IJCRR - 4(18), September, 2012
Pages: 78-85
Date of Publication: 29-Sep-2012
Print Article
Download XML Download PDF
MICROBIAL DEGRADATION OF HYDROCARBONS FROM OIL CONTAMINATED SOIL BY USING PSEUDOMONAS SP.
Author: B. Kamaladevi, Prabhavathi. P, Sankareswaran. M
Category: General Sciences
Abstract:Aims: To study the microbial degradation of hydrocarbon from oil contaminated soil sample using Pseudomonas sp. and were analyzed the different physicochemical characters of normal and oil contaminated soil. Method and Results: The soil sample was collected from oil contaminated site, in Sivakasi and then the oil degrading microorganism (Pseudomonas sp) was screened from oil contaminated soil by using enrichment technique. After, the isolated microorganisms were identified by using standard characterization method. From the oil contaminated soil, 10 bacterial strains were isolated. Among them, tolerance of two strains was used for further studies. The physico-chemical characters of normal and oil contaminated soil samples were analyzed by standard method. In this study, the pH, moisture, carbon, phosphorous and potassium content of normal and oil contaminated soil samples were analyzed and compared. In the present investigation, the various concentration of aromatic hydrocarbon (toluene) was degraded by Pseudomonas sp and rate of the degradation was analyzed by HPLC (High Performanace Liquid Chromatography). The chemo taxis properties of the Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Pseudomonas fluorescens were studied by chemo taxis assay and also studied biosurfactant production of Pseudomonas sp. simultaneously the biomass, emulsification activities of Pseudomonas sp on toluene was studied. This biosurfactant production was detected by Thin Layer Chromatography. Conclusions: In this present investigation, the aromatic hydrocarbon degradation efficiency, chemotaxis properties and biosurfactant production of Pseudomonas sp. was compared with MTCC cultures of Pseudomonas stutzeri. Significance and impact of the study: Treatment with adapted bacteria could degrade the hydrocarbons.
Keywords: Oil degrading microorganism, Thin layer chromatography, Biosurfactant.
Full Text:
INTRODUCTION
As we dig deeper into the modem industrial age technologies, several aspects of human life change. People benefit largely from life development and many live in prosperity, but property has price. This price is paid by our environment that suffers daily from pollutants and destruction. People now have to find ways to cure this destruction. One of the most destructive pollutants known today is oil contamination. Oil contamination is one of the most dangerous pollution factors. It can cause a threat to the environment. It is very feared by environmentalists and it’s very hard to control if it gets out hand. Oil spillage still occur through tanker accidents, well blow out, Sabotage and accidental rupture of pipelines, resulting in the release of crude and refined oil in terrestrial and aquatic environments (Atlas, 1981; Colwell and Walker, 1977). Oil contamination can be either at sea or in soil level. Sea oil contamination poses a threat on marine life and the death of hundreds of marine organisms. Soil contamination on the other hand is slow and lethal. It acts over a long period of time by poisoning food crops, water supplies etc. Oil contamination in soil results in an imbalance in the carbon-nitrogen-phosphorus ratio in the spill site, because crude oil essentially a mixture of carbon and hydrogen. This cause a nitrogen deficiency in oil soaked Soil, which retards the growth of bacteria and utilization of carbon sources (Regina et al., 2006). Furthermore, large concentrations of biodegradable organics in the top layer deplete oxygen reservoirs in the soil and slow down the rate of oxygen diffusion into deeper layers. Toluene is widely as an organic solvent, and its world wide production is estimated to be more than 80,000 metric ton per year. Toluene and other solvents, such as xylene, benzene and ethyl benzene are ubiquitous pollutants (Atlas, 1995) and several environmental protection agencies have declared the removed of there pollutions to be a high priority. In many environments indigenous microorganisms are able to remove aromatic hydrocarbons. This is to be expected, as many catabolic pathways for the metabolism of these compounds have been described, particularly in strains belonging