IJCRR - 4(18), September, 2012
Pages: 154-159
Date of Publication: 29-Sep-2012
Print Article
Download XML Download PDF
ASSESSMENT OF DISABILITY IN TERMS OF ACTIVITIES OF DAILY LIVING (ADL) IN LEPROSY AFFECTED PEOPLE OF LEPROSY COLONIES AT BIJAPUR CITY, KARNATAKA
Author: Vinod S Kamble, Aparna Y Takpere, Santosh M Biradar
Category: Healthcare
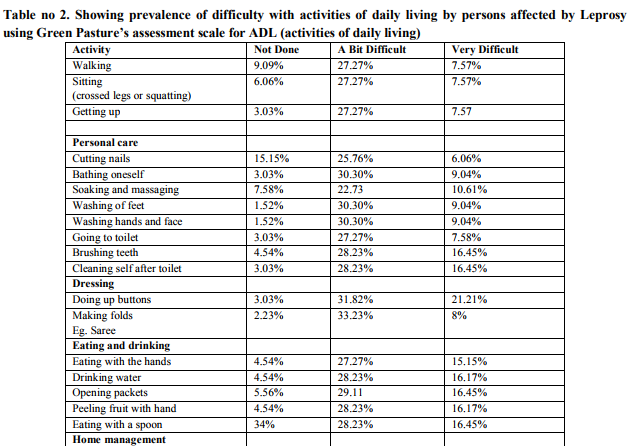
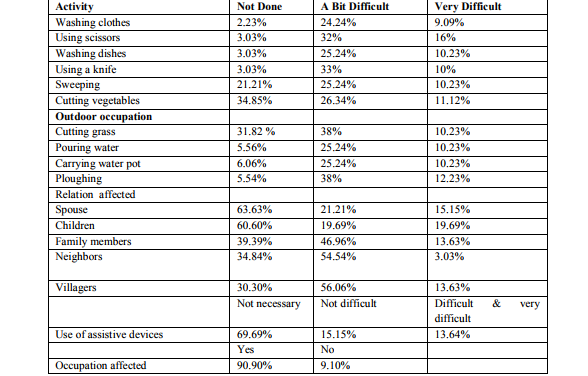
Abstract:Background: Disability in leprosy affects the activities of daily life which has got a negative impact on the quality of life. Further due to disability and social stigma there is restriction in participation in social functions. All these factors must be considered while measuring disability and rehabilitation. Objectives: 1) To assess the disability in persons suffering from leprosy and to find out the effect of disability on activities of daily living and social life. Design: A cross sectional descriptive type of study. Subjects: 132 people affected by leprosy, living in leprosy colonies at Bijapur, Karnataka, India were involved in the study. Methodology: A house to house survey and interview was carried out using the standard questionnaire of the Green Pasture's assessment scale. Results: The prevalence of different types of impairments ranged from 31% in Lower Limbs, 35.9% in Upper Limbs and 45.46% in Eyes. The most commonly affected indoor activities were bathing (30.30%), washing hands and feet (30.30%), going to toilet (27.27%), dressing (31.82%), using scissors and knife (33%), eating and drinking (28.23%). Among the outdoor activities affected were cutting grass (51%), ploughing (61%) and carrying water pot (48%). Conclusion: Experiencing severe difficulties with the activities of daily living is a common problem in persons with chronic impairments due to leprosy. This leads to restrictions in social participation and sometimes even isolation as a result of disfigurement and social stigma. The level of difficulty can be assessed and measured using Green Pasture's assessment scale based on subjective difficulty, which could be more helpful in rehabilitation.
Keywords: impairment, social participation, rehabilitation, leprosy, Green Pasture’s assessment scale.
