IJCRR - 4(16), August, 2012
Pages: 62-68
Date of Publication: 28-Aug-2012
Print Article
Download XML Download PDF
EFFECT OF VARIED FEEDBACK SCHEDULE ON MOTOR LEARNING IN PARKINSON'S DISEASE PATIENTS
Author: Md Haider Ali, Bhaskar Munjal, Nusrat Hamdani, Shahnawaz Anwer
Category: Healthcare
Abstract:A simple reaction time task was used to investigate augmented feedback on motor learning in Hoehn and Yahr stage 2 of Parkinson's disease patients. During acquisition, participant received knowledge of results (KR) about their error after every trial (100%) or every alternate trial (50%). Participants then performed an immediate retention test after 5 minutes and delayed retention test after 24 hours without KR. Parkinson's disease patient showed superior retention with 50% KR. This suggests that the Parkinson's disease patients with simple task are more reliant on decrease frequency of KR for learning motor skills.
Keywords: Knowledge of Results; Parkinson’s disease; Motor learning, Feedback training
Full Text:
INTRODUCTION
The acquisition of motor skill is a process, usually acquired through practice, that leads, for example, to improvement in speed and accuracy of voluntary movement.1 Parkinson disease is regarded as a movement disorder associated with basal ganglia dysfunction.1,2,3,4 Clinical and physiological studies of patients with Parkinson’s disease have clearly shown the importance of basal ganglia in voluntary movement control.3,1 For example, Parkinson’s disease patients are slower than normal in starting and executing movements.3,1 In addition, rapid single joint or multi joint, simultaneous, and sequential movements are executed abnormally in Parkinson’s disease, and impairments in executing movements of differing complexity may be task dependent.5 Parkinson’s disease patients have impaired sensory motor processing. Short term practice widely activates the cerebellar cortex, whereas prolonged practice decreases cerebellar activity and increases activation in the basal ganglia and frontal lobe.4 These patients are overly reliant on augmented feedback to monitor their movements.3 Experimentally, augmented feedback has been termed knowledge of results (KR), and is defined as error information provided by an external information source (e.g. computer, experimenter) after task has been completed.2 K. R. for optimal learning. For a relatively simple task and / or practiced subjects, a high frequency of KR enhances acquisition performance, but retards retention performance.2 However, with a relatively difficult task and/or little practice a high frequency of KR enhances both acquisition and retention performance. The explanation of these results is that proprioceptive information is available and utilized with a relatively simple task, and therefore, less augmented feedback is necessary.2 Therefore, it is predicted that in the current study, Hoehn and Yahr stage 2 of Parkinson’s disease patients would show superior retention after having learned the skill with a low frequency of Knowledge of Results (50% KR).
METHODS
Subjects:
A total of 30 patients with idiopathic Parkinsonism with stage 2 Hoehn and Yahr, age 50-72 years were selected. MMSE score was greater than 24 of all the patients. All participants were on phase of medication, tested after an overnight abstinence of at least 12 hours from their usual medication regimen. Patients did not exhibit side effect (e.g. dyskinesia) that interfered or delayed completion of task during testing, and no clinical fluctuation of Parkinson’s disease were observed during experimental session. All participants were naive with respect to the experimental design.
Study design:
The study has two groups (Group A and Group B). Each group was 15 patients of Parkinson’s disease. The 100% KR group (Group A) got the verbal feedback about the total number of errors (number of time patient touched with switch of machine) after every trial. The 50% KR group (Group B) received Knowledge of Results on every alternate trial. An immediate reaction test was conducted 5 minutes6 after the end of last trial of practice session. Then, a delayed retention test was conducted 24 hours6, 7 past the end practice session.
Apparatus:
A standardized chair without arm support with appropriate height and width with respect to patient’s height was used. These chairs were medium, large and extra large size, wooden table was used for the placement of apparatus. A Reaction Time Apparatus (fig 1.1) – RTM608 manufactured by medical systems, Chandigarh, India- 160002 (An ISO 9001: 2000 Company). This instrument can be used for the study of reaction time in normal subjects, smokers, diabetics, psychiatric patients and neurologically affected patients. The machine is such that a physical barrier provided between the examiner and Subjects, so the movement of the examiner does not influence that subject.
