IJCRR - 4(18), September, 2012
Pages: 01-09
Date of Publication: 29-Sep-2012
Print Article
Download XML Download PDF
BIOCONTROL AND BIOREMEDIATION POTENTIALS OF PSEUDOMONAS ASSOCIATED WITH RHIZOSPHERE REGIONS OF SUNFLOWER (HELIANTHUS ANNUUS L)
Author: Raval A.A., Desai P.B.
Category: General Sciences
Abstract:Background and Aims: To combat the extensive use of chemical pesticides and other agrichemicals on plant growth which may be hazardous to soil and in turn human health, a group of rhizobacteria- the Plant Growth-Promoting Bacteria- can be employed. This study focuses on the mechanisms exhibited by these rhizobacteria that can further help to promote plant growth. Methods: Antifungal activities of different Pseudomonas isolated from sunflower (Helianthus annuus L.) rhizosphere were tested against four phytopathogenic fungi. Study of other biocontroling factors like production of Hydrocyanic acid (HCN) and Ammonia were also taken into consideration. The other study was pertaining to the production of several lytic and detoxification enzymes that these bacteria possess. Tolerance of these isolates to heavy metal stress was also found out, as heavy metal pollution is one of the major problems of environmental concern. Important Findings: Results indicated that 30% of isolates inhibited the growth of Fusarium, Aspergillus and Helminthosporium, 50% were antagonistic against Curvularia. Among the other biocontrolling factors studied, two isolates showed presence of HCN and Ammonia. Study of hydrolytic enzyme showed that protease production was observed in five isolates, one produced amylase. Three isolates produced lipase and cellulase enzymes. Two of the isolates tolerated about 120 mM concentration of Chromium and three isolates grew in presence of 9.9 mM concentration of Zinc.
Keywords: Rhizosphere, Plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria, Biocontrol, Antifungal, Agrichemicals.
Full Text:
INTRODUCTION
In the Bio-Era of today the rhizobacteria are playing a major role in various aspects to sustain agricultural development. Among these, the plant growth promoting rhizobacteria (PGPR) [1] are the beneficial ones that help to stimulate and enhance plant growth[2]. These bacteria exhibit a wide array of potentials for plant growth promotion. They directly benefit the plant by providing them with phytohormone indole acetic acid, Gibberellic acid, cytokinins etc., solubilizing minerals like Phosphorous and providing Nitrogen. Indirectly the PGPR may act as biocontrolling agents[3] , suppress plant diseases by secreting antifungal metabolites that support plant growth. May they be antibiotics[4], other volatile compounds, ironchelating siderophores, HCN[5], Ammonia[6] , Hydrolytic enzymes[7]. Here the study is focused on an important group of PGPR, the Pseudomonas, which have good potentials of Biocontrol[8] and tolerance to specific amount of heavy metals Lead, Chromium (VI)[9] and zinc.. The Helianthus annuus L. plant in association with these rhizobacteria can help improve phytoremediation[10] and rhizoremediation. Different agricultural plants assimilate and accumulate heavy metals[11] in a specific manner depending on a variety of factors controlling the soil plant system. Microorganisms are an important element in this system. The use of such associations in the rhizosphere may help in improving the structure of derelict and contaminated soils. Sunflower is one of the important oil seed crops in India. India has fourth largest area under Sunflower cultivation in the world and accounts for 10% of world acreage. Its share in total world production is about 5%. However the yield at 570 kg/ha is lowest among the major Sunflower producing countries in the world[12] . The seeds of Sunflower may be subjected to attack by different soil borne and seed borne fungi. The fungi can hinder seed germination and seed quality of Sunflower. Use of PGPR may thus help in controlling such seed borne diseases in these plants. Some common fungi associated with all the Sunflower varieties are Alternaria tenuis (32- 35%), Aspergillus flavus (0.5-47%), Aspergillus niger (8.7-40%). Species of Aspergillus, Fusarium, Alternaria and Penicillium have also been recorded on stored seeds [13] .