Full Text:
INTRODUCTION
Leprosy is one of the major causes of preventable disability, including impairments, problems in activities of daily life and social exclusion resulting from stigma.1 Impairment and deformities (visible impairments) may cause limitations of activities of daily living (disability) and adverse social reactions (restriction of participation).2 Leprosy is still a major public health problem in several leprosy endemic countries with a worldwide prevalence of 212,802 patients at the beginning of 20083. In various studies done in India, the ratio between grade 2 and grade 1 disabilities ranged from 0.4-7.8.4 WHO disability grading does not grade disabilities but impairments. It is insensitive to change in the patient’s condition. 2 This leads to inappropriate way of rehabilitation and sometimes its failure, as it is based on impairment and not the subjective difficulties faced by the leprosy affected individuals. Therefore, a cross-sectional descriptive study was designed to find out the impairment and disability effect on the activities of daily living using Green Pasture’s assessment scale.5
Aims and Objectives
1. To assess the disability in persons suffering from Leprosy 2. To find out the effect of disability on activities of daily living and social life.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
A house to house survey and interview was carried out using the standard questionnaire of the Green Pasture’s assessment scale. 132 people were interviewed with informed verbal consent.
RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
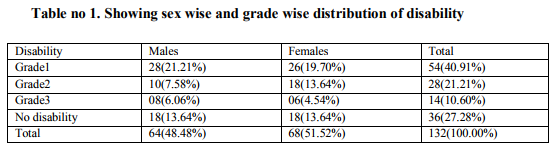
As there is no well-defined concept of disability and there is confusion over terminology, less attention is paid in assessing disability.2 For rehabilitation the cause of the impairment that resulted in the disablement is less important than problems experienced by the person affected.2 Rehabilitation therefore aims at reducing disability and handicap.6,7,8 Hence this study was carried out to find the disability in terms of (ADL)Activities Of Daily Living using Green Pastures Assessment Scale which is based on subjective feelings or perception regarding disability. From the interview using the standard questionnaire the data obtained and analysed was as follows: From the interview it was found that maximum numbers of people affected with leprosy are in the age group 56-65 years. This may be because in the olden days, proper health infrastructure was not present, adequate man power was not available, and health awareness was not spread up to the grass-root level which is consistent with the study done by The Salsa Collaborative Study group.9 In the present study, 48.48% were males and 51.58% were females. In a similar study by Wim H van Brakel et al 74% were males and 26% were females.2 and by Fredrick J Slim et al 59% were males and 41% were females.4 It is seen that both the sexes have approximately similar prevalence rate in percentage suggesting that both sexes are equally prone to the disease. In our study, 84.85 %( 112) had taken MDT treatment. This finding is consistent with the study by Annamma Succhanda John et al where 90% patients had taken treatment for leprosy.10 This indicates that majority of people affected by leprosy have good compliance towards MDT treatment. The hurdles in good compliance are social stigma, tendency to hide disability and disfigurement, repeated hospital visits required for treatment, domestic responsibilities and cost or loss of daily wages due to hospital visit.11 Also women suffer more isolation and rejection than males.12 104 people (78.79%) said that their job/occupation was affected due to disability. In a study by F.J.Slim et al 23.8% people affected by leprosy said that their job/occupation was affected due to disability.2 82 people (62.12%) felt that they are physically and financially dependent on others. In study by Gopal et al 35% of the leprosy affected people and their family members faced social and economic problems. 13 In a study done by Nandgoankar Hemant et al 65.19% had problems in the work area due to disability.14 Hence activity limitation were found to be major determinants of participation restrictions and occupational loss which depends upon environmental, social and cultural variations along with gender discrimination.2,12This restriction affects the physical and financial dependency. Also certain occupations in leprosy affected may lead to deterioration of deformities causing further disability. 14 Due to muscle paralysis, ulceration, digital shortening, stiffness of fingers there is loss of skillful work and the affected people become jobless with no other alternative but begging because of social stigma. 15 94 people (71.21%) stay with the family members in the colony. 38 people (28.79%) are staying alone. In the study by Gupte M D et al, 8% of the leprosy affected people faced social isolation.16 In another study in India by Leprosy International Union, 43% of the leprosy affected people faced dehabilitation .17 To become dehabilitated is to get devalued, dispossessed of ones roles and functions in society and loose ones social identity. Social and financial factors are interlinked with each other and hence while planning for rehabilitation these 2 factors and the characteristics of the target population should be considered. 15 RELATIONSHIP: Relationship with family members and others with some and many problems was as under:

