IJCRR - 3(10), October, 2011
Pages: 47-54
Print Article
Download XML Download PDF
COMPARATIVE STUDY OF EFFICACY OF VASTUS MEDIALIS OBLIQUUS Vs RECTUS FEMORIS USING
OPEN KINEMATIC AND CLOSED KINEMATIC EXERCISES IN PATELLOFEMORAL PAIN SYNDROME
Author: Shashi Kumar C.G, Nafeez Syed, N.Mohan
Category: Healthcare
Abstract:Background: Patellofemoral pain syndrome (PFPS) is often treated conservatively with voluntary
exercise for the Quadriceps femoris. Nevertheless, a substantial percentage of patients remain
symptomatic. Although exercise seems a crucial element for treatment, it may serve to increase patellar
irritation with the resulting dilemma that patients exercising the muscles may be simultaneously irritating
the knee. Patients with PFPS have been using quadriceps strengthening exercises with varying results on
muscle strength and pain. However, there are various problems associated with these forms of traditional
quadriceps strengthening exercises. This study sought to explore the effects of progressive functional
retraining of Vastus Medialis Obliquus (VMO) in the context of PFPS. Purpose: To compare the efficacy
of strengthening of VMO Vs Rectus femoris (RF) using open kinematic and closed kinematic chain
exercises in PFPS. Methods: This study was conducted at Yenepoya Medical College Hospital,
Mangalore. Forty subjects with anterior knee pain fulfilling the inclusion criteria were randomly assigned
to two groups with the mean age of 25.85 in group 1 and 27.65 in group 2. Group 1 received RF
strengthening exercises. Group 2 received strengthening of VMO. Visual Analog Scale (VAS) and
anterior knee Pain Scale were noted before and after the interventions. (i.e. either RF strengthening or
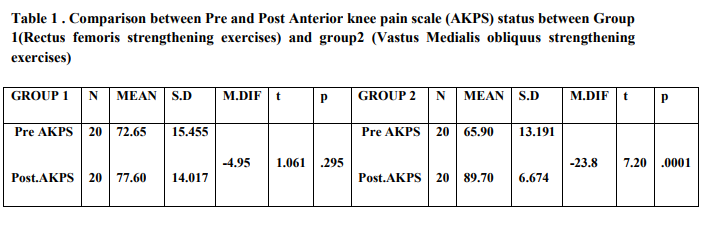
strengthening of VMO).Results: After 2weeks of intervention in Group 1 there was a significant increase
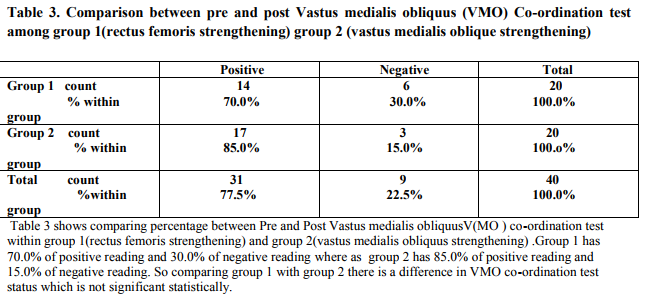
Anterior knee pain scale(AKPS) with mean difference of 4.95 and VMO co-ordination test status. There
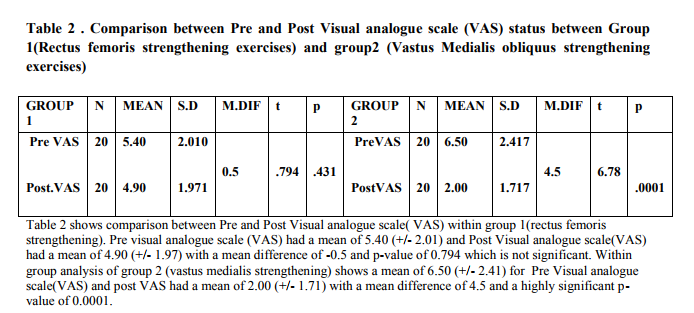
was also a significant decrease in the VAS scale and with mean diff of 0.5 , whereas in Group 2, AKPS
with mean diff of -23.8 , VAS with the mean diff of 4.5 were all highly significant and there was a
increase in VMO co-ordination test but statistically not significant. Conclusion: Strengthening of VMO
clinically as well as statistically suggest that strengthening of VMO is more effective than the traditional
strengthening of RF in patients with PFPS.
