IJCRR - 4(13), July, 2012
Pages: 101-107
Date of Publication: 18-Jul-2012
Print Article
Download XML Download PDF
A SEROEPIDEMIOLOGICAL STUDY OF HERPES SIMPLEX VIRUS TYPE 2 IN HIV POSITIVE INDIVIDUALS IN RAJAHMUNDRY, ANDHRA PRADESH , INDIA
Author: A. Heraman Singh, Ranjan Basu, Soujanya P.
Category: Healthcare
Abstract:Objectives : This study was done to find out the seroprevalence of herpes simplex virus type 2 (HSV-2) and its association with certain factors like age , gender as well as other demographic and behavioural factors in 166 human immunodeficiency virus ( HIV ) positive adults . Methods : This is a cross sectional study . 166 HIV positive adults were selected , informed consent was obtained and detailed history was taken. Serum samples were then screened for HSV-2 type specific IgG antibodies by ELISA . Results : HSV-2 seroprevalence was 42.1 % and it was higher among women ( 56.3% ) than among men ( 31.6 % ) . HSV-2 seroprevalence increased along with advancement of age and it was associated with high promiscuous behaviour . Conclusions : Only 14.2 % of the HSV-2 seropositive group gave history of symptoms suggestive of genital herpes . This demonstrates the need for regular HSV-2 seroprevalence surveys particularly in high risk groups. HSV-2 infected individuals can therefore be identified and institution of proper counselling and treatment not only reduces the rate of transmission of HSV-2 infection but also decreases the incidence of HIV infection.
Keywords: Human immunodeficiency virus , seroprevalence , Herpes simplex virus type 2
Full Text:
INTRODUCTION
Herpes simplex virus type 2 ( HSV-2 ) infection is a common cause of genital ulcer disease (1) . It is a lifelong infection which is highly infectious and often transmitted sexually in the absence of symptoms. HSV-2 prevalence is increasing worldwide and has become a prominent public health issue over recent years in relation to its potential role in facilitating HIV transmission (2). There is an epidemiological synergy between HSV-2 and HIV-1. HSV-2 infection is associated with a 2 - 4 fold increase in HIV-1 acquisition . In addition , HSV-2 is reactivated and transmitted more frequently in persons co-infected with HIV-1 and HSV-2 than in persons not infected with HIV-1 . HSV - 2 infection is an independent risk factor for the acquisition and transmission of infection with HIV-1. Among co-infected persons, HIV-1 virions can be shed from herpetic lesions of the genital region . This shedding may facilitate the spread of HIV through sexual contact (3) . The majority of the HSV-2 infections are unrecognised and represent the major reservoir for HSV-2 transmission . Antibody prevalence rates correlate with past sexual activity and vary greatly among different population groups(3) . Therefore seroepidemiological studies are critical to understanding the pattern and distribution of infection within populations (4) . Data on the prevalence of HSV-2 infection among HIV positive adults are scarce (5). The potential role of HSV-2 infection in facilitating HIV transmission highlights the need for including anti-HSV-2 testing and therapy in the management of HIV positive patients , especially for reducing the risk of transmission of HIV through herpetic lesions (6) . This study was done to find out the seroprevalence of HSV-2 and its association with certain factors like age , sex as well as other demographic and behavioural factors among HIV positive adults .
