IJCRR - 3(12), December, 2011
Pages: 41-48
Print Article
Download XML Download PDF
PHYSIOLOGICAL COST INDEX (PCI) IN PATIENTS WITH CHRONIC OBSTRUCTIVE PULMONARY DISEASE (COPD) BEFORE AND AFTER GIVING TWO COMMONLY USED BREATHING EXECISES
Author: Ajith S, Ivor Peter D‘Sa, Mohamed Faisal C K, Anandh V, Sreejith Namboothiri
Category: Healthcare
Abstract:Background and purpose: Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) is a major cause of morbidity and mortality in India. It is characterized by dyspnoea and limited exercise capacity. It
has been proved that breathing exercises spontaneously reduce dyspnoea and mechanical work of
breathing in subjects with COPD, thus gaining an important part in pulmonary rehabilitation. The
aim of this study was to determine the energy expenditure in people with COPD before and after
performing three commonly used breathing exercises by using the Physiological Cost Index (PCI)
as a tool. Study Design: Experimental pre test \?post test. Materials and Methods: The PCI of 30 male patients were studied on two occasions, before performing exercise and after performing
two commonly used breathing exercise viz, Diaphragmatic Breathing (DB) and Pursed Lip
breathing (PLB). Results: Following the breathing exercise the PCI decreased in 22 patients, in 6 patients it was unchanged and in 2 patients it was increased. The mean PCI value before
breathing exercise was .3099(range .13 - .67) and that after breathing exercise was .2387(range
.07 -.75). Conclusion: The Physiological Cost Index (PCI) of subjects suffering from Chronic
Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) was seen to decrease after performing two commonly
used breathing exercises, thus indicating a favourable decrease in energy expenditure following
the breathing exercises.
Keywords: Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD), Energy expenditure, Physiological Cost Index (PCI), breathing exercises.
Full Text:
INTRODUCTION
The term Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) refers to chronic disorders that disturb airflow. COPD is a major cause of morbidity and mortality in India1 . The principal symptoms are dyspnoea and limited exercise capacity. Patients with COPD demonstrate exercise limitation as a consequence of both an increased ventilatory requirement and a decreased ventilatory capacity. The increased ventilatory requirement arises from the elevated wasted ventilation fraction of each breath and hypoxemia secondary to ventilation- perfusion mismatching, both of which stimulate minute ventilation to increase 2 . The reduced ventilatory capacity is primarily the result of airflow obstruction, which causes an increased work of breathing 3 . Due to their increased ventilatory demands, people with COPD have a higher resting oxygen consumption than do people without pulmonary disease.4, 5 This higher resting oxygen consumption may be explained by increased mechanical work of breathing or reduced ventilatory muscle efficiency, or both, in patients with severe COPD. Consequently, hyperinflation of the lungs and the chest wall causes the diaphragms to become depressed, which contributes further to breathing inefficiency and increased metabolic cost 6 7.
and increased metabolic cost 6 7 . To help relieve the symptoms and physical limitations of patients with COPD, physical therapists have been teaching breathing exercise in the form of Diaphragmatic Breathing (DB) and Pursed Lip Breathing(PLB)8 9 10 .The overall effects of these two types of breathing exercise are to improve ventilation gas exchange, decrease work of breathing, maintain or improve mobility of chest wall, reduce the respiratory rate, increase tidal volume, reduce dyspnoea, improve gas mixing at rest and facilitate relaxation.11 Controlled breathing manoeuvres appear to be widely used in the physical therapy management of patients with COPD, both individually and in pulmonary rehabilitation programs12,17,18,19 . The energy expenditure in patients with COPD is an interesting subject that has not been studiedextensively. Better understanding of breathing patterns in people without pathology and in patients who are prone to ventilatory distress, such as those with COPD ,could yield information about enhancing non-invasive physical therapist interventions used to reduce the mechanical work of breathing and to improve ventilatory efficiency. In this study the energy expenditure before and after the breathing exercise is calculated. The energy expenditure is calculated by using a simple tool, the Physiological Cost Index (PCI). The PCI is a simple tool used to measure energy expenditure