IJCRR - 4(2), January, 2012
Pages: 136-145
Print Article
Download XML Download PDF
STUDY OF STATUS OF PREVAILING MISCONCEPTIONS OF HIV/AIDS IN A RURAL COMMUNITY IN SOUTH INDIA
Author: Shankar R, Pruthvish S, Varun Malhotra
Category: Healthcare
Abstract:Background: AIDS (Acquired immunodeficiency syndrome) is a disease syndrome that represents the late clinical stage of infection with HIV (human immunodeficiency virus). Now with more than 5 million people estimated to be living with HIV/AIDS, its prevalence in India is second only to South Africa. India is considered to be a ?next wave? country. Most HIV infections in India are due to sexual transmission (84-86%). In the North East, however, injection of drugs is the main mode of transmission. Women account for 39% of India's estimated HIV/AIDS prevalence Aim: To assess the status of prevailing misconceptions of HIV/AIDS in a rural community in South India. Methodolgy: Study Area The administrative limits of primary health center, Kaiwara, Chintamani Taluk,.Study Population People living in the administrative limits of Primary Health Center Kaiwara, which is approximately 32, 772 Study Design: Cross sectional study Sample size: 1332 Results : From the study that only 30% of the study population knew that HIV is a virus; 54% of the subjects knew all the 4 modes of transmission where as 22.40% had no knowledge about all the modes of transmission. Conclusion: The most common misconception with respect to modes of transmission was that, HIV/AIDS can be transmitted by mosquito
bites (34%). The misconceptions other than the modes of transmission like HIV being transmitted to the children by playing with the HIV affected children(14.3%) and also HIV can be transmitted by just buying vegetables from a vegetable vendor(18%) who is affected by HIV is quite prevalent among the study population.v
Full Text:
INTRODUCTION AIDS (Acquired immunodeficiency syndrome) is a disease syndrome that represents the late clinical stage of infection with HIV (human immunodeficiency virus). The syndrome was first recognized in 1981, but probably existed at a low endemic level in Central Africa before epidemic HIV spread began to occur in several areas of the world during the 1970s1 . The first case of HIV disease was reported in India in 1986. Later that year, Government of India established a National AIDS Control Committee under the Ministry of Health and Family Welfare to formulate a strategy for responding to HIV/AIDS in the country; it launched National AIDS Control Programme in 1987. India‘s National AIDS Control Organization (NACO), established in 1992 by the Ministry with major support from the World Bank is the implementing agency of the National AIDS Programme. Phase I of the Programme spanned 1992-1999. Phase II Programme spanned 1999-2006.Phase III Programme on span being 2007-2012. NACO has facilitated the development of 38 State AIDS Control Societies (SACS) which operate in all states and Union Territories.
Now with more than 5 million people estimated to be living with HIV/AIDS, its prevalence in India is second only to South Africa. India is considered to be a ?next wave? country Most HIV infections in India are due to sexual transmission (84-86%). In the North East, however, injection of drugs is the main mode of transmission. Women account for 39% of India‘s estimated HIV/AIDS prevalence. HIV prevalence has been increasing among pregnant women in many regions within the country. Among young people of age ranging from 15- 24, the estimated number of young women living with HIV/AIDS was almost twice that of young men2.
In the present circumstances, AIDS prevention largely depends on health education and behavioural changes based on AIDS awareness. Ignorance of the disease and of the mode of transmission of the virus can generate fear and prejudice against those who are infected and those who are providing care to the patients living with HIV/AIDS. So, by assessing the prevailing knowledge with respect to the misconception of HIV/AIDS in the community, we can delineate the role the community, the need to take effective control of the situation.
Aim: To assess the status of prevailing misconceptions of HIV/AIDS in a rural community in South India.
