IJCRR - 8(17), September, 2016
Pages: 35-40
Date of Publication: 11-Sep-2016
Print Article
Download XML Download PDF
ISOLATION AND PHARMACOLOGICAL STUDIES OF KARANJACHROMENE FROM THE SEEDS OF PONGAMIA PINNATA (L. PIERRE)
Author: Devendra N. Kage, Nuzhahat Tabassum, Vijaykumar B. Malashetty, Raghunandan Deshpande, Y. N. Seetharam
Category: Healthcare
Abstract:Context: Isolation of chemical compound karanjachromene from the Seeds of Pongamia Pinnata and evaluation of its anti-inflammatory and analgesic activities.
Materials and methods: Karanjachromene has been successfully extracted from the seeds of Pongamia Pinnata using n-hexane, petroleum ether and alcohol with Soxhlet extraction. Anti-inflammatory and analgesic activities of the some were assessed administering in Swiss albino mice. The anti-inflammatory activity of the test compound was determined by mice paw edema inhibition method. The analgesic activity was determined by both acetic acid induced writhing and tail immersion methods.
Results: Karanjachromene at doses 25 mg/kg and 50 mg/kg shown 40.48% and 59.6% inhibition of paw edema respectively, at the end of 3 h standard drug diclofenac sodium produced 63.01% inhibition in paw volume at 10 mg/kg. The oral administration of test compound karanjachromene significantly inhibited writhing response induced by acetic acid in a dose dependent manner. Karanjachromene produced 29.64% and 42.14% inhibition of writhing at doses 25 mg/kg and 50 mg/kg respectively. Standard drug diclofenac sodium produced 56.47 % inhibition of writhing at 10 mg/kg.
Discussion and Conclusion: The administration of karanjachrome is potent to inhibit the paw edema starting from the 1st hour and during all phases of inflammation, which may be due to inhibition of different inflammatory mediators. The acetic acid induced writhing response could be mediated by peritoneal mast cells, acid sensing ion channels and the prostaglandin pathways. The test compound inhibited both mechanisms of pain and inflammation and are more found active peripherally than centrally. Karanjachromene exhibited significant anti-inflammatory and analgesic agents
Keywords: Anti-inflammatory activity, Analgesic activity, Karanjachromene
Full Text:
INTRODUCTION
Pongamia pinnata belongs to the family Fabaceae. All parts of the plant viz, root, stem, leaves, flower, bark, seeds and its oil too are used in Ayurveda for the treatment of Antihyperglycemic (Badole SL, Bodhankar 2008, Badole SL, Bodhankar 2009), Antilipid peroxidase (Tamrakaretal., 2008; Ahmadetal., Punitha and Manoharan 2006a; Punitha and Manoharan 2006b), Antifungal and antibacterial (Siminetal., 2002, Amit et al., 2011), Antimicrobial (Koysomboon et al.,2004, Alam, 2004, Krishna and Grampurohit, 2006), antiviral (Elanchezhiyan, 1993), antidiarrheal activity (Brijesh et al., 2006), antiplasmodial (Simonsen et al.,2001), anticonvulsent (Ashish and sunita, 2010; Ashish and sunita 2009), antidiabetic (Badole and Bodhankar, 2010), Antioxident (Sachin et al., 2011), anti-filarial (Uddin et al., 2003), Antiulcerant (Prabhaetal., 2009), antihyperammonic activity (Chopade et al., 2010, Dahanukumar et al., 2000), Cures leprosyand gonorrhea (Kirtikar and Basu, 1975), liver infections (Nadkarni, 1982) and the oil is used for scabies and rheumatism (Burkill, 1996, Bimla et al., 2003). Many biologically active chemical compounds have been isolated from various parts of the plant. An aliphatic waxy mat ter kaempferol, pongamin, γ-sitosterolglucoside, quercertin, neoglabrin (A complex amino acids) resembling glabrin and galbrosaponin A furanoflavone (i.e., Penguin) (The Wealth of India 2003). Pongaglabol, a hydroxyfuranoflavone, and aurantiamide acetate, phenyl alanine dipeptide, have been isolated together with four furanoflavones (karanjin, lancheolatin B, kanjone and pinnatin (Talapatraetal., 1980) have been isolated from flowers. Various chemical constituents are isolated from the bark of