IJCRR - 8(18), September, 2016
Pages: 16-20
Date of Publication: 21-Sep-2016
Print Article
Download XML Download PDF
CHANGE OF PROTEIN CONTENT IN CEREBRO-SPINAL FLUID(CSF) WITH THE DIFFERENT TYPES OF MENINGITIS
Author: Srabonti Saha, J. D. Sharma, Mahmood A. Chowdrury, Mohammad Alauddin
Category: Healthcare
Abstract:Aim: In our study we observed that changes in the findings of CSF differs and increase in the protein content of the CSF in particular varies with the types of meningitis. The study was aimed at finding the relationship of the range of elevation of protein with different types of meningitis.
Methodology: Total 40 subjects were included in this study. The subjects were selected from the patients admitted in the Pediatric in-patient department of the Chattagram Ma-Shishu O General Hospital Medical College, Chittagong and Bangladesh. This study was done during the period of November 2008 to June 2009. Among the cases, preceding other infections were very high e.g. Pneumonia was present in 15, Measles in 2,Tuberculosis in 5 cases and preceding Seizure disorder was present in 4 cases. Most of the patients had the features of meningism, i.e. Neck rigidity was positive in 30%, Kernig sign in 22%, and Brudziniski sign in 24% patients respectively. Pyogenic meningitis was diagnosed in 68%, viral meningitis in 12% of the patients and Tubercular meningitis was clinically diagnosed in 2 patients.
Results: The protein level was significantly increased (>80mg/dl) in 65%, moderately increased (61-80mg/dl) in 20% and mildly increased (46-60mg/dl) in 15% of the patients. Patients with Pyogenic meningitis and Tubercular meningitis had significantly increased protein level (>240mg/dl) in their CSF whereas in viral meningitis the CSF protein level is highly variable and in between 62-178.3 mg/dl. Furthermore, lymphocyte and neutrophils were also detected in the CSF of 5 (12.5%) and 34 (85%) of the patients respectively. In pyogenic meningitis, the Neutrophil count was very high compared to that in viral meningitis - the finding which helps in disease management.
Conclusion: The study demonstrates that protein level in CSF might be a potential tool for detecting and differentiating different types of meningitis more precisely.
Keywords: Protein, Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF), Meningitis
Full Text:
INTRODUCTION
Meningitis is a common disease of the central nervous system (CNS) resulting from inflammation of the meanings (1) The inflammation is mainly caused by infection with viruses, bacteria or other microorganisms. (2) Meningitis can be life-threatening because of the inflammation’s proximity to the brain and spinal cord; therefore the condition is classified as a medical emergency. (3) Bacterial cell wall components, such as the lipopolysaccharide (LPS) molecules of gramnegative bacteria and teichoic acid and peptidoglycans of S. pneumoniae, induce meningeal inflammation by stimulating the production of inflammatory cytokines and chemokines by microglia, astrocytes, monocytes, micro vascular endothelial cells, and CSF leukocytes. This cytokine response is quickly followed by an increase in CSF protein concentration and leukocytosis. (4) The classic CSF abnormalities in bacterial meningitis are: (1) Polymorphonuclear(PMN) leukocytosis (>100 cells/L in 90%), (2) Decreased glucose concentration (45 mg/dl) in 90%) and (4) Increased opening pressure (>180 mmH2 O in 90%).Suspicion of viral meningitis is based on the clinical presentation and presence of certain CSF findings. Presence of less than 500 mononuclear cells/ mm3 of CSF (pleocytosis) is characteristic.(5) CSF pressure may be elevated, whereas the glucose level is characteristically normal or only modestly decreased and CSF protein level usually is elevated (50-100 mg/dl). PCR screening of CSF has become an important diagnostic tool and can help in the isolation of several viruses (6). The diagnosis of tuberculous meningoencephalitis (TBM) can be difficult and may be based only on clinical and preliminary cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) findings without definitive microbiological confirmation.(7)Characteristic CSF findings of TBM include the following: (1)Lymphocytic-predominant pleocytosis,(2) Elevated protein levels, typically between 100 and 500 mg/ dl,(3)Low glucose, usually less than 45 mg/dl.(8)Despite culture is time consuming and with variable sensitivity(40 – 80%), it should be performed to determine drug susceptibility because isoniazid(INH) resistance is associated with twofold increase in mortality.(9)Neuroimaging like Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) showing basal meningeal enhancement, hydrocephalus, hypo densities due to cerebral infarcts, cerebral edema and nodular enhancing aids to the diagnosis of TBM. (7).