Keywords: patello femoral pain syndrome, anterior knee pain scale, strengthening, visual analogue scale.
Full Text:
INTRODUCTION
Patellofemoral pain syndrome (PFPS) refers to the clinical presentation of anterior knee pain related to changes in the patellofemoral joint. This can be brought on by prolonged sitting (the so called 'theatre goer's sign'); by ascending and descending stairs, squatting, kneeling and by athletic activity. Clinical assessment of patients reveals a general paucity of abnormal physical findings. PFPS is considered to have an uncertain etiology with numerous theories propounded, including tightness of soft tissue and periarticular structures, patellofemoral malalignment and maltracking, tibial torsion and gait abnormalities. These commonly sited theories for PFPS have recently been supplemented by theories about nerve damage in the lateral retinaculum and patellar bone hypertension. Another proposal is that PFPS may develop due to a dysfunction of the extensor mechanism described to be due to generalized quadriceps weakness and wasting, decreased eccentric function, or differences in the activation patterns of the Vastus Medialis. To date, it is still unknown if the quadriceps dysfunction causes the patellar pain or the pain causes the dysfunction1 . Recently, based on human and cadaveric studies, authors have reported that the vastus medialis is composed of sets of fibers namely proximal, middle and distal fibers. The proximal and middle fibers get attached to the tendon common to the rectus femoris and the distal fibers get inserted into the medial aspect of the patella, which resists the valgus vector because of the ?Q‘ angle thereby controlling the patellar tracking movements2 . During voluntary ankle movements, anticipatory postural adjustments are initiated at the knee which co activates the Vastus Lateralis (VL) and the Vastus Medialis Obliquus (VMO) and this guides the normal patellar tracking. Studies have reported that there is a 5 ms delay in the VMO activation when compared to the VL. This shows that there is an altered VMO recruitment and change in the motor control in subjects with PFPS that should be considered for effective rehabilitation3 . In the analysis of patellofemoral joint reaction forces the results showed an increase in the patellofemoral joint reaction forces (PFJRF) with increasing knee flexion in Closed Kinetic Chain (CKC), whereas in Open Kinetic Chain (OKC) it increased from 90º of knee flexion to knee extension. Therefore, it is important to consider these specific ranges of knee motion in the rehabilitation of PFPS 4 The strength of evidence for routine terminal range knee extension exercises in OKC and squatting exercises in CKC for Vastus medialis strengthening is insufficient. Hence there is a need to identify efficient techniques in the rehabilitation of PFPS for improving the motor control around the knee considering rectus femoris which has the main attachment over the base of patella, correcting the abnormal patellar tracking, reversing the delayed onset of the VMO and decreasing the PFJRF for better outcomes. As there are not much studies done on rectus femoris in PFPS, this we have taken as a consideration and progressed with a study on RF and VMO in PFPS.
METHOD
Forty subjects aged between 20 to 40years with PFPS referred for Physiotherapy at Yenepoya medical college hospital were enrolled in the study. The inclusion criteria were (a) Anterior, peripatellar or Retro patellar knee pain more than 3months at least two of prolonged sitting, stairs, squatting, running, kneeling and hopping/jumping.(b)insidious onset of symptoms unrelated to traumatic incident (c)average pain level of 5cm or more than that on a VAS scale (d)age 40years or less to avoid degerative changes in Patellofemoral joint (e)symptoms for atleast 2weeks. Subjects were excluded if they had (a)signs and symptoms of their co-existing pathology (b)recent history of knee surgeries (c) evidence of OA changes (d)history of patellar subluxation or dislocation (e)ligamentous instability,meniscal lesion,plica syndrome (f)pregnancy (g)patellar tendon pathology (h)referred pain from the spine (i)knee joint effusion (j)illiteracy/inability to understand and answer questionnaires. Subjects were randomly allocated to the group 1 and group 2 using simple randomization with provided written consent informed consent.
