IJCRR - 3(11), November, 2011
Pages: 05-12
Print Article
Download XML Download PDF
A COMPARATIVE STUDY OF EFFECT OF PHYSICAL EXERCISE ON PLATELET AGGREGATION BETWEEN
HEALTHY PERSONS AND ISCHEMIC HEART DISEASE PATIENTS
Author: Shrimali Lalit, Khan Mohd.Iqbal, Patil Rajkumar, Agarwal Lokesh
Category: Healthcare
Abstract:Aim of The Study:To find out the effect of physical exercise on platelet aggregation on normal
and Ischaemic Heart Disease patients.
Methodology:The present study was conducted on 50 male volunteers between the age of 40
to 60 years who were categorized in two groups of 25 each. Group 1 (n=25) Healthy group.
Group II (n=25) IHD group. Venous blood sample (4 ml) was collected before and at the end of
completion of stage III of Bruce protocol on the TMT and subjected for estimation of platelet
aggregation on ELVI-840 aggregometer and Omniscintro chart recorder.
Results:The effect of stress by Tread Mill Test (TMT) on platelet aggregation in normal
individuals was a significant (P< 0.05) decrease in platelet aggregation after stress induced by
ADP and collagen. . ADP induced platelet aggregation decreased which was statistically
significant .Similarly collagen induced platelet aggregation also significantly decreased.
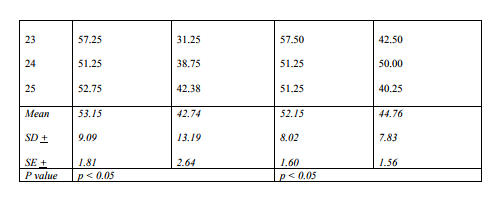
The effect of stress (TMT) on Platelet aggregation in patient of Ischemic Heart Disease (IHD)-
There was an increase in ADP induced platelet aggregation after stress from a mean of
47.40+12.18 to 59.79+12.43 percent which was statically significant (p< 0.001). Similarly there
is also an increase in collagen induced platelet aggregation after exercise, from a mean of
39.79+11.19 to 57.30+8.79 percent. This was statistically significant (p< 0.001).
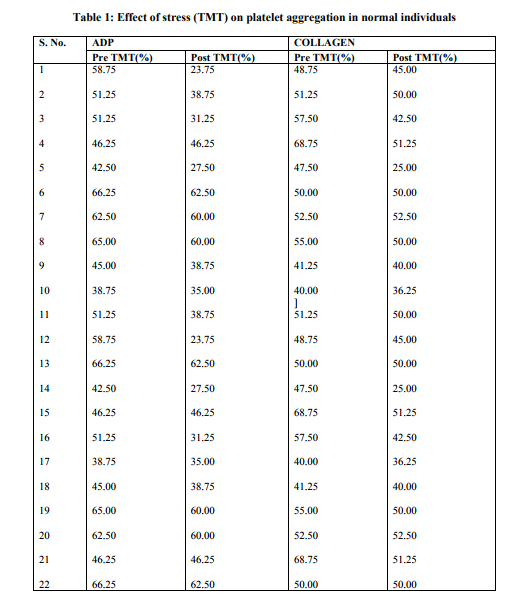
Conclusion:The effect of stress (TMT) on healthy individuals reduced platelet aggregability in
both ADP and collagen, showing that regular exercise helps to prevent platelet aggregation
Keywords: IHD, TMT, ADP, Collagen
Full Text:
INTRODUCTION
The burden of atherothrombotic vascular disease in patients and community is enormous. One way of reducing the burden is to reduce the platelet aggregation in people predisposed to such high risk. Platelets have been implicated as being pathophysiologically important in hypertension and ischemic heart diseases1 . Rheological factors also affect the platelet functions in many ways. It has been discovered that rheological factors mediate the binding of von Willebrand Factor (vWF) to platelets in vivo2 It is mostly dependent on mechanical force i.e. shear stress, which is defined as the force per unit area between laminae of blood. When the time averaged mean shear stress level in the arterial circuit reaches pathological level, as in stenosed arteries, it A COMPARATIVE STUDY OF EFFECT OF PHYSICAL EXERCISE ON PLATELET AGGREGATION BETWEEN HEALTHY PERSONS AND ISCHEMIC HEART DISEASE PATIENTS Shrimali Lalit1 , Khan Mohd.Iqbal1 , Patil Rajkumar2 , Agarwal Lokesh2 1Department of General Medicine, Geetanjali Medical College and Hospital, Udaipur, Rajasthan 2Department of Community Medicine,Mahatma Gandhi Medical College and Research Institute, Pondicherry E-mail of Corresponding Author: drlalitshrimali@yahoo.co.in 6 International Journal of Current Research and Review www.ijcrr.com Vol. 03 issue 11 November 2011 results in thrombus formation. Prostacyclin derived from endothelial cells, inhibits shear-stress induced platelet thrombus formation on subendothelium2 . Many vessel wall factors also influences the thrombus formation such as vascular endothelium, collagen, insoluble vWF, fibrinogen, thrombospodin, laminin, fibronectin etc. Endothelium produces vasorelaxing and antiplatelet factor2 which in healthy conditions are known