to the genus Pseudomonas. Aromatic hydrocarbons are extremely toxic for microorganisms because they dissolve in the cell membrane (Sikkema et al., 1995). Therefore a critical issue in the degradation of aromatic hydrocarbons in polluted sites is tolerance to these compounds. Recently a number of Pseudomonas strains have been shown to be tolerant to organic solvents such as Toluene, Xylene, styrene and others. Solvent tolerance in bacteria belonging to the genes Pseudomonas involves (industry) an increase in cell membrane rigidity as a result of increase in both the level of the trans isomers of unsaturated fatty acid and level of cardio lipid a component of phospholipids head groups (Ramos et al., 1997), and oil removed of solvents from membranes via efflux pumps (Isken and Bont, 1996; Ramos et al., 1995). Bioremediation methods are currently receiving favorable publicity as promising environmentally friendly treatment technologies for the remediation of hydrocarbons (Desai and Banat, 1997). Biodegradation enables oil to be converted from harmful organic substances in to harmless inorganic substance (Zhao and Zhu, 1993). Three major factors affects the biodegradation of crude oil and these are chemical composition of oil, dissolved oxygen content of water and nutrient availability for microorganisms (Zhao and Zhu, 1997). The pH, temperature, the type and number of microbial species involved in degradation may influence the rate and extend of the process (Colwell and Walker, 1977). Apart from the presence of microorganisms capable of degrading crude oil compound the type, concentration and distance of pollutant, limit the biodegradation of the inherent compounds and other factors also involved in biodegradation. If the hydrocarbon is not available to the microorganisms and the appropriate enzymes, do not come in contact with the substrate in the proper way degradation will not occur (Atlas, 1981). Mainly enzyme activity, chemo taxis property and surfactants production of microorganisms response to the hydrocarbon degradation. Recently the soil bacterium Pseudomonas bacterium was reported to be attracted to the pollutant naphthalene and other chemicals. This expanded the range of organic compounds that are known to serve as bacterial chemo attractants to include aromatic hydrocarbons. However nothing is known about chemo taxis towards other common aromatic hydrocarbons such as toluene and benzene. Chemo taxis gives motile bacteria the advantage of the being able to locate compounds such as toluene that can support their growth (Parales et al., 2000). Biosurfactants are surface-active substances synthesis by living cells. They have the properties of reducing surface tension, stabilizing emulsion, promoting foaming and are generally non toxic and biodegradable, Interest in microbial surfactant has been steadily increasing in recent years due their diversity, environmentally, friendly nature, possibility of large-scale production, selectivity, performance under extreme condition and potential application in environmental protection (Rahman et al., 2002). Biosurfactants enhance the emulsification of hydrocarbons, have the potential to solublize hydrocarbon contaminants and increase their availability for microbial degradation. Biosurfactants producing microorganisms may play an important role in the accelerated bioremediation of hydrocarbon contaminated sites (Rosenberg and Ron, 1999). These compounds can also used in enhanced oil recovery and may be considered for their potential application in environmental protection. This research was aimed at determining the hydrocarbon degrading microorganisms present in the oil contaminated soil. The determined microorganisms (Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Pseudomonas fluorescens) were used to study the efficiency of the aromatic hydrocarbon (toluene) degradation on various concentrations. Simultaneously studied their chemo taxis properties and biosurfactant production of the above same microorganisms and also it was compared to MTCC culture of Pseudomonas stutzeri.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Sample collection
The soil sample (100g) was collected from diesel contaminated site in a polythene bag for the isolation of oil degrading microorganisms. Samples were taken with shovels after removing 20 cm of the surface layer of the soil. Collected soil was stored aerobically at 4ºc for further analysis.
