IJCRR - 4(16), August, 2012
Pages: 01-08
Date of Publication: 28-Aug-2012
Print Article
Download XML Download PDF
EFFECT ON BASE PRESSURE IN SUDDENLY EXPANDED FLOWS WITH VARIABLE LOCATION OF MICROJETS
Author: Maughal Ahmed Ali Baig, Sher Afghan Khan, E. Rathakrishnan
Category: Technology
Abstract:This paper presents results of an experimental investigation to study the effectiveness of micro jets to control the base pressure in suddenly expanded axi-symmetric ducts when the micro jets are placed at different location (i.e. at the base, at the duct, and at base as well as at the duct). The purpose of this study is to study the individual as well as the combined effectiveness of the micro jet as the active controller of the base pressure. The area ratio of the present study is 3.24. The nozzle generating the above jet Mach numbers were operated with nozzle pressure ratio (NPR) in the range 3 to 11. In addition to base pressure, wall pressure field along the duct was also studied. As high as 70 percent increase in base pressure was achieved for Mach number 2.58 at NPR 11 when the micro jets are placed at the base as well as the duct.
Keywords: Area Ratio, Nozzle Pressure Ratio, Wall pressure, Sudden Expansion
Full Text:
INTRODUCTION
Vortex shedding in the wake of bluff bodies is an important flow phenomenon. At subsonic and transonic speeds, it has long been recognized that the wake behind an isolated twodimensional section with a blunt trailing edge may break into a vortex street. The direct result of this is an increase in drag, mainly as a result of reduced pressure. Further, the subject of base flows at high Reynolds numbers has been and continues to be an important area of research in view of its relevance in external aerodynamics. Base drag arising from flow separation at the blunt base of a body, can be sizeable fraction of total drag in the context of projectiles, missiles and after bodies of fighter aircraft; for example, the base drag component can be as high as 50 percent of the total drag for a missile with power off (i.e. with no jet flow at the base). Large-scale flow unsteadiness, often associated with a turbulent separated flow, can cause additional problems like base buffeting which are undesirable.
LITERATURE REVIEW Wick
[l] studied the effect of boundary layer on sonic flow through an abrupt cross-sectional area. He observed experimentally that the pressure in the corner of expansion was related to the boundary layer type and thickness upstream of the expansion. He considered boundary layer as a source of fluid for the corner flow. The base corner was thought of as a sump with two supplies of mass. The first was the boundary layer flow around the corner and the second source was the back flow in the boundary layer along the wall of the expanded section. This back flow occurred because of the pressure difference across the shock wave originating where the jet strikes the wall. He concluded that the mechanism of internal and external flow was principally the same and base pressure phenomenon in external flow could be studied relatively easily by experiments with internal flow. Korst [2] investigated the problem of base pressure in transonic and supersonic flow for cases in which the flow approaching the base is sonic or supersonic after the wake. He devised a physical flow model based on the concepts of interaction between the dissipative shear flow and the adjacent free stream and the conservation of mass in the wake. Anderson and Williams [3] worked on base pressure and noise produced by the abrupt expansion of air in a cylindrical duct. With an attached flow the base pressure was having minimum value, which depends mainly on the duct to nozzle area ratio and on the geometry of the nozzle. The plot of overall noise showed a minimum at a jet pressure approximately equal to that required producing minimum base pressure. Rathakrishnan and Sreekanth [4] studied flows in pipe with sudden enlargement. They concluded that the non-dimensionalized base pressure is a strong function of the expansion area ratios, the overall pressure ratios and the duct length-to-diameter ratios. They showed that for a given overall pressure ratio and a given area ratio, it is possible to identify an optimal length-to-diameter ratio of the duct that will result in maximum exit plane total pressure at the nozzle exit on the symmetry axis (i.e. minimum pressure loss in the nozzle) and in a minimum base pressure at the sudden enlargement plane. The separation and reattachment seemed to be strongly dependent on the area ratio of the inlet to enlargement. For a given nozzle and enlargement area ratio, the duct length must exceed a definite minimum value for minimum base pressure. Tanner [5] studied base cavity at angles of incidence. He concluded that a base cavity could increase the base pressure and thus decrease the base drag in axi-symmetric flow. He varied the angle of incidence from 0 to 25°. At a. = 2°, he found the maximum drag decrease. Kruiswyk and Dutton [6] studied effects of base cavity on subsonic near-wake flow. They experimentally investigated the effects of the base cavity on the near-wake flow field of a slender twodimensional body in the subsonic speed range. Three basic configurations were investigated and compared; they are a blunt base, a shallow rectangular cavity base of depth equal to one half of the base height and a deep rectangular cavity base of depth equal to the base height. Schlieren photographs revealed that the base qualitative structure of the vortex street was unmodified by the presence of the base cavity. The weaker vortex street yielded higher pressures in the near-wake for the cavity bases, and increases in the base pressure coefficients of the order of 10-14%, and increases in the shedding frequencies of the order of 4 -6% relative to the blunt-based configuration. M. A. Baig and S.A. Khan [9] studied effect on base pressure due to active control in the form of Microjets at area ratio 2.56, and concluded that Microjets do not disturb flow field and base pressure increases for certain combinations of parameters of study. Suddenly expanded flow with control seems to be of interest with many applications. This will help in minimizing the base pressure in the case of combustion chamber to maximize the mixing, and maximize the base pressure in case of rockets, projectiles, aircraft bombs and missiles to result in base drag reduction. Therefore, an attempt has been made to investigate the control of base pressure field with micro jets by changing the location of the micro jets.
