IJCRR - 9(14), July, 2017
Pages: 07-13
Date of Publication: 28-Jul-2017
Print Article
Download XML Download PDF
Growth Promoting and Probiotic Potential of the Endophytic Bacterium Rhodococcus globerulus colonizing the Medicinal Plant Plectranthus amboinicus (Lour.) Spreng
Author: R.M. Murugappan, S. Benazir begum, C. Usha, S. Lok kirubahar, M. Karthikeyan
Category: General Sciences
Abstract:Objectives: It was intended to isolate endophytic bacteria from Plectranthus amboinicus leaves to elucidate the plant growth promotion potential.
Methodology: Phytochemical constituents of Plectranthus amboinicus leaves were analyzed following standard procedures. Endophytic bacteria were isolated in nitrogen limited medium after surface sterilization process as described by Coombs & Franco (2003) and identified by biochemical, molecular analyses. Plant growth promotion and quorum quenching potential of the isolate was determined as described by Patel et al. (2011). Probiotic potential of the isolates was elucidated following a series of assays (Ahire et al. 2011).
Results: Phytochemical investigation of the leaves revealed the presence of alkaloids, flavonoids and terpenoids. An endophytic bacterium with probiotic properties was isolated and identified as Rhodococcus globerulus. Plant growth promotion (PGP) traits such as phosphate solubilization, IAA production and ACC deaminase activity of R. globerulus was estimated to be 37.3 \?g ml-1, 36.7 \?g ml-1 and 35.00 \? 1.2 nmol \a-ketobutyrate mg-1 h-1 respectively at 60 h of incubation. The isolate was found to produce trihydroxamate siderophores with hexadentate ligands. Presence of the bacterium within the leaf tissues was confirmed by SEM imaging. R. globerulus was found to produce quorum sensing inhibitor (QSI) molecules. Endophytic isolate was also found to possess probiotic potential.
Conclusion: The results illustrate that the plant-associated microbiome serve as a repertoire of metabolic products that facilitate nutritional and defense pathway of the host plant. Probiotic properties of the endophyte confer an added advantage to the therapeutic potential of the plant P. amboinicus.
Keywords: Plant growth promotion, Plectranthus amboinicus, probiotic, quorum sensing, Rhodococcus globerulus, siderophores
DOI: 10.7324/IJCRR.2017.9143
Full Text:
Introduction
Plant tissues constitute a nutrient rich niche for metabolically versatile microorganisms called endophytes. Bacon and White [1] defined endophytes as “microbes that colonize, living, internal tissues of plants without causing any immediate, overt negative effects”. Unlike a random collection, endophytic microbes are specific and inextricably associated with the host plant [2]. Endophytes stimulate plant growth by nitrogen fixation, phosphate solubilization, iron chelation, phytohormone and 1-aminocyclopropane-1-carboxylate (ACC) deaminase enzyme synthesis and / or by the prevention of pathogen infections [3]. Endophytes are reported to attenuate microbial pathogenicity by the synthesis of quorum sensing (QS) inhibitors [4].
Due to the long co-existence, there is a possibility of horizontal gene transfer which facilitates the endophytes to synthesize bioactive compounds of plant origin [5]. For example, piperine was isolated from endophytic fungus Periconia sp. colonizing the host plant Piper longum L. [6].
Despite their innate importance, endophytic microbial community in medicinal plants remains largely uncharacterized. Plectranthus amboinicus (Lour.) Spreng (Lamiaceae) a large succulent aromatic perennial herb commonly known as Indian borage is a native species of Asia. Leaves of P. amboinicus are taken orally for the treatment of respiratory infections, digestive diseases, mumps and wounds [7]. Screening the probiotic potential of the microbes associated ensures the safety in the uptake of P. amboinicus leaves for disease prevention.
Synthetic antioxidants and antimicrobials in use are reported to possess various side effects. Therefore, the search for natural antioxidants, especially of plant origin has attracted great attention. Medicinal plants represent a potential source of antioxidants that are more effective and less toxic.