Isolation, identification and characterization of bacteria from oil contaminated soil enrichment technique
The hydrocarbon degrading microorganism was isolated by following the enrichment technique prescribed by Karpagam and Lalitha Kumari (1998). Identification was based on the criteria of Bergey’s Mannual of Determinative Bacteriology. Physico-Chemical Parameters Both the pH and moisture content of sample was analyzed by standard method and also the chemical parameters of carbon, phosphorous and potassium content of the sample was analyzed by standard methods. Hydrocarbon Estimation Hydrocarbon extraction After incubation, soil and hexane (1:20) were mixed for 5 minutes in a vortex and soil free hexane extracts was separated using a membrane filter and it was dried. The dried samples (dissolved hydrocarbon) were again dissolved HPLC methanol. After dissolving the sample in solvent, it was used for HPLC analysis. Hydrocarbon Determination The extracted hydrocarbon was analyzed by HPLC (C18 silica capillary column: 10AT VP Shimadzu company). Peak obtained at 5 minutes (retention time) has been considered as level of hydrocarbon degradation. Hence it was compared to the respective standard peak. Chemo Taxis Assay Agarose plug assays were carried out with slight modification. Plugs containing 0.5% of low melting temperature agarose in chemo taxis buffer. Chemo taxis Buffer (Potassium phosphate - 40mM Glycerol - 0.05%EDTA - 10mM). 10% (vol/vol) toluene and a few crystals of coomassie blue were used to provide contrast. A drop (20µl) of the molded agarose mixture was placed on a microscopic slide and the harvested cells flooded in to the microscopic slide to surround the agarose plug and incubate for 30minutes. After incubation, results were noted.
Bacterial Growth and Biosurfactant Production
A series of 500ml flask containing 200ml of sterile mineral salt medium with 1% glucose as a substrate were prepared, and the pH was maintained at 7.5. Each of the individual bacterial cultures was inoculated and the flasks were incubated at 30ºC in a shaker at 200rpm followed by the addition of 1% toluene after 24 hours. At every 24 hours intervals, biomass, biosurfactant production and emulsification activity were measured.
RESULTS
In this study, the bacterial strains were isolated from oil contaminated site in Sivakasi. From the oil contaminated soil, 10 bacterial strains were isolated. Among them, only two strains were used for further studies because they have the ability for survive that oil contaminated area.
Isolation and Characterization of Isolates
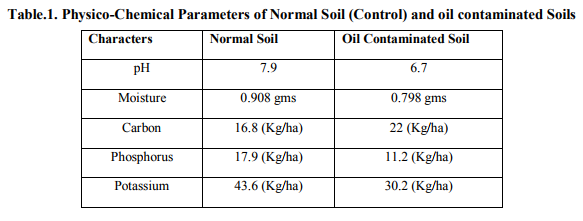
The cultural morphological and biochemical characterization of isolates were carried out and results were noted. Various biochemical and carbohydrates tests were carried out for isolated microorganisms and identified as Pseudomonas sp. Physico-Chemical Parameters The normal soil sample showed pH 7.9, but the oil contaminated soil sample showed low pH 6.7 than normal soil. The moisture content of the normal soil showed 0.908gms. But the oil contaminated soil showed low value (0.798gms) than normal soil (Table.1). The carbon content of the normal soil was found to be 16.8 (Kg/ha) but the carbon content of the oil contaminated soil was 22 (Kg/ha), because the oil contain increased content of carbon and hydrogen in their composition. In this study, the carbon, phosphorous and potassium content of the normal and oil contaminated soil was estimated. The results showed higher carbon content in the oil contaminated soil, because the oil contain large amount of hydrocarbons in their composition. During analysis of phosphorus estimation, the normal soil showed 17.9 (Kg/ha) of phosphorus content, but in the oil contaminated soil 11.2 (Kg/ha) of phosphorus content. During the estimation of presence of potassium in the normal soil, it was found to be 43.6 (Kg/ha). Whereas, the oil contaminated soil was found to be 30.2 (Kg/ha) of potassium. In the above study revealed that phosphorus and potassium content was rapidly metabolized by microorganisms amended with oil contaminated soil.