this plant include seven flavonoids viz., pongaflavone, karanjin, pongapin, pongachrome, 3,7-dimethoxy-3’,4,7-tetramethoxyflavone (Yin et al.,2004) two prenylated flavonoid derivatives viz., pongaflavonol and tunicatachalcone (Yinetal., 2006) cycloart-23-ene-3?, 25-diol (Badole et al., 2011) phenylpropanoids viz., pongapinone A and B (Kitagawa et al., 2008). Moreover, two hydroxychalcones – onganones I and II – have been isolated from the bark and characterized (Rastogi et al., 2011). Three furano flavonoids (Pongamosides A, B and C) and a flavonol, glucoside Pongamoside D, have been reported from the n-butanol-soluble fraction of the ethanolic extract P. pinnata fruit (Ahmad et al., 2004).The seeds contain traces of essential oil, complex amino acid termed glabrin, furano flavones, karanjin, kanjone, pongaglabrone, furano flavone (Rastogi et al., 2011; Li et al., 2006) and pyrano flavonoid called Karanjachromene (Naghmana et al., 2008). Furoflavones viz. Keranjin, pongapin and pinnatin isolated from the seeds, leaves and bark (Chopra, 1969; Parmar et al., 1976) and roots also indicated the presence of protocatechuic, elegiac, ferulic, gallic, gentisic, 4-hydroxybenzoic and 4-hydroxycinnamic acids in bark, sorbic, ferulic, gallic, salicylic and p-coumaric acids in leaves; vanillic, gallic and tannic acids in seeds as the main phenolic acids (Sajid et al., 2012), flavonoids and its related compounds including flavones, furanoflavonoids, chromenoflavone, chromenocalchones, coumarins, flavone glycosides sterol, terpenes and modified phenylalanine dipeptides are found to be present (Khare, 2004). Since flavonoids are effective anti-inflammatory and analgesic compounds, and as per our knowledge there are no reports of anti-inflammatory and analgesic activities of Karanjachromene, hence we have carried out these experiments.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Chemicals
All chemicals and reagents used to carry out the research work were analytical grade and were obtained from Hi-Media Mumbai, India.
Plant material
P. pinnata pods were collected from Gulbarga University campus in October 2010. This plant is as identified by using Flora of Gulbarga District (Seetharam et al., 2000) (Voucher No. HGUG-169). The voucher specimen is kept for the record in the Department of Botany Gulbarga University, Gulbarga.
Flora of Gulbarga District (Seetharam et al., 2000) (Voucher No. HGUG-169). The voucher specimen is kept for the record in the Department of Botany Gulbarga University, Gulbarga.
Extraction and Isolation of karanjachromene
P. pinnata seeds were finely ground for an approximate particle size of 2 mm). The oil content of the seed was extracted with Soxhlet extractor with n-hexane for 20 h and maintaining the temperature at 60?C. Oil recovered was stored at 4?C in airtight container for further analysis. After 15 days of storage, granular particles were settled at the bottom of the container. These particles were separated and washed with n-hexane followed by petroleum ether repeatedly. These fine powdered particles were re-dissolved in double distilled alcohol; pointed yellowish crystals were formed at the bottom of the container within a week. This is most convenient and easiest method of isolation of this compound as compared to the previous methods of isolation.
Characterization
The characterization of the compound have been made by taking melting points, infrared spectra, 1 H and 13C nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) and mass spectral analysis.
Structure of Karanjachromene
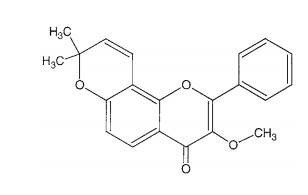
Animal experiments
Experimental animal Albino mice of either sex weighing 20-25 g were taken for experimental study. They were acclimated to animal house conditions fed with commercial pellets (Hindustan Lever Ltd., Bangalore, India), and tap water ad libitum. The experimental protocol was approved by the Institutional Animal Ethics Committee.
