IJCRR - 4(4), February, 2012
Pages: 149-158
Print Article
Download XML Download PDF
STUDY ON LEAKAGE POWER REDUCTION TECHNIQUES AND ITS IMPACT ON 16NM CMOS
CIRCUITS
Author: R. Udaiyakumar, K. Sankaranarayanan, M.Valarmathy
Category: Technology
Abstract:High leakage current is becoming a significant contributor in power dissipation of CMOS circuits whenever threshold voltage, channel length and gate oxide thickness are reduced. Threshold voltage scaling, results in the substantial increase of sub threshold leakage current. To maintain reasonable short channel effect (SCE) immunity, while scaling down the channel length, oxide thickness has to be reduced in proportion to the channel length. But, decrease in oxide thickness results in increase in the electric field across the gate oxide. In this review paper, attempts are made to analyze the previously published works in the specified area. Some of the power optimization techniques have been verified with 16nm Silicon On Insulator (SOI), High K Dielectric, Strained Silicon Predictive Technology Model (PTM) files in ISCAS C17 benchmark circuit.
Keywords: Leakage Current, ITRS, MTCMOS, SCCMOS, FTS, SS, GALEOR, LECTOR, PTM
Full Text:
1. INTRODUCTION
As per International Technology Roadmap for Semiconductors (ITRS), the number of transistors per circuit will continue to increase as predicted by Moore‘s law, whereas the transistor sizes will continue to shrink and it is expected to keep the total chip size within practical and affordable limits. From a technology perspective, the continuous increase in the integration density proposed by Moore‘s Law was made possible by a dimensional scaling [1]. The Integration density is increased by reducing the critical dimensions while keeping the electrical field constant. With increasing Integration density as well as aggressive technology scaling, power consumption has become a major challenge in digital system design and Power Optimization become the major problem of the microelectronics industries. Despite a decreased supply voltage, the total power will continue to increase. The reduction of the supply voltage is dictated by the need to maintain the electric field constant on the ever shrinking gate oxide. Unfortunately, to keep transistor speed within (proportional to the transistor ?on? current) the acceptable limit, the threshold voltage must be reduced too, which results in an exponential increase of the ?off? transistor current, i.e. the current constantly flowing through the transistor even when it should be ?non-conducting?. As projected by, power will continue to be a limiting factor in future technologies. There is an increasing need to address power issues in a systematic way at all levels of the design process.
2. POWER COMPONENTS IN CMOS CIRCUITS
In CMOS circuits, the overall power consumption shall be from three components namely static, dynamic and short circuit power.
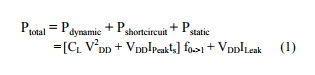
In submicron technology dynamic power consumption (Pdynamic) contributes significantly to overall power consumption. Every time a capacitive node switches from VSS to VDD, energy of CL V 2 DD is consumed. It depends on the switching activity of the signal. Signals in CMOS devices transit back and forth between two logic levels resulting in the charging and discharging of parasitic capacitance. This is the dominant factor of power dissipation (transient switching). For a small instant of time both PMOS and NMOS will be ?on? simultaneously. The duration depends on the input and output transition (rise and fall times). So a direct path exists between VDD and VSS (short circuit). The current flowing through this short circuit path will be the peak current and denoted as IPeak and the Power consumed to this current is known as Short Circuit power (Pshortcircuit). When a CMOS integrated circuit is not switching, there should be no DC current paths from VDD to VSS and the device should not draw any supply current at all. However, due to the inherent nature of semiconductors, a small amount of leakage current flows across all reverse-biased junctions on the integrated circuit and responsible for static power consumption (Pstatic). These leakages are caused by thermally-generated charge carriers in the diode area. As the temperature of the diode increases, so do the number of these unwanted charge carriers also increases [2]. As the device dimensions shrinks, the leakage current increases and has become a major contributor to the total power Consumption. The major leakage mechanisms contribute to the total leakage are identified as: Sub threshold leakage, Gate leakage, Reverse biased drainsubstrate and source-substrate junction BandTo-Band-Tunneling leakage [3-4].
In scaled devices each of these leakage components increases drastically resulting in a dramatic increase in the total leakage current. Moreover, each component depends differently on the transistor geometry (gate length (Lg), Source-Drain extension length (LSDE), oxide thickness (Tox), junction depth (Yj), width (W)), the doping profile (channel doping (Ndep) and ?halo? doping (Npocket) concentration), the flatband voltage (Vfb), and the supply voltage (Vcc) [4].