MATERIALS AND METHODS
It is a hospital based cross sectional study . The study was conducted in GSL General Hospital , a tertiary care hospital located in Rajahmundry , Andhra Pradesh . The study group consisted of 166 HIV positive adults with age ranging from 15 to 60 years , diagnosed at the hospital between January, 2010 and November , 2011 . Written informed consent was obtained and detailed history was taken on age, gender, education, socioeconomic status, address, marital status, occupation, condom usage, sexual orientation, number of sexual partners in the preceding years, years of sexual activity, history of genital herpes and history of any other STDs in past or present . Serum samples were collected from each patient and screened for HSV-2 type specific IgG antibodies by enzyme linked immuno sorbent assay [ ELISA ] . Test procedure was done and results interpreted as per manufacturer‘s guidelines [ Manufacturer : EUROIMMUN ] . This ELISA test specifically detects IgG class antibodies directed against HSV-2 specific glycoprotein G2 . Cross reactivity with antibodies against HSV-1 leading to false positive results does not occur with this type of ELISA ( 7,8 ) . The specificity of this ELISA with respect to the gold standard western blot test is 98% and the sensitivity is 100% (7) . Statistical Methods : All statistical analysis were performed by using SPSS software , version 16 and data have been summarised as counts and percentages. Unpaired proportions have been compared using Chi Square test or Fisher‘s Exact Probability test , as appropriate . All analysis was two tailed and p < 0.05 was considered statistically significant .
RESULTS
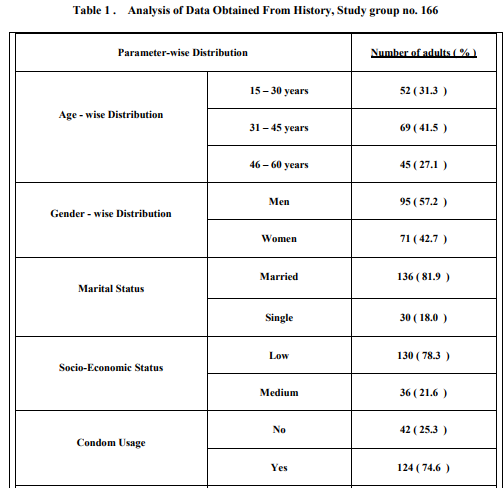
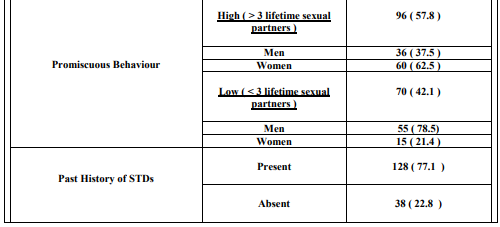
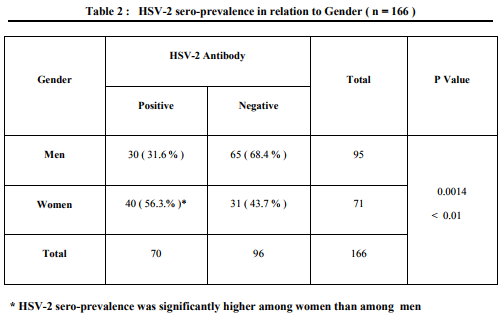
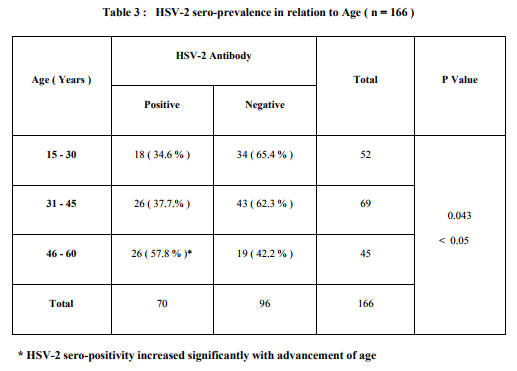
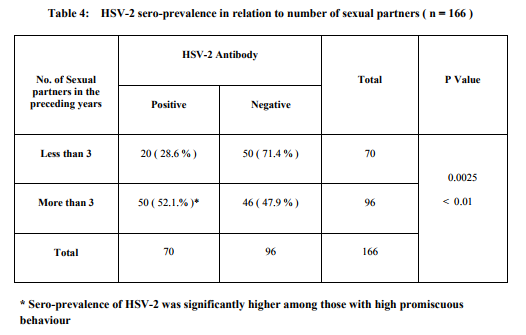
Data obtained from history was analysed and shown in Table - I . All were heterosexuals . The overall HSV - 2 sero-prevalence was 42.1 % and it was higher among women than among men ( Table - II ) . HSV-2 seropositivity increased along with advancement of age ( Table - III ) . Sero-prevalence of HSV-2 was higher among those with high promiscuous behaviour ( Table – IV ) . These associations were found significant statistically . Only 14.2 % of individuals with antibody to HSV-2 gave history of symptoms suggestive of genital herpes .