Determination of median lethal doses (LD50) LD50 values were estimated by the acute toxicity test as described. The test compound is dissolved in 3% DMSO administered orally to different groups with increasing doses. Four animals were taken in each group. Mortality was determined after 24 h of treatment. The dose, at which the 50% mice survived, was considered as LD50 value of the compound. Anti-inflammatory activity The anti-inflammatory activity (Winter et al., 1962) of the compound was determined using the carrageenan induced mice paw edema inhibition method employing 1.0% carrageenan solution as the phlogestic agent. The test compound was administered orally as suspensions in 3% DMSO, 30 min before the injection of phlogistic agent, at the dose level 25 and 50 mg/kg body weight. Diclofenac sodium was used as a standard at a dose level of 10 mg/kg body weight. 3% DMSO served as a control. Groups of four albino mice of either sex were used in each experiment. The volume of paw edema was measured with the help of plathysmograph by mercury displacement method at 0h (soon after injection of carrageenan). Then, the volume of paw edema was observed at 1, 2 and 3 h and the results are presented in the Table 1. The percentage inhibition of paw edema was calculated using the formula. % Inhibition =1-Vt/Vcx 100 Vt and Vcx the volumes of paw edema in treated and control group, respectively. Acetic acid induced writhing test for analgesic activity The analgesic activity of the test sample was studied (Ahmed et al., 2004) using acetic acid induced writhing model in mice. Swiss albino mice of either sex were divided into control, standard and different test groups contain four mice in each. The control group received 3% DMSO and standard group was treated with diclofenac sodium at a dose level of 10 mg/kg test sample and the vehicle were administered orally 30 min before intraperitonial administration of 0.6% acetic acid but diclofenac sodium was administered intraperitonially 15 min before injection of acetic acid. After an interval of 5 min, the mice were observed for specific contraction of the body referred to as writhing for the next 30 min the analgesic activity was expressed as percentage inhibition of writhing in mice. The results are given in table 2. Tail immersion test for analgesic activity The procedure was based on the observation that morphine like drugs selectively prolongs the reaction time of the typical tail withdrawal reflex in mice (Palanichamy and Nagarajan 1990). The animals were treated as discussed above. From 1-2 cm of the tail of mice was immersed in warm water kept constant at (54±1) ?C and the reaction time was the time taken from the mice to deflect their tails. A cutoff period of 5 sec was observed to avoid damage to their tail. Reaction time was recorded when animal picked up their tails from the hot water at 0, 30, 60 and 90 min after the administration of drugs. The results are shown in Table 3. Statistical analysis Data obtained from the experiments are expressed as Mean ± SEM. The difference between the control and the treatments in these experiments was tested for significance using one way ANOVA followed by a Dunnett’st – test.
RESULTS
LD50 value of karanjachromene was found to be 500 mg/kg body weight. Two doses of Karanjachrome25 mg/kg and 50 mg/kg have been selected throughout the work. In the carrageenaninduced mouse paw edema test (Table 1) for acute inflammation, the test compound Karanjachromene at doses 25 mg/kg 50 mg/kg shown 40.48 and 59.6% inhibition of paw edema, respectively, at the end of 3 h standard drug diclofenac sodium produced 63.01% inhibition in paw volume at 10 mg/kg.
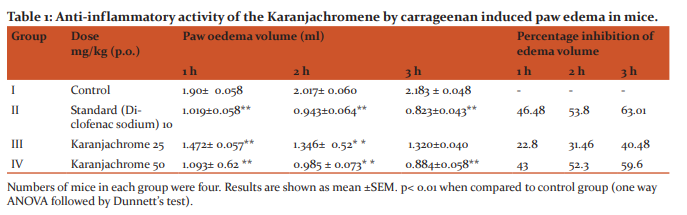
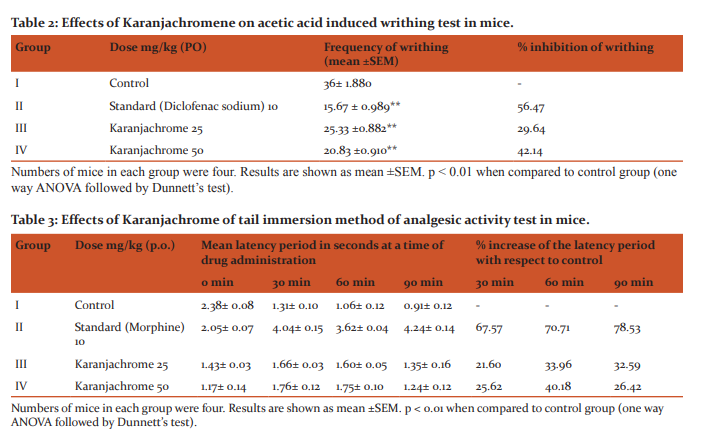
Table 2 shows the effect of Karanjachromene on acetic acid-induced writhing in mice. The oral administration of test compound Karanjachromene significantly inhibited writhing response induced by acetic acid in a dose dependent manner. Karanjachromene produced 29.64% and 42.14% inhibition of writhing at doses 25 mg/kg and 50 mg/kg respectively. Standard drug diclofenac sodium produced 56.47 % inhibition of writhing at 10 mg/kg the tail withdrawal reflex time following administration of the test compound was found to increase with increasing dose of the samples. The results were statistically significant and comparable to that of the reference standard drug morphine. The data are shown in Table 3.