3. LEAKAGE CURRENT MECHANISMS
Six short-channel leakage mechanisms are illustrated in Figure 1.
a. I? is the reverse-bias p-n junction leakage;
b. I2 is the sub threshold leakage;
c. I3 is the oxide tunnelling current;
d. I4 is the gate current due to hot-carrier injection;
e. I5 is the Gate- induced drain leakage current ;
f. I6 and is the channel punch through current.
Currents I2, I5 and I6 are off-state leakage mechanisms, while I? and I3 occur in both ON and OFF states. I4 can occur in the off state, but more typically occurs during the transistor bias states in transition.
To suppress the power consumption in lowvoltage circuits, it is necessary to reduce the leakage power in both the active and standby modes of operation [3]. The reduction in leakage current has to be achieved using both process- and circuit-level techniques. At the process level, leakage reduction can be achieved by controlling the dimensions (length, oxide thickness, junction depth, etc.) and doping profile in transistors. At the circuit level, threshold voltage and leakage current of transistors can be effectively controlled by controlling the voltages of different device terminals [drain, source, gate, and body (substrate)] [5].
4. LITERATURE SURVEY
From a very detailed study of various papers relating static power optimization in CMOS devices, some circuit level techniques that consume less power have been selected for detailed analysis on their impacts on static CMOS circuit implemented with 16 nm process technology. They are Input vector control, dynamic threshold CMOS (DTCMOS), Genetic algorithm (GA), Panoptic dynamic voltage scaling (PDVS), Dual threshold, Multi threshold voltage CMOS (MTCMOS), Body bias control, Programmable Dual VDD, Power gating, Minimum leakage vector (MLV), Zerodelay ripple turn on (ZDRTO), Gate- level dualthreshold static power optimization (GDSPOM) based on STA, Dynamic power cutoff technique (DPCT), Single electron transistor (SET), Self controllable voltage level (SVL) method, Independently driven double gate FinFET (IDDG- FinFET),GALEOR and LECTOR method.[6] Detailed explanations of all these techniques and their impacts and percentage of power savings wherever possible are also given. Anderson and his colleagues [7] proposed a novel approach in their paper that the leakage current in a digital CMOS circuit depends strongly on the state of its inputs.
They have considered only the active leakage power and ignored leakage in the unused part of FPGA. The average leakage power for passing logic ?1? is substantially smaller than the average leakage power for passing logic ?0‘. The reason behind these is, when logic 1 (Vdd) is applied to the drain terminal of an ON NMOS transistor, a weak ?1‘ (Vdd-Vth) occurs at the source terminal. This weak ?1‘ leads to reduction in sub threshold leakage power in other multiplexer transistors that are being in OFF state. In this paper they have assigned a polarity to each signal in an FPGA so that it enables signals to maintain majority of the time in logic 1 state. This is possible due to the static probability (fraction of time a signal spends in the logic 1 state) property of digital signals. If the static probability of a signal is greater than 0.5, it spends more than 50% of its time in logic 1 state. A unique property of FPGA is that it does not require any area or delay penalty for signal inversion. The signal inversion is achieved by permuting the bits in the SRAM cells of each downstream Look Up Table (LUT). Permuting is just interchanging the contents of the top two SRAM cells in the downstream with the bottom two SRAM cells in the LUT. Each signal must be checked whether it can be inverted. The optimization was performed in 90nm commercial FPGA with 1.2V. The improvement in power saving using this technique is 25% with no impact on circuit area or delay and requires no hardware changes. Shah [8] et.al proposed silicon on insulator dynamic threshold transistor (SOIDTMOS) technique for low leakage and high current drive.