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Sample Collection: An intact plant Helianthus annuus L. was uprooted with a surface sterilized garden trowel and placed in a sterile plastic bag along with the adhering soil. Three samples were collected. Non rhizosphere soil was collected and suspension was prepared in sterile 0.1 M MgSO4 to disperse the microorganisms [14] . Root systems from the experimental plants with adhering soil were used to isolate rhizosphere microorganisms. Root segments of the plant were shaken vigorously for 3-5 min. in a test tube of sterile 0.1 M MgSO4 to dislodge the adhering soil and attendant microorganisms [2]. To isolate the endophytic bacteria excised surface sterilized roots were macerated with a sterile mortar and pestle diluted in PBS (Phosphate Buffer Solution), containing 20% glycerol. The suspensions were plated onto specialized media for Pseudomonas, King’s B medium. Plates were then incubated at ambient temperature after which growth of bacteria allowed differentiation by morphological characteristics of colonies. All three types of samples were processed and analyzed as follows. Isolation and characterization of isolates: Colony morphology was observed on the specialized media. Then the bacterial strains were characterized by morphological, biochemical and physiological tests including pigment production, gram reaction, catalase and oxidase production, nitrate reduction activities by standard microbiological procedures. Ten different bacterial strains were selected and characterized. Then the bacterial strains were assessed for the antifungal activity. 1. To assess the ability of the bacterial strains to inhibit fungi, each isolate was tested against four different phytopathogenic fungi with the circle method. Briefly bacterial isolates were seeded in a 9 cm diameter circle on a PDA plate. After 24 hr at room temperature, a 5 mm plug of each fungus was placed on the centre of the circle. Plates were incubated at 28° C for 3 days. Plates without bacterial strains were used as control. Fungal growth inhibition was assessed by measuring the mycelial radial growth [3] . 2. Testing of these bacteria in liquid media was also assessed in dual culture. The growth medium for in vitro test of fungal antagonism was sterile yeast extract sucrose-mineral salts broth (YESM). Twenty ml of sterile YESM broth was dispensed into sterile 9 cm glass petri plates. The procedure used in screening for in vitro antagonism of Pseudomonas strains against Fusarium was as follows. One ml bacterial suspension (2.5 x 106 CFU/mL) prepared from a 24 hr culture of each strain was dispensed into 20 mL sterile YESM broth in 9 cm glass petri plates and incubated for 48 hr at ambient temperature for growth of bacteria, after which three 5-mm agar plugs cut from 3 day-old culture of Fusarium were placed in the centre of each plate and further incubated in the dark for three days. Cultures were frequently agitated during incubation for proper aeration of the medium. Control treatment consisted of YESM containing three agar plugs of the fungus but without bacteria. Mycelia of the fungus were collected after three days by passing the culture through weighed Whatman No. 1 filter paper. Then washed twice with 50 mL deionized water. The harvested mycelia on the filter paper were oven dried over night at 60° C. In vitro antagonism of each strain was assessed by comparing the mycelium dry weight of the fungus in the control treatment with that of the fungus in the fungus-bacteria dual culture [14] . Then HCN production by the isolates was detected by the method of Bakker & Schippers [15]. Freshly grown cells were spread on King’s B medium amended with 4.4 g/L Glycine. A sterilized filter paper saturated with 0.5 % solution of picric acid and 2% sodium carbonate was placed in the upper lead of the petri dish. The petri dish was then sealed with parafilm and incubated at 30° C for 4 days. A change in colour of the filter paper from yellow to reddish brown as and index of cyanogenic activity was recorded. An uninoculated control was kept for comparison of results [16] . Production of Ammonia: Production of ammonia was determined by the method of Dye, 1962 by growing the isolates in peptone water in tubes and detecting it by adding Nesslar’s reagent in each tube [17] . The enzymatic activity such as protease and amylase were determined as described by Smibert & Kreig, 1994. Hydrolysis of Tween 20 was recorded as white precipitation around the colonies [18] . Production of cellulase was determined in M9 medium [19] amended with yeast extract and carboxymethyl cellulose. After 8 days incubation at 28º C, isolates surrounded by clear halos were considered positive. Alternatively the plates were flooded with Congo Red solution for 15 minutes then rinsed with 1 M NaCl for 10-15 mins. Clear zones were considered positive. Pectinase production was determined in the same M9 medium with pectin (4.8 g/L). After 2 days of incubation at 28º C, the plates were flooded with 2 M HCL and isolates surrounded by clear halos were considered positive for pectinase production [3] . Heavy metal tolerance: The bacterial strains were grown in a nutrient medium with different concentrations of heavy metals to assess their tolerance to these metals. Metals like Chromium, Zinc and Lead were analyzed. Organisms were grown in increasing concentration of the metals Zn+2, Cr (IV) and Pb+2 and the broth was incubated at 37° C for 48 hr. Bacterial growth was monitored by optical density measurement (OD 660 nm). Maximum resistance level was determined [20] .