a) It was noticed that Relationship with the spouse and children was affected in the range of 7-16.66%. In the study by Ms. W. Chitra the percentage was between 6-24%.18 A study by International Leprosy Union showed that 43% of the total 1071 leprosy affected people faced dehabilitation and had to leave their homes.17In a study done in Orissa it was found that 45.90%(308) of families with leprosy patient faced social isolation in which 48.3%( 150) had deformity and 51.30%(158) had no deformity.19 The various reasons for social isolation are 1) fear of infection 2) denial and rejection by the community members due to stigma. 3) Stigmatizing and isolating oneselves.20 Hence along with physical treatment and rehabilitation, social, vocational and mental rehabilitation is very much required. 19.69%(9) people found some difficulty in the use of assistive devices and 9.09% had much difficulty while the study by Ms.W. Chitra showed that 66% found some difficulty and 22% found more difficulty in use of assistive devices.18 69.69% people said assistive devices were not necessary and 28.28% said there is a need of the devices. This suggests that the use of assistive devices to help in activities and participation in life areas such as work and employment is not utilized on a broad scale. 11This is because of lack of knowledge and awareness of assistive devices, non-provision of the assistive devices by the health services and underestimation of disability with underutilization of the assistive devices for hiding the disability due to stigma by the leprosy affected people themselves. In the present study, 90.90% people were unemployed and 9.10% were employed. Out of the employed 41.66% were employed daily and 58.34% were employed sometimes. In present study only 4 people were farmers and 8 people were laborers. 90.91% (120) people had no jobs and so they did begging for survival. In the study by Wim H. van Brakel et al. 63% were farmers, 9.7% were working in the house, 6.3% were students, only 0.7% were beggars and 145 were doing some other work.2 All the people affected by leprosy face difficulty in their jobs. For the less disabled who still could work in the field, life was easier than for those who were older and with severe disability. Due to severe disability, disfigurement and social stigma most of these leprosy affected people have no other alternative but to succumb to begging for the livelihood. Hence along with physical rehabilitation, vocational and financial rehabilitation is very much required.
Impairment: In our study impairment in vision was 45.46%, for lower limbs it was 31% and upper limbs was 35.9%. In a study by Nandgoankar Hemant et al, the percentage of involvement of eyes, upper limbs and lower limbs was 5% , 79% and 63%, which is high compared to the present study.14 and by Fredrik J Slim et al it was reported to be 41%, 68% and 82% which is also high.4 Here in the study, upper and lower limb impairment was low in percentage and vision impairment is similar when compared with other studies above. Impairment of the eyes, hands and feet leads to severe disability while performing activities of daily living and social responsibilities which in turn changes to social handicap. Though the measurement of impairment helps the clinician to plan for physical and medical rehabilitation, the measurement of impairment do not give the true picture of disability as disability is contextdependent and subjective. One individual with a given impairment may experience much more difficulty with certain activities than someone with the same impairment living under different conditions. Hence rehabilitation requires us to look at the situation from the patient’s point of view.2
CONCLUSIONS
Facing severe difficulties with the activities of daily living is a common problem in people affected with leprosy related impairments and the level of difficulty can be assessed and measured using Green Pastures Assessment Scale. People affected by leprosy have problems in social participation as a result of disability, disfigurement and social stigma. Disability in activities of daily life has a negative impact on the quality of life. The relations amongst the family members and others are also stressed. Jobs are affected leading to unemployment, leaving the leprosy affected people no other option for survival but begging because of insufficient government schemes. All these factors must be considered while measuring disability and planning for rehabilitation. Recommendations: It is recommended that disability assessment should be a standard activity for planning, monitoring and evaluation of rehabilitation, both for individuals and at various rehabilitation programs. Knowledge of the disability status of a person will be valuable in needs-assessment for rehabilitation interventions and in clinical decision making.