Protocol for data collection:
Instruction to the participants: All the patients were explained about the procedure and demonstrated the activity. They also instructed to press the start switch as soon as they are ready and then response to the appropriate and corresponding stimulus as quickly as possible. The entire subject signed an informed consent approved by IEC of Hamdard University, New Delhi, India. A closed environment with least possible distraction was selected as site for data collection. General demographic data was taken. The subjects performed the activity after a demonstration and a trial session. All participants practiced the sequence for three blocks (18 trials). A short break of 1-2 minutes was provided at the end of each block. A pattern was given on three consecutive blocks as given bellow.8.
Day 1; 6 trials × 3 blocks = 18 trials; Day 2; 6 trials × 3 blocks = 18 trials; Day 3; 6 trials ×3 blocks = 18 trials; Day 4; 6 trials × 3 blocks = 18 trials; Day 5; 6 trials × 3 blocks = 18 trials.
Procedure:
The emphasis of this section was to focus on improvement of learning in terms of reaction time reading. The procedure for the collection of data closely followed those described by Kimberly Steinhauer et al6 and Carole J Winstein9 in their studies. The procedure followed in the study is as follows: Mini Mental Status Examination was conducted to ensure that entire subject fulfil the cognitive criteria for study. Those who fulfil the criteria were randomly assigned into two groups A and B having 15 subjects in each group. Group A: 100% relative frequency Knowledge of Results.
Group B: 50% relative frequency Knowledge of Results. The apparatus was shown to each subject and task goal were explained. The subject was seated in comfortable position and was asked to place his/her limb in the prescribed site. Subjects were informed to press the button of reaction time machine with index finger of the dominant hand when the corresponding light was illuminated. Participants were instructed to respond as quickly as possible. The stimulus was presented before the subjects on the reaction time machine. The digital timer started with the initiation of this stimulus. The subjects were instructed to press the corresponding button which was marked for that particular kind of stimulus. Then timing circuit automatically switched off as soon as the subject pressed the button with index finger. Acquisition phase consisted of 5 days. 18 trials on each day were blocked in three (6 trials in three blocks). The 100% group (Group A) was got the verbal feedback about the total number of errors (number of times patient touched with switch of machine) after every trial. The 50% group was given Knowledge of Results on every alternate trial. An immediate retention test was conducted 5 minutes6 after end of last trial of practice session. Then, a delayed retention test was conducted 24 hours6, 7 past the end of practice session.
Statistical Analysis:
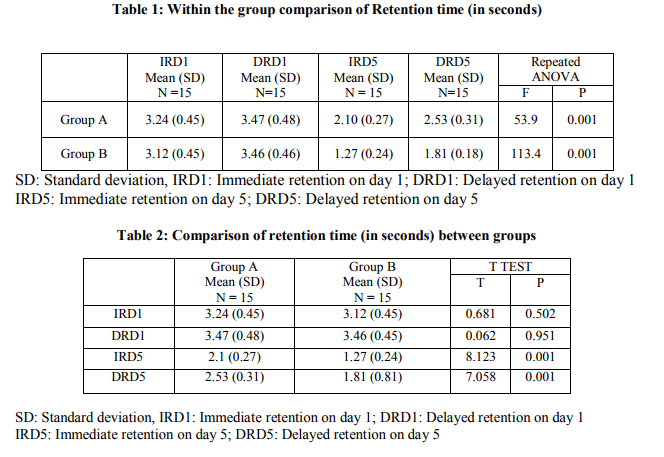
A pretest-posttest experimental group design is used for the study. The pretest values for immediate retention on day 1 (designated as IRD1) and delayed retention on day 1 (designated as DRD1) was taken. Post test values for immediate retention on day 5 (designated as IRD5) and delayed retention on day 5 (designated as DRD5) was taken. The data was analyzed using the SPSS 15.0 Software. Repeated measure ANOVA applied for comparison of immediate and delayed retention time within the groups. Further post hoc analysis done using bonferroni test to compare the retention time in each group. An independent ttest was used to compare the retention time between two groups. The results were taken to be significant if p0.05). Similarly, on comparing the value of DRD1 between group A (100% KR) and group B (50%KR), the result was found to be non significant (p>0.05).
