IJCRR - 4(4), February, 2012
Pages: 70-80
Print Article
Download XML Download PDF
EMERGING PATTERN OF ELECTROPHYSIOLOGY IN PATIENTS DIAGNOSED CTS - A STUDY IN INDIA
Author: Lata D Parmar, Vikas Doshi
Category: Healthcare
Abstract:Context: Establishment of classification of CTS on various basis have been reported. However surgery or conservative' intervention may still remain a dilemma. In last 2 years we had electro diagnosis data collected of patients clinically diagnosed and electro physiologically confirmed CTS.Aim: to study if the emerging pattern of NCS can be categorized. Design: Hospital based, Retrospective Analysis Methods and Material: Data CTS patients referred for NCS analyzed afterelectro physiologically confirmation. The data were grouped on the basis of SML. Statistical analysis used: Descriptive statistics, Regression analysis Results: Total No. of cases 70, females 64, males 06, age range 23 \? 72 yrs. Clinically involved hands Rt.19, Lt.23 and 28 bilateral. No. of hands electro physiologically normal (sensory latency < 3.05ms) were 31, 50% were symptomatic, analyses indicated changes in ILDMU, SNCV, FML, although Sensory Latency and SNAP amplitude with Motor parameters remained in normal limits.Progressively Group I to V showed SNCV significantly decreases (49 to 12 m/s) and ILDMU(sensory) significantly increases (0.8 to 9 ms) SNAP shows progressive reduction (51 to 14\?V), motor distal latencies and FMLM was progressively prolonged across groups. Regression analysis for the ILDMU difference and the SNCV show high predictability. Retrograde degeneration was obvious from group I. Conclusions: The emerging pattern established categories similar to that reported in literature. In view of CTS natural history, conservative treatment is suggested in mild to moderate cases.
Keywords: Nerve conduction studies, classifications, electro diagnosis, treatment outcome.
Full Text:
INTRODUCTION
Carpal tunnel syndrome (CTS) is one of the most common entrapment but none of the tests are diagnostic on their own. The gold standard test is nerve conduction studies (NCS) however; they are associated with false positive and false negative results. The severity of the condition definitely needs to be spelt as conservative treatment may be attempted first unless there is a progressive motor and sensory deficit or severe electrophysiological abnormalities1,2,5,6,7,9,14,17. Conservative treatments include Physiotherapy, modification of daily activities, immobilization by wrist splint, non steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, diuretics, and intra carpal and oral steroids. Splinting is used and has been recommended by several investigators.1, 2, 6 . However, in moderate to severe cases, surgery may be the only treatment that provides cure. The establishment of severity / classification of CTS on different basis have been reported1,2,3,7,9,14,23,25,26. However surgery as the ?option‘ may still remain a dilemma. In last 2 years we had electro diagnosis data collected of the patients clinically diagnosed and electro physiologically confirmed CTS.
The aim of the study therefore was in retrospect to:
- Study the emerging pattern of NCS if it can be categorized.
The objective was:
- Identify and study the electrophysiological changes in a clinically diagnosed, electro physiologically confirmed CTS patient.
METHODS
The study was conducted at ? K M Patel Institute of Physiotherapy, Shree Krishna Hospital, Karamsad, approved by the Human Research Ethics Committee of the institute.
Study Design: Retrospective Analysis The data of clinically diagnosed CTS, referred for NCS was taken up for analysis after electro physiologically too, it was confirmed.
Inclusion Criteria. The data, of all the cases clinically diagnosed CTS by a competent medical personnel, and which were electro physiologically too confirmed as CTS, were included for analysis. Exclusion Criteria The data of known case of any underlying systemic diseases such as diabetes, hypothyroidism, etc was excluded. Patients with wrist joint pain, trauma with involvement of the median nerve or cervical radiculopathy were also excluded. No patient was pregnant. The study included the data analysis of total 70 cases which satisfied the inclusion / exclusion criteria. The electro physiological studies in these cases were done using standardized method32. The norms are as established of the upper limb nerves in our laboratory.