Although there is a plethora of information on the medicinal properties of P. amboinicus, knowledge on the diversity, plant growth promotion and probiotic potential of its endophytic bacteria are limited. Therefore, the present study was intended to isolate endophytic bacteria from the leaves of P. amboinicus and to assess their growth promotion activities.
Materials and methods
Screening of phytochemical constituents
Fresh and healthy leaves of Plectranthus amboinicus were collected, washed and air-dried. Dried leaves (10 gm) were powdered and extracted with 10ml of milli-Q water by boiling at 45 ?C for 30 min. The extract was filtered and concentrated in a rotary evaporator (IKA RV-10, Germany) at 45 ?C under reduced pressure. The concentrate was subjected to qualitative phytochemical analyses following standard procedures [8].
Antioxidant and antimicrobial activity
Antioxidant potential of the leaf extract was measured by DPPH (2, 2-Diphenyl-1-picrylhydrazyl) method [9]. Susceptibility of bacterial pathogens to different concentration (20, 40, 60, 80 and 100 μg/ml) of leaf extract was determined by well diffusion method. Dose-response influence of aqueous leaf extract on pathogenic strains was calculated using prism software (ver. 6.04).
Isolation and identification of endophytic bacteria
For the isolation of endophytic bacteria, P. amboinicus leaves were cut into small discs (0.5 cm dia.) using sterile cork borer. Leaf discs were surface sterilized following the five step procedure described by Tiwari et al. [10]. Surface-sterilized leaves were air dried, triturated with phosphate buffered saline, serially diluted and spread onto the nutrient agar medium free of inorganic nitrogen. The plates were incubated for 48 h at 30 ºC. The endophytic bacteria were identified by conventional biochemical characteristics following Bergey’s Manual of Systemic Bacteriology [11] as well as by 16S rRNA gene sequencing by standard procedures [12]. Phylogenetic analysis was performed using Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis software package (MEGA ver. 4.0) after multiple alignments of data by Clustal X.
Plant growth promotion (PGP) traits
Phosphate solubilization and indole acetic acid production
Phosphate solubilizing ability of the isolate was determined qualitatively and quantitatively by stannous chloride method [13] using Pikovskaya medium with 0.5 % tricalcium phosphate [Ca3 (PO4)2]. Indole acetic acid (IAA) production by the isolate on the utilization of L- tryptophan was determined using Salkowski reagent [14]. IAA production by the isolate was also confirmed by HPLC analysis.
ACC deaminase enzyme activity
ACC deaminase activity of the isolate was determined following the method of El-Tarabily [15]. Using Dworkin–Foster (DF) salts minimal medium amended with 3 mM of 1-aminocyclopropane-1-carboxylic acid (ACC) as a sole nitrogen source. ACC production was quantified by measuring the absorbance at 540 nm against a standard curve of α- ketobutyrate (Sigma, USA).
Screening of siderophore production
Siderophore production by the isolate was determined by FeCl3 test and chrome azurol sulphonate (CAS) agar plate method [16]. The amount of siderophore in the culture supernatant was quantified at different intervals by Chrome azurol sulphonate shuttle assay. Furthermore, the culture supernatant was subjected to Csaky, Arnow and Vogel’s assay to ascertain the nature of siderophore produced. Siderophore was further distinguished into mono-, di- or trihydroxamates based on the absorption maxima and electrophoretic mobility [17]. The iron-binding property of siderophore was determined by the color reaction at different pH values.
Production of HCN and ammonia
The isolate was screened for hydrogen cyanide production following the standard procedures [18]. Ammonia producing ability of the isolate was determined by the development of yellow color on the addition of Nessler’s reagent.