Review of literature: In a study by Sudha RT, et al(2005) to assess the awareness, attitudes, and beliefs of the general public toward HIV/AIDS in Hyderabad, the capital city of Andhra Pradesh, it was observed that approximately 80.63% (645/800) of the study population were sketchily aware of HIV/AIDS, but had incorrect perceptions about the mode of transmission or prevention. 3 M Steyn etal (1993) ?A study on knowledge, attitude, perception and beliefs of the general South African public regarding Human Immune Deficiency Virus and AIDS?, interviews were conducted with 5,360 participants Overall awareness of AIDS was high, but it was a mixture of appropriate and inappropriate knowledge in terms of modes of transmission, nature of disease, seriousness, prevention and cure 4 . In a study by Rimjhim M. Aggarwal (2004) on ?Determinants of Knowledge regarding HIV/AIDS among Women in India? among age group 15–49, showed that around 45% of women in the sample had heard about HIV/AIDS5 . In contrast to this, only 17% of women had heard about HIV/AIDS in the first round of NFHS conducted in 1992-93. Interestingly, although a higher proportion of women had heard about HIV/AIDS by 1998-99, their knowledge regarding prevention options was found to be much more superficial than of them in 1992-93. In a Cross-Sectional Population-Based Study by Anand D etal (2004) on Knowledge, Attitudes, and Practices regarding HIV/AIDS in Dakshina Kannada District of Karnataka, India, an assessment was made on HIV/AIDS-related knowledge, attitudes, and practices among the general population in South India. Although 54% of participants knew that AIDS is caused by "HIV" virus and 44% could correctly identify all modes of transmission, 52% believed in one or more myths, 41% did not know that condoms can prevent HIV, and 18% had not heard of a condom. Higher HIV knowledge scores were significantly associated with male gender, higher education, currently married, higher frequency of reading newspapers, listening to radio or watching television, and willingnessto get tested for HIV6 . Patel R (2006) in his cross sectional study regarding knowledge, attitude and source of information on HIV/AIDS among teachers of secondary and higher secondary schools of Ahmedabad city has observed that 88% of his study subjects knew that AIDS could be transmitted by having multiple sex partners while 79% were aware of the risk due to transfusion of infected blood and use of contaminated needles. Among his study subjects 19% of males and 8% of females believed that AIDS can be transmitted by kissing an AIDS patient while 12% of females and 20% of male teachers believed that HIV patients must not be allowed to do any job or business. Only 67% of the respondents knew that AIDS could be prevented by proper use of condoms.7 . S Sarkar (2007) in his study on ?Knowledge and Attitude on HIV/AIDS among Married Women of Reproductive Age Attending a Teaching Hospital,? found, that majority i.e. 64% women belonged to the younger age group (<30 years). It was observed that 96% of women had heard about HIV/AIDS. This finding is less (99.6%) than that obtained by NACO.
The sources of knowledge were television (81.98%), radio (42.79%), newspaper (15.76%) and health care providers (10.8%). Around 30% were aware of the type of people usually affected by this disease and its signs and symptoms (28.4%). 83% women knew one or more modes of the spread of this disease. However, only 44.6% knew about any method of preventing the spread. Only 3.2% actually knew that HIV virus is the agent responsible for this disease. Half of the sample population were aware that laboratory investigation could detect HIV status of individuals. Around 62% women knew what condoms were but only 30.2% had the knowledge that its use could prevent STD and HIV/AIDS8 .
Misconceptions with regard to HIV/AIDS considered for study:
HIV/AIDS can be transmitted by
- Using public toilets
- Mosquito bites
- By donating blood
- Caring for an HIV positive person
- Shaking hands/embracing
- Sharing meals with infected person
- Talking with infected persons
- No treatment for HIV/AIDS Child could become infected with HIV if he/she plays with a child who has HIV/AIDS
- HIV can also be transmitted when you buy vegetables from a shop keeper or vendor living with HIV/AIDS12
METHODOLOGY
Study Area The administrative limits of primary health center, Kaiwara, Chintamani Taluk, Chikkaballapur District.Kaiwara is a small township situated about 75 kms from Bangalore city.