Median neuropathy is defined as Distal Motor Latency (DML) above 4.5 ms or wrist-digit sensory latency above 3.7 ms 16. Sensory symptoms are crucial for the diagnosis of CTS, therefore the data was divided in to various groups for study as shown below on the basis of sensory latency. These five groups were as follows:
Median nerve sensory latency (SML) (in ms)
< 3.59 I
3.6 – 4.59 II
4.6 – 5.59 III
5.6 – 6.59 IV
> 6.6 V
Sensory unrecordable
There were 31 cases affected either unilaterally or bilaterally who had SML <3.05, of these 16 were symptomatic, these were analyzed separately. Similarly the very severe group VI where the sensory nerve (digit II) was not recordable was analyzed separately.
The diagnosis of CTS in our laboratory is based on
1. Delayed Motor Distal Latency (DML) >4.4 ms
2. Prolonged Sensory Median Latency (SML) >3.7 ms
which were electro physiologically too confirmed as CTS, were included for analysis.
Exclusion Criteria
- The data of known case of any underlying systemic diseases such as diabetes, hypothyroidism, etc was excluded.
- Patients with wrist joint pain, trauma with involvement of the median nerve or cervical radiculopathy were also excluded.
- No patient was pregnant.
The study included the data analysis of total 70 cases which satisfied the inclusion / exclusion criteria. The electro physiological studies in these cases were done using standardized method32. The norms are as established of the upper limb nerves in our laboratory.
Median neuropathy is defined as Distal Motor Latency (DML) above 4.5 ms or wrist-digit sensory latency above 3.7 ms 16. Sensory symptoms are crucial for the diagnosis of CTS, therefore the data was divided in to various groups for study as shown below on the basis of sensory latency.
Group
I
II
III
IV
VI
3. Slowing of Sensory Nerve Conduction Velocity (SNCV) digit II < 50 m / sec
4. Inter latency difference between ipsi lateral median and ulnar sensory (ILDMU Sensory) (digit II and V ) >0.5 ms
5. Inter latency difference between the distal motor latencies of ipsi lateral median and ulnar (ILDMU Motor) > 1.1 ms
Normal Values of electrophysiological parameters (mean ± SD) established in the department on 70 cases (unpublished)
RESULTS
Total numbers of cases were 70 The numbers of females 64 and the numbers of males 06 The age range of the subjects varied between 23 – 72 yrs Total numbers involved with Right hands: 19 Total numbers involved with Left hands: 23 Total numbers involved Bilateral hands were: 28 Total numbers of hands clinically and electro physiologically normal were: 15 Total number of hands with sensory latency ≤ 3.05 were 31 of this 16 hands were symptomatic, either Left, Right, or bilateral hand involved. As compared to norms the average sensory conduction velocity (50.851 m/sec) was in the lower normal limit and the ILDMU sensory (0.734ms) higher than cut off value 0.4 ms , the SML (2.69 ms) and Sensory Nerve Action Potential (SNAP) amplitude (64.125 µv) still well within normal limits. The average DML (3.502 ms) is again on the upper limit, Compound Motor Action Potential (CMAP) amplitude (15.615mv) and average motor conduction velocity (53.214 m/s) are in normal limits. The average F-minimum latency of median (FMLM) was seen to be minimally prolonged compared to ipsi lateral ulnar. The range of SML in the symptomatic subjects varied from 2.33ms to 13.54ms. The asymptomatic hands also showed SML varying between 2.33 and 5.42 TABLE I a and b shows data of various groups; GROUP I: Total number of hands with SML < 3.59 were (Right) 31 and (Left) 36, the average latency of this group 2.8729 (0.3205) ms and 2.9886 (0.3840) ms respectively, apparently within normal limits, but ILDMU Sensory is increased Right 0.8919 (0.4188) ms and Left 0.9850 (0.3852) ms. The average SNCV of the median nerve was 49.087 (6.625) m/s of the Right median and 46.6731 (6.3714) m/s of the Left side, both showing slowing. The average SNAP amplitude however was 51.88 (19.65) µV on the Right side while it was 55.767 (28.398) µV on the Left side which are compatible with the norms except for the higher SD.