DISCUSSION
The carrageenan induced paw edema is characterized by a biphasic event with the involvement of various inflammatory mediators. In the first phase (during 1st and 2nd hour after carrageenan injection), inflammatory mediators like serotonin and histamine play their role, while in the second phase (i.e., 3rd hour after carrageenan injection) bradykinins and prostaglandins are involved (Crunkhorn and Meacock, 1971). Our results revealed that administration of Karanjachrome is potent to inhibit the paw edema starting from the 1st h. and during all phases of inflammation, which may be due to inhibition of different inflammatory mediators. Acetic acid-induced writhing model shows pain by enhancing localized inflammatory response. Such pain stimulus leads to the production of free arachidonic acid from phospholipids in the tissue. The acetic acid induced writhing response is a highly sensitive procedure to evaluate peripherally acting analgesics. The response could be mediated by peritoneal mast cells (Ronaldo et al., 2000) acid sensing ion channels (Voilley, 2004) and the prostaglandin pathways. The tail immersion test is considered to be selective to examine compounds acting through opioid receptor, the test compound increased mean basal latency which indicates that they may act via centrally mediated analgesic mechanism (Dinesh Kumar, 2011). Narcotic analgesic inhibits both peripheral and central mechanisms of pain, while non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs inhibit only peripheral pain (Elisabetsky et al., 1995). Through the test compound inhibited both mechanisms of pain, these are more active in peripherally than centrally.
CONCLUSION
The experimental findings in this study suggest that the Karanjachromene possesses analgesic and anti-inflammatory activities, possibly mediated through central and peripheral mechanisms involving inhibition of release or the actions of vasoactive substances like prostaglandin and histamine, serotonin and kinins. The results obtained justify the use of the seed oil in traditional Indian medicine for the treatment of painful and inflammatory conditions. Further work is going on to elucidate the exact mechanism of action. Conflict of interests The authors report no conflicts of interest. The authors are merely responsible for the content and writing of the paper.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENT
Authors acknowledge the immense help received from the scholars whose articles are cited and included in references of this manuscript. The authors are also grateful to authors / editors / publishers of all those articles, journals and books from where the literature for this article has been reviewed and discussed.
References:
1. Ahmad G, Mishra PK, Gupta P, Yadav PP, Tiwari T, Tamrakar AK, Arvind KS, Rakesh M. Synthesis of novel benzofuranisoxazolines as protein tyrosine phosphatase 1B inhibitors. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2006; 16: 2139-2141.
2. Ahmad G, Yadav PP, Maurya R. Furanoflavonoid glycosides from Pongamiapinnata fruits. Phytochemistry 2004; 65: 921- 924.
3. Ahmed F, Selim MST, Das AK, Choudhuri MSK. Anti-inflammatory andantinociceptive activities of Lippianodiflora Linn. Pharmazie. 2004; 59: 329-333.
4. Alam S. Synthesis and studies of antimicrobial activity of lanceolatin B. Acta Chim Slov. 2004; 51: 447-452.
5. Amit S, Sapna T, Ruchi N, Arjit C, NAG TN. Antimicrobial activity and cellular toxicity of flavonoid extracts from Pongamia pinnata and Vitex nigundo. Romanian Biotechnological Letters 2011; Vol. 16, No. 4, 6396-6400.
6. Ashish M, Sunita P. Anticonvulsant study of pongamia pinnata Linn against Pentylenetetrazole induced convulsion in rats. International journal of pharma and bio sciences 2010; 2: 1-4.
7. Ashish M, Sunita P, Jitender M, Huma A. Evaluation of anticonvulsant activity of PongamiapinnataLinn in experimental animals. International Journal of PharmTech Research 2009; 1(4): 1119-1121.
8. Badole SL, Bodhankar SL. Investigation of antihyperglycaemic activity of alcoholic extract of stembark of Pongamia pinnata on serum glucose level in diabetic mice. Pharma Biol. 2008; 46: 900-905.
9. Badole SL, Bodhankar SL. Antihyperglycaemic activity of cycloart-23-ene-3?, 25-diol isolated from stem bark of Pongamia pinnata in alloxan induced diabetic mice. Res J Phytochem 2009; 3: 18-24.