Procedure:
A total of 40 subjects were randomly assigned to both the groups, Group 1 (Rectus femoris Strengthening) having n = 20 and Group 2 (VMO Strengthening) having n = 20. All the subjects assessed for their cause of knee pain. When the evaluation concluded that the subjects are victims of Patellofemoral pain syndrome (PFPS), an informed consent was obtained from the subjects for the purpose of this study. The subject‘s intensity of pain is documented using a VAS scale for the usual and worst pain. The subject is then provided with an Anterior Knee Pain Scale, which consisted of a questionnaire. The questions on the pain scale are explained in detail and the subject is then asked to choose the most appropriate alternative. The Visual analogue scale (VAS) consisted of a simple 10 cm line, one end being marked with a zero and the other end being marked with a ten. The points zero and ten indicated the pain level, zero representing no pain and ten indicating the worst and most severe type of pain. All the other numbers from one to ten would indicate a gradual increment in the pain level. The subject was asked to indicate on the line where the pain is, in relation to the two extremes. The subject is then expected to choose a number on the scale rating his/her own pain appropriately. The Anterior Knee Pain Scale is a 13 item questionnaire which includes questions that ask the subject to describe their ability during walking, stair climbing, squatting, running, prolonged sitting, hoping and bar jumping. It instructs the subject to circle the latest choice, which corresponds to their knee symptoms. The focus of the anterior knee pain scale (AKPS) on symptoms may lead the subject to emphasize pain rather than function. The scale consists of discrete categories within which each item is weighted and responses are summed to provide an overall index in which 100 represents no disability In the Vastus medialis (VMO) co-ordination test, the subject is in the supine lying position. The examiner places the fist below the knee and the subject is asked to extend the knee slowly without pressing down or lifting the knee away. The test is considered positive when there is a lack of a coordinated full knee extension. After the pain scale questionnaire was completed, physiotherapy intervention was commenced for the subjects. Subjects in Group 1 received strengthening exercises of rectus femoris for 2 weeks. Rectus femoris strengthening included OKC which avoids terminal knee extension and CKC which avoids excessive knee flexion exercises. Knee extension exercises in OKC are given to the subject who is in a seated position in an extension curl pulley system. 10-RM is taken by a maximum amount of weight lifted 10 times through the prescribed range. An initial weight is reasonably chosen and based on that 10-RM was calculated a rest interval of 5 minutes should be given prior to attempting to lift the next heavier weight. CKC exercises include mini squatting with 0° to 40° of knee flexion with the subject standing against a Swiss ball supported on a wall. It was performed in 3 sets with each set comprising of 10 repetitions. Step exercises were started after the subject could descend 5 steps without pain. Subjects in Group 2 received strengthening of vastus medialis obliquus for 2 weeks. OKC exercises were given in sitting with the knee at 90° flexion. 10 RM was taken by a maximum amount of weight lifted 10times through full knee extension with lower leg lateral rotation to facilitate maximum contraction of the vastus medialis obliquus. An initial weight is reasonably chosen and based on that 10RM is calculated and then knee extension is performed till 0° CKC exercises were done by using step-down exercises where the subjects were made to step down from the step which is of 25cms in height. When the subject could complete 5 step downs from a 25 cm step without pain, the step down exercise and VMO retraining with isometric hip abduction in standing and stretching of tightened soft tissue structures are included. Outcome was measured at the end of 2nd week. Outcome measures: All the data on the scales of Visual analogue scale (VAS), Anterior knee pain scale (AKPS) and Vastus medialis obliqqus (VMO) Co-ordination were obtained before the initiation of the treatment and 2 weeks after the completion of the treatment. Anterior knee pain scale (AKPS) questionnaire was used with a set of questions based on the symptoms, the results of which were summed up and the scores were taken. Similarly, Visual analogue scale (VAS) was used to document the pain. Data analysis: The software programme used for data analysis was SPSS Ven15. Microsoft Excel was used for graphs. Demographic data of anterior knee pain scale (AKPS) and Visual analogue scale (VAS) status of both the groups were analyzed by using paired?t‘ test. Probability values of less than 0.05 were considered statistically significant. Demographic data of Vastus medialis obliquus (VMO) Coordination test status was analyzed by using the ?Fishers test‘. Probability values of less than 0.05 were considered significant.
