurology, ophthalmology, nephrology for diabetic complications was noted. A complete record of the previous 6 months blood sugar level was obtained from the records available with the patients. Each day 2 or 3 patients were interviewed and questionnaires were administered.
Assessment Instruments are socio demographic profile sheet, disease measures, Becks depression inventory, Ferrans and Power diabetic quality of life index III - 1985.
Assessment Procedure: All subjects were informed that they have to spend a minimum of 1 hr for the study. They were also informed that it would not affect their diabetic treatment and further no medications will be prescribed to them. A detailed demographic variables regarding the patients, such as age, sex, marital status, occupation, income etc. were noted. Patient‘s records were also used to obtain more accurate data. The patient‘s diabetic status was assessed using the records available with patient. A detailed family history of diabetes, family systems and family harmony were obtained. Family harmony was graded on a 3 point scale as well adjusted, occasional quarrels and frequent quarrels.
Beck’s depression inventory: The BDI - III (5) includes 21 items with total scores ranges from 0-84. Scores of 0-9 are considered minimal 10 - 16 mild, 17 - 29 moderate and 30-63 severe. This was used in measuring the depth of depression.x
Diabetic quality of life index - Ferrans and Powers
The instrument consists of 2 parts. The first measures satisfaction with various aspects of life and the second measures importance of those same aspects. Scores are calculated for quality of life overall and in 4 domains, health and functioning, psychological spiritual, socio economic and family. The instrument takes approximately 10 min for self administration.
Reliability and validity
Reliability
Internal consistency reliability for the QLI (total scale) was supported by Cronbachs alpha ranging from : 0.82 to 0.98 across 26 studies. Temporal reliability: For the total scale support for temporal reliability was provided by test retest correlations of 0.87 with a two week interval and 0.81 with one month interval (8)
Validity : Content validity : Support for content validity was also provided by an acceptably high rating using the content validity index (F and P). Construct validity of the QLI was supported by strong correlation between the overall QLI score and measure of life satisfaction. Further evidence for construct validity was provided by factor analysis.
Statistical analysis
Chi square test is used to compare sociodemographic pattern of patient and controls. Prevalence was calculated as an aggregate mean weighed by the combined number of subjects included in the study. Chi square test was used to compare by BDI score of patients and controls. Multiple regression analysis is used to find the predictive factors correlated with depression.
RESULTS
The statistical data obtained was analyzed to answer three questions.1)The prevalence of depression in the diabetic population, the odds of depression in the diabetic group compared with the non - diabetic control group - odds ratio. 2)The independent contribution of each the three potential group of stressors Demographics :(Age, Sex, Marital Status, Occupation, Education, income),Disease Status:(Duration of illness, type of treatment, glycaemic control, presence of complications),Family Stress :(Family history of diabetic, family system, family harmony).Multiple regression equation assessed the independent contribution of each predictor on depression.3)Health related quality of life in depressed diabetic compared with the non - depressed diabetic group.
Analysis of data
Depression was assessed using the ICD - 10 criteria for depression episode and DSM IVR and quantified using the Becks depression inventory (9). Depression prevalence was equal to the percentage of subjects with scale scores above a specified threshold value. The threshold score used to identify depression cases varied across studies (10, 11,12) in which a BDI score ? 10 was used .Since a majority of studies used a cut of score of ? 10,in this study this score was used to assess the presence of depression. Depressive episode according to ICD-10 was present in 18% of patients with diabetes. However elevation in depressive symptoms on the BDI scales were significantly more common and were present in 36% of patients with diabetes (p <0.00).
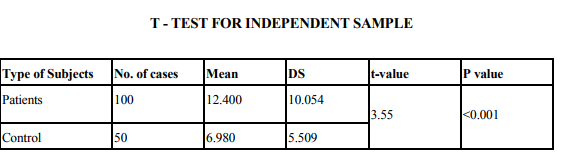
Depression prevalence was calculated as an aggregated mean, weighted by the number of subjects in the study. X2 tests were used to statistically compare the prevalence of depression in the diabetic and non-diabetic comparison group. The p value is 0.001 indicating that depression is highly significant in the diabetic group compared to the non - diabetic control group. This reflects the study carried out by (13, 3).The presence of diabetes doubles the odds of co-morbid depression (1). The depression is more consistent across studies than the prevalence, which varies by sex, study design, subject source and method of depression assessment.