Screening of anti-quorum sensing activity
Anti-quorum sensing activity of endophytic bacteria against the reporter strain Chromobacterium violaceum (MTCC 2656) was determined following the procedure described by Mani et al. [19]. Mid log phase culture (18 h) of C. violaceum was inoculated in LB medium containing different concentration (25, 50, 75 and 100 μl) of endophytic bacterial culture filtrate. A control without culture filtrate was maintained. Culture tubes were incubated with shaking at 30ºC for 48 h. After incubation, 2 ml of culture was centrifuged at 8000 rpm for 10 min to precipitate the insoluble violacein and 2 ml of DMSO was added to the precipitate and vortexed (30 sec) to solubilize the violacein. The extracted violacein was quantified using a UV-vis spectrophotometer (OD585). The percentage of violacein inhibition was calculated by following the formula:
Percentage of violacein inhibition = (control OD585nm - test OD585nm / Control OD585nm) × 100.
Plant inoculation assay
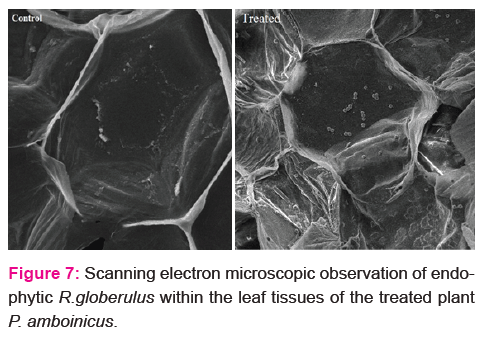
For plant inoculation assay, shoot tips (5 inch) of healthy P. amboinicus with a pair of leaf nodes were excised using a scalpel, surface sterilized with 5 % sodium hypochlorite for 3 min and rinsed repeatedly with sterilized distilled water. Surface-sterilized shoot cuttings were immersed in endophytic bacterial cell suspension (107 CFU per ml of phosphate buffer pH 7.0) for 1 h, subsequently a control was maintained by immersing in sterile water. Treated and control shoot cuttings were planted in plastic pot (10×15 cm). Five replicates were maintained. The plants were grown in a greenhouse at 37ºC with 16 h light: 8 h darkness photoperiod. The plants were watered daily with sterile deionised water. After 3 weeks, the plants were uprooted and growth parameters such as shoot and root length and number of leaves were measured. The presence of endophytes within the leaf tissues was established by scanning electron microscopic (SEM) imaging.
Screening for probiotic properties
Acid and bile salt tolerance
A probiotic microorganism must overcome physical and chemical barriers in the gastrointestinal tract. Therefore, in this study acid tolerance property of the isolate was determined following the standard procedure [20]. The isolate was grown in nutrient broth for 24 h at 30ºC. Cells were harvested and re-suspended in 1 ml of sterile phosphate buffered saline (PBS) at different pH for various time intervals (0, 60, 120 and 180 min) and transferred to nutrient broth. The growth was measured at A620nm after 24 h. For bile salt tolerance, one ml (3×107 cells ml-1) of the isolate was inoculated on a nutrient broth supplemented with different concentration of oxgall (w/v) and the growth of the isolate was measured (A620nm) at different time intervals. Auto-aggregation was calculated by measuring the absorbance (660 nm) of the bacterial suspension in PBS (pH7.3) at different time intervals as described by Ahire et al. [21]. Antibiotic susceptibility and hemolytic ability of the isolate was determined following standard procedure.
Results
Phytochemical constituents
Qualitative determination of phytochemical constituents in the leaves of Plectranthus amboinicus revealed the presence of tannins, flavanoids, saponins, alkaloids, cardiac glycosides and terpenoids (Table 1). Absence of steroids and acidic compounds in the leaf extract are notable.
Antioxidant activity
The leaf extract of P. amboinicus showed a concentration dependent free radical scavenging activity with an EC50 value of 65.26 μg/ml. Maximum radical scavenging activity (61.06 %) was observed at 80 μg/ml. However, scavenging activity of ascorbic acid, a known antioxidant, which is used as a positive control in this study, was greater than that of leaf extract.