DISCUSSION
Few surveys describing the seroepidemiology of HSV-2 using type-specific tests in HIV sero-positive adults from Andhra Pradesh have been published . In our study HSV-2 seroprevalence among HIV seropositive adults was 42.1 %. A similar study on HIV positive adults done at Visakhapatnam, a nearby city in Andhra Pradesh , reported HSV-2 seroprevalence of 49 % ( 9 ). A larger study on general population done at Guntur district of Andhra Pradesh , reported HSV-2 seroprevalence of 5.87 % ( 10 ) . A community based study in New Delhi found that the seroprevalence of HSV-2 was 7 % and 8.6 % in men and women respectively (11) . These findings support that there is a strong association between HSV-2 and HIV infections. The higher rate of HSV-2 seen in HIV seropositive individuals may indicate that individuals who are infected by HSV-2 are more likely to acquire HIV infection , and vise-versa ( 1 ,5 ,12 , 13 ) . HSV-2 sero-prevalence was high among women ( 56.3 % ) than among men ( 31.5 % ) . This difference between men and women may be due to the difference in the nature of promiscuous behaviour by gender ( 62.5 % of women had high promiscuous behaviour compared to 37.5 % of men ) . HSV-2 seroprevalence increased along with advancement of age. Prevalence rates of 34.6%, 37.7% and 57.8% were found among the groups aged 15 - 30 , 31 - 45 and 46 – 60 years respectively . The increase in prevalence of each higher level of age may be related to increasing years of sexual activity along with advancement of age . HSV-2 sero-prevalence was high among those with sexual partners more than 3 in the preceding years than among those with less than 3 ( 52.1% versus 28.6% ) . These findings were found significant statistically and were in tandem to observations reported in various studies ( 14 , 15 , 16 , 17 ) . Only 14.2% ( 10/70 ) of individuals with antibody to HSV-2 gave history of symptoms suggestive of genital herpes . This indicates that only a low proportion of the patients were aware of the HSV-2 infection. Similar observation was also made in other studies ( 5 , 14 ,15 ,17) . This emphasizes the importance of studying the disease by serological methods .
CONCLUSION
HSV-2 prevalence is more common in HIV positive individuals compared to those of general population . This shows a strong association between HSV-2 and HIV infections. HSV-2 positive individuals are more likely to acquire HIV infection . There is a need for regular HSV-2 screening particularly in high risk groups . HSV-2 infected individuals can therefore be identified and institution of proper counselling and treatment not only reduces the rate of transmission of HSV-2 infection but also decreases the incidence of HIV infection. However, more rigorous study designs are needed to confirm these possibilities.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENT
Authors acknowledge the immense help received from the scholars whose articles are cited and included in references of this manuscript. The authors are also grateful to authors / editors /publishers of all those articles, journals and books from where the literature for this article has been reviewed and discussed.
References:
1. Corey Lawrence, Wald Anna, Celum, Connie L, Quinn, Thomas C . ?The effects of Herpes Simplex virus 2 on HIV – I Acquisition and Transmission : A review of two overlapping epidemics?. JAIDS Journal of Acquired Immunodeficiency Syndromes : volume 35 ( 5 ) 15 April 2004 .
2. Herpes Simplex virus type 2 : Programmatic and research priorities in developing countries . Report of A WHO / UNAIDS / LSHTM workshop . London , 14-16 , February .WHO HIV AIDS /2001.05.2001 .
3. Fausi, Braunwald, Kasper, Houser, Longo, Jameson, Loscalzo . Harrison‘s principles of internal medicine .17th edition .2008 .volume I :p. No. 1097 .