DISCUSSION
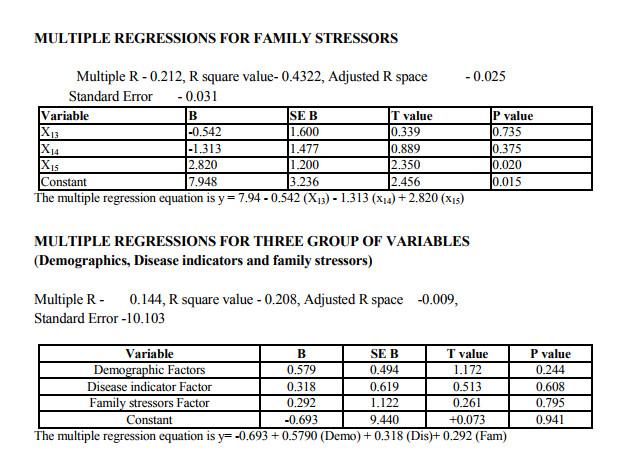
Multiple regression findings
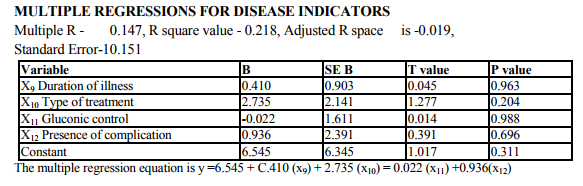
Multivariate analysis considers the relation between combinations of two or more variables. The data in column are termed variables and those in rows are called observations. The dependent variable (y) is depression, is predicted from a linear combination of variable x1 x2 x3. The linear combination of variable was expressed as,y1 = a + b1x1 + b2x2 + b3x3 - bk xk ,where Y1 is the predicted value of y, a is the consent,x1x2 are variables, b1x2 are regression coefficient. Variables that are important in this combination will be associated with largest regression coefficients. The strength of association between the predictors and the outcome is expressed as a correlation coefficient usually term multiple R. Squaring R provides as estimate of the amount of variance Y explained by the predictors XS. The 14 variables were grouped into three stress related areas. (Patient demographics, disease indicators and family level stress). Each variable had shown significant relationship with depression in patient with diabetes in previous research (13,14)
Independent variables
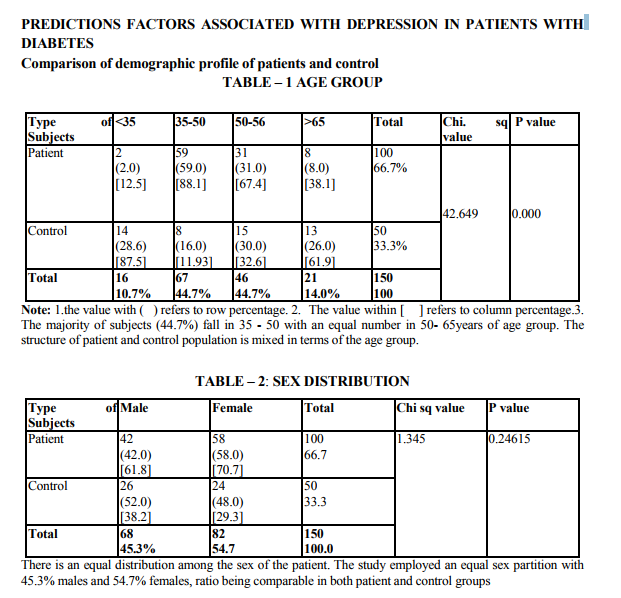
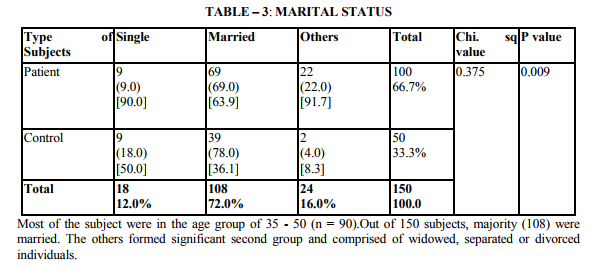
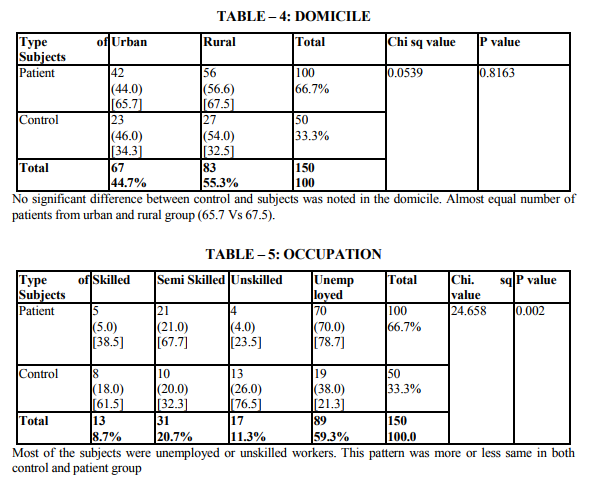
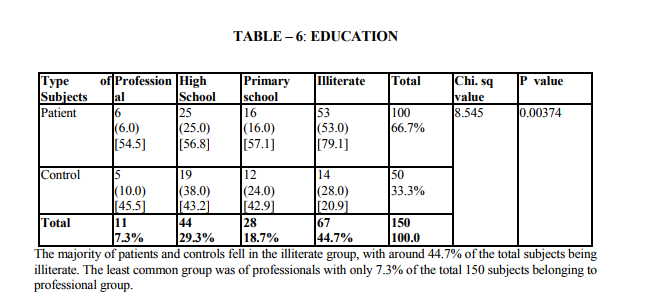
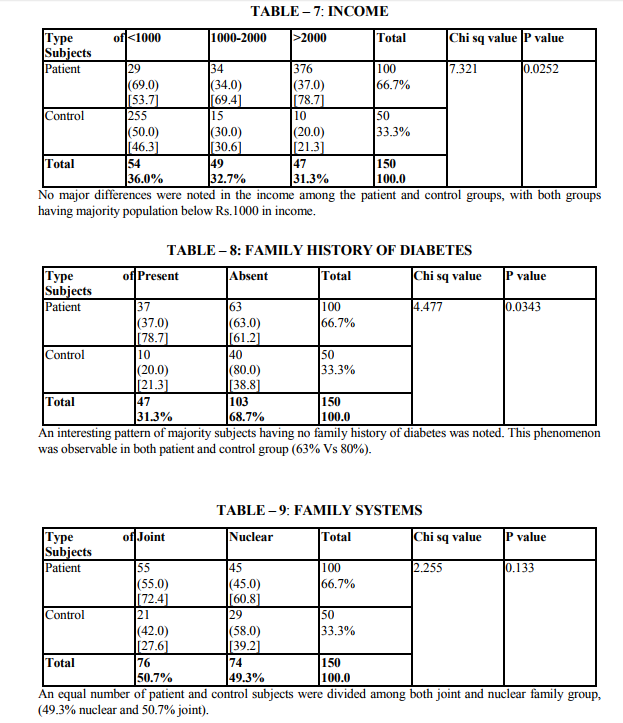
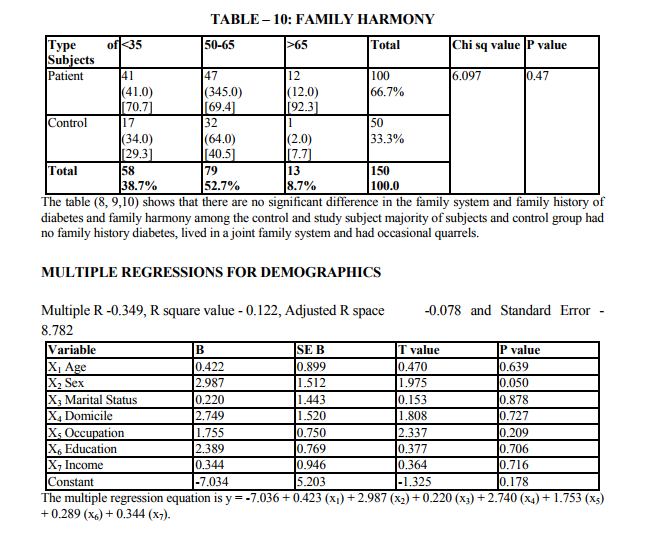