Degradation of Hydrocarbon (Toluene)
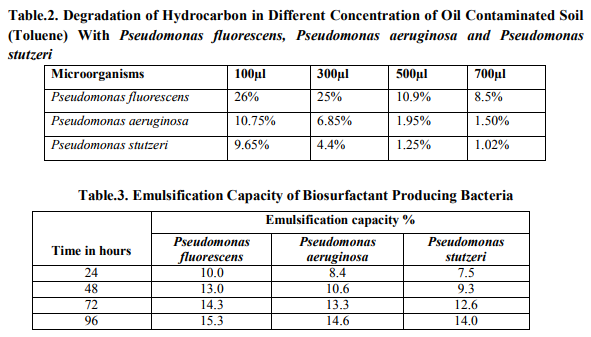
The degradation of hydrocarbon was analyzed by High Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC). Among the different strains of Pseudomonas sp. Pseudomonas fluorencens was found to be potassium in degrading the hydrocarbons (Table.2). When the concentration of toluene was increased, the rate of degradation was found to be decreased in the all experiments. Toluene and related aromatic hydrocarbons are highly toxic for living organisms because the preferential partitioning of these compounds in cell membrane disturbs the membrane structure, which leads to cell death. Hence the present investigation of toluene degradation was done, investigate certain the role of hydrocarbon which cause contamination to the environment. An oil spills in the environment leads to an adaptive process and if metabolically active hydrocarbon utilizing microorganisms could be added quickly, the long period before the indigenous population could respond would be reduced considerably (Chhatre et al., 1996).
Chemotaxis Assay
In the chemo taxis assay, a chemotactic response was observed in the form of a band of cells that accumulated in a ring surrounding, but not touching, toluene containing agarose plug. The Pseudomonas fluorescens was showed positive result to the chemo taxis assay within 30minutes and the Pseudomonas aeruginosa was showed positive result to the chemo taxis assay with in 45 minutes but Pseudomonas stutzeri was showed positive result to the chemo taxis assay after 45 minutes (within 1 hour). Besides, the roles of biosurfactant property in biodegradation were analyzed (Fig.1). Generally aromatic hydrocarbon compounds bind to soil components and are difficult to remove or degrade due to their limited availability to microorganisms.
Culture Biomass
During biosurfactant production, simultaneously the culture biomass was also observed and calculated. It was found out that total biomass of Pseudomonas fluorescens was increased from 1.021 to 1.20gms/ 100ml during 12 hours to 72 hours of incubation. Simultaneously the Pseudomonas aeruginosa showed 1.03grams/100ml during 12 hours of incubation and increased to 1.23 grams/100ml during 72 hours. Simultaneously growth of Pseudomonas stutzeri was found to be 1.01grams/100ml in 12 hours, increased to 1.21 grams/100ml during 72 hours of incubation. Emulsification Rate Emulsification rate was measured by height of the emulsion layer divided by total height of the reaction mixture and multiplying in to hundred. The rate was increased in Pseudomonas fluorescens 10 to 17.3%, Pseudomonas aeruginosa 8.4 to 16.6% and Pseudomonas stutzeri 7.5 to 16. 3% (Table.3).