10. Badole SL, Bodhankar SL. Antidiabetic activity of cycloart-23- ene-3, 25-diol (B2) isolated from Pongamia pinnata (L. Pierre) in streptozotocin-nicotinamide induced diabetic mice. Eur J Pharmacol. 2010; 632: 103-109.
11. Badole SL, Zanwar AA, Khopade AN, Bodhankar SL. In vitro antioxidant and antimicrobial activity cycloart-23-ene-3?, 25- diol (B2) isolated from Pongamia pinnata (L. Pierre). Asian Pac J Trop Med. 2011; 10: 910-916.
12. Bimla M, Kumar S, Kalidhar SB. A review of chemistry and biological activity of P. pinnata. J Med Arom Plant Sci. 2003; 25: 441-465.
13. Brijesh S, Daswani PG, Tetali P. Studies on Pongamia pinnata (L.) Pierre leaves: Understanding the mechanism(s) of action in infectious diarrhea, J Zhejiang Univ Sci B. 2006; 7: 665-74.
14. Chopade VV, Tankar AN, Pande VV, Tekade AR, Gowekar NM, Bhandari SR, Khandake SN. Pongamia pinnata: Phytochemical constituents, traditional uses. Nature and Science 2010; 8(11).
15. Chopra RN, Choptra IC, Varma BS. Supplement to Glossary of Indian Medicinal plants Pub and Inf. Directorate , 1969; New Delhi -12, p – 82.
16. Crunkhorn P, Meacock SER. Mediators of the inflammation induced in the rat paw by carrageenan. Br J Pharmacol. 1971; 42: 392-402.
17. Dahanukumar SA, Kulkarni RA, Rege NN. Pharmacology of medicinal plants and natural products. Indian J Pharmacol. 2000; 32: 81-118.
18. Dinesh Kumar, Anti-inflammatory, analgesic, and antioxidant activities of methanolic wood extract of Pterocarpus santalinus L. J Pharmacol Pharmacother. 2011; 2: 200-202.
19. Elanchezhiyan M, Rajarajan S, Rajendran P, Subramanian S, Thyagarajant SP (1993). Antiviral properties of the seed extract of an Indian medicinal plant, Pongarniapinnata, linn., against herpes simplex viruses: in-vitro studies on vero cells. J Med Microbiol. 1993; 38: 262-264.
20. ElisabetskyE, AmadorTA, Albuquerque RR, Nunes DS, Ado CC. Analgesic activity of Psychotriacolorata (Willd.exR. and S.). Muell. Arg. Alkaloids. J Ethnopharmacol. 1995; 48: 77-83.
21. J. H. Burkill. A dictionary of economic products of the Malay peninsula, vol. 2 (Art printing Works, Kuala Lumpur. 1966.
22. Khare CP. Indian Medicinal Plants, an illustrated dictionary. Springer-verlag Berlin/Heidelberg, New York, USA. 2004.
23. Kirtikar KR, Basu BD. (eds) Indian medicinal plants. India, M/s Bishen Singh Mahindrapal Singh. 1975; 830-832.
24. Kitagawa I, Zhang R, Hori K, Tsuchiya K, Shibuya H. Indonesian medicinal plants. II. Chemical structures of pongapinones A and B, Two new phenylpropanoids from the bark of Pongamiapinnata (Papilionaceae). Chem and Pharm Bull. 2008; 40(8): 2041-2043.
25. Koysomboon S, Altena IV, Kato S, Chantrapromma K. Antimycobacterial flavonoids from Derris indica. Phytochem. 2006; 67: 1034-1040.
26. Krishna VN, Grampurohit ND. Studies on the alkaloids of stem bark of Pongamiapinnata Linn. Indian Drugs 2006; 43: 383- 387.
27. Li L, Li X, Shi C, Deng Z, Fu H. Pongamone A–E, five flavonoids from the stems of a mangrove plant, Pongamiapinnata. Phtochemistry 2006; 67:1347- 1352. 28. Nadkami, KM. Indian MateriaMedica, Popular Book Depot. Bombay, 1982; ed.3. p – 1003. 29. Naghmana R, Muhammad SAA, Muhammad KT, Nurdiyana MY, Bohari MY. Isolation and Crystal Structure of Karanjachromene. Analytical Sciences 2008; Vol. 24X21.
30. Palanichamy S, Nagarajan S. Analgesic activity of Cassia alata leaf extract and kaempferol 3 -o-sophoroside. J Ethnopharmacol 1990; 29: 73-78.