RESULTS
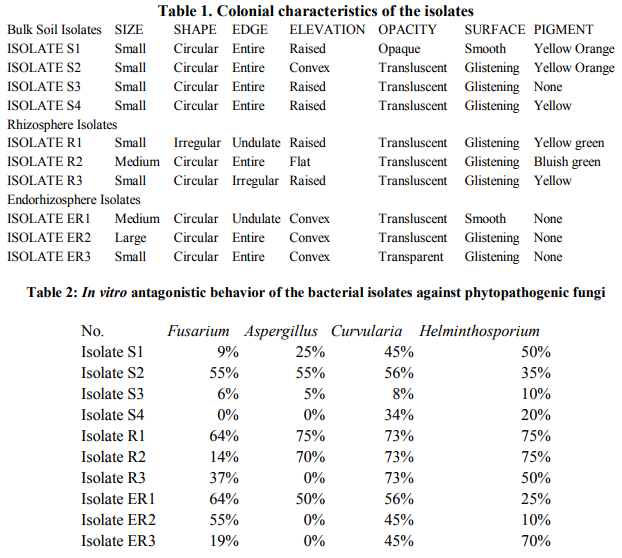
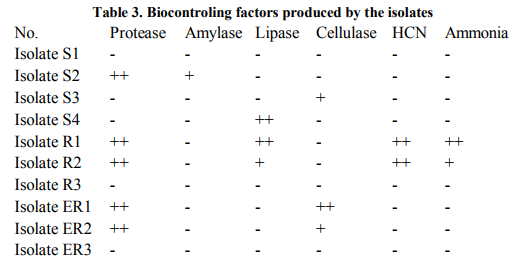
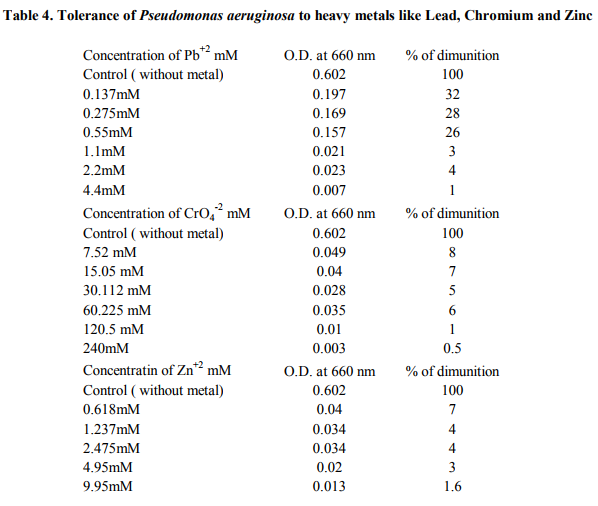
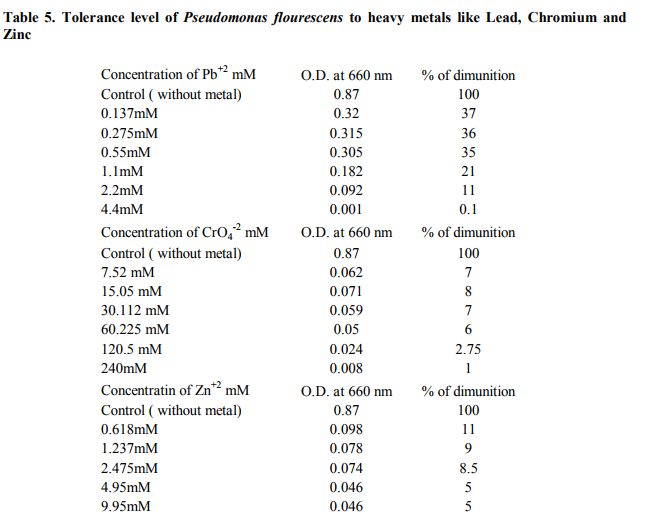
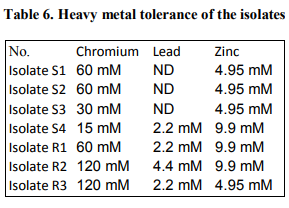
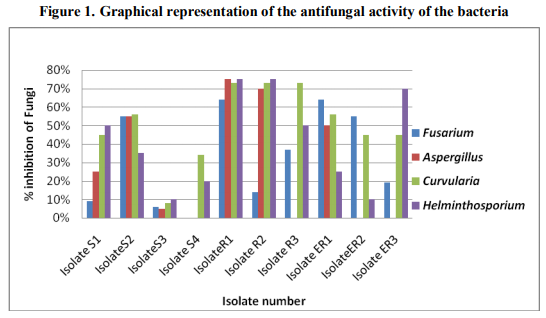
A total of ten different strains of bacteria were isolated associated with Sunflower rhizosphere regions. Isolates S1 to S4 were bulk soil isolates, isolates R1, R2, R3 were rhizosphere isolates and isolates ER1, ER2 and ER3 were isolated from endorhizosphere regions. The strains were recovered on King’s B medium. The data presented in table 1 shows the colonial characteristics. Isolates S1, S2, R1, R2 and R3 produced diffusible and nondiffusible pigments of yellow to bluish green colour. The strains were identified from their biochemical, morphological and nutritional characteristics. Assessment of the antagonistic activity of the isolates showed that four of the strains showed more than 50% inhibition of Fusarium. Isolate R1 & ER1 showed 64% inhibition against this fungus. Two of the rhizosphere isolates R1 & R2 showed 75% and 70% inhibition respectively against Aspergillus niger and 56% inhibition was seen in isolate S2. Isolates R1, R2 and R3 showed 73% inhibition against Curvularia species. Isolate S1 and R3 showed 50% inhibition against Helminthosporium and isolate R1, R2 and ER3 showed 75% inhibition against this fungus as compared to controls (Table 2, Figure 1). Dual liquid culture method which was carried out by dry weight determination also showed 48% inhibition of growth of Fusarium in isolate R1 and 36% inhibition of growth in case of isolate R2. From the data presented strain identified as Pseudomonas aeruginosa (R1) was inhibitory against all the four phytopathogenic fungi tested. These two strains also produced other biocontroling factors like the hydrolytic enzymes, protease, lipase and volatile metabolites HCN and Ammonia (Table 3). The tolerance of the isolates towards heavy metals like Chromium, Zinc and Lead is as shown in the table 4 and 5. Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Pseudomonas flourescens tolerated 60 mM and 120 mM concentration of Chromium, 2.2 mM and 4.4 mM concentration of Zinc respectively. 9.9 mM concentration of Lead was tolerated by both of them (Table 6). These data are in accordance with several authors [21] .
DISCUSSION