Thin Layer Chromatography
After the production of biosurfactant was confirmed by the thin layer chromatography analysis and the Rf value (relative frond) value was calculated. The Rf value calculated from distance traveled by solute dividedly the distance traveled by the solvent on thin layer plates were calculated. The biosurfactant play an important role in degradation of hydrocarbons. In this study, the Pseudomonas sp. was found to be capable of producing surfactants exhibited emulsification activity on toluene. Emulsification activity is an indicator used extensively to enhanced identify and quantify biosurfactants produced by microbial culture of three Pseudomonas sp. Among them, three different species of Pseudomonas, Pseudomonas fluorescens revealed higher emulsification activity and also the amount of biosurfactant production simultaneously increased when compared to the Pseudomonas stutzeri and Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Crude surfactants were detected by Thin Layer Chromatographic technique (Fig. 2). Distance traveled by the solute Rf value = --------------------------------------- Distance traveled by the solvent
DISCUSSION
The oil spillage introduces non-organic and growth inhibiting chemicals present in the crude oil their toxicity to microorganisms and man is well known. The natural recovery of crude oil from polluted soils is slow (Ebuehi et al., 2005).Generally the natural degradation is show due to various reasons; they may be bioavailability, physical, chemical factors unsatisfactory. pH, oxygen requirement, moisture, redox potentsial, concentration of pollutant, recalcitrance (basic chemistry of pollution responsible), and xenobiotic nature of pollutant. Bioremediation ameliorates these factors through optimization of environmental conditions (Romas et al., 1995). In this study, the carbon, phosphorous and potassium content of the normal and oil contaminated soil was estimated. The results showed higher carbon content in the oil contaminated soil, because the oil contain large amount of hydrocarbons in their composition. Hence after oil spills, carbon content of the contaminated soil was increased than carbon level of normal soil. The microorganisms use the hydrocarbon as their carbon and energy source. The low amount of phosphorous and potassium content in the oil contaminated soil was found to be decreased than normal soil, because the available nutrients were rapidly assimilated by microbes, thus depleting the nutrient reserves in the contaminated soil. This coincides with the work of Vasudevan and Rajaraman, 2001. Where in they here described as increase in concentration leads to increase in microbial activity and role of biodegradation following adding the inorganic nutrients.
The biosurfactant play an important role in degradation of hydrocarbons. In this study, the Pseudomonas sp. was found to be capable of producing surfactants exhibited emulsification activity on toluene. Emulsification activity is an indicator used extensively to enhanced identify and quantify biosurfactants produced by microbial culture of three Pseudomonas sp. Among them, three different species of Pseudomonas, Pseudomonas fluorescens revealed higher emulsification activity and also the amount of biosurfactant production simultaneously increased when compared to the Pseudomonas stutzeri and Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Crude surfactants were detected by Thin Layer Chromatographic technique. Besides, the roles of biosurfactant property in biodegradation were analyzed. Generally aromatic hydrocarbon compounds bind to soil components and are difficult to remove or degrade due to their limited availability to microorganisms. This is in accordance with the work of Banat et al., 2000. According to him the biosurfactant (BS) can emulsify hydrocarbons, thus enhancing their water solubility, decreasing surface tension and increasing the displacement of oily substances from soil particles. In specific, among the three bacterial symbiasis such as Pseudomonas fluorescens, Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Pseudomonas stutzeri carried out for degradation studies, Pseudomonas fluorescens proved to be efficient in degradation of toluene, production of biosurfactant and chemotaxis property. Hence the present investigation entitled “Microbial Degradation of Hydrocarbons from Oil Contaminated Soil by using Pseudomonas sp” was studied.
CONCLUSION
Among the Various types of microorganism used in biodegradation process, pseudomonas Sp., in specific Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Pseudomonas fluorescence and Pseudomonas stutzeri play a vital role in degradation of hydrocarbons hence the present investigation, by using Pseudomonas sp., to degrade the toluene hydrocarbon. Pseudomonas sp., is recognized has one of the most important ecofriendly microorganisms in the world for clean-up technology by an adapting manner. The enzyme path way and their role in hydrocarbon degradation studies will be perform in future research.
References:
1. Atlas, R.M. (1995) Efficacy of bioremediation chemical and risk based determinations. In Bioremediation: The Tokyo 94 Workshop. OECD Documents, Paris. France.
2. Atlas, R.M. (1981) Microbial Degradation of Pertroleum Hydrocarbon. An Environmental perspective. Microbial. reviews 45, 180 – 209.