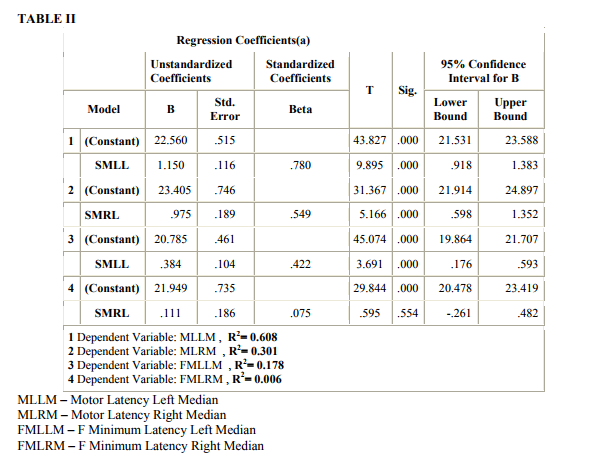
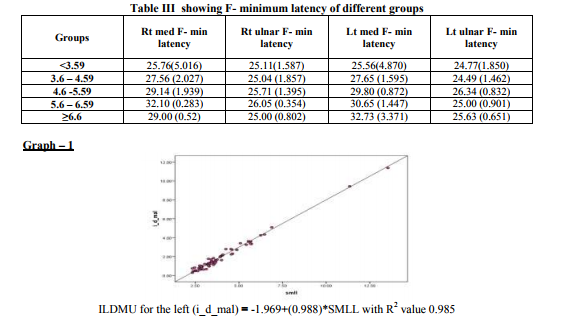
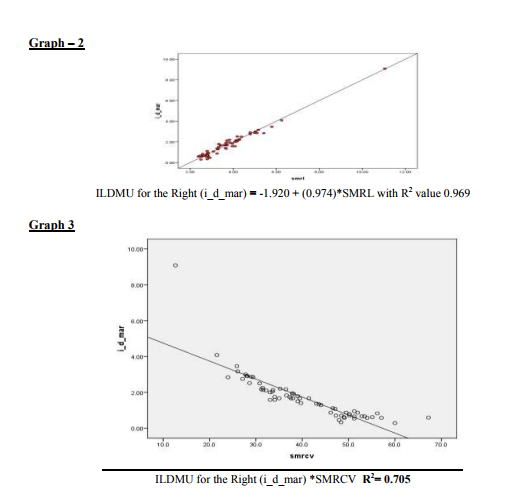
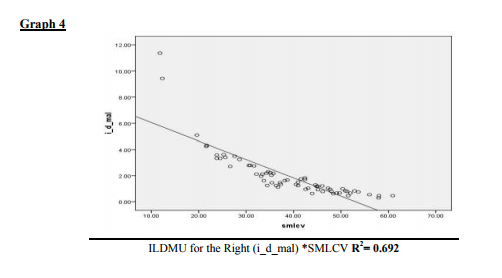
The average DML was 3.8527 (0.7089) of Left median and was 3.7106 (0.6263) of the Right median both although in upper normal limit are still less than < 4.4 ms an accepted cut off. The FMLM in this group was also seen to be prolonged compared to ipsi lateral ulnar bilaterally (table III). Referring further table Ia and b we can see that progressively as we proceed from the 1st group, the SNCV progressively significantly decreases and the ILDMU Sensory significantly increases. The SNAP also shows progressive reduction. This pattern is seen both on the right and the left side. Also prolonged DMLs were seen from group II onwards and in the group V the DML were markedly prolonged ie; DML (Left) was 7.4180 (2.7315) and DML(Right) was 7.6400 (3.5619). In the group VI in which the median sensory was unrecordable the DMLs were markedly prolonged. The average DML was 9.20 on the right and 7.085 ms on the left respectively. The regression analysis of both the right and the left side show that as the SML increases the ILDMU Sensory increases. The regression lines for right and left sides are as follows with corresponding R2 values (graphs 1 and 2). ILDMU Sensory = -1.969 (0.988)*SMLL with R 2 value 0.985 for the left (graph 1) and ILDMU Sensory = -1.920 (0.974)*SMRL with R 2 value 0.969 (graph 2). High values of R2 suggest that the regression models are valid for prediction. Similarly we have obtained regression lines for sensory median conduction velocity, it decreases with increasing ILDMU (graph 3and4). In relation to the motor latencies also this was statistically significant bilaterally but apparently not effective for prediction (Table II). FMLM are consistently prolonged progressively compared to ipsi lateral ulnar, bilaterally, as seen in table III, although statistically significant, effectiveness for prediction is poor, R2 values as shown in the table II. In the present study the retrograde degeneration is obvious from group I and does not show drastic difference across the groups.