ACKNOWLEDGMENT
The authors wish to acknowledge all the staff who was involved in the study. Also we wish to thank the people affected by leprosy living at leprosy colonies for their cooperation and participation in the study. The immense help received from the scholars whose articles are cited and included in references of this manuscript cannot be forgotten. Authors are also grateful to authors/editors/publishers of all those articles, journals and books from where the literature for this article has been reviewed and discussed.
References:
1. Wim H Brakel –Disability And Leprosy: The Way Forward-Annals Academy Of Medicine Jan 2007, VOL.36 No 1:86-87
2. Wim H. van Brakel, Alison M.Anderson. A survey of problems in Activities of Daily Living among persons affected by Leprosy Asia Pacific Disability Rehabilitation Journal, vol.9,no 1, 1998
3. WHO Weekly epidemiological record no 50 WHO 2008;83:293-300.
4. Frederik J Slim,MD, Carine H.van Schie ,PhD, Renske Keukenkamp, MSc, William R. Faber, MD, PhD and Frans Nollet ,MD, PhD. Effects of impairments on activities and participations in people affected by Leprosy in Netherlands. J. Rehab Med. 2010; 42: 536- 543)
5. W.H.VanBrakel,A.M.Anderson,F.C.Worpel,R .Saiju,H.B.BK,S.Sherpa,S.K.Sunwar,J.Gurung ,M.Deboer and E.Scholten A scale to assess Activities of Daily Living in persons affected by leprosy. Asia Pacific Disability rehabilitation Journal,1998; vol.9,no 1, 1-12
6. Van BennekomC A M,Jelles F,Lankhorst G J. Rehabilitation activities profile:The ICIDH as a framework for a problem-oriented assessment method in rehabilitation medicine.Disabil.Rehabil.1995;17:169-175.
7. Jiwa-Boerrigter H,Van Engelen H G M ,Lankhorst G J.Application of the ICIDH in rehabilitation medicine.Int Disabilities Studies 1990;12:17-19.
8. Whiteneck G G,Charlifue S W,Gerhart K A,Overholser J D,Richardson G N.Quantifying handicap:a new measure of long- term rehabilitation outcomes. 9. The Salsa Collaborative Study group. The development of a short questionnaire for screening of activity limitation and safety aware-ness(SALSA) in clients affected by leprosy or diabetes. Disabil. Rehabil 2007; 29: 689-700
10. Annamma Succhanda John,Pamidipani Samuel Sunder Rao and Sonali Das. Assessment of needs and quality care issues of women with leprosy.Lepr Rev.2010;81:34-40.
11. Johan Borg and Stig Larsson. Assistive devices for people affected by leprosy: underutilized facilitators of functioning? .Lepr Rev.2009 Mar;80(1):13-21.
12. Sanjay P. Zodpey, Rajnarayan R. Tiwari and Atul D. Salodkar. Gender differentials in the social and family life of leprosy patients. Lepr Rev.2000; 71: 505-510
13. Gopal P K. Methods to identify the Leprosy Patient Needing Rehabilitation. Indian Journal of Leprosy1997; 69:133-152
14. Nandgaonkar Hemant P,Mancheril Joy,Ebenezer.J,Samy A.A. Activities of Daily Living (ADL) Assessment :A measure for grading activity limitation in Leprosy patients . The Indian Journal of Occupational Therapy 2003; vol34 (3): 8-12.
15. H Srinivasan .Developmental Articles: The problems and challenges of disability and rehabilitation in leprosy. Asia Pacific Disability Rehabilitation Journal1998.Vol.9;No.1
16. Gupte M D et al.-Personal Communication 17. International Leprosy Union .A Study of social Aspects of Dehabilitation in Leprosy, Pune, 1994.
18. Ms. W Chitra. Impairment of activities of daily living. IJCM2006;31(2):115-116
19. 15.Srinivasan H and Sivakumar S S.Personal Communication.
20. Chen, Tongsgeng Chu and Qihua Wang. Qualitative assessment of social, economic and medical needs for ex-leprosy patients living in leprosy villages in Shandong Province, The People’s Republic of China ,Shumin. Lepr Rev 2005; 76: 335–347
|






 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License