RESULTS
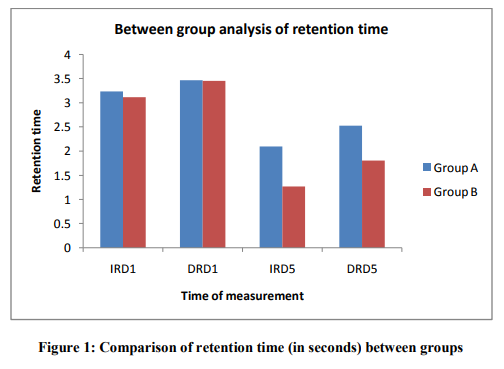
Table 1 and Table 2 details the results of present study. Within group analysis revealed significant improvement of delayed retention on day 1(DRD1) and immediate and delayed retention on day 5 (IRD5 and DRD5) when compared to immediate retention on day 1 (IRD1) (p0.05). Similarly, on comparing the value of DRD1 between group A (100% KR) and group B (50%KR), the result was found to be non significant (p>0.05). However, comparison of immediate and delayed retention on day 5 (IRD5 and DRD5) between two groups was found to be statistically significant (P<0.001). Above result showed that on day 5 both immediate and delayed retention was better in group B as compared to group A.
DISCUSSION
This study was designed to compare the effect of varied feedback schedule on motor learning in Parkinson’s disease patients. The results of our study found significant differences between the two groups that is Group A (100%KR) and Group B (50%KR). Result of our study shown that 50% KR is better than 100% KR. The findings of our study contradict the work done by Mark A. Guadagnoli et al2 . In their study, Parkinson’s disease patients showed superior retention with 100% KR. They had taken the patient of Hoehn and Yahr stage 3 of Parkinson’s disease. However, in our study we selected Hoehn and Yahr stage 2 of Parkinson’s disease patients. The results of our study support the previous work done by K Steinhuer et al6 . They performed a study on the normal subjects and concluded that increase in relative frequency of Knowledge of Results led to a decrease in motor performance and learning. That means those subjects in the 100% KR has poorer learning than compared with 50% KR. Comparison of the baseline performance (retention of day one) with that of retention test of last day of protocol within group analysis shows a significant decrease in retention time. This can be attributed to the practice effect of the total trials during acquisition phase. The study conducted by K Steinhuer et al6 , on normal individual, reported that a significant difference in both the groups. And they concluded that subjects performed better during retention test as compared to each other in both groups. When immediate retention of day five and delayed retention of day five of group A (100% KR) was compared to immediate retention of day five and delayed retention of day five of group B (50% KR) respectively. Then it was shown that there was significant difference in terms of improvement in the reaction time on the retention test. But when the mean value of immediate retention and delayed retention was studied, more improvement in the immediate retention rather than the delayed retention test was found. These results have shown that the improvement which was obtained on immediate retention test on day five was not maintained on delayed retention test of day five. Though, it was much better than on immediate retention on day one. Although both the groups improved on immediate as well as delayed retention, but group B improved better than group A. Study by Carolee J. Winstein et al1 reported that markedly reduced KR relative frequency during practice session was effective for learning as measured by various retention tests, compared with a 100% KR practice condition. These results are in accordance with our study. In group A percentage mean value change of immediate retention was decreased to 35.01 % and percentage changed of delayed retention was decreased to 26.99 %. Similarly in group B percentage mean value changed of immediate retention was decreased 59.05 % and percentage change of mean value of delayed retention was 47.47 %. Hence improvement was greater in group B than group A. That means 50% KR is better than 100% KR in Hoehn and Yahr stage 2 of Parkinson’s disease patients. The study conducted by M.A. Guadagnoli et al2 on Hoehn and Yahr stage 3 of Parkinson’s disease patient, for a relative simple task and/ or well practiced subjects; a high frequency KR enhances acquisition performance, but retards retention performance. However, with a relatively difficult task and/or well practice a high frequency of KR enhances both acquisition and retention performance. That means proprioception information is available and utilized with a relatively simple task, and therefore, less augmented feedback is necessary. If frequent feedback is given under these conditions, participant may become dependent on the feedback rather than processing their own proprioceptive information and when feedback is withdrawn performance (retention test) suffers. Therefore it predicted that in our current study, low frequency KR (50% KR) enhanced retention performance than compared with high frequency KR (100% KR). Because of our study had taken simple task (only to press the button of corresponding light of reaction time machine) as well as we had taken the Hoehn and Yahr stage 2 of Parkinson’s disease patient. According to result and above discussion showed that an increase in relative frequency of knowledge of results led to a decrease in learning in Hoehn and Yahr stage 2 of Parkinson’s disease patients. Other studies such as Gabriele Wulf10, Richard et al11 says that reduced K R frequency enhanced generalized motor program (GMP) learning on the normal person also holds true for Parkinson’s disease patients in Hoehn and Yahr stage 2.