Antimicrobial activity
Aqueous leaf extract of P. amboinicus was found to inhibit the growth of the pathogenic microorganism viz., S.aureus, E.coli, M.luteus, P.aeruginosa, B.subtilis and S.typhi. Dose response curves illustrated that the pathogen inhibition was linearly associated with the concentration of the leaf extract (Fig.1) Inhibitory efficiency was found to be more effective against E. coli and M. luteus.
Isolation and identification of endophytic bacteria
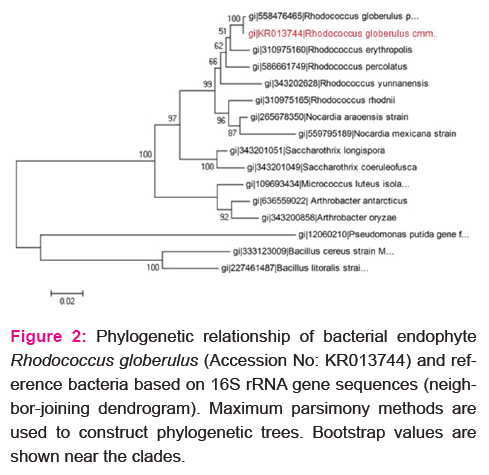
Two phenotypically different endophytic bacterial strains were isolated from the leaves of P.amboinicus. The isolates were identified as Pseudomonas sp. and Rhodococcus sp. Of the two, Rhodococcus sp. was subjected to further analyses based on its non-haemolytic and catalase positive response. Based on 16 s rRNA gene sequencing (accession number KR013744) and phylogenetic analysis (Fig.2) the isolate was confirmed as Rhodococcus globerulus.
In vitro screening of Rhodococcus globerulus for PGP traits
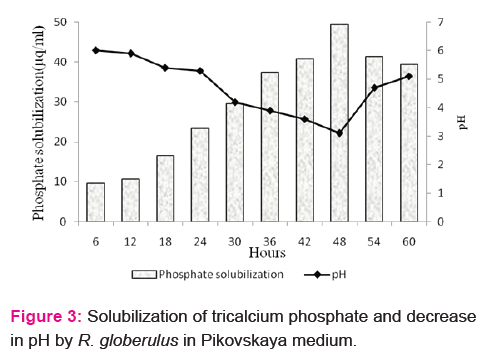
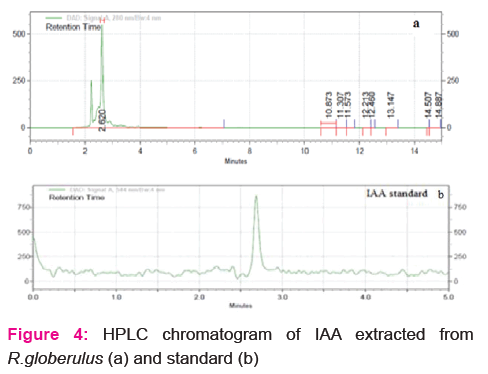
Phosphate solubilization and indole acetic acid production by the isolate was determined qualitatively and quantitatively. Appearance of halo zones on Pikovskaya agar indicates phosphate solubilizing ability of the isolate (results not shown). The level of soluble phosphate in the medium was found to be 37.33μgml-1 at 60 h of incubation. In the present study, the isolate was found to solubilize the inorganic phosphate with the concomitant decline in medium pH (Fig. 3). Biosynthesis of 3-indole acetic acid by the isolate was estimated to be 6.33, 14.67, 21.33, 33.67, 36.69 and 28.67 μgml-1 at 12, 24, 36, 48, 60 and 72 h of incubation, respectively. HPLC chromatograms of the IAA produced by the isolate was compared with the standard (retention time 2.62) and presented in Fig. 4. Growth of the isolate in DF medium supplemented with ACC confirms ACC deaminase enzyme activity. Quantitative determination revealed high ACC deaminase activity (35.00 ±1.2 nmol α-ketobutyrate mg-1 h-1) by the isolate (Table 2).