RESULTS
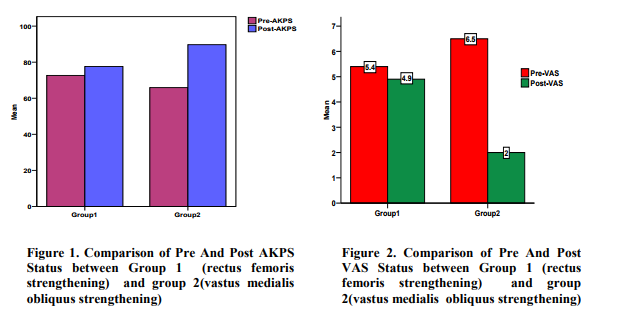
When subjects performed rapid strengthening exercises for rectus femoris under group 1 and VMO under group 2, there were differences in both the groups but more significantly in group 2. In table 2 comparisons are done between Pre and Post Anterior knee pain scale (AKPS) within group 1(Rectus femoris strengthening). Pre Anterior knee pain scale (AKPS) had 20 subjects having mean of 72.65 (+/-15.45) where Post Anterior knee pain scale(AKPS) had 20 subjects having mean of 77.60 (+/-14.01) and a mean difference of -4.95 with p-value of 0.295 which is not significant. Group 2 analysis showed Pre Anterior knee pain scale(AKPS) with 20 subjects having mean of 65.90 (+/- 13.19) where Post Anterior knee pain scale (AKPS) had 20 subjects having mean of 89.70 (+/- 6.67) and a mean difference of -23.8 with a significant p-value of 0.0001.
 DISCUSSION
DISCUSSION
At the end of our study, strengthening of the VMO showed very good improvement in PFPS subjects than in strengthening of rectus femoris muscle and by this it is clear that Rectus femoris strengthening is not much effective in patients with patellofemoral pain syndrome. There was also a reduction in VAS status in subjects under VMO strengthening programme than in the rectus femoris strengthening programme. Even in the Anterior knee pain scale questionnaire there was an improved scoring in group 2 with VMO strengthening programme at the end of 2week programme up to 100%, but there was no any significant change in the VMO Co-ordination test, so this test cannot be used as an assessment tool in the subjects with Patellofemoral pain syndrome. Several studies suggest that VMO dysfunction could lead to PFPS, so for effective rehabilitation one has to concentrate on the strengthening of VMO. The tension developed in VMO acts both medial and posterior aspect of knee joint and is known to resist lateral patellar displacement. Clinical observation linking loss of active full knee extension to VMO atrophy has led to the belief that VMO has its main role in the last 15º of active knee extension. Many conservative treatments were based on this hypothesis. In contrast, recent studies have failed to find selective VMO activity in this arc5 . In our study we have done a VMO Coordination test to find out the VMO dysfunction as described by Souza5 . But most of the subjects showed a negative result even with severe symptoms that is most of these patients had no difficulty in accomplishing extension. Thus in our study VMO Co-ordination test showed no significance in both the groups. Clinically relevant results were achieved without treatment strategies like taping and stretching regimens, which suggest that the underlying cause of Patellofemoral pain syndrome(PFPS) may not be restricted to the Patellofemoral joint(PFJ). Mascal et al 6 did case studies and suggested that patients with PFPS demonstrated abnormal kinematics at the hip that responded favorably to an exercise programme specifically targeting the hip, pelvis and trunk musculature. Turnia et al7 have proposed that the increased risk of PFPS in females was due to structural differences in the pelvic width, femoral anteversion, ?Q‘ angle, tibial torsion, hormonal differences and the effect of estrogen on theconnective tissues. In our study the two groups were divided with equal number of males and females. Thus, statistically it showed that age is not significantly varying among the groups as the mean age in Group 1 and Group 2 was 25.85 and 27.65 respectively. Herrington et al8 found that the relative difference in the overall activity between VMO and VL was not influenced by gender, hip position and mode of exercises. The findings of their study indicates that when choosing exercises for the rehabilitation of patients with patellofemoral pain, the aim would be to select exercises which minimize joint loading rather than exercises which recruit VMO as this would be unlikely to occur. Therefore, in our study we have followed the exercises with minimal joint loading and specific degrees of knee movements, i.e. 90º to 50º in OKC and 0º – 40º in CKC. In our study, most of the patients have more pain during descending stairs than ascending. This