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Patient selection
The study was conducted in the Department of Pediatrics and Pathology and Microbiology and Biochemistry laboratory of ChattagramMaa-Shishu-O-General Hospital, Agrabad, Chittagong, during the period of November 2008 to June 2009. Total 40 subjects presenting with the complaints of fever and features suggestive of meningitis were included in this study without any specific predilection for race, religion and socioeconomic status. In all cases, the suspected meningitis subjects were between 0 and 12 years old. The study subjects were subdivided into four groups including 27subjects with pyogenic meningitis, 5 subjects with viral meningitis, 2 Subjects with tubercular meningitis and 6 subjects were normal. The observations were recorded with relevant information of demographic and socio-economic data including anthropometric data, birth history, immunization history, past medical history and clinical information.
CSF collection
CSF was collected from suspected patients by lumber puncture, a process that done usually in the space between 3rd and 4th lumber vertebra. The procedure was done with a sterile needle and collected the fluids into three sterile vials. First one for biochemical, second one for cytological and third one for microbiological examinations. In each vial 10 ml samples were collected and sent to laboratory after proper labeling.
Estimation of protein in CSF
The quantity of protein in cerebrospinal fluid was estimated by automated clinical chemistry analyzers (Humalyzer 2000, Germany, Ultrasensitive protein). In short, 20 µl of the reagent (Pyrogallol-red-molybdate) complexes were mixed with 20 µl of CSF supernatant and incubated at room temperature for 10 minutes. The binding of pyrogallol-red-molybdate to the proteins in the CSF causes a shift of the absorbance peak to 600nm. The increase of absorbance at 580 nm is directly proportional to the protein concentration. (10)(11)(12)(13) and (14).
Microbiological study
5µl of CSF was placed on agar plate and incubated at 37°C for overnight. Depending on the development of colonies and colony morphologies, the presence and absence of organism was detected.
Cytological study of CSF
Cell counts were done by spreading a drop of CSF on a microscope slide. The slide was stained with a Giemsa stain and examined under a microscope at 100X. The neutrophils were detected with their granules and polymorphic nucleus. On the other hand granules and polymorphic nucleus are not present in lymphocytes. Lymphocytes were detected with their single nucleus.
RESULTS
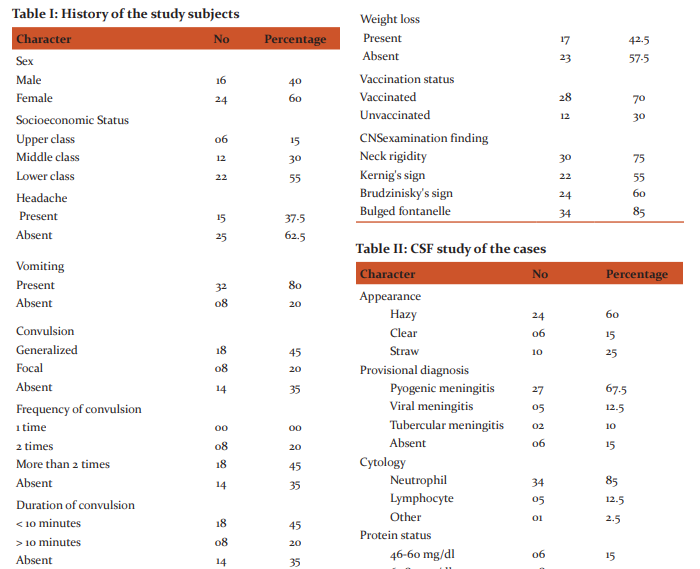
The risk factors and side effects were determined by different parameters such as socio-economic condition of both rural and urban areas. Family history, birth history, immunization history, developmental history including the time of the appearance of social smile, neck control, sitting, standing, walking and speech were also undertaken. Anthropometric variables like height, weight, age, sex, pattern of feeding, occipitofrontal circumference were also studied. Among the 40 patients, 40% were male and 60% were female (Table-I). In terms of socio-economic status, the distribution of the patients were upper class (15%), middle class (30%) and lower class (55%), indicating that the disease can affect people regardless of their socioeconomic status with lower class people being more susceptible(Table-I). Moreover, most of the patients exhibited the sign and symptoms of meningitis i.e. vomiting (80%), headache (15%), convulsion (65%) and as well as those of microbial infection (Table-I). It was also observed that meningitis occurred even in vaccinated children (Table-I). Although meningitis can be caused by many causes, in this study only three types were found predominant i.e. Bacterial, Viral and Tubercular. Among them bacterial cases were 68%, viral 12% and tubercular cases were 5% respectively (Table-I).