Study Population People living in the administrative limits of Primary Health Center Kaiwara, which is approximately 32, 772 (as per Primary Health Center records January 2007) constituted the study population
Study Design: Cross sectional study Inclusion Criteria: Persons aged more than 13 years.
Exclusion Criteria: Persons not willing to participate in the study for their own reasons. Estimation of Sample Size: From the review of literature, Sudha RT, et al conducted a study to assess the awareness, attitudes, and beliefs of the general public toward HIV/AIDS in Hyderabad, the capital city of Andhra Pradesh. The results showed approximately 80.63%8 of the study population were sketchily aware of HIV/AIDS and so assuming that the knowledge and awareness of the community towards HIV/AIDS is 80.63%, the sample size is determined with a precision of 5% level of significance and with absolute allowable error of 3% The following formula was used to calculate the sample size
N= Z 2 *p*q e 2 Sample Size - 1332 Method Of Sampling: Cluster sampling The total study population of 1332 is selected from 12 villages with about 111 persons from each village. For choosing 12 villages as 12 clusters it is kept in mind that the numbers of clusters are sufficiently large that statistical precision at the population level is adequate and the number of clusters for the survey remains logically feasible.
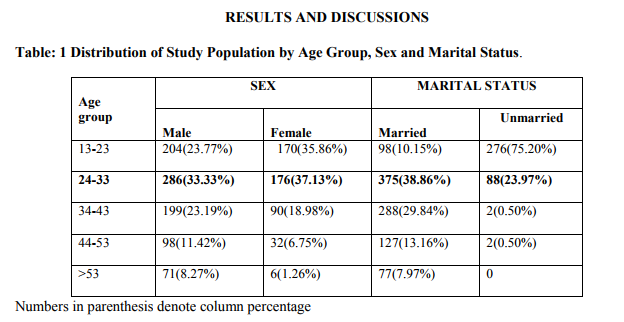
It was observed that majority 462 (34.68%) of the subjects in the study population were in the age group of 24-33 years and the proportion of males and females in the same age group was observed to be 286(33.3%) and 176(37.13%) respectively It was observed that majority of the study population 965(72.4%) were married and 375 (38.86%) of them were in the age group of 24 – 33. Observation made in the present study is similar to the one made by S.Sarkar 8 (2007) where it was found that majority (64%) of the women belonged to the younger age group (<30 years). Most of these women (47.7%) were married before 20 years of age and the largest group (40.5%) married for <5 years.
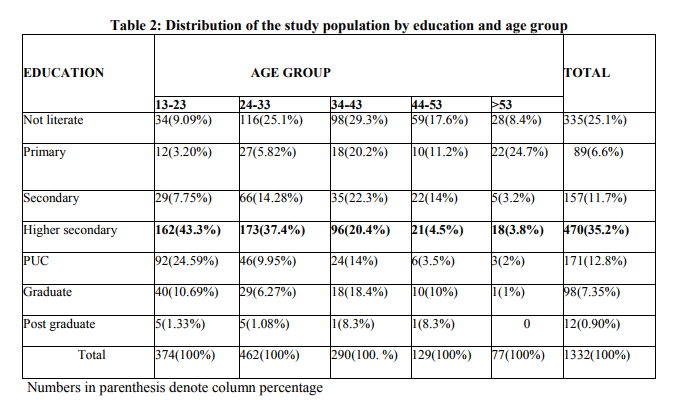
It was observed that majority 470(35.28%) had education upto higher secondary level. Post graduates constituted 12(0.90%) of the study population. In the age group 13-23, 162(43.31%) were educated upto higher secondary and only 5(1.3%) were post graduates. In the age group of 24-33, 173(37.44%) were educated upto higher secondary and only 5(1.08%) were post graduates. In the age group of 34-43, 98 out of 290 i.e. (33.79%) were not literate and only 1(0.34%) were post graduates. In the age group of 44-53, 59(45.73%) were not literate and only 1(0.77%) were post graduates. In the age group >53, 28(36.36%) were not literates and 4(1.2%) were graduates. In the present study 335 of 1332(25%) were not literate. S.Sarkar 8 (2007) has observed that 18.5% of the study population were not literate and 52.3% have studied upto SSLC. In the present study 470(35.28%) had studied upto higher secondary. From the study it was observed that majority 492(36.93%) of the study population were partly agriculturists, labourers & other unskilled workers. Professional workers of intermediate class constituted only 53(3.97%) of the study population.