31. Parmar BS, Sahrawat KL and Mukharjee SK. Pongamiaglabra: constituents and uses. J SciInd Res. 1976; 35: 608-611.
32. Prabha T, Dorababu M, Goel S, Agarwal PK, Singh A, Joshi VK, Goel RK. Effect of methanolic extract of Pongamiapinnata Linn. seed on gastro-duodenal ulceration and mucosal offensive and defensive factors in rats. Indian J Exp Biol. 2009; 47: 649- 659.
33. Punitha R, Manoharan S. Antihyperglycemic and antilipidperoxidativ eeffects of Pongamiapinnata (Linn.) flowers in alloxan induced diabetic rats. J Ethnopharmacol. 2006; 105: 39-46.
34. Punitha R, Vasudevan K, Manoharan S. Effect of Pongamiapinnata flowers on blood glucose and oxidative stress in alloxan induced diabetic rats. Ind J Pharmacol. 2006; 38: 62-63.
35. Rastogi RP, Mehrotra BN, Sinha S, Pant P, Seth R. Compendium of Indian medicinal plants. Central Drug Research Institute and Publications and Information Directorate, New Delhi, India. 2011.
36. Ronaldo AR, Mariana LV, Sara MT, Adriana BPP, Steve P, Ferreira SH, Cunha FQ. Involvement of resident macrophages and mast cells in the writhing nociceptive response induced by zymosanand acetic acid in mice. Eur J Pharmacol. 2000; 387: 111-118.
37. Sachin LB, Anand AZ, Abhijeet NK, Subhash LB. In vitro antioxidant and antimicrobial activity cycloart-23-ene-3, 25-diol (B2) isolated from Pongamiapinnata (L. Pierre) Asian Pacific Journal of Tropical Medicine 2011; 910-916.
38. Sajid ZI, Anwar F, Shabir G, Rasul G, Alkharfy KM, Gilani AH. Antioxidant, antimicrobial properties and phenolics of different solvent extracts from bark, leaves and seeds of Pongamiapinnata (L.) Pierre. Molecules 2012; 17(4): 3917-32.
39. Seetharam YN, Kotresha K, Upalaonkar. Flora of Gulbarga District. Gulbarga University, Gulbarga. 2000.
40. Simin, K, Ali Z, Khaliq-Uz-Zaman SM, Ahmad VU. Structure and biological activity of a new rotenoid from Pongamiapinnata. Nat Prod Lett. 2002; 16: 351-357.
41. Simonsen HT, Nordskjold JB, Smitt UW. In vitro screening of Indian medicinal plants for antiplasmodial activity. J Ethnopharmacol. 2001; 74: 195-204.
42. Talapatra SK, Mallik AK, Talapatra B. Pongaglabol, a new hydroxyfuranoflavone, and aurantiamide acetate, a dipeptide from the flowers of Pongamiaglabra. Phytochemistry 1980; 19: 1199-1202.
43. Tamrakar AK, Yadav PP, Tiwari P, Maurya R, Srivastava AK. Identification ofpongamol and karanjin as lead compounds with antihyperglycemic activity from Pongamiapinnata fruits. J Ethnopharmacol. 2008; 118: 435-439.
44. The Wealth of India. A Ready Reckoner on Biodiversity and Bioresources of India, NISCAIR, CSIR, New Delhi, India. 2003.
45. Uddin Q, Parveen N, Khan NU, Singhal KC (2003). Antifilarial potential of the fruits and leaves extracts of Pongamiapinnata on cattle filarial parasite Setariacervi. Phytother Res. 2003; 17: 1104-1107.
46. Voilley N. Acid-sensing ion channels (ASICs): New targets for the analgesic effects of non-steroid anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs). Curr Drug Targets Inflam Allerg. 2004; 3: 71-79.
47. Winter CA, Risely EA, Nuss GW. Carrageenan induced oedema in hind paw of the rats as an assey for anti-inflemmatory drugs. Proc Soc Exp Bio Med. 1962; 111: 544-547.
48. Yin H, Zhang S, Wu J. Study on flavonoids from stem bark of Pongamiapinnata. Zhong Yao Cai. 2004; 27(7): 493-495.
49. Yin H, Zhang S, Wu J, Nan H, Long L, Yang J. Pongaflavanol: a prenylated flavonoid from Pongamiapinnata with a Modified Ring A. Molecules 2006; 11: 786-791.
|






 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License