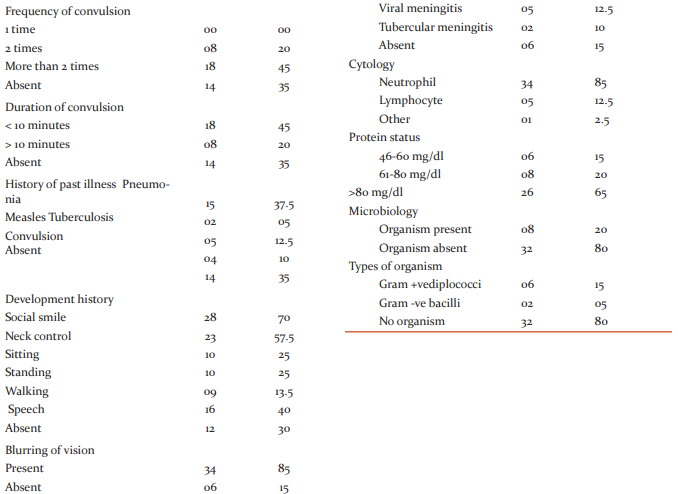
The microbiological studies further revealed the presence of Diplococci and Gram -ve bacilli in 6 (15%) and 2 (5%) patients respectively, while no microbial pathogens were detected in the rest 32 patients (Table-II). But the changes in their CSF were suggestive of bacterial meningitis. In thirtytwo patients no organism was isolated (culture -ve bacterial meningitis). On the other hand, the present study revealed a previous history of Pneumonia in 15, measles in 2, convulsion in 4 and Tuberculosis in 5 cases (Table-II), visual problem especially blurring of vision in 34 cases and a history of weight loss in17 cases (Table-II). This study also documents two cases of TBM admitted to the hospital over the 8-month period and compare the clinical picture with that of meningitis of pyogenic origin. Most of the patients of both bacterial and viral meningitis shared the common features of meningism; Neck rigidity in 30%, Kernig’s sign in 22%, Brudziniski sign in 24% cases. Bulged Fontanels was present in 85% patients (Table-II). In our study, we observed high lymphocyte count in 5 patients, high neutrophil count in 34 patients (Table-II). In this study it was found that protein content in CSF was significantly increased in 65% while moderately and mildly increased in 20% and 15% of the patients respectively (Table-II). More specifically, in Streptococcus-mediated meningitis, the protein level was 243mg/dl while that in culture negative bacterial meningitis and in viral meningitis were 223mg/dl and 112.12mg/dl respectively (Table-II). In two cases of tubercular meningitis the protein contents were 319.5 and 312.6 mg/dl.