could be explained by a study on PFJ stresses. During stair ascent Patellofemoral Joint Reaction Force (PFJRF) decreases because of decreased cadence and the forward lean of the trunk, thereby reducing the knee extensor moment. During stair descent, there is no significant reduction in the PFJRF and the PFJ stress value remains the same. On comparison of ascending and descending stairs, the PFJ stress – time integral is 1.5 times greater than descending stairs and thus an increase in pain is felt during descent9,10 As there are not many studies done on role of Rectus femoris in patients with patellofemoral pain syndrome we suggest that further studies to be done to find out the relationship between rectus femoris with vastus medialis obliquus and vastus lateralis rehabilitation. Limitations of the study Most of the chief complaints of the patients were pain during kneeling but the AKPS does not have a question related to kneeling. Some of the questions on the AKPS have posed a problem for patients including ?atrophy of the thigh‘, ?flexion deficiency‘ and ?subluxation.‘ VMO Co-ordination test, which was considered to be a diagnostic test for PFPS, also gave negative results in many subjects with PFPS. VMO Coordination test may hence, not be considered as a diagnostic test in patellofemoral pain syndrome (PFPS).
Future Scope
Further research is warranted to determine the relationship between rectus femoris and vastus medialis obliquus by using electromyographic study, and another study can be done on the existing Anterior knee pain scale questionnaires could be modified or the development of a more responsive questionnaire could be devised which can include all the factors of patients with patellofemoral pain syndrome. Further study can be done on Athletes with patellofemoral pain syndrome to find efficacy of rectus femoris with vastus medialis obliquus. Comparative study between rectus femoris and vastus medialis obliquus can be done using different treatment methods like taping, ultrasound therapy in patients with patellofemoral pain syndrome.
CONCLUSION
In this study it was found that vastus medialis obliquus strengthening is more effective compared to strengthening of rectus femoris in patients with patellofemoral pain syndrome.
References:
REFERENCES
1. Oatis CA. Structure and function of the bones and non-contractile elements of the knee. Kinesiology. Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams and Wilkins; 2002. 710 – 15
2. Lefebvre R, Lerone A, Pounarat G, Boncher JP. Vastus Medialis: Anatomical and functional consideration and implication based upon human and cadaveric studies. J manipulative physio Ther 2006; 29: 139 – 44.
3. Cowan SM, Hodges PW, Bennell KL, Crossley. Altered Vasti Recruitment when people with patellofemoral pain syndrome complete a postural task. Arch phys med Rehabil 2002; 83: 1989 – 99.
4. Tillman MD, Chiumento AB, Trimble MH, Bauer JA, Cauraugh JH, Kaminski TW, Hass CJ. Tibiofemoral rotation in landing: the influence of medially and laterally posted orthotics. Physical Therapy in Sport 2003; 4: 34 – 39.
5. Nijs J, Geel CV, Vanderauwera C, Van de Velde B. Diagnostic value of five clinical tests in patellofemoral pain syndrome. Manual Therapy 2006; 11: 69 – 77.
6. Mascal CL, Landel R, Powers C. Management of patellofemoral pain targeting hip, pelvis and trunk muscle function: 2 case reports. J ortho Sports Phys Ther 2003; 33:642 – 60
7. Alfonso VS, Sastre ER. Anterior knee pain in the young patient – what causes the pain? Acta Orthop Scand 2003; 74: 697 – 03.
8. Herrington L, Blacker M, Enjuanes N, Smith P, Worthingtom D. The effect of limb position, exercise mode and contraction type on overall activity of VMO and VL. Physical Therapy in sport 2006; 7: 87 – 92.
9. Brechter JH, Power CM. Patellofemoral joint stress during stair ascent and descent in persons with and without patellofemoral pain. Gait and Posture 2002; 16:115-23
10. McClinton S, Donatell G, Weir J, Heiderscheit B. Influence of Step Height on Quadriceps Onset Timing and activation During Stair ascent in Individuals with Patellofemoral Pain Syndrome. J OrthopSports Phys Ther 2007; 37: 239 –
|






 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License