during walking. The PCI was formulated by Macgregor (1979)13 20 who recognized the need for a simple, functional and non-invasive method of measuring the physiological cost of walking that could be equally applied in domiciliary and clinical environments. Mechanical work in biological systems is achieved when a force applied to a structure results in movement. The amount of work produced is the product of the force applied and the distance moved. The PCI is founded on the principle that heart rate and walking speed are linearly related to oxygen consumption (VO2) at sub maximal levels of exercise (Astrand and Rodahl,1986).14 While the measurement of VO2 is the conventional means of determining energy expenditure , a major drawback is its requirement to collect expired gas. This involves the use of equipment that is cumbersome to wear and often unavailable in the clinical environment. The PCI offers a practical alternative; it is an empirical index and is defined by Mac Gregor (1979) as follows

also to determine the positive effects of breathing exercise on energy expenditure in subjects
METHODS
Subjects This study was approved by the Institutional Ethical Committee of Nitte Institute of Physiotherapy. 30 male subjects from the outpatient department of K S Hegde Medical Academy Mangalore, who were diagnosed by the physician as having COPD were selected for the study. The diagnosis was confirmed by assessment with the COPD assessment form. Subjects were included if their forced expiratory volume in 1 second (FEV1) was ≤ 60% of the predicted value. Written consent was taken before conducting the study. The subjects were excluded if they had recent respiratory exacerbation, significant cardiac disease, resting pulse oximetry < 85%, a diagnosis of cor pulmonale, orthopaedic exercise limitations or were on supplemental oxygen.
Experimental design Resting heart rate (RHR) was recorded after the subject had been seated for 15 minutes15 . After measuring the RHR the patient was made to walk up and down the 100-ft walkway at a comfortable walking speed for 6 minutes .The heart rate and walking speed at the end of 6 minutes was recorded. The RHR and WHR was measured by ambulatory pulse meter (PM 60 Am. Pulse oximeter). After this procedure PCI was calculated with the above mentioned equation.
After calculating the value, two breathing exercises were given; the patients were positioned in a treatment couch in long sitting position with back rested on adequate pillows. The exercises were Diaphragmatic Breathing and Pursed Lip Breathing.
Diaphragmatic breathing occurs when there is a conscious appreciation of inspiring air to the lung bases with slight forward abdominal displacement and passive relaxed expiration. The instruction given to the patient was ?breathe in slowly through your nose and aim at getting the air to the lower part of your lungs; remember to relax your tummy and upper chest allow the air to go under here (the investigator put his hand on the subjects epigstric/sub costal region). Then relax and let all air out through your mouth, allowing your tummy to sink gently?.16
Pursed lip breathing in this study consisted of each patient‘s normal pattern of inspiration, but expiration was performed by gently blowing through pursed lips. The instruction given to the patient was ?Breathe in through your nose and exhale by blowing gently against your loosely closed lips, like blowing a candle flame, so that it bends but doesn‘t blow out?.16
Patients were observed while performing the breathing exercise to ensure that each exercise was performed as instructed. No other verbal instruction or encouragement was given during the recording. Each breathing exercise was performed 5 times. After a 3-minute rest, PCI was again calculated by the above- mentioned method.
RESULTS
The mean age of the subjects who participated in the study was 60.1 with SD ± 5.4 (range 43-70). 44% of the patients were of the age group 55-60 years and 43% of the age group 60-65. Only 3% of the subjects were of age group 40-45. (Table 1,Figure 1). All the 30 patients who were selected for the study completed the procedure. The mean age of the thirty patients was 60 (range= 43- 70), standard deviation was 5.40. (Table 2)
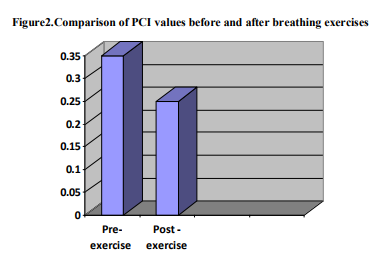
The mean PCI value before breathing exercise was 0.3099 (range 0.13-0.67) with a standard deviation 0.1299. The mean PCI after breathing exercise was 0.2387 (range 0.07 – 0.75) with standard deviation 0.1404. (Table 3, Figure 2) Following the breathing exercise the PCI decreased in 22 patients, in 6 patients it was unchanged and in 2 patients it was increased.