to increase with exercise3 . Atherosclerosis and the attending endothelial dysfunction may reduce the capacity of endothelial cells to release these products during exercise, thereby enhancing the platelet activating effect of shear4 . Moderate and sternous exercise is known to increase the platelet aggregation5,6 but even low grade exercise, too transiently enhances the whole blood platelet aggregability in patients with obstructive coronary artery disease(CAD). In contrast, the same degree of exercise does not significantly affect the platelet function in subjects without apparent CAD7 . To see the effect of stress on platelet aggregation in IHD patients,the study was planned.
MATERIAL AND METHODS The present study was conducted at Geetanjali Medical College and Hospital,Udaipur,Rajasthan. Total 50 male volunteers in age group of 40 to 60 years were categorized in two groups of 25 each: Group 1 (n=25) Healthy group, with no evidence of any non-communicable disease. Group II (n=25) Coronary Artery Disease group, known patients with documented IHD. Both the groups were matched for the age. All the participants were subjected to stress test on computerized treadmill so as to complete stage III of Bruce protocol to be eligible for the study. Informed written consent was obtained from the participants before the study. Inclusion criteria For Group I Healthy Persons: Persons with no history and evidence of any non communicable disease. For Group II CAD : Persons having documentation of old healed myocardial infarction.In ECG ST depression of > 2mm in consecutive leads with or without symptoms. In ECHO- Regional wall motion abnormalities (RWMA). Positive TMT: Horizontal or down ST segment depression of > 1mm from previous level during TMT with or without symptoms. Junctional depression with slowly rising ST slope that remains depressed 1.5 mm or more than 0.80 m seconds after the J point. Slowly upsloping ST segment being depressed in excess of 2.5 mm, 80 m seconds after the J point. Downsloping or flat, ST segment depression in excess of 2.5 mm. Horizontal or Downsloping ST segment depression appearing during the first stage of exercise and/or persisting beyond 8 minutes in the recovery phase. Complex ventricular ectopic activity, including multiform ventricular or occurrence of ventricular fibrillation. Exclusion criteria Patients with liver disease, thyroid disease, stroke and those who were on antiplatelet agents or NSAIDS were excluded by history and relevant investigations. Similarly those who used to consume tobacco in any form were also be excluded from the study. 7 International Journal of Current Research and Review www.ijcrr.com Vol. 03 issue 11 November 2011 Stress Test The stress test was done by asking the volunteer to complete stage III of the Bruce protocol. Bruce multistage maximal treadmill protocol has 3 minute periods to allow achievement of a steady state before work load in increased. The speed of the treadmill is as followsStage Speed Stage I 2.8 Kms/hr Stage II 4.2 Kms/hr Stage III 5.7 Kms/hr Stage I has an elevation grade of 10 Percent, increasing by 2 percent for every stage. Study Protocol After an overnight fast, venous blood sample (4 ml) was collected without undue pressure from the selected patient. The patient after brief history, physical examination & written consent was subjected to the stress test. Another sample (4 ml) was collected at the end of completion of stage III of Bruce protocol the TMT. Both the blood samples were subjected for estimation of platelet aggregation on ELVI-840 aggregometer and Omniscintro chart recorder. Statistical Analysis Data were entered in SPSS software and analysed. T test was used to observe any difference between healthy and IHD patients.