The positive results with FeCl3 test, CAS assay and development of orange halos in CAS agar plate confirm siderophore production by the isolate (results not shown). Maximum siderophore production was observed only after 60 h of incubation and it was found to be 42.23 ± 0.67 % units. Absorbance maximum at 404 nm indicates hydroxamate nature of the siderophore produced and it was further confirmed by positive Csaky test. A narrow shift in λ-max (up to 8 nm) with different pH and electrophoretic mobility results indicate trihydroxamate nature of the siderophore (Table 3). The isolate exhibited other plant growth promotion traits such as HCN and ammonia production.
Anti-quorum sensing activity
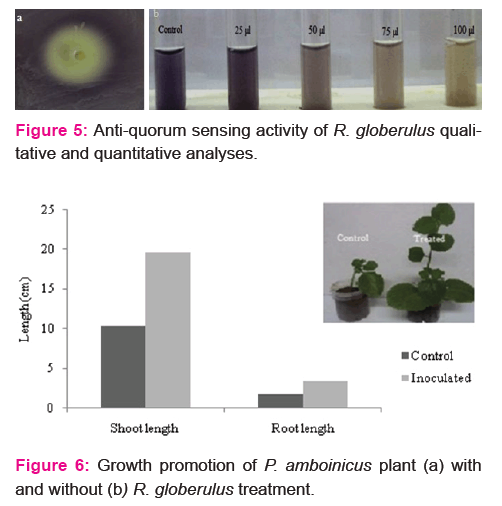
In this study, quorum quenching ability of the R. globerulus was confirmed by the appearance of opaque zone on the periphery of reporter strain C. violaceum colonies (Fig. 5a). Violacein production was found to be decreased with increasing concentration of R. globerulus (Fig. 5b) culture filtrate.
Plant inoculation studies
Biopriming of P. amboinicus shoot with endophytic bacteria R. globerulus enhanced plant growth (Fig. 6). SEM imaging confirmed the colonization of isolate within the leaf tissues (Fig. 7).
Probiotic properties
R. globerulus was found to be viable at high acidic conditions (pH 2). Percent survival of R. globerulus after 3h of exposure to pH 2 and pH 4 was found to be 46.83 and 87.65 respectively (results not shown). In addition to acid tolerance, the isolate was able to survive at 2-4% concentration of bile salt. R. globerulus was found to be susceptible to tetracyclin, kanamycin, gentamycin and erythromycin but resistant to penicillin and rifampicin.
Discussion
Phytochemical screening ascertains the leaves of P. amboinicus are a rich source of tannins, flavanoids, saponins, alkaloids, cardiac glycosides and terpenoids (Table 1). Results on the qualitative analyses of phytochemicals are consistent with the available literature. Tannins and terpenoids are known to possess antimicrobial, anti-inflammatory and immunomodulatory properties [22]. Absence of steroid reveals the advantage of using P. amboinicus leaves in disease treatment. Antioxidant potential of the leaf extract might be due to the presence of phenolic compounds. The result obtained on free radical scavenging activity falls in line with the findings of Yadav et al. [23].
P. amboinicus leaf extract found to inhibit the growth of bacterial pathogens (Fig. 1). Neuwinger [24] reported the efficiency of Plectranthus sp. leaf extract in the prevention of microbial infections. Screening of surface sterilized leaf tissue of P. amboinicus revealed the presence of Pseudomonas sp. and Rhodococcus sp. Occurrence of Rhodococcus sp. within the leaf tissue of medicinal plants was reported in earlier studies [25]. It is still not clear whether plants benefit from an endophyte or if the advantage is higher for the bacteria to become endophyte. However it is evident from the results, the benefits conferred by endophytes are more conspicuous by growth promotion.
Growth promotion traits like indole acetic acid production, ACC deaminase, siderophore, HCN, ammonia production and phosphate solubilization confers the benefit of endophytic colonization of R. globerulus within the tissues of P.amboinicus. Solubilization of insoluble phosphates illustrate that the isolate can be deployed as a bioinoculants to minimize the fertilizer application. The role of ACC deaminase in decreasing the ethylene levels by the enzymatic hydrolysis of ACC into α-ketobutyric acid and ammonia was reported as one of the major traits of endophytes in promoting root and plant growth. Penrose and Glick [26] reported that greater or equal to 20 nmol α-ketobutyrate mg-1 h-1 ACC production by the isolate is sufficient to promote plant growth.