4. Cowan FM, French RS, Mayaud P, Gopal R, Robinson NJ, Artimos De Oliveira, S Faillace T, Vuscula A, Nigard-Kibur M, Ramalingam S, Srdharan G, L Aouad R, Alami K, Rbai M, Sunil Chandra N, Brown DW 2003 . Seroepidemiological study of Herpes Simplex virus type 1 and 2 in Brazil, Estonia, India, Morocco and Srilanka .Sex Trans Infect 79 : 286-290
5. Flavia Cunha Santos, Solange Artimos De Oliveira, Sergio Setubal, Luiz Antonio Bostos Canacho, Tereza Faillace, Jose Paulo, Gagliardi Leite, Luis Guillermo Coca Velarde, The HSV International study group. Seroepidemiological study of Herpes Simplex virus type 2 in patients with the acquired immune deficiency syndrome in the city of Niteroi, Rio De Geneiro , Brazil . Mem Inst Oswaldo Cruz ,Rio De Geneiro , vol 101 ( 3 ) : 315-319 , May 2006 .
6. Suligo B, Dorrucci M, Volpi A, Andreoni M, Zerboni R, Rezza G and the Italian Seroconversion study group 2002, Prevalence and determinants of Herpes Simplex virus type 2 infection in a cohort of HIV positive individuals in Italy . Sex Trans Dis Is : 665-667 .
7. EUROIMMUN – Anti HSV – 2 – ( gG 2 ) – ELISA ( IgG ) . EUROIMMUN AG . D – 23560 Lubeck ( Deutschland ) . Seekamp 31 .
8. Haliona B, JE Malkin . Epidemiology of Genital Herpes : Recent advances . European Journal of Dermatology 1999 : 9 : 177-84 .
9. K Anuradha, H Maan Singh, KVT Gopal, R Raghu Rama Rao, T V Ramani, Jyothi Padmaja . Herpes Simplex virus type 2 infection : A risk factor for HIV infection in heterosexuals . Indian J Dermatol Venerol Leprol. 2008 ; 74 : 230 - 3 .
10. John A Schneider, Venu Lakshmi, Rakhi Dandona, G Anil Kumar, Talasila Sudha, Lalit Dandona, Population - based seroprevalence of HSV – 2 and Syphilis in Andhra Pradesh state of India . BMC Infectious diseases 2010
11. R Chawla, P Bhalla, K Bhalla, M Meghachandra Singh, S Gorg . Community - based study on seroprevalence of Herpes Simplex virus type 2 infection in New Delhi Indian Journal of Medical Microbiology ,(2008 ) 26 (1) : 34 – 9 .
12. Russel DB, Tabrizi SN, Russel JM, Garland SM 2001 . Seroprevalence of Herpes Simplex virus type 1 and 2 in HIV infected and uninfected homosexual men in a primary care setting . J Clin Virol 22 : 305 - 313 .
13. Genital herpes and human immunodeficiency virus : double trouble .Connie Celum , Ruth Levine , Maria Weaver , Anna Wald , . Bulletin of the World Health Organization / June 2004 , 82 ( 6 ) .
14. Varela JA, Gorcia Corbeira P, Aguanell MV, Boceta R , Ballesteros J, Aguilar L. et al,. Herpes Simplex virus type 2 seroepidemiology in Spain . Sexually Transmitted Diseases 2001 ; 28 : 47 – 50.
15. Gottleib SL, Douglas JM, Schmid S . Seroprevalence and correlates of Herpes Simplex virus type 2 infection in 5 STD clinics . Journal of Infectious Diseases 2002 : 186 : 1381 – 1389 .
16. Cowan FM, Johnson AM Ashley R, Corey L, Mindel A . Antibody to Herpes Simplex virus type 2 as serological marker of sexual lifestyle in populations. BMJ 1994 ; 309 :1325 – 1329 .
17. Janier M, Lassau F, Bloch J . Seroprevalence of HSV 2 antibodies in an STD clinics in Paris. Int J STD AIDS 1999 ; 10 : 522 .
|






 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License