RESULTS Table 1 shows the effect of stress (TMT) on platelet aggregation in normal individuals. There was a significant (P<0.05) decrease in platelet aggregation after stress included by ADP and collagen. ADP induced platelet aggregation decreased from a mean of 53.15 + 9.09 to 42.74 + 13.19 percent. This decrease was around 20 percent which was significant (p<0.05). Similarly collagen induced platelet aggregation also decreased from a mean of 52.15+ 8.02 to 44.76+ 7.83 percent, which was around 21 percent and statistically significant (p<0.05). Table 2 shows the effect of stress (TMT) on Platelet aggregation in patient of Ischemic Heart Disease (IHD). There was an increase in ADP induced platelet aggregation after stress from a mean of 47.40+12.18 to 59.79+12.43 percent. This increase was around 29 percent which was statically significant (p<0.001). Similarly there was also an increase in collagen induced platelet aggregation after exercise, from a mean of 39.79 +11.19 to 57.30+8.79 percent. This increase was around 45 percent and also statistically significant (p<0.001).
DISCUSSION The present study was designed with the aim to observe the effect of stress (TMT) on platelet aggregation in normal individuals, Group I constituted of healthy individuals and Group II had established patients of coronary artery disease. In the present study of stress (TMT) on normal individuals, ADP induced platelet aggregation as well as collagen induced platelet aggregation also decreased significantly (p<0.05). In patients with Ischemic Heart Disease (IHD), stress (TMT) increased platelet aggregation induced by ADP and collagen, both were significant (p<0.001). Many studies have reported that the response of platelet aggregation in healthy individuals is quite variable. In a study maximal exercise lowered platelet activity in young volunteers8 . Other studies on the effect of exercise on platelet aggregation had given 8 International Journal of Current Research and Review www.ijcrr.com Vol. 03 issue 11 November 2011 variable results9-14. Some of the inconsistency surrounding the effect of exercise on platelet aggregation could be explained by differences in physical condition: healthy young individuals who do not engage in regular exercise, platelets show increase in aggregability during exercise, whereas those already participating in an exercise programme show the opposite15,16.Similarly, the failure of exercise to reduce platelet aggregability in elderly people could be explained by their generally low level of physical activity. There is another factor that young people release more platelet inhibitors (prostacyclins and nitric oxide) from the vessel wall than do the elderly, who have a feebler functional capacity of the vascular endothelium as a result of atherosclerosis, In our study it was found that there is a decrease of platelet aggregation, which suggest a healthy endothelium with normal release of platelet inhibitors. In studies in patients of IHD, exercise showed an increase in platelet aggregation which was substantiated by our study which demonstrated a very significant increase (p<0.001). This shows that stress is harmful and may precipitate cardiovascular events. It is likely that other forms of stress have similar effect as that of exercise (TMT), and therefore stress in any form should be avoided in patients of IHD. Plasma platelet factor 4 (PF-4)17 (a heparin neutralizing protein) is found to increase in IHD during exercise and may account the increase in platelet aggregation. It has also been found that that vascular that vascular endothelium produces vasorelaxing and antiplatelet factors18,19 which in healthy conditions are know to increase with exercise20,21. Atheroselerosis and the attending endothelial dysfunction may reduce the capacity of the endothelial cells to release these products during exercise 22,23 hereby enhancing the platelet activating effects of shear.
CONCLUSION The effect of stress (TMT) on healthy individuals reduced platelet aggregability in both ADP and collagen, showing that regular exercise helps to prevent platelet aggregation.The effect of stress (TMT) in patients with IHD showed a statistically significant (p<0.001) increase in platelet aggregation induced by both ADP and collagen. ln view of the above factors the importance of regular exercise cannot be overemphasized. Past studies have documented that in patients with coronary artery disease physical exercise induced platelet aggregation may not be checked by regular administration of common anti platelet agent - aspirin. This fact needs further attention in management of patients with IHD in order to offer better therapeutic options.
References:
1. Conti C.R., Mehta J.L.: Acute Myocardial ischemia: Role of atherosclerosis, thrombosis, platelet activation, coronary vasospasm and altered arachidonic acid metabolism. Circulation 75 (suppl.l): V-84, 1987.