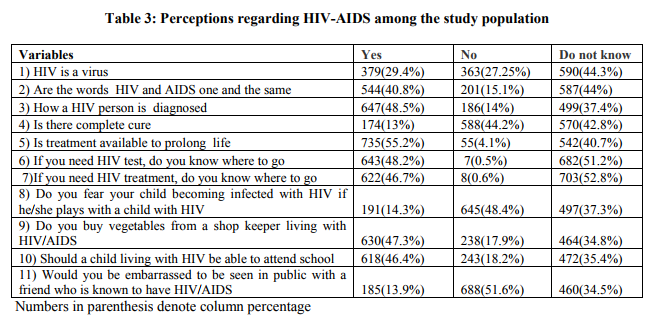
From the above table it is seen that the misconceptions other than the modes of transmission varied from 40.8% for saying both HIV and AIDS are one and the same to 27.25% for saying that HIV is not a virus but the most striking thing here is majority of them had neither correct response nor the misconception.
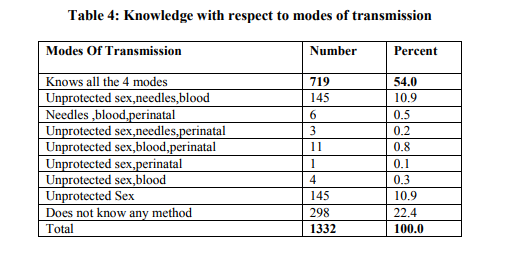
It was observed that, 719(54%) of the subjects knew all the 4 modes of transmission where as 22.40% had no knowledge about the modes of transmission rest of the combinations varied between 0.1% and 10.9%. K. M. Börsum (2004) 9 had observed in his study that 44%of his study population could correctly identify all modes of transmission. The observation made in the present study is more or less similar i.e., 54% of the study population knew all the 4 modes of transmission. Raheel H(2004)10 in his study has observed that 62% were aware that disease can be transmitted by sexual contact, 69% of the adolescents had heard of HIV/AIDS and 55% named two correct modes of its transmission. Sudha etal (2005)3 had observed in her study that the awareness of HIV/AIDS were sketchy and had incorrect perception about the mode of transmission and prevention.W.Al Serouri etal (2000)11 had observed that despite a majority of study population being aware of the major modes of transmission there were large areas of misconception that would impede the management of the situation.
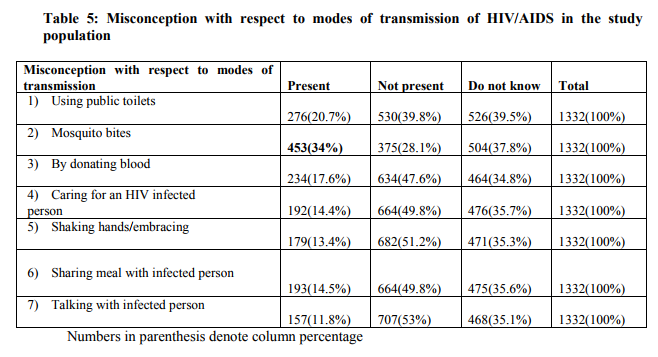
Centre for Disease Control/HIV/AIDS/200112 have identified the following misconceptions with regards to HIV/AIDS. They are, HIV/AIDS can be spread by using public toilets, mosquito bites, by donating blood, caring for an HIV positive person, shaking hands/embracing, sharing meals with infected person, talking with infected persons, no treatment for HIV/AIDS, child could become infected with HIV if he/she plays with a child who has HIV/AIDS, HIV can also be transmitted when you buy vegetables from a shop keeper or vendor living with HIV/AIDS. In the present study however 453(34%) thought that HIV/AIDS was transmitted through mosquito bites.