Siderophore production in endophytic bacteria illustrates iron sequestration mediated pathogen inhibition and plant growth promotion. Siderophore produced by R. globerulus was found to be of trihydroxamate with hexadentate nature.
This study is the first to report the QSI potential of endophytic isolate R. globerulus. Based on the results it can be postulated that secondary metabolites in the cell free lysate of endophytic bacteria degrade HHL and thereby prevents the expression of violacein production. Unfortunately, most of the QSIs available are toxic and unsuitable for human use. Therefore, quorum sensing blockers of probiotic bacteria is an intriguing target for future antimicrobial chemotherapy.
Drenching of P. amboinicus shoot tips with R. globerulus enhanced the number of leaves, shoot and root length with that of untreated plants. Increased herbage yield of O. sanctum on seed treatment with endophytic bacteria in field trials was reported earlier [27]. In the present study, colonization of endophytic bacterium within the leaf tissue of treated plant was confirmed by SEM imaging.
The leaves of P.amboinicus are taken orally to cure different respiratory and intestinal ailments. So, it is inevitable to screen the probiotic potential of endophytic bacteria that resides within the leaves of the plant. Tolerance to different concentration of bile salt and viability at high acidic conditions (pH 2) reflects the probiotic nature of R. globerulus.
Conclusions
Phytochemical constituents of P. amboinicus attribute for its nutraceutical and pharmacological properties. Nonetheless, our research findings confirm that the plant-associated microbiome is a repertoire of metabolic products that contribute for the nutritional and defense pathway of the host plant. QS inhibition by R. globerulus provides a scientific basis for the prevention of pathogen infection in host plant. Probiotic properties of the endophyte confer an added advantage to the therapeutic value of the plant P. amboinicus. Phytochemical constituents and probiotic potential of the endophytic microbiome is a proof of principle for the safety and efficiency of the raw intake of P. amboinicus in ailment prevention. Screening of culture-independent endophytic microbiota of P. amboinicus using high-throughput techniques are in progress.