2. Michael H.K., Helluins J.D., Larry V., Mcintre Andrew 1 et al. 61.Platelets and shear stress. Blood 88: 1525, 1996.
3. Chow T.W., Hellums J.D., Moake J.L., Kroll M.H., Shear stress induced, von Willebrand factor involving platelet glycoprotein lb. initiates calcium: flux associated with aggregation. Blood 1:113, 1992.
4. Blevel T., Hellurns ID., Soli R.T.: The kinetics of platelet aggregation induced by fluid shearing stress. Microvas. Res 28: 279, 1984.
5. Wallen N.H., Hold C, Rahnguist N., Hjendah P: Effects of mental and physical stress on platelet function in patients with stable angina pectoris and healthy controls. Eur. Heart J.l8: 807, 1997.
6. Takule J., Hayashi .1., Hata Y., Nakahara K. and Ikeda Y.: Enhanced platelet aggregability under high stress after treadmill exercise in patients with effort angina. Thromb Haemost 75: 833, 1996.
7. Andreotti F., Lanza G.A., Sciahbasi A., Fischetti D., Sestits A., Cristofaro R.D. and Maseri A: Low grade exercise enhances platelet aggregability in patients with obstructive coronary disease independently of myocardial ischemia. Am . J cardiol 87: 16, 2001.
8. G.Gleerup, K.Winther. The effect of ageing on platelet function and fibrinolytic activity. Angiology 46: 715, 1995.
9. Warlow C.P., Ogston D. Effect of exercise on platelet count, adhesion and aggregation. Acta Haemat 52: 47, 1974.
10. Knudsen J.B., Brodthagen U. Gamsen J., Jardal R., Narregaard-Hansen K., Paulev P.E. Platelet function and fibrinolytic activity followed distance running. Scand J. Haematol 29: 425, 1982.
11. Mant M.J., Kappagoda C.T., Quinlan J. Lack of effect of exercise on platelet activation and platelet reactivity. J Appl physiol 57: 1333, 1984.
12. Winther K., Trap-Jensen J. The effect of exercise on platelet betaadrenoceptor function and platelet aggregation in healthy human ? volunteers. Clin phyo 8; 147, 1988.
13. Kestin A.S., Ellis P.A., Barhard M.R., Errichetti A. Rosner B.A., Michelson A.D., Circulation 88(Pt.1): 1502, 1993.
14. FitzGerald D.J., Roy L., Catella F., FitzGerald G.A. Platelet activation in unstable coronary disease. New Engl J .Med 315: 983; 1986.
15. Watts E.J. Haemostatic changes in long distance runners and their, relevance to the prevention of ische1nic heart disease. Blood coagul Fibrinolysis 2:221, 1991.
16. Beisiegel B, Treese N, Hafner G., Meyey J., Darius H. Increase in endogenous fibrinolysis and platelet activity during exercise in young volunteers. Agents Actions Suppl. 37, 183:1992.
17. Green L.H., Seroppian E., Handin R.I., platelet activation during exercise induced myocardial ischemia. N.Engl .1.Med 302(4): 193, 1980.
18. Moncade S, Gryglewski R., Bunting S., Vabe J.R. An enzyme isolated from arteries transforms prostaglandin endoperoxides to an unstable substance that inhibits platelet aggregation. Nature 263,: 663, 1976.
19. Andreotti F., Sciahbasi A., De Marco E., Maseri A. Preinfarction angina and improved reperfusion of the infarct related artery. Thromb Haemost 82:68, 1999.
20. Piret A, Niset G., Depiesse E., Wyns W., Boeynaems J.M., Poortmans J., Degre S. Increased platelet aggregability and prostacyclin biosynthesis induced by intense physical exercise. Thromb Res 57: 685, 1990.
21. Wennmalm A., Fitzgerald G.A., Excretion of prostacyclin and thromboxane A2 metabolites during leg exercise in humans. Am J.Physiol 225: H 15, 1988.
22. Diodati J.G., N.Dakak, D.M. Gilligan, A.A. Quyyumi. "Effect of atherosclerosis on endothelium dependent inhibition of platelet activation in human. Circulation, 98; 17, 1998.
23. Kishi Y., Ashikagea T. Numano F., Inhibition of platelet aggregation by prostacyclin is attenuated after exercise in patients with angina pectoris. Am Heart J., 123 : 291, 1992.
|






 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License