The adverse effects of pesticides and other agrochemicals on the environment and human health have generated interest in searching for alternative ways to control pests and diseases in plants. It is more crucial for developing countries like India. Biological control of plant diseases involve the use of antagonists selected by testing their ability in vitro and in vivo [2]. Here the study was carried out on the free living strains of rhizobacteria specifically associated with and important oil crop, the Sunflower (Helianthus annuus L.). The bacteria which are native to the crop and therefore can be more effective as biocontroling agents and may indirectly help plant growth promotion. Treatment of seeds with such bioagents i.e. Pseudomonas flourescens gave superior results and was at par with chemicals like triadimefom (12.23 q/ha), Carboxin (12.54 q/ha), Carbendazin (13.03 q/ha) and Captan (12.59 q/ha) [23]. Again, taking into consideration the bioremediation aspects, the selected strains were also able to tolerate specific concentrations of heavy metals tested. As pollution by heavy metals is posing a problem to the environment Chromium in higher concentration may prove toxigenic and carcinogenic [21] Chromium toxicity includes poor growth and leaf chlorosis [22]. Lead is also classified as a ‘possible human carcinogen ‘by IARC which lead to lung cancer, stomach cancer and gliomas [24]. Such bacteria possessing multiple capacities of biocontroling and bioremediation capabilities can be effectively used for plant growth promotion as plant growth promoting rhizobacteria (PGPR). Such strains when used could be able to survive for carrying out its plant growth promoting functions in soils containing high concentration of these metal ions.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENT
I am grateful to the management Shri Bhartiya Vidya Mandal, The Principal Arts, Science & Commerce College, for their co-operation and support. I also acknowledge my sincere thanks to The Director, SRICEAS, for providing me excellent research facilities.
References:
1. Glick BR. The enhancement of plant growth by free-living bacteria. Can. J. Microbiol. 1995; 41: 109-117.
2. Kloepper JW, Hume DJ, Scher FM, Singleton C, Tipping B, Laliberte M et al. Plant growthpromoting rhizobacteria on Canola (rapeseed). Plant disease. 1988; 72: 42-46.
3. Cattelan AJ, Hartel PG and Fuhrmann JJ. Screening for plant-growth promoting rhizobacteria to promote early soybean growth. Soil Science Society of America Journal 1999; 63: 1670-1680.