Future Research:
Science is dynamic and there is always a scope of improvement and change in time to come ahead. With the progressive aim to move ahead we aspire to achieve highly accurate and reliable results. Thus, every study leaves back scopes for other researcher to do something more advanced and varied in order to touch the height of perfection. This study examined only 30 subjects in total and data collection was confined to closed setup with minimum distractible conditions. Thus future researchers can expand the study by including more number of subjects so as to make generalization of results and practice such experiments in variable environmental setups such as open environment. Thus it could be applied to real life situation. In this study the task used included visual stimuli and reaction time task. But future researchers can progress the study by modifying the tasks like incorporating both visual stimuli and auditory stimuli in the task given, tasks related to the real life situations could be used, such as using advanced reaction time software instead of reaction machine. The scope of the study can be expanded to patients with Parkinson’s disease with Hoehn and Yahr stage of 3 and comparison with stage 4, comparison can also be done with younger age group and with elderly and those with other neurological impairments such as stroke.
Relevance to clinical practice:
The results obtained in this study suggest that 50% KR is more beneficial than 100% KR, so, these results have shown that less frequent KR that is 50 % KR should be used for training tasks to patients with Parkinson’s disease in Hoehn and Yahr stage 2.
Limitations of the study:
The study is limited to only Hoehn and Yahr stage 2 of Parkinson’s disease patients with less number of practice trials in a small group of patients. More advanced equipments may be used to increase reliability of this study.
CONCLUSION
The results of this study conclude that improvement in motor learning with feedback after every alternate trial (50 % KR) was significantly better than feedback after every trial (100% KR) in Parkinson’s disease patients.
ACKNOWLEDGMENT
We acknowledge the immense help received from the scholars whose articles are cited and included in references of this manuscript. We are also grateful to authors/editors/publishers of all those articles, journals and books from where the literature for this article has been reviewed and discussed.
References:
1. Carolee J Winstein. Knowledge of result and motor learning implication for physical therapy. Physical Therapy 1991;71:140-149.
2. Mark A. Guadagnoli, Berta Leis, et al. The relationship between knowledge of results and motor learning in Parkinsonian patients. Parkinsonism and Related Disorders 2002;9:89-95.
3. Katrina Gwinn Hardy. Genetics of Parkinsonism. Movement disorders 2002;17: 645-656.
4. Singhal B et al. Epidemiology and treatment of Parkinson’s disease in India. Parkinson’s and related disorders 2003 Aug;9 Suppl 2:S105-9.
5. Rocco Agostino et al. Motor skill learning in Parkinson’s disease. Journal of Neurological Sciences. 1996;139:218 –226.
6. Kimberly Steinhuer, Judith Preston Grayback. The role of Knowledge of Result in performance and learning of a voice motor task. Journal of Voice 2000;14(2):137 – 145.
7. A.L. Smiley-Oyen, C.J. Worringham, C.L. Cross. Motor learning processes in a movement scaling task in olivopontocerebellar atrophy and Parkinson’s disease. Exp Brain Res 2003;152:453 – 465.
8. Swinnen SP, Steyvers M, Van Den Bergh L, Stelmach GE. Motor learning and Parkinson’s disease: refinement of withinlimb and between limb coordination as a result of practice. Behaviour Brain Research. 2000;111:45 – 59.
9. Carole J. Winstein, Richard A. Schmidt. Reduced Frequency of Knowledge of Results enhances motor skill learning. J Exp Psychology: Learning, Memory and cognition 1990; 16:677-691.
10. Gabriele Wulf et al. Reduced feedback frequency Enhances Generalized Motor Program but not parameterisation Learning. J Exp Psychology: Learning, Memory and cognition 1993;19(5):1134-1150.
11. Richard A. Schmidt, Duglas E. Young, et al. Summary Knowledge of Results for skill acquisition: Support for the guidance hypothesis. J Exp Psychology: Learning, Memory, and Cognition, 1989;15(2):352- 359.
|






 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License