DISCUSSION
Our data clearly indicates the female preponderance with regards to CTS. Sensory symptoms are crucial for the diagnosis of CTS 1, 2, 6, 9, 10, 13, 15, 16, 17, 18, 20, 21, 30. Sensory conduction studies have been preferred to motor conduction studies in CTS by almost all, we found only one article which has concluded striking and unusual electrophysiological finding when compared to idiopathic CTS, they found predominant DML abnormality instead of SML. They state that there was a distinctly different pattern of involvement of all fascicles of the median nerve not sparing the motor fascicles as in some mild idiopathic CTS11 . Various studies have considered SML as <3.5 ms as normal1,2,4,8, 31. In the present study the group, so called normal latency < 3.0514, 50 % of the subjects were with symptoms, rest were probably sub clinical - is still debated 19, as although all the parameters were in the normal limits, ILDMU Sensory was more than the cut off limit of 0.5ms used by some authors 1, 16, 25 , a number of authors have also used 0.4 ms as cut off limit8, 22. Atroshi and colleagues‘ and others16,22,25 recommend use of a 0.8- millisecond median-to ulnar peak latency difference to define median mono neuropathy, accordingly anything on the higher value than 0.5ms would certainly reduce false-positive is emphasized22, 30. Accordingly median-ulnar digit-wrist sensory latency difference had a significantly higher diagnostic accuracy 8, 16 . Massino Lama 22 used the criteria of sensory amplitude less than 50μV, or DML ulnarmedian difference exceeding 0.4 milliseconds. The SNAP amplitude in the present study also showed progressive deterioration however in the groups so called normal and mild the SNAP was within normal limits indicating that initially there is predominant demyelination the axonal loss follows9 .