DISCUSSION
In order to differentiate between different types of meningitis analysis of the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) changes was done in patients admitted in ChattagramMaa-Shishu-OGeneral Hospital, Chittagong from November 2008-June 2009, with the signs and symptoms of meningitis (headache, nausea, vomiting, fever, restlessness, irritability, neck pain, poor feeding, neck rigidity, Kernig’s sign, Brudzinski’s sign, etc.).(15) (16) the study was designed on the basis of detailed background history including previous records of infectious diseases/illness, vaccination, socioeconomic status etc. and detailed clinical, cytological and biochemical examinations of their cerebrospinal fluid. The microbiological studies further revealed the presence of Diplococci and Gram -ve bacilli in6 (15%) and 2 (5%) patients respectively, while no microbial pathogens were detected in the rest 32 patients. But the changes in their CSF were suggestive of bacterial meningitis. These observations though greatly deviated from a previous observation but also showed some similarities(17) where the authors showed that among the 86 bacterial meningitis patients, Meningococci was isolated in 36 (41.86%), S. Pneumoniae in 22 (25.58%), Staph. Aureus in 2 (2.32%), Klebsiella Pneumoniae in two (2.32%), Strept. Agalactiae in one (1.16%) and E.Coli in 1(1.16%) patient. In twenty-two (25.58%) patients no organism was isolated (culture -ve bacterial meningitis). On the other hand, the present study revealed a previous history of Pneumonia in 15, measles in 2, convulsion in 4 and Tuberculosis in 5 cases, visual problem especially blurring of vision in 34 cases and a history of weight loss in 17 cases, suggesting the risk factors of meningitis. Therefore, observations in this study regarding the absence of any microbial pathogens in their CSF could be due to the fact that from the beginning of the disease the patients were treated with antibiotics. This study also documents two cases of TBM admitted to the hospital over the 8-month period and compare the clinical picture with that of meningitis of pyogenic origin. At present, the diagnosis of TBM is difficult in the absence of microbial isolation, as the clinical presentation is often deceptive and the response to treatment is not as satisfactory as in pyogenic meningitis. (18)(19) and (20)The key to diagnosis of infections is the isolation of the causative microorganism from the tissues involved. In case of TBM, TB bacilli can be isolated directly by Ziehl-Neelsen stain or culture from CSF. To extract more information regarding the disease initiation followed by pathophysiological lesions after the onset of the disease could benefit the disease management process At present differentiating the diagnosis of viral and bacterial meningitis is very difficult. Most of the patients of both bacterial and viral meningitis shared the common features of meningism; Neck rigidity in 30%, Kernig’s sign in 22%, Brudziniski sign in 24% cases. Bulged Fontanels was present in 85% patients, which is clearly in line with a previous study. (21) It is well reported that all forms of pyogenic meningitis are frequently associated with neutrophilic leucocytosis and a raised ESR (erythrocyte sedimentation rate) and viral meningitis is associated with high lymphocyte count though in a few cases lymphocyte count were found normal. In our study, we observed high lymphocyte count in 5 patients, high neutrophil count in 35 patients which are in line with the results of Negrini et.al (22). They showed that the CSF leukocyte count was higher with predominant polymorphs (95%) in bacterial than viral (7%) cases. Most of the patients with aseptic meningitis had a PMN predominance where neutrophils accounted for >50% of CSF leukocytes.(22). In this study it was found that protein content in CSF was significantly increased in 65% while moderately and mildly increased in 20% and 15% of the patients respectively. More specifically, in Streptococcus-mediated meningitis, the pro-tein level was 243mg/dl while that in culture negative bacterial meningitis and in viral meningitis were 223mg/dl and 112.12mg/dl respectively. A similar observation has also been reported by Zeni et.al. (23) (24) and (25). These observations thus clearly indicate that protein content in the CSF could be good a parameter for differentiating the bacterial and viral meningitis.
CONCLUSION
Meningitis is highly prevalent in third world country especially in Bangladesh. Accurate and rapid diagnosis of acute bacterial meningitis (ABM) is essential for favorable outcome, especially in infants and children. Although immediate confirmation of ABM is diagnosed by the examination of CSF but sometimes it is insufficient to distinguish between ABM and acute viral meningitis (AVM). Current guidelines recommend starting antibiotics whenever a bacterial etiology cannot firmly be ruled out. However, the cost of antibiotic therapy and its attendant hospitalization, as well as its potential side effects, have raised concern about unnecessary administration of antibiotics in patients with AVM. It was observed that the identification of the causative agents of meningitis, medical history of the patients, microbiological/ cytological and detailed biochemical investigations of the CSF of patients suffering from meningitis could aid more accurate discrimination of different meningitis in children. Especially, the protein status of the CSF can guide in identification of the types of the disease to facilitate the disease management more precisely avoiding unnecessary administration of antibiotics.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENT
Authors acknowledge the immense help received from the scholars whose articles are cited and included in references of this manuscript. The authors are also grateful to authors / editors / publishers of all those articles, journals and books from where the literature for this article has been reviewed and discussed.