Demographic indicators included patient‘s age, sex, marital status, domicile, occupation, education and income. Marital status was scored as being single, married and others. The others included divorced, separated and widowed. The three were merged as one single group because the number in each variable was very small. Occupation was scored as a skilled worker, semiskilled or unemployed. Educational status was scored as illiterate, primary (0 - 8), high school (8 - 12 yrs) and as professional as one who holds a degree (or) diploma. The income scale was classified as having the income of 2000.The duration of illness was clarified as 0 - 1 year and 1 - 2 years, 2 - 3 years, 3 - 5 years and > 5 years. Patients were classified into 3 group as receiving only diet, only drugs and diet, drugs, diet and insulin. Glycemic control was assessed using the patient records of the blood sugar levels over the past 1 year. Fasting blood sugar level below 105 mgs % was taken as a criteria of good control (American Diabetes Association, 1984).Post prandial blood sugar levels above 250 mgs % and mean fasting blood sugar level above 102 mg % was taken to indicate poor control. The glycosylated hemoglobin level indicates the control of blood sugar over the past 3 months. The normal level range varies between 5 - 8% while a level below 12.5 is indicates of fair control and a level above 12.5% is indicates good control. However since the glycosylated hemoglobin levels were not available to all patients in the study the longitudinal diabetics control as included in the study. Patient‘s record was also used to assess the presence or absence of complications. The family level stressors were assessed as having a family member with diabetes, family system and family harmony .The other factors were assessed individually to find out the contribution of each of the variable separately to depression.