Leakage current increases as Vdd and Vt scales down as the drive strength of transistors depends on the relation Vdd-Vt Reduction in Vt will cause an exponential increase of device sub threshold leakage, so that the static power increases to unacceptable levels. In DTMOS technique threshold voltage is dynamically controlled by connecting the body to the gate. For voltage greater than 0.6V the drain/body diode starts conducting so there is need for current limiters. Moreover this technique has two drawbacks, one is increased area and the other is larger gate capacitance. This is commonly known as ?DTMOS? in USA and ?MTCMOS? (Multi-threshold CMOS) in Japan. As the voltage on the gate rises, the body voltage is forward biased and hence leads to drop in Vt . This technique is mostly suitable for synchronous circuits. Hung [9] et.al proposed a genetic algorithm based power optimization framework, for minimizing total power consumption using multiple Vdd, multiple Vth, device sizing and stack forcing and have maintained system performance. The overhead created by insertion of level converters have also been taken into account. They verified the experimental results with a number of circuit topologies such as SRAM decoder, multiplier and 32bit carry adder using the 65nm benchmark technology. They have concluded that the combination of the above four power reduction techniques is more effective for low power. This is the first joint optimization technique that uses more than three techniques. Genetic algorithm (GA) is a class of search and optimization method. The solutions are encoded into a binary string known as the chromosome. Instead of working with a single solution, the search begins with a random set of chromosomes known as the initial population.
The optimization flow is an iterative procedure. The circuit size ranges from 8 to 1050 gates. Benton [10] et.al proposed panoptic dynamic voltage scaling (PDVS). PDVS uses header switches to switch each component between several available supply voltages. Instead of changing voltages between large rails, the header switch provides fast and efficient voltage transitions. Adding extra header switches gives only few percent of total leakage due to reduced VDS across the headers. A large header width results in lower channel resistance thus decreasing the voltage drop. In PDVS system the bulk terminal of the active circuit should be connected to the virtual rail. PDVS can greatly improve the efficiency of a system. One drawback in PDVS is that noise is created in the global VDD rail that results from switching the header for the particular block. Ndubuisi Ekekwe [5] et.al presented several device and circuit level techniques to control static power dissipation. Device level includes controlling the doping profile and physical dimension of transistors.
Circuit level involves manipulation of Vth and source biasing of the transistor. In dual threshold method high Vth is assigned to devices in non-critical paths and low Vth to devices in critical paths [11]. This is applicable both in the standby and active mode. In multi threshold voltage control method a high Vth device is connected in series to a low Vth block, thereby creating a virtual power rail instead of connecting the block to the main power rail. . In active mode of operation high Vth transistors are switched on and hence the low Vth transistors operate at high speed. The insertion of NMOS is preferable to PMOS because the on-resistance is lower at the same width. But use of these transistors increase circuit delay and area. Body biasing a transistor is another effective way for reducing the active and standby leakage power. Vth is increased by applying a reverse body bias and therefore the sub threshold leakage current is reduced. In standby mode, a strong negative bias is applied to the NMOS bulk and the PMOS bulk is connected to the VDD rail. Since Vth is related to the square root of the bias voltage a significant voltage level is needed to raise Vth. Gayasen [12] et.al proposed a programmable dual VDD architecture in which low VDD is assigned to non-critical paths, and high VDD to the timing critical paths in the design. This technique has an average power saving of 61% in 65nm technology. The VDD of each block is connected between VDDH and VDDL by using two high VT (supply) transistors. The ON/OFF of each supply transistor is set controlled by a configuration bit which is done by VDD assignment algorithm. In their technique level conversion takes place only at the CLB pins. They have experimented using two algorithms high to low (h2l) and low to high (l2h). In h2l all the CLB‘s are initially kept at high voltage and then some of them are changed to low VDD. The h2l performs better than the l2h. D. Helms [13] presented design techniques to reduce leakage power at all levels of abstraction. In power gating technique an additional transistor is implemented between gate and ground or between gate and supply or even both. This technique has low switching speed as well as low leakage currents. But this requires additional area. In Minimum leakage vector (MLV) technique a data input is identified such as the overall leakage is minimized and this input is forced to the block when it becomes idle. This reduces an average leakage power of 20-50%. Carlos [14] et.al proposed a zero delay ripple turn on (ZDRTO) wakeup technique for gated asynchronous pipelines. In ZDRTO power gating technique the wakeup latency of downstream stages is hidden by the computational latencies of upstream stages hence wake up is ?zero delay?. The pipeline stages are grouped into clusters each having its own sleep transistors and associated local power nets. They had evaluated their technique in 65 and 90nm technologies running at 25°C.
They had applied this technique in a 128-bit advanced encryption standard (AES) encryption/decryption standard because of its complexity, wide data path and low duty cycle. Chung [15] et.al proposed gate level dual threshold static power optimization (GDSPOM) based on static timing analysis for high speed and low power SOC applications. In 90nm technology it has 50% less leakage power consumption compared to single low- threshold cell library. Static timing analysis is done to report the cells that are swapped from HVT to the low voltage type (LVT). Moreover it calculates the signal propagation delay of each path individually. GDSPOM replaces minimum amount of cells from HVT to LVT and hence results in least leakage power. It does not alter the design architecture and hence there is no area overhead. Baozhen YU [16] in his research work presented dynamic power cutoff technique (DPCT) to reduce the active leakage power. In his technique he has first identified the switching window for each gate during transitions using static timing analysis.