4. Keel C, Schnider U, Maurhofer M, Voisard C, Laville J, Burger U et al. Suppression of root diseases by Pseudomonas flourescens CHAO: importance of bacterial secondary metabolite, 2, 4-diacetylphloroglucinol. Mol PlantMicrobe Interact 1992; 5: 4-11.
5. Bano N and Musarrat J. Characterization of a New Pseudomonas aeruginosa, strain NJ-15 as a Potential Biocontrol Agent. Current Microbiology 2003 Vol. 46, 324-328.
6. Dye DW. The inadequacy of the usual determinative tests for identification of Xanthomonas spp. NZT Sci. 1962; 5:393-416.
7. Compant S, Duffy B, Nowak J, Clement C and Barka EA. Use of plant growth promoting bacteria for biocontrol of plant diseases: Principles, Mechanisms of Action and Future Prospects.
8. Johri BN, Rao CVS, Goel R. Flourescent Pseudomonads in plant disease management. In: Dadarwal KR (ed.) Biotechnological approaches in soil microorganisms for sustainable crop production. Jodhpur, India: Scientific Publishers, 1997; 193-221.
9. Faisal M and Hasnain S. Plant growth promotion by Brevibacterium under Chromium stress. Research Journal of Botany. 2006; 1(1): 24-29
10. Zadeh BM, Firozabadi GRS, Alikhani HA and Hosseini HM. Effect of Sunflower and Amaranthus culture and Application of Inoculants on Phytoremediation of the Soils Contanimated with Cadmium. AmericanEurasian J. Agric. Environ. Sci., 2008; 4(1): 93-103
11. Tahsin N, Hristeva T and Masheva V. Productivity and Rhizosphere microflora of different Sunflower Genotypes grown in an industrially polluted region. Journal of Environmental Protection and Ecology 4, 2003; No. 1, 39-43.
12. Anonymous, Sunflower in India, Directorate of Oilseed Research, Hyderabad, 2003; 3-5.
13. Ramegowda, Studies on seed viability in relation to storage in Sunflower. M.Sc. (Agri.) thesis, University of Agricultural Sciences, Bangalore. 1980
14. Wocoma E C. Studies on plant growth promoting rhizobacteria isolated from Choba rivers state Nigeria. Asian Jr. of Microbiol. Biotech. Env. Sc. 2008; Vol. 10, No. (4):739- 747
15. Bakker AW, Schippers B. Microbial cyanide production in the rhizosphere in relation to potato yield reduction and Pseudomonas sp. Mediated plant growth stimulation. Soil Biol Biochem. 1987; 19:451-457.
16. Samuel S and Muthukkaruppan SM. Characterization of plant growth promoting rhizobacteria and fungi associated with rice, mangrove and effluent contaminated soil. Curr. Bot. 2011; 2(3): 22-25.
17. Saxena AK, Lata, Shende R and Pandey AK. Culturing of plant growth promoting rhizobacteria in Basic Research and Applications of Mycorrhizae (Eds.) Podila G K, Varma A. I., K. I. Pvt. Ltd. New Delhi. (2005)
18. Egamberdiyeva D. The effect of plant growth promoting bacteria on growth and nutrient uptake of maize in two different soils. Applied Soil Ecology. 2007; 36: 184-189.
19. Miller JH. Experiments in molecular genetics. 2 nd ed. Cold Spring Harbour lab. Cold Spring Harbour. New York. 1974
20. Upadhyay A and Srivastava S. Evaluation of multiple plant-growth promoting traits of an isolate of Pseudomonas fluorescens strain Psd. Indian Journal of experimental Biology. 2010; Vol. 48 pp 601-609.
21. Losi ME, Amrhein C., Frankenberger WTJ. Environmental biochemistry of chromium. Rev Environ Contam Toxicol. 1994; 136:91- 131.
22. Faisal M and Hasnain S. Growth improvement in Sunflower seedlings by Cr (VI)-resistant bacteria. Iranian Journal of Biotechnology. 2005; Vol. 3, No. 2; 114-120.
23. Lakshminarayana Rao MS, Dept. of plant pathology, College of Agriculture, University of Agricultural Sciences, Dharwad. Ph.D. thesis. (2006)
24. Jarup L. Hazards of heavy metal contamination. British Medical Bulletin. 2003; Vol. 68:167-182. DOI: 10. 1093/bmb/ldg 032.
25. Smibert RM, Kreig NR. Phenotypic characterization. In: Gerhardt P., et al. (Eds.), Methods for General and Molecular Bacteriology. American Society for Microbiology, Washington DC. 1994; 607- 654.
|






 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License