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful to Thiagarajar College management. Assistance extended by Gandhigram Rural Institute, Gandhigram for SEM analysis is greatly acknowledged. Authors acknowledge the immense help received from the scholars whose articles are cited and included in references of this manuscript. The authors are also grateful to authors/editors/publishers of all those articles, journals and books from where the literature for this article has been reviewed and discussed.
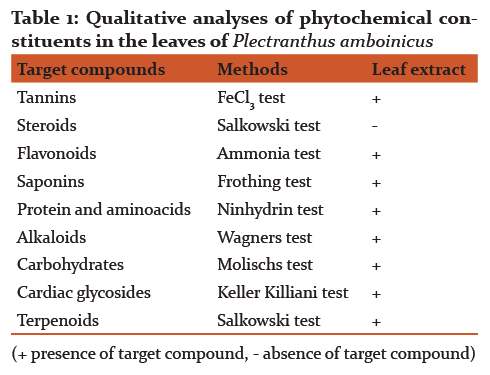
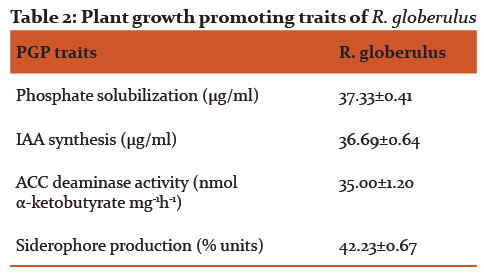
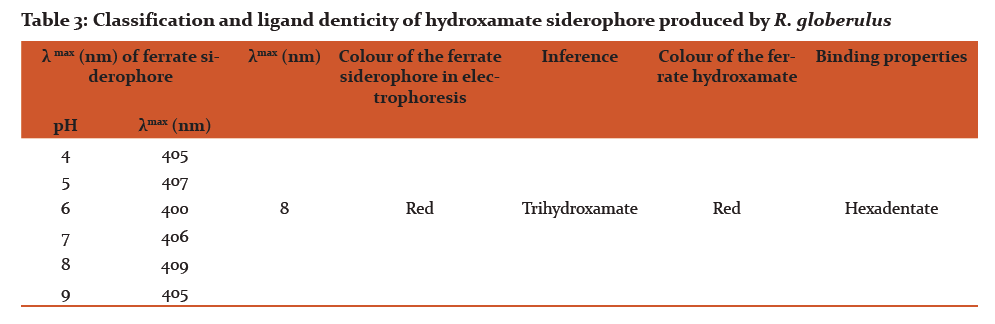
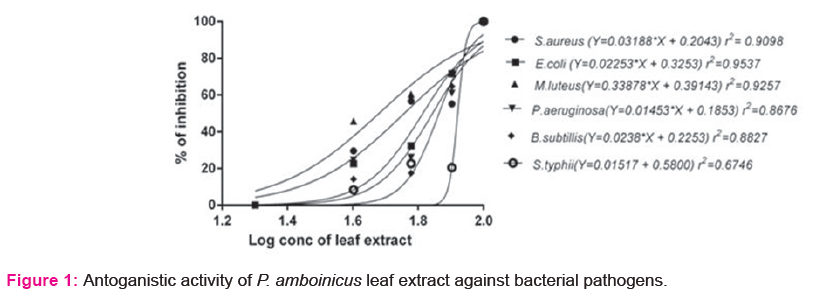
Fig. 2 Phylogenetic relationship of bacterial endophyte Rhodococcus globerulus (Accession No: KR013744) and reference bacteria based on 16S rRNA gene sequences (neighbor-joining dendrogram). Maximum parsimony methods are used to construct phylogenetic trees. Bootstrap values are shown near the clades.
References:
- Bacon CW, White JF. Microbial endophytes. Marcel Dekker Inc., New York, USA. 2000: 487.
|
- Gaiero JR, Mccall CA, Thompson KA, Day NJ, Best AS, Dunfield KE. Inside the root microbiome: Bacterial root endophytes and plant growth promotion. Am J Bot. 2013; 100: 1738-1750.
|
- Richardson AE, Barea JM, McNeill AM, Prigent-Combaret C. Acquisition of phosphorus and nitrogen in the rhizosphere and plant growth promotion by microorganisms. Plant Soil. 2009; 321: 305–339.
|
- Rajesh PS, Rai RV. Hydrolytic enzymes and quorum sensing inhibitors from endophytic fungi of Ventilago madraspatana Gaertn. Biocat Agri Biotechnol. 2013; 2: 120-124.
|
- Alvin A, Miller KI, Neilan BA. Exploring the potential of endophytes from medicinal plants as sources of antimycobacterial compounds. Microbiol Res. 2014; 169: 483–495.
|
- Verma VC, Lobkovsky E, Gange AC, Singh SK, Prakash S. Piperine production by endophytic Periconia sp. isolated from Piper longum L. J Antibiot. 2011; 64: 427–431.
|
- Bhatt P, Negi PS. Antioxidant and antibacterial activities in the leaf extracts of Indian borage Plectranthus amboinicus. Food Nut Sci. 2012; 3: 146-152.
|
- Manjamalai A, Sardar R, Singh S, Guruvayoorappan C, Grace VMB. Analysis of phytochemical constituents and antimicrobial activity of some medicinal plants in Tamil Nadu, India. Global J Biotechnol Biochem. 2010; 5(2): 120-128.
|
- Ferreira ICFR, Aires E, Barreira JCM, Estevinho LM. Antioxidant activity of Portuguese honey samples: different contributions of the entire honey and phenolic extract. Food Chem. 2009; 114: 1438-1443.