In the study by Chang et al 10 the normal sensory latency is given as 2.43 (0.15), abnormal cut off values with SD 2.5 were set at ≥ 2.9ms and for DML it was set at ≥ 4.3 (normal ≤ 3.52 SD 0.29). These authors also concluded that W-P motor CV is equivalent to W-P sensory CV in the early diagnosis of CTS suggesting that motor segmental conduction is more commonly affected than originally thought, they also state that trans carpal motor conduction measurements were able to diagnose several additional patients who had normal MSL values or normal values for both MSL and DML. A number of studies have almost similarly set their cut off values1,2,7, 12 . One of the studies report the median sensory onset latency / peak latency to be the most sensitive to other sensory parameters, possible reasons include the median-range velocity fibers (represented by the peak latency) as affected relatively more common than the fastest conducting fibers (represented by onset latency) in CTS. Another possible reason is that the majority of median sensory nerve fibers are made up of median-ranged velocity fibers15 . The minimal, mild, moderate criteria have been differently proposed by various authors 1,2,3,7,9,14,23,25,26. Many authors put 4-5 criteria‘s and require at least one to be fulfilled7 , however according to the present study simultaneously changes are seen in various tests i.e. ILDMU sensory along with SNCV Median and the FMLM along with DML and retrograde degeneration seen as decreased conduction velocity of forearm segment almost all show changes and thus need to be taken in to consideration before concluding on CTS. C W Chang et al7 classified Prolonged distal motor latency but less than 150% of the highest normal value (5.4 ms) and slowed SNCV but greater than 75% of the lowest normal value (30.1 m/s) as mild. This and as similarly suggested by many authors 1, 3, 8, 7, 14, 23 , correspond to our group I and II both of which fall in the mild category. Across the groups the average FMLM of median is seen to be progressively prolonged compared to ipsilateral ulnar (Table III), normally the FMLM of median is lesser than the ipsilateral ulnar, Daniel L. Menkes, Ashraf Hussain et al also found prolongation of FMLM in the median nerve, and a statistically significant reduction of F-ratio in all CTS patients emphasizing its importance in diagnosis of CTS 28,29,30, 31 . For DML the cutoff values used in different studies have ranged from 3.8 ms to 4.6 ms. In the present study prolonged DML were seen from group II onwards. Indeed, the lack of diagnostic sensitivity of this technique may be because motor fibers are relatively spared in CTS even when sensory fiber conduction is impaired in CTS 10, 27. Prolonged DML over 200% of the highest normal value (7.2 ms), slowed SNCV less than 50% of the lowest normal value (20 m/s) or not obtainable was considered as severe 2,7 . Yasunobu Tsaiweichao-Shozawa21 studied the severe group, their distal motor latency was 9.5 ± 2.9 (6.3-17ms), (normal ≤ 3.7ms), amplitude was 4.2 -3.7 (0.08–10.8), the normal amplitude was ≥ 7.8 mv, their antidromic latency was 5.8 ± 0.9 (4.8-8.0), the normal limit was ≤ 2.7, SNAP amplitude was 2.9 ± 2.4 (0.4-9.3), the normal was ≥4.5 µv., this is seen in the group IV and V in the present study, the sensory conduction velocity in this group is decreased to 23.76 m/s and 23.8 m/s of right and left respectively. These authors never experienced the grade 4 patients of the Bland classification: DML between 4.5 and 6.5 milliseconds and SNAP is lost. Therefore they suggested that the grading criteria should be more accurately defined as ?the SNAP amplitude is less than a certain value21 . In the present study the DML averaged to 6.562 (1.226) and 9.06 (1.900) ms on the left side, on the right it was 7.29 (0.735) and 7.19 on the left and right in the group IV and V respectively. In the group VI in which the median sensory was un recordable the DML were markedly prolonged. The average DML was 9.20 on the right and 7.085 ms on the left resp., which is not different from that in the severe group of others. We had subjects with bilateral hands involved and SNAP unrecordable. Absence of thenar response is considered as extreme / very severe2,3,7,23,24. We did not have absent motor in any, also neurogenic pattern was prominent on electromyography (EMG) from group III onwards. The regression analysis for the ILDMU sensory difference and the SNCV show high predictability, according to R. Aygu¨l et al. (2005), the ILDMU of median sensory digit II is a most sensitive of the rest in the early stages4 . The regression analysis for the DML and for the FMLM when compared to the ipsi lateral ulna was also statistically significant but the R² being low effectiveness for prediction decreases, not as reported by some studies 28,29 . Presence of retrograde degeneration: i.e. retrograde degeneration defined as when the mixed nerve conduction velocity was slower than 45 m/s in the forearm segment of the median nerve, has been used by Chang et al7 as one of the criteria for CTS. A recent study demonstrates that retrograde axonal atrophy and dying back may cause slowed motor nerve conduction velocity in the forearm segment of the median nerve (Chang et al., 2003). In the present study the retrograde degeneration is obvious from the group I and does not show drastic difference across the groups. Although CTS has become a significant public health problem, it remains unclear how to make a decision with regards to non-surgical or surgical treatments. As seen in the present study the range of SML in the symptomatic subjects varied from 2.33ms to 13.54ms similarly the asymptomatic hands also showed the SML varying between 2.33 and 5.42 ms. It is important thus as seen from the study that a battery of tests should be done and considered before one concludes on the severity of compressive median nerve neuropathy at the carpal tunnel2, 10, 14,17 This is specially so in the early stage according to the present study.