3. Banat, I.M., Makkar, R.S. and Cameotra, C.S. (2000) Potential commercial application of microbial surfactance. Applied and Environmental Microbiology 58(5), 495-508.
4. Chhatre, S., Purohid, H.J., Shanker, R. and Khanna, P. (1996) Bacterial consortia for crude oil spill remediation. Water Sci.Technol 34, 187-193.
5. Colwell, R.R. and Walker, J.D. (1977) Ecological Aspects of Microbial Degradation of Petroleum in the Marine Environment CRC Critical Reviews in Microbiology 5(4), 423- 445.
6. Desai, J.G., and Banat, I.M. (1997) Microbial production of surfactants and their commercial potential. Microbiology and Molecular biology Reviews 61, 47- 65.
7. Ebuehi, O.A.T., Abibo, I.B., Shekwolo, P.D., Sigismund, K.I., Adoki, A and Okoro, I.C. (2005) Remediation of Crude Oil Contaminated Soil by enhanced Natural Attenuation Technique. J.Appl. Sci.Environ 9(1), 103- 106.
8. Isken, S. and De Bont, J.A.M. (1996) Active efflux of toluene in a solvent resistant bacterium. J. Bacteriol 178, 6056-58.
9. Karpagam, S. and Lalitha Kumari, D. (1998) Enumeration of hydrocarbon degrading bacteria in the petroleum polluted soils on Chennai city. Indian J. Env. Prot 18, 520.
10. Parales, R.E., Ditty, J. and Harwood, C.S. (2000) Toluene Degrading Bacteria Are Chemotactic towards the Environment Pollutant Benzene, Toluene and Trichloroethylene. Applied Environmental Microbiology 4098-04.
11. Rahman, K.S.M., Rahman, T.J., Lakshmanaperumalsamy, P. and Banat, L.M. (2002) Towards efficient crude oil degradation by a mixed bacterial consortium. Bioresource Technology 85, 257-261.
12. Rahman, K.S.M., Rahman, T.J., Kourkoutas, Y., Petsas, I., Marchant, R. and Banat, I.M. (2003) Enhanced bioremediation of n-alkane in petroleum sludge using bacterial consortium amended with rhamnolipid and micronutrients. Bioresource Technology 90, 159-168.
13. Regina, O.E., Emuobonuvie, I.F. and Roseline, U.E. (2006) Growth response of bacterial isolate on various concentration of crude oil. Journal of American Science 2(2), 13-16.
14. Romas, J.L., Duque, E., Huertas, M.J. and Haidour, A. (1995) Isolation expansion of the catabolic potential of Pseudomonas putida strain able to grow in the presence of high concentration of aromatic hydrocarbons. J.Bacteriol 117, 3911-3916.
15. Romas, J.L., Duque, E., Rodiguez, J.J., Godiy, P. and Fernandez Barrerro, A. (1997) Mechanisms for solvent tolerance in bacteria. J. Biol. Chem 272, 3887-3890.
16. Rosenberg, E. and Ron, E.Z. (1999) High and low molecular mass microbial surfactants. Appl. Microbial. Biotechnol 52, 154-162.
17. Scholler Berger, C.J. and Simo, R.H. (1945) Determination of exchange capacity and exchangeable bases in soil ammonium acetate method. Soil Science 59, 13-24.
18. Sikkema, J., De-Bont, J.A.M. and Poolman, B. (1995) Mechanisms of membrane toxicity of hydrocarbons. Microbiol. Rev 59, 201-222.
19. Walkley, A. and Black, I.A. (1934) An examination of the Degtjareff method for determining soil organic matter and proposed modification of the chromic acid titration methods. Soil Science 34, 29-38.
20. Zhao, J. and Zhu, J. (1993) Biodegradation of crude oil compounds. International oil spill conference 431-438.
21. Zhao, J and Zhu, J. (1997) Study on the Biodegradation of oil spilled on the sea. International oil spill conference 989-990.

|






 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License