Then he optimally partitioned the circuit into different groups based on the minimal switching window. Finally he has introduced power cutoff transistors to each group. The power of each gate is turned on only during a small timing window with each clock cycle that results in significant active leakage power savings. Using, DPCT he has achieved an excellent power saving of 73.6% active leakage power and 34.7% of total power under process variations. He has used 70nm CMOS Berkeley Predictive Models, a BSIM3v3 model, for his simulation. Gates having same switching window are treated as one group and the power connections of all gates within the same group are controlled by one pair of power cutoff MOSFETs, a pMOSFET and an nMOSFET. To minimize the extra delay caused by the cutoff MOSFETs, the size of cutoff MOSFETs has to be appropriate. The cutoff control signals are generated by the cutoff control generator using the global clock signal. One pair of cutoff control signals is required for each group, one for nMOSFET and the other for pMOSFET. One special case of using DPCT is that a gate in one group drives another gate in another group. The advantage of the MSW is that its width only depends on the maximal delay of the gate itself, which is usually less that 1/10th of the worst-case circuit delay in big circuits. By turning on the power of a gate only within its switching window, the gate can make transitions only when all of its inputs are ready. This automatically balances the delay differences between the inputs of each gate.
Therefore, glitches, which are unnecessary transitions of the output due to different delays on inputs, are automatically eliminated. He also implemented the layouts of a 16-bit multiplier and c432 using DPCT. The 16-bit multiplier with DPCT saves 54.7% of the total power, 85.7% of the active leakage power and 38.1% of the dynamic power with 7.7% delay overhead and 8.6% area overhead. The c432 circuit with DPCT saves 22.5% of the total power, 73.6% of the active leakage power and 2.3% of the dynamic power with 9% delay overhead and 13.7% area overhead. A.Venkataratnam et.al [17] proposed single electron transistor (SET) method for developing nanoscale logic circuits. In their paper they have designed CMOS architecture based NAND and NOR gates using set style and studied their characteristics. In their design the layout is a small conducting island coupled to the source and drain that are capacitively coupled to control gates and one or more input gates. SET uses quantum effects to perform operations similar to conventional CMOS transistors. The charges in single electron devices are transported in a quantized way rather than continuously.
Complementary operation can be achieved by controlling the charge on the island. From there simulation they have observed that the gate bias should be 0.1V for NMOS and 0.3V for PMOS for the SET to operate. They have performed their simulation using SET-SPICE model. Shyam Akashe [18] et.al designed 1KB SRAM cell using self controllable voltage level (SVL) method. They have observed that this method has an average power saving of 5.4% compared to the conventional memory cell array and speed remaining constant. They have implemented using 45 nm technology. The USVL circuit is constructed as a wide channel pull-up pMOSFET switch (pSW) and multiple nMOSFET resistors connected in series. Similarly, the L-SVL circuit incorporates a wide channel pull-down nMOSFET switch (nSW) and multiple series-connected pMOSFET resistors (pRSm). When the load circuit is active both the pSW and nSW are turned on, but the nRS1 and pRS1 are turned off. Thus the U SVL and L-SVL circuits can supply a maximum supply voltage and a minimum ground-level voltage respectively, to the active load circuit. Thus, the operating speed of the load circuit can be maximized. Varun P. Gopi [19] et.al proposed independently driven double gate FinFET (IDDG- FinFET) scalable to 10nm that maintains the sub threshold factor for a given gate length. IDDG FinFETs have been proposed for dynamic threshold-voltage control and transconductance modulation. Since channel is formed on the side vertical surface of the Si-fin, the current flows parallel to the wafer surface.