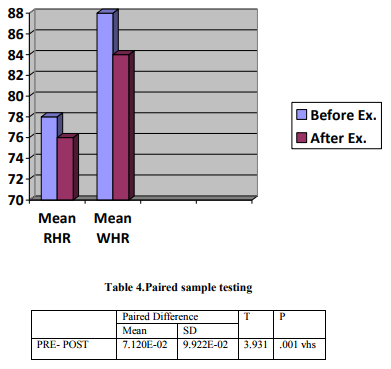
Among the 30 patients, 9 patients had no change in resting heart rate, 3 patients had increase in resting heart rate and 18 patients had a decrease in resting heart rate after performing the breathing exercise. The walking heart rate of 26 patients were decreased, those of 2 patients increased and those of 2 patients remained unchanged after performing the breathing exercise. (Figure 3)
In the paired sample testing, the mean of pre- treatment to post treatment difference in PCI was seen to be 7.120E-02 with standard deviation 9.922E-02. The difference was found to be very highly significant (p = 0.001) (Table 4)
DISCUSSION
The significant difference obtained between the mean PCI before breathing exercise (0.3099±.1291) and the mean PCI after breathing exercise (.2387,SD±.1404)given in table II reflects the decrease in energy expenditure of walking in the subjects after doing the breathing exercise. Since there was no difference in walking speed before and after the breathing exercise, the difference in PCI can be attributed to the lowering of both resting heart rate and heart rate during walking after breathing exercise. In people suffering from COPD, hyperinflation of the lung and chest wall causes the diaphragm to become depressed, which contributes further to breathing inefficiency and increased metabolic cost. The mechanical stress and work of breathing is more in people with COPD. This increased physiological work of breathing may lead to an increased resting heart rate and heart rate during walking in people with COPD. Due to increased ventilatory demands in patients with COPD, the heart has to pump more blood to deliver oxygen to the harder- working ventilatory muscles. This increased work of the heart leads to increased heart rate both during rest and during activities in patients with COPD.
18 patients had a decrease in resting heart rate and 9 patients had no change in resting heart rate after performing the breathing exercise. This can be explained in the following manner: breathing exercise in the form of diaphragmatic breathing and pursed lip breathing help to relieve the symptoms and physical limitations of patients with COPD. A study by Gosselink proved that deep breathing exercise which includes diaphragmatic breathing and pursed lip breathing resulted in immediate decrease in heart rate, respiratory rate anxiety and dyspnoea 10. The stress and mechanical work of breathing will reduce after performing breathing exercises. This decreased physiological work of breathing may lead to decreased resting heart rate.
Among the 30 patients, the heart rates during walking of 26 patients were decreased. Evidence indicates that diaphragmatic breathing and pursed lip breathing appears to be an effective way to decrease dyspnoea and improve gas exchange in patients with COPD. Walking after performing breathing exercise causes a lesser energy expenditure because the dyspnoea is reduced, thereby reducing the work of breathing. There is lack of conclusive evidence as to the mechanism 45 International Journal of Current Research and Review www.ijcrr.com Vol. 03 issue 12 December 2011 behind the reduction of the heart rate following breathing exercises.
A few studies have demonstrated positive effects during diaphragmatic breathing exercise. Evidence suggests that diaphragmatic breathing does not change regional ventilation in people with COPD. These techniques may increase total ventilation but if so, the evidence suggests this may be due to the slower, deeper breathing patterns that may occur during diaphragmatic breathing rather than an exaggeration of abdominal motion. Some authors have noted an increase in the work of breathing; this may be due to increased paradoxical rib motion during diaphragmatic breathing.
One of the limitations of the study was that the sample size of 30 patients may not have been enough to provide the statistical weightage needed to establish the results. Rose et al (1991) have shown that when calculating the PCI the resting heart rate is sensitive and must be measured with accuracy. In this study the extrinsic factors which may have influenced the resting heart rate (for instance administration of drugs like antihypertensive, bronchodilators, beta blockers etc and intake of caffeine in the diet may have substantial effects on the resting heart rate) were not considered when including patients in the study
Scope for further study The changes in the energy expenditure following individual breathing exercises can be further studied to determine which breathing exercises would be most beneficial to patients undergoing pulmonary rehabilitation.