CONCLUSIONS
The pattern emerging from this retrograde analysis clearly indicates that
- Emerging categories are similar to that reported in literature.
- Early in the stage 50% of the cases with normal NCS data could be symptomatic and vice versa.
- The regression analysis for the ILDMU Sensory and the SNCV show high predictability.
- The retrograde degeneration is obvious from the group I but does not show drastic difference across the groups.
Assessing severity / classifying is essential to guide intervention and must be given due consideration before surgery.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
Authors acknowledge the immense help received from the scholars whose articles are cited and included in references of this manuscript. The authors are also grateful to authors / editors / publishers of all those articles, journals and books from where the literature for this article has been reviewed and discussed. The authors are also grateful to the trust ? Charutar Arogya Mandal? for all the support provided.
References:
1. Manente G., Torrieri F., Di blasio F., Staniscia T., Romano F., and Uncini A., An innovative hand brace for carpal tunnel syndrome: A randomized controlled trial. Muscle Nerve. 2001; 24: 1020–1025.
2. Calogero Alfonso, Stefano Jann, Roberto Massa, and Aldo torreggiani. Diagnosis, Treatment and Follow-up of the carpal tunnel syndrome: A review. Neurol Sci 2010; 31: 243–252.
3. Padua l., Lo Monaco M., Padua R., Gregori B., and Tonali P. Neurophysiological classification of carpal tunnel syndrome: Assessment of 600 symptomatic hands. Ital J Neurol Sci. 1997; 18: 145-150.
4. Recep Aygu¨l, Hizir Ulvi, Saliha Karatay, Orhan Deniz, and Asuman Orhan Varoglu. Determination of sensitive electrophysiologic parameters at Followup of different steroid treatments of carpal tunnel Syndrome. J Clin Neurophysiol. 2005; 22: 222–230.
5. Amir-Hessein Hashemi, Mehran Homa, Saeed Naghibi, Bahram Hejrani, Sahar Sobhani, Abdoreza Afsharian, and Mahsan Shaban. Wrist Sonography Versus Electrophysiologic Studies in Diagnosis of Carpal Tunnel Syndrome. Neurosurgery Quarterly. 2009 September; 19 (3): 171-173.
6. Ingeborg BC Korthals-de BOS, Annette Am Gerritsen, Maurits W Vantulder, Maureen Pmh Rutten-Van Mölken, Herman J Adèr, Henrica CW De Vet and Lex M Bouter. Research article: Surgery is more cost-effective than splinting for carpal tunnel Syndrome in the Netherlands: Results of an economic evaluation alongside a randomized controlled trial. BMC Musculoskeletal Disorders. 2006; 7: 86.
7. Chang C. -W., Y. -C. Wang and K. -F. Chang. A practical electrophysiological guide for non-surgical and surgical treatment of carpal tunnel syndrome. The Journal of Hand Surgery (European Volume). 2008; 33E (1): 32–37.
8. Hans M. Schrijver, Annette A. M. Gerritsen, Rob L. M. Strijers, Bernard M. J. Uitdehaag, Rob J. P. M. Scholten, Henrica C. W. De vet, and Lex M. Bouter. Correlating nerve conduction studies and clinical Outcome measures on carpal tunnel syndrome: Lessons from a randomized controlled trial. J Clin Neurophysiol. 2005; 22: 216–221.
9. Marcelo Ribeiro Caetano. Axonal degeneration in association with carpal tunnel syndrome. Arq Neuropsiquiatr. 2003; 61(1): 48-50.