The heart of the FinFET is a thin Si fin, which serves as body of the MOSFET. The poly-Si film greatly reduces the Source/Drain series resistance and provide a convenient means for local interconnect and making connections to the metal. A gap is etched through the poly-Si film to separate the source and drain. A single IDDG transistor can operate as two transistors with common source and drain terminals. The proposed IDDG FinFET has a sub threshold slope of 72mV/decade, threshold voltage of 150mV, DIBL of 46mV/V with a minimum threshold voltage roll off. The simulation was performed using SILVACO. Srinivasa Rao [20] et.al presented two techniques GALEOR (Gated Leakage transistor) and LECTOR (Leakage Controlled Transistor) to reduce the leakage power. They have designed a full adder using the above two techniques, estimated power and compared it with the conventional CMOS full adder. They simulated in TANNER tool in 250 nm technology. In LECTOR technique two leakage control transistors (a p-type and a n-type) are introduced within the logic gate for which the gate terminal of each leakage control transistor (LCT) is controlled by the source of the other. One of the LCTs is always ?near its cutoff voltage? for any input combination. The significant feature of LECTOR is that it works effectively in both active and idle states of the circuit, resulting in better leakage reduction. It is based on the observation that ?a state with more than one transistor OFF in a path from supply voltage to ground is far less leaky than a state with only one transistor OFF in any supply to ground path.? GALEOR technique reduces the leakage current flowing through the NAND gate for all possible input combinations by introducing stack effect. In GALEOR technique, a gated leakage NMOS transistor is placed between output and pull-up circuit and a gated leakage PMOS transistor is placed between output and pull-down circuitry.
5. Analysis of various Leakage current reduction Techniques
5.1 Experimental Setup
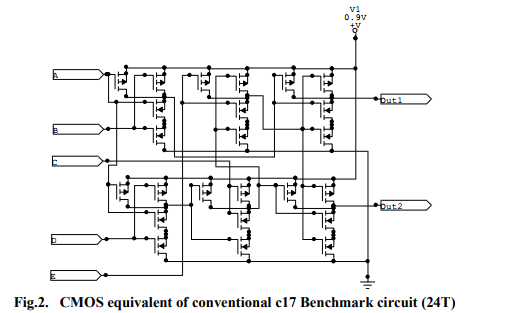
In this paper, we have used a CMOS equivalent ISCAS85 c17 benchmark circuit for analysis. C17 benchmark circuit consists of 6 two input NAND gates and requires 24 MOS Transistors for its implementation. Simulation is performed in TSPICE platform for conventional and various power optimized circuits using 16nm Low Power, High K-Dielectric, strained Silicon, SOI technology PTM model files[21]-[22]. We have compared the average power consumed by the circuit with and without various power optimization techniques. The CMOS c17 circuit is shown in Figure 2.

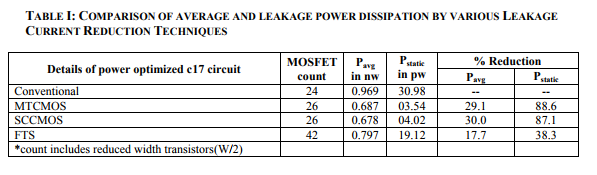
5.2 RESULTS On Simulation, Comparison of Power results for various optimization Techniques implemented with ISCAS85 c17 Benchmark circuit are tabulated below. Snap shot of the power (Figure 3(a) and 3(b) ) and output simulation results (Figure 4(a) and 4(b)) for a conventional c17 bench mark circuit are shown below:

6.CONCLUSION
In nanoscale CMOS devices, leakage current is becoming a major contributor to the total power consumption. With current technology and devices with decreasing threshold voltage levels, Sub threshold and gate leakage are becoming dominant sources of leakage power. To manage the increasing leakage in nano scale CMOS circuits, solutions for leakage reduction have to be sought both at the process technology and circuit levels. At the process technology level, a lot of research works are taken for replacing SiO2 with high K materials for the gate insulation to reduce gate tunneling current and improve short-channel characteristics. From Table 1, it is observed that, at the circuit level, transistor stacking (active mode), multiple threshold devices techniques (static mode) can effectively reduce the leakage current in nanoscale CMOS circuits.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
Authors acknowledge the immense help received from the scholars whose articles are cited and included in references of this manuscript. The authors are also grateful to authors / editors / publishers of all those articles, journals and books from where the literature for this article has been reviewed and discussed.