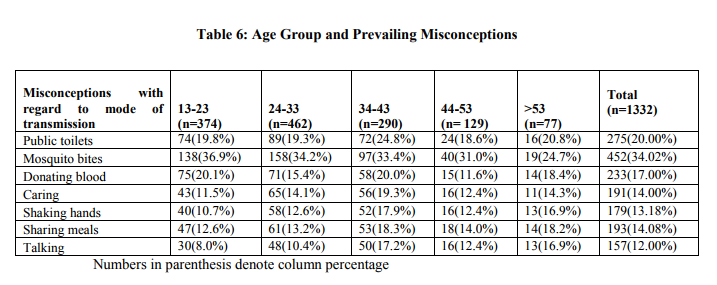
It was observed from the table that 452(34.02%) of the study population had the misconception that HIV/AIDS can be transmitted by mosquito bites and 157(12.00%) of the study population thought that HIV/AIDS can be transmitted by just talking to HIV/AIDS affected person. The same was true to the extent of 138(36.9%) & 30(8.0%); 158(34.2%) % 48(10.4%); 97(33.4%) & 50(17.2%); in the age groups of 13-23, 24-33, 34- 43 respectively. In the age group of 44-53, 40(31.0%) thought that it was transmitted through mosquito bite while 16(12.4%) thought that HIV/AIDS was transmitted by shaking hands, talking and caring for HIV/AIDS affected persons. Among those aged 53 years and over, 19(24.7%) thought that HIV/AIDS can be transmitted by mosquito bites and11 (14.30%) thought that HIV/AIDS can be transmitted by caring for those affected with HIV/AIDS. Sanjay Sangole etal (2003)13 observed that 72% of his subjects thought that HIV could be transmitted via casual contact such as hugging, shaking hands, sharing foods, glasses, toilet seats, etc .
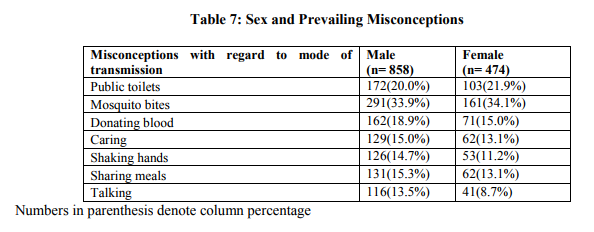
From the table it was revealed, the misconception that HIV/AIDS can be transmitted by mosquito bites was 291(33.9%) and 161(34.10%) among males and females respectively. One hundred and sixteen of males and 41(8.7%) of females thought that it was transmitted through talking to HIV/AIDS affected persons.
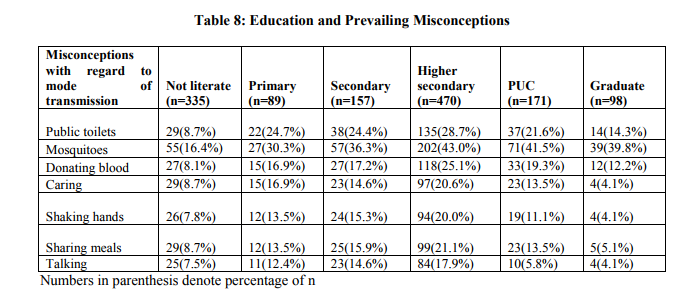
It shows that the misconceptions are comparatively low in not literate groups when compared to other levels of education this is because majority of the not literate people neither had correct knowledge nor misconceptions.
CONCLUSIONS
- It can be concluded from the study that only 30% of the study population knew that HIV is a virus; 54% of the subjects knew all the 4 modes of transmission where as 22.40% had no knowledge about all the modes of transmission.
- The most common misconception with respect to modes of transmission was that, HIV/AIDS can be transmitted by mosquito bites (34%).