The exact mechanism behind the reduction of heart rate following exercise and the relationship between the change in heart rate and breathing exercise can be studied in more detail.
Studies could be conducted to evaluate the correlation between energy expenditure measured by PCI and energy expenditure measured by laboratory techniques like calorimetry.
CONCLUSION
The PCI of subjects suffering from COPD was seen to decrease after performing two commonly used breathing exercises, viz, diaphragmatic breathing and pursed lip breathing. The PCI has established value as a measure of energy expenditure. The lowering of PCI following the breathing exercise may provide a better understanding of the effects of breathing exercise, and go on to prove that a reduction of dyspnoea is not all that is achieved by breathing exercises, thus reinforcing their role in a pulmonary rehabilitation program. The value of the PCI as a simple tool to measure energy expenditure can be highlighted, especially in contrast to the conventional methods, which can often be expensive and cumbersome.
References:
1. Singh V et al .Pulmonary rehabilitation in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Indian j chest Dis Allied Sci.2003 Jan –mar; 45 (1): 13-7.
2. Cooper CB. Determining the role of exercise in patients with chronic pulmonary disease. Med Sci Sports Exerc.1995 Feb;27(2): 147-57.
3. Brown HV, Waserman K. Exercise Performance in Chronic obstructive Pulmonary Disease. Med Clin North Am.1981 May;65(3): 525-47.
4. Donahole M et al Oxygen consumption of the respiratory muscles in 46 International Journal of Current Research and Review www.ijcrr.com Vol. 03 issue 12 December 2011 malnourished patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Am Rev Respir Dis.1989;140:385-391.
5. Schols AMWJ, F Redrix EWHM, Soeters PB. Resting energy expenditure in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Am J Clin Nutr.1991;54:983-987.
6. Rodarte JR, Hyatt RE. Respiratory mechanics: basics of respiratory disease. Am Thor Soc.1976;4:1-6
7. Marini JJ Inkacmarek RM ,Stoller JK, Eds. Work of breathing.. Current Respiratory Care .Philadelphia,Pa:BC Decker Inc,1988:188-194.
8. West JB .Pulmonary Pathophysiology:The Essentials.4th Ed.Baltimore, Williams and Wilkins, 1992.
9. Juzar A , Summer WR ,Levitzky MG, Eds. Pulmonary Pathophysiology. New York,NY:McGraw-Hill Inc,1999.
10. Gosselink et al Diaphragmatic breathing reduces efficiency of breathing in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Am J Respir Crit Care Med.1995;151:1136- 1142.
11. Rose Sgarlat Myers. Saunders Manual of Physical Therapy.1995:303-307.
12. Karen C Peebles ,Angela D Woodman ,Margot A Skinner .The Physiological Cost index in Elderly Subjects During Treadmill and Floor Walking.NZ Journal of physiotherapy.2003 Mar; 31(1):11-16.
13. Mac Gregor J .The objective measurement of physical surveillance equipment. In:proceedings of 3rd international symposium on ambulatory monitoring. London:academic Pr;1979.p 29-39.
14. Astrand P ,Rodahl K (1986).Textbook of Work Physiology 3rd ed. London,England:Mc Graw Hill ,pp.372.
15. American Thoracic Society. Guidelines for the Six- Minute Walk test. Am J Respir Crit Care Med Vol 166.pp 117- 117,2002.
16. Alice YM Jones, Elizabeth Dean, Cedric CS. Comparison of the Oxygen cost of breathing Exercise and Spontaneous Breathing in patients with stable Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease.Physical Therapy .2003 May ;83:424-431.
17. Steven E Weinberger. Principles of Pulmonary Medicine, 3rd Edition (chapter 6)
18. Ellen A Hillegass, H.Steven Sadowsky. Essentials of Cardiopulmonary Physical Therapy second edition (chapter6)
19. Jong C, Chang W , Wai PM, Chou CL. Comparison of oxygen consumption performing daily activities between patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease and a healthy population. Heart Lung .2003 Mar – April; 32(2):121-30.
20. Alexandra Hough. Physiotherapy in Respiratory care ,A problem –solving approach to respiratory and cardiac management, 2nd edition (chapter 3)
|






 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License