10. Ming-Hong Chang, Yi-Chu Liao, YiChung Lee, Peiyuan F. Hsieh, and Lu-Han Liu. Electrodiagnosis of Carpal Tunnel Syndrome: Which Transcarpal Conduction Technique is Best?. Journal of Clinical Neurophysiology. 2009 October; 26 (5), 366-371.
11. João Aris Kouyoumdjian, Rogério Gayer Machado De Araújo. Carpal tunnel syndrome and manual milking nerve conduction studies in 43 cases. Arq Neuropsiquiatr. 2006; 64(3-b): 747-749.
12. Rogério Gayer Machado De Araújo, João Aris Kouyoumdjian. Cooling modifies mixed median and ulnarpalmar studies in carpal tunnel syndrome. Arq Neuropsiquiatr. 2007; 65(3-B): 779-782.
13. João Aris Kouyoumdjian, Maria P. A. Morita, Amalia F. P. Molina. Usefulness of additional nerve conduction techniques in mild carpal tunnel syndrome. Arq Neuropsiquiatr. 2002; 60(4): 923-927.
14. Karsidag S., Sahin S., Hacikerim Karsidag S., Ayalp S.. Longterm and frequent electro physiological observation in carpal tunnel syndrome. EURA MEDICO PHYS. 2007; 43: 327-32.
15. Prakash KM, Fook-Chong S, Leoh TH, Dan YF, Nurjannah S, Tan ye, Lo Y. Sensitivities of sensory nerve conduction study parameters in carpal tunnel syndrome. J Clin Neurophysiol. 2006 Dec; 23(6): 565-7.
16. Isam Atroshi, Christina Gummesson, Ragnar Johnsson and Ewald Ornstein. Research article- Diagnostic properties of nerve conduction tests in population-based carpal tunnel syndrome. BMC Musculoskeletal Disorders. 2003, 4. Biomedcentral: http://www.biomedcentral.com 1471- 2474/4/9.
17. Somaiah Aroori, Roy AJ Spence. ReviewCarpal Tunnel Syndrome. Ulster Med J. 2008; 77 (1): 6-17. 18. Wilder-smith E. P., Lirong L., Seet R. C. S., and Lim E. C. H.. Symptoms associated with electrophysiologically verified carpal tunnel syndrome in Asian patients. Journal of Hand Surgery (British and European Volume). 2006; 3: B: 3: 326-330.
19. Alfred Franzblau, Robert A. Werner. Editorials- What is Carpal Tunnel Syndrome? JAMA, 1999 July 14; 282 (2): 186-187.
20. Berna Celik, and Zeynep Guven. Review of Different Electrodiagnostic Studies in Mild Carpal Tunnel Syndrome. Neurosurg Q. 2008 June; 18(2): 83-88
21. Yasunobu Tsaiweichao-Shozawa, Masahiro Sonoo, and Teruo Shimizu. Original article- Patterns of Nerve Conduction Abnormalities in Severe Carpal Tunnel Syndrome. Journal of Clinical Neurophysiology. 2008 Octo; 25(5): 281-286.
22. Massimo lama. Carpal tunnel release in patients with negative neurophysiological examinations: Clinical and surgical findings. Neurosurgery. October 2009 supplement; 65(4).
23. Demet ILHAN, Serdar TOKER, Volkan KILINCIO?LU, Erim GÜLCAN. Assessment of the Boston Questionnaire in Diagnosis of Idiopathic Carpal Tunnel Syndrome: Comparing Scores with Clinical and Neuro physiological Findings. Düzce T?p Fakültesi Dergisi. 2008; 3: 4-9.
24. Tay L B, Urkude R, Verma K K. Original Article- Clinical Profile, Electrodiagnosis and outcome in patients with carpal tunnel syndrome: A Singapore perspective. Singapore Med J. 2006; 47(12): 1050-52.
25. Isam Atroshi, Christina Gummesson, Ragnar Johnsson, Ewald Ornstein, Jonas Ranstam, Ingmar Rose´n. Prevalence of Carpal Tunnel Syndrome in a General Population. JAMA. 1999; 282(2): 153- 158.