- The misconceptions other than the modes of transmission like HIV being transmitted to the children by playing with the HIV affected children(14.3%) and also HIV can be transmitted by just buying vegetables from a vegetable vendor(18%) who is affected by HIV is quite prevalent among the study population.
Recommendations
- A lot of misconceptions are prevailing in IEC activities should mainly focus on the modes of transmission of HIV/AIDS, the ways by which HIV/AIDS will not be transmitted like bite of a mosquito and finally it should emphasise on the methods of prevention of HIV/AIDS.the community with respect to HIV/AIDS
- So, it has to be addressed by conducting a need based, targeted, and focused Information, Education and Communication activities in the villages as a priority primary measure
- IEC activities should mainly focus on the modes of transmission of HIV/AIDS, the ways by which HIV/AIDS will not be transmitted like bite of a mosquito and finally it should emphasise on the methods of prevention of HIV/AIDS.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENT
Authors acknowledge the immense help received from the scholars whose articles are cited and included in references of this manuscript. The authors are also grateful to authors / editors / publishers of all those articles, journals and books from where the literature for this article has been reviewed and discussed.
References:
1. Joint United Nations Programme on HIV/AIDS. UNAIDS and the World Health Organization. AIDS Epidemic Update. 2007.
2. National Aids Control Organization. Facts and Figures. Oct 2006 Available at http://www.naco.nic.in. Accessed on 22/09/2006.
3. Sudha RT., Vijay DT and Lakshmi V. ?Awareness, attitudes, and beliefs of the general public towards HIV/AIDS in Hyderabad, a capital city from South India?. Indian Journal of Medical Science. 2005 vol 59 pp 307-316.
4. M Steyn etal, ?Study of Knowledge, attitude, perceptions and beliefs regarding HIV/AIDS? Memorandum presented to the Directorate Primary Health Care Of the development of National Health and Population Development. 1993.
5. Rimjhim M. Aggarwal and Jeffrey J. Rous, ?Determinants of Knowledge regarding HIV/AIDS among Women in India?- a document paper Department of Economics, University of North Texas. 2004.
6. Anand D etal, ?Cross-Sectional PopulationBased Study of Knowledge, Attitudes, and Practices Regarding HIV/AIDS in Dakshina Kannada District of Karnataka, India? Indian Journal of Public Health. 2004 vol 34 (5).
7. Patel R, ?An epidemiological study regarding knowledge, attitude and source of information on HIV-AIDS among the teachers of secondary and higher secondary schools of Ahmedabad City?, India European Society of Clinical Microbiology and Infectious Diseases 16th European Congress of Clinical Microbiology and Infectious Diseases, Nice, France. April 2006.
8. S Sarkar, M Danabalan, ?Knowledge and Attitude on HIV/AIDS among Married Women of Reproductive Age Attending a Teaching Hospital? Indian Journal of Community Medicine. 2007 vol 32.
9. K. M. Börsum and P. E. Gjermo, ?Relationship between knowledge and attitudes regarding HIV/AIDS among dental school employees and students? European Journal of Dental Education. 2004 August vol 8 (3) pp 105-110.
10. Raheel H, ?White FM Knowledge and beliefs of adolescents regarding HIV/AIDS in a rural district Mirpurkhas, Sindh, Pakistan?. Int Conf AIDS at Bangkok. 2004 July.
11. Al-Serouri A.W., Takioldin. M, Oshish.H. Aldobaibi.A and Abdelmajed.A ?Knowledge, attitudes, and beliefs about HIV/AIDS in Sana, a Yemen? Eastern Mediterranean Health Journal. 2002 vol.8 (6).
12. HIV/AIDS –Myths and Misconception. Fact Sheet CDC. Oct 2006.
13. Sanjay Sangole etal, ?Evaluation of Impact of Health Education Regarding HIV/AIDS on Knowledge and Attitude among Persons Living with HIV? Indian Journal of Community Medicine. 2003 vol 28 (1).
|






 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License