DEPENDENT VARIABLE:
The study shows that there are significant indicators in the demographics of patient which predict a high likelihood of depression. Of these variables are of patient (p value 0.000) marital status (p value 0.009) and occupation (p 0.000) were found to be highly significant predictors of depression in diabetics. The educational status (p value 0.03), income (p 0.02) were significant predictors and contrary to the expectation of sex and domicile were found to be not significant. There were no significant difference in the rates of likely depression between males and females. The level of depression is high in younger subjects (15).However numerous other studies in the literature find that females are at high risk for being depressed even in otherwise healthy adults (1,2,16).The reason for this difference is not known, however it may be presumed that female more readily seek help than their male counter- part which lead to better recognition and treatment of depression. Considering marital status being single, widowed or divorced had a high likelihood of been depressed (17,16). Domicile had not any significant contribution to the likelihood of depression. Being a skilled worker, with high educational status has been higher possibility of being depressed, whereas unskilled, illiterate seem to be less affected by depression (14).Although high income seem to other less chance of being depressed it is not highly significant compared to marital status and age. These finding suggest that among the demographic factors, age, marital status and occupation were the significant predictors of depression in the diabetic group. Although female sex was a significant factor in other studies, this has not been the case in the current study. Significant predictors of depression were not found in any of the disease indicators in this study (2,18).A meta analysis review of literature revealed association of depression with diabetes complication (13).However the findings of other studies have not replicated consistently. Among the family level of stress family history diabetes and family harmony were found to be significant predictors of depression. These findings were similar to the one reported by (17). However the type of family, joint or nuclear was expected to be a significant predictor of depression. Because living in a closely knit family offers to share responsibilities and provides psychological help. It is not so in the study.
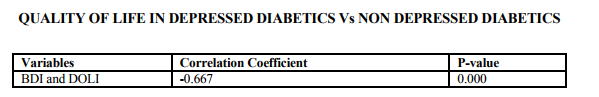
On comparison the quality of life in depressed diabetic with those of nondepressed diabetics the p-value obtained was <0.000 which is highly significant showing that the quality of life in depressed patients was much affected when compared to the non-depressed diabetics. These findings have been more consistently reported across studies. Finally each of the three group of stressors were compared to find out which contributes more to depression perdition. Multiple regression analysis was used. The results were, no group individually predicts the high possibility of depression this is contrary to be findings in literature where heavy emphasis is made on disease related factors like glycemic control, duration of illness, type of treatment in the prediction of depression. The findings echo the studies (19,16) reported multiple independent predictors of depression not just predictors from diabetes related stresses alone.
SUMMARY AND CONCLUSION
The study hypothesised that prevalence of depression is more in diabetics compared to the non-diabetic group. The study established the fact that the odds and prevalence of depression is double in diabetics than in the non diabetic control group. This is similar to the study (1).The evidence from prospective studies indicated that depression doubles the risk in incident type 2 diabetes independent of association with other risk factors (20, 21). In patients with pre existing diabetes, depression is an independent risk factor for coronary heart disease and appears to accelerate the presentation of coronary heart disease (22, 23).The psychosocial factors play important role in the etiology of depression in individuals with diabetes .This study has identified the prevalence and the independent factors that are associated in depression in individuals with diabetes. The quality of life in the depressed diabetic versus non depressed diabetic, depression significantly (p 0.001) affects the quality of life of the diabetic patients.