26. Joao Aris Kouyoumdjian, Maria Da Penha Ananias Morita, Paulo Ricardo Fernando Rocha, Rafael Carlos Miranda, Gustavo Maciel Gouveia. Body Mass Index and Carpal Tunnel Syndrome. Arq. NeuroPsiquiatr. 2000 June; 58(2A): 252-256.
27. Murthy JM, Meena AK. Carpal Tunnel Syndrome - Electrodiagnostic aspects of fifty seven symptomatic hands. Neurol India. 1999; 47: 272-5.
28. Daniel L. Menkes, Daniel C. Hood, and Anneke C. Bush. Inversion of the F-waves in median neuropathy at the wrist (Carpal Tunnel Syndrome)- An adjunctive electrodiagnostic method. Contemporary Neurology. 1997 March 18.
29. Ashraf Husain, Syed A. Omar, Syed S. Habib, Abdul- Majeed Al-Drees, Durdana Hammad. F-Ratio, A surrogate marker of carpal tunnel syndrome- Original Article. Neurosciences (Riyadh). 2009 Jan;14(1):19-24.
30. Mohammad YAZDCHI , Reza KHANDAGHI , Mohammad Ali ARAMI. Evaluation of F-Wave in Carpal Tunnel Syndrome (CTS) and Its Prognostic Value. Journal of Neurological Sciences (Turkish) 2005, Volume 22, Number 1, Page(s) 015-020
31. www.medceu.com/index/index.php?pag… 5/15/2011 Welcome to Medceu Carpal Tunnel Syndrome
32. Kalita J, Misra U. K., Clinical Neurophysiology, Nerve Conduction, Electromyography, Evoked Potentials, Churchill Livingstone Pvt. Ltd.
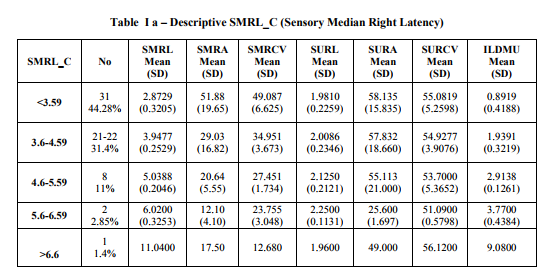
SMRL – Sensory Median Right Latency,
SMRA – Sensory Median Right Amplitude
SMRCV – Sensory Median Right Conduction Velocity SURL – Sensory Ulnar Right Latency,
SURA – Sensory Ulnar Right Amplitude
SURCV – Sensory Ulnar Right Conduction Velocity
ILDMU – Inter Latency Difference Median and Ulnar
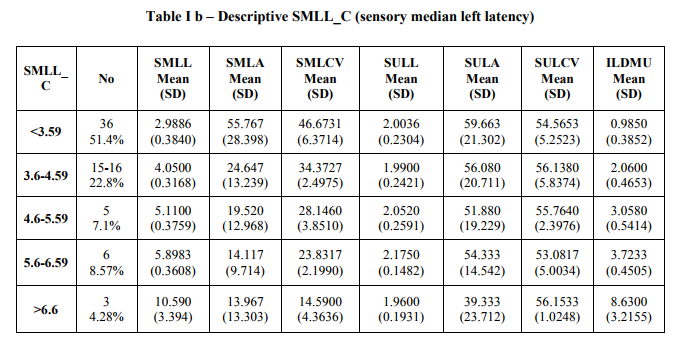
SMLL – Sensory Median Left Latency,
SMLA – Sensory Median Left Amplitude
SMLCV – Sensory Median Left Conduction Velocity
SULL – Sensory Ulnar Left Latency,
SULA – Sensory Ulnar Left Amplitude
SULCV – Sensory Ulnar Left Conduction Velocity
ILDMU – Inter Latency Difference Median and Ulnar

|






 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License