|
- Tiwari R, Kalra A, Darokar MP, Chandra M, Aggarwal N, Singh AK, Khanuja SPS. Endophytic bacteria from Ocimum sanctum and their yield enhancing capabilities. Curr Microbiol. 2010; 60: 167– 171.
|
- Brenner DJ, Krieg NR, Staley JT. The Proteobacteria, In: George GM, editor. Bergey’s manual of systematic bacteriology, vol 2. New York: Springer pub. 2005; 491–545.
|
- Indananda C, Matsumoto A, Inahashi Y, Takahashi Y, Duangmal K, Thamchaipenet A. Actinophytocola oryzae gen. nov., sp. nov., isolated from the roots of Thai glutinous rice plants, a new member of the family Pseudonocardiaceae. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol. 2010; 60: 1141–1146.
|
- Gaur AC. Physiological functions of phosphate solubilizing microorganisms, In: Gaur AC, editor. Phosphate solubilizing microorganisms as biofertilizers. New Delhi: Omega Scientific. 1990; 16–72.
|
- Patten CL, Glick BR. Role of Pseudomonas putida indole acetic acid in development of the host plant root system. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2002; 68: 3795–3801.
|
- El-Tarabily KA. Promotion of tomato (Lycopersicon esculentum Mill.) plant growth by rhizosphere competent 1-aminocyclopropane-1-carboxylic acid deaminase producing streptomycete actinomycetes. Plant Soil. 2008; 308: 161–174.
|
- Schwyn B, Neilands JB. Universal chemical assay for the detection and determination of siderophores. Anal Biochem. 1987; 160: 47–56.
|
- Jalal MAF, Helm D. Isolation and spectroscopic identification of fungal siderophores. In: Winklemann G, editor. Handbook of microbial iron chelates. USA. CRC Press, 1990; 235–269.
|
- Bakker AW, Schippers B. Microbial cyanide production in the rhizosphere in relation to potato yield reduction and Pseudomonas sp. mediated plant growth stimulation. Soil Biol Biochem. 1987; 19: 451–457.
|
- Mani A, Hameed SS, Ramalingam S, Narayanan M. Assessment of quorum quenching activity of Bacillus species against Pseudomonas aeruginosa MTCC 2297. Global J Pharmacol. 2012; 6 (2): 118-125.
|
- Erkkila S, Petaja E. Screening of commercial meat starter cultures at low pH and in the presence of bile salts for potential probiotic use. Meat Sci. 2000; 55: 297–300.
|
- Ahire JJ, Patil KP, Chaudari BL, Chincholkar SB. A potential probiotic culture ST2 produces siderophore 2, 3-dihydroxybenzoylserine under intestinal conditions. Food Chem. 2011; 127: 387–393.
|
- Okwu DE, Josiah C. Evaluation of the chemical composition of two Nigerian medicinal plants. Afr J Biotech. 2006; 5: 357-361
|
- Yadav A, Bhardwaj R, Sharma RA. Free radical scavenging potential of the Solanum surattense: An important medicinal plant. Int J Pharm Pharm Sci. 2014; 6: 39-42.
|
- Neuwinger HD. African traditional medicine: a dictionary of plant use and applications. Medpharm Scientific, Stuttgart, Germany. 2000; pp. 589.
|
- Zhao K, Penttinen P, Guan T, Xiao J, Chen Q, Xu J, Lindstro K, Zhang L, Zhang X, Strobel GA. The diversity and anti-microbial activity of endophytic actinomycetes isolated from medicinal plants in Panxi Plateau, China. Curr. Microbiol. 2011; 62, 182–190.
|
- Penrose DM, Glick BR. Methods for isolating and characterizing ACC deaminase-containing plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria. Physiol Plantarum 2003; 118: 10–15.
|
- Murugappan RM, Begum SB, Roobia RR. Symbiotic influence endophytic Bacillus pumilus on growth promotion and probiotic potential of the medicinal plant Ocimum sanctum. Symb. 2013; 60, 91–99.
|






 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License