References:
1. Anderson. R.J, Freedland K.E, Clouse R.E, Lustman P.J 2001: The prevalence of co morbid depression in adults with diabetes: a meta-analysis. Diabetes Care 24: 1069-178.
2. Lustman. P.J, Gavard .J.A; Closue .R.E 1993: Prevalence of depression in adults with diabetes: An epidemiological evaluation: Diabetes Care 16:1167-1178.
3. Lustman.P.J, Freedland.K.E, Griffith.L.S, Clouse.R.E, 2000: Fluoxetine for depression in diabetes: A randomized double-blind placebocontrolled trial. Diabetes Care 23: 618- 623.
4. Paul Goodnick: Treatment of depression in co morbid medical illness: 2000; Exp.Opin.Pharmcotherapy:1.1367-84.
5. Jacobson.L, Sapolsky.R;1991:The role of the hippocampus in feedback regulation of the hypothalamic-pituitaryadrenocortical axis. Endocr. Rev. 12: 118-134
6. Lustman.P.J, Anderson.R.J, Freeland.K.E et.al; (2000);Depression and poor glycemic control; A metaanalytic review of literature. Diabetis Care 23:434-442
7. Mayou. R,Hawton .K 1986; Psychiatric disorder in the general hospital. British Journal of Psychiatry: 149;172-190.
8. Ferrans.C and Powers. M (1985). The quality of life index. Development and psychometric properties. Advances in Nursing science: 8;15-24.
9. Beck.A.T,Beamesderfer.A;1974:Assess ment of depression: The depression inventory. Mod Probl. Pharmaco - psychiatry 7:151-169
10. Songar.A, Kocabasoglu.N, Balcioglu.I, Karaca E, Kocabasoglu.C, Haciosman.M,Somay.G;1993 : The relationship between diabetics metabolic control levels and psychiatric symptomatology. Integr. Psychiatry ; 9:34-40.
11. Stone. J.E, Bluhm .H.P, White .M.I ;1984: Correlates of depression among long-term insulin-dependent diabetics. Rehabilitation. Psychology 29: 85-93.
12. Leedom .L, Meehan.W.P, Procci .W, Zeidler.A ;1991: Symptoms of depression in patients with type II diabetes mellitus. Psychosomatics 32: 280-286
13. De Groot.M, Lustman.P.J;2001: Depression among African-Americans with diabetes: A dearth of studies. Diabetes Care 24:407-408.
14. Hanninen .J.A, Takala.J.K, KeinanenKiukaanniemi.S.M; 1999: Depression in subjects with type II diabetes: Predictive factors and relation to quality of life. Diabetes Care 22:997-998.
15. Abass Yavani, Naimeh Mashinchi ;2010: Diabetes and Depression; Journal of stress physiology and Biochemistry; Vol;6 No; 3
16. Leonard E.Egede, Deyi Zheng et.al; 2002;Co morbid depression is associated with increased health care use and expenditures in individuals with diabetic care: Vol. 25; No.8;464-470.
17. Fisher.L, Chesla.C.A, Mullan.J.T, Skaff.M.M, Kanter.R.A 2001: Contributors to depression in Latino and European-American patients with type II diabetes. Diabetes Care 24:1751-1757.
18. Manjin.D.Pawsken, Roger.T, Anderson 2007;Self-reported predictors of depressive symptomatology in an elderly population with type II diabetis milletus;Prospective cohort study; Health and Quality of life outcomes 5:50;1477-75.
19. Alkens.J.E, Perkins.D.W, Piette.J;D2008:Association between depression and concurrent type II diabetis, Outcomes varies by diabetis regimen; Journal of British Diabetic Association: 25 (11):1324-9.
20. Eaton .W.W, Armerian. H.A, Gallo .J, Pratt. L, Ford D.E 1996: Depression and risk for onset of type I diabetes: a prospective population-based study. Diabetes Care 19:1097-1102
21. Kawakami.N,Takatsuka.N,Shimizu .H, Ishibashi .H 1999: Depressive symptoms and occurrence of type II diabetes among Japanese men. Diabetes Care 22:1071-1076.
22. Lloyd .C, Wilson. R, Forrest. K; 1997: Prior depressive symptoms and the onset of coronary heart disease (Abstract). Diabetes 46: 3A.
23. Peyrot M. Rubin.R.R1999: Presistence of depressive symptoms in diabetic adults. Diabetis Care: 22: 448-452.
|






 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License