References:
1. Wolfgang Arden et.al. ?More-than-Moore? White Paper, International Technology Roadmap for Semiconductors, ITRS 2010 update, http://www.itrs.net
2. Jan N. Rabaey, Anantha Chandrakasan and Borivoje Nikolic, Digital Integrated Circuits- A Design perspective, 2nd Edition, Prentice Hall of India, 2003
3. Kaushik Roy, Saibal Mukhopadhyay and Hamid Mahmoodi-Meimand, Leakage current mechanisms and Leakage current reduction techniques in Deep Sub Micrometer CMOS Circuits, in Proceedings oh IEEE, Vol-91, No-2, 2003
4. Y. Taur and T. H. Ning, Fundamentals of Modern VLSI Devices, Cambridge University Press, 1998.
5. Ndubuisi Ekekwe and Ralph EtienneCummings, Power Dissipation sources and Possible Control Techniques in ultra deep micron CMOS Technologies, Elsevier, Micro Electronics Journal 37 (2006) 851-860.
6. V. De, Y. Ye, A. Keshavarzi, S. Narendra, J. Kao, D. Somasekhar,R. Nair, and S. Borkar, ?Techniques for leakage power reduction,? in Design of High-Performance Microprocessor Circuits, NJ: IEEE, 2001, ch. 3, pp. 48–52.
7. Jason H.Anderson, Farid N.Najm and Tim Tuan. Active Leakage Power Optimization for FPGAs. In International symposium on FPGA , pages 33-41,2004
8. P.J shah, B.P Patil, V.M Deahmukh and P.H Zope. Low- Power VLSI design using dynamic threshold logic. In Proceedings of SPIT-IEEE colloquim and International conference, volume 2: 2010, 121-126.
9. W. Hung, Y. Xie, N. Vijaykrishnan, M. Kandemir, M. J Irwin and Y. Tsai. Total power optimization through simultaneously Multiple- VDD MultipleVTH assignment and device sizing with stack forcing. In proceedings of the International Symposium on Low power Electronics and Design (ISLPED‘04), pages 144-149, 2004.
10. Benton Highsmith Calhown, Joseph F. Ryan, sudhanshu khanna, Mateja putic and John Lach. Flexible Circuits and Architectures for Ultralow power. In proceedings of IEEE. Volume 98, page no: 267-282, 2010.
11. HeungJun Jeon,Yong-Bin Kim and Minsu Choi, Standby Leakage Power Reduction Techniques for Nanoscale CMOS VLSI Systems, IEEE Transactions on Instrumentation and Measurements, Vol. 59, No. 5, May 2010
12. Gayasen, K. Lee, N. Vijaykrishnan, M. Kandemir, M. J. Irwin and T. Tuan. A Dual- VDD for Low Power FPGA architecture. In International conference on FPGA. Aug-Sept 2004.
13. D.Helms. System level optimization of static power consumption in nano-CMOS circuits. In International symposium for low power design,2006
14. Carlos Ortega, Jonathan Tse and Rajiv Manohar. Static power reductiontechniques for asynchronous circuits. In International conference for low power VLSI designs.
15. K. Chung and Kuo, Gate-level dualthreshold static power optimization methodology (GDSPOM) using path-based static timing analysis (STA) technique for SOC application, Elsevier, Integration, the VLSI journal 41 (2008) 9–16
16. Baozhen YU. A novel dynamic power cutoff technology (DPCT) for active leakage reduction in deep submicron VLSI CMOS circuits. In the thesis of New Brunswick, New Jersey, October, 2007, pages 1-101.
17. A.Venkataratnam and A.K Goel. CMOS architectures for NOR and NAND logic gates using single electron transistors. In the proceedings of NSII- Nanotech, volume 3, 2005, pages 176-179.
18. Shyam Akashe, Deepak Kumar Sinha and Sanjay Sharma. A low-leakage current power 45-nm CMOS SRAM. In Indian Journal of Science and Technology Vol. 4 No. 4 (April 2011), page no 440-442.
19. Varun P. Gopi and V. Sureshbabu. Independently driven double gate FinFET scalable to 10nm. In 10th National Conference on Technological Trends (NCTT09) 6-7 Nov 2009, pages 320-326.
20. Sreenivasa Rao, D.Srinivas, B.Ram Paramesh, V.Malleswara Rao. Leakage current reduction ?GALEOR and LECTOR? techniques. In International Journal of Communication Engineering Applications-IJCEA, Vol 02, Issue 02; May 2011, pages 57-60.
21. http://ptm.asu.edu/ Latest Models
22. W. Zhao, Y. Cao, "New generation of Predictive Technology Model for sub- 45nm early design exploration," IEEE Transactions on Electron Devices, vol. 53, no. 11, pp. 2816-2823, November 2006.
|






 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License