References:
1. Sáez-Llorens X, Mc Cracken GH. Bacterial meningitis in children. Lancet 2003; 361 (9375): 2139–48.
2. Ginsberg L. Difficult and recurrent meningitis.J NeurolNeurosu rgPsychiatry.2004;75(suppl1):i16–21.
3. Tunkel AR, Hartman BJ, Kaplan SL, Kaufman BA, Roos KL,Scheld MW, et al. Practice guidelines for the management of bacterial meningitis. Clinical Infectious Diseases 1994; 39 (9):1267–84.
4. Kasper DL. Braunwald E. Fauci AS. Hauser SL. Longo DL, Jameson JL. Harrison’s Principles of Internal medicine. 16th ed. New York:McGraw-Hill Professional;2004.
5. Jeffery KJ, Read SJ, Peto TE, Mayon-White RT, Bangham CR. Diagnosis of viral infections of the central nervous system. Lancet 1997;349:313-17.
6. Kumar R, Singh SN,Kohli N. A diagnostic rule for tuberculous meningitis. Arch Dis Child 1999; 81(3): 221 – 24.
7. Thwaites, GE. Chau TTH. Stepniewska K, Chuong LV, Sinh DX, White NJ. Diagnosis of adult tuberculous meningitis by use of clinical and laboratory features. Lancet 2002 ; 360(9342):1287- 92.
8. Micheal DI. A Clinician guide to Tuberculosis.1sted. New York: Lippincott William and Wilkins publisher; 2000.
9. Vinnard, C, Winston CA, Wileyto EP, Macgregor RR, BisonGP. Isoniazid resistance and death in patients with tuberculous meningitis: retrospective cohort study. BMJ 2010; 341: 4451.
10. Bablok W, Passing H, Bender R, Schneider B. A general regression procedure for method transformation.J ClinChemClinBichem 1988; 26:783-90. 11. Iwata I, Nishikaze O. ClinBiochem 1979; 25(7): 1317-19.
12. Koumantakis G. Fluorescein Interference with Urinary Creatinine and Protein Measurements.ClinChem 1991; 37(10):1799.
13. Luxton R, Patel P, Keir G, Thompson E.A micro-method for measuring total protein in cerebrospinal fluid by using benzethonium chloride in microtiter plate wells. ClinChem 1989; 35(8): 1731-34.
14. Passing H, Bablok W. A new biometrical procedure for testing the equality of measurements from two different analytical methods.J Chin Chem. ClinBiochem 1983;21:709-20.
15. Thomas KE, Hasbun R, Jekel J. The diagnostic accuracy ofKerning’s sign,Brudzkinski’s sign and nuchal rigidity in adults with suspected meningitis.Clin Infect Dis 2002;35:46-52.
16. Schuchat A, Robinson K, Wenger JD, Harrison LH, Farley M, Reingold AL. Bacterial meningitis in the United States in 1995. N Engl J Med 1997; 337:970–76.
17. Hussein AS, Shafran SD. Acute bacterial meningitis in adults: A 12-year review. Medicine (Baltimore) 2000;79:360-68.
18. Satya SS. In: Textbook of pulmonary and extra pulmonary tuberculosis.2nd ed. New Delhi: 1995 pp. 206–208, 221–230.
19. Daniel TM. New approaches to the rapid diagnosis of tuberculous meningitis.J Infect Dis 1987; 155(4):599–602.
20. Anoymous. The treatment of tuberculous meningitis. Tubercle 1989 ; 70: 679- 82.
21. Abro AH, Abdou AS, Ali H, Ustadi AM, Hasab AAH. Cerebrospinal fluid analysis acute bacterial verses viral meningitis. Pak J Med Sci 2008. 24(5):645-50.
22. Negrini B, Kelleher KJ, Wald ER.Cerebrospinal fluid findings in aseptic versus bacterial meningitis. Pediatrics 2000; 105:316-19.
23. Zeni F. Villon A. Assicot M. Procalcitonin serum concentrations and severity of sepsis. Clin Intensive Care 1994; 5(5):2.
24. Jaeger F, Leroy J, Duchêne F, Baty V, Baillet S, Estavoyer JM, et al. Validation of a diagnosis model for differentiating bacterial from viral meningitis in infants and children under 3.5 years of age. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis 2000; 19:418–21.
25. Departments of Pathology, Primary Children’s Medical Center and University of Utah College of Medicine, Salt Lake City, USA ; 1991.
|






 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License