EXPERIMENTAL SET UP
Figure 1 shows the experimental setup used for the present study. At the exit periphery of the nozzle there are eight holes as shown in the figure, four of which (marked c) were used for blowing and the remaining four (marked m) were used for base pressure (Pb) measurement. Control of the base pressure was done, by blowing through the control holes (c), using the pressure from the blowing chamber by employing a tube connecting the chamber and the control holes (c). Pressure taps are provided on the duct wall to measure wall pressure distribution in the duct. First nine holes are made at an interval of 4 mm each and remaining holes are made at an interval of 8 mm each. Experiments were conducted for Mach numbers 1.87, 2.2 and 2.58. For each Mach number, NPR employed was 3, 5, 7, 9, and 11. PSI model 9010 pressure transducer was used for measuring pressure at the base and the stagnation pressure in the settling chamber. It has 16 channels and pressure range is 0-300 psi.
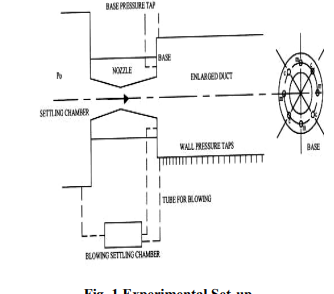
Fig. 1 Experimental Set-up
RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
The measured data consists of the base pressure (Pb), wall static pressure (Pc) distribution along the length of the enlarged duct and the nozzle pressure ratio (NPR) defined as the ratio of stagnation pressure (P0) to the back pressure (Pa). All the measured pressures were nondimensionalized by dividing them with the ambient atmospheric pressure (i.e. the back pressure). In addition to the above pressures, the other parameters of the present study are the jet Mach number (M), the area ratio (enlarged duct cross sectional area/nozzle exit area), length to diameter ratio of the duct (L/D) and the blow pressure ratio. To quantify the increase in base pressure achieved with active control, cross plots of base pressure in the form of percentage increase in base pressure is used for presenting the results. The percentage change in base pressure as a function of NPR has been shown in Fig. 2 to 4 for area ratio 3.24 at Mach 1.87, 2.2, and 2.58 under the influence of favorable as well as adverse pressure gradients (i.e. for correctly expanded, over expanded, and under expanded cases). Figure 2 shows percentage change of base pressure as a function of NPR for the cases (i.e. with control micro jets are located at base, at the duct and at both) at Mach 1.87. It is found that at lower NPRs the micro jets are not effective when placed at base and increase in base pressure is only marginal. When micro jets are placed at the duct the effectiveness is enhanced and it is effective for all the NPRs tested and the maximum gain is 10 percent. When micro jets are placed at base as well as at the duct its effectiveness is getting enhanced for all the NPRs tested. At NPR 11, 25 percent increase in base pressure is achieved. The physical reason for this trend may be that when micro jets are at base they are not able to break the powerful vortex positioned at the base, which otherwise they are able to do so when they are either placed at duct or at the base or both.
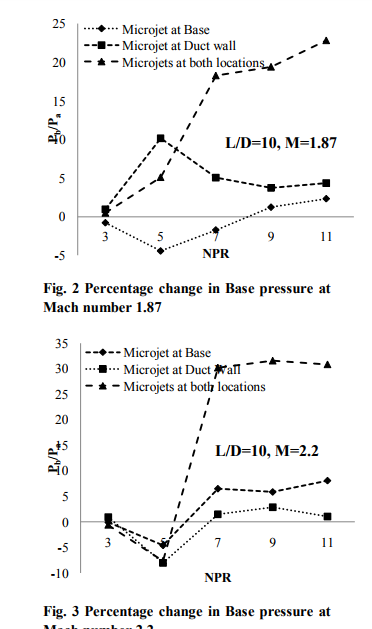
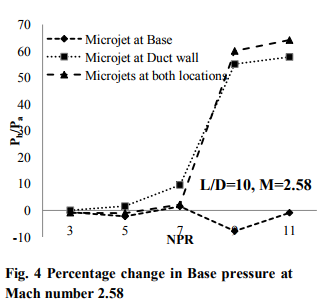
Base pressure results for Mach number 2.2 are shown in Fig. 3. They exhibit similar behavior as discussed above with the exception that the magnitude of increase in base pressure has changed. When the micro jets are at the base and at the enlarged duct the effectiveness is only marginal. This behavior seems to be due to the Mach number effect. However, when the micro jets are at the base as well as at the duct the control effectiveness has increased significantly and 30 percent increase in base pressure is achieved. Similar results for Mach number 2.58 are shown in Fig. 4. It is seen that for this case when micro jets are activated control results in decrease of base pressure when they are placed at base only. For the case of micro jets being placed at duct wall it was found that up to NPR 7 they are not very effective, however, their effectiveness gets enhanced when NPR is more than 7. When the combined effect is considered their effectiveness is increased and as high as 70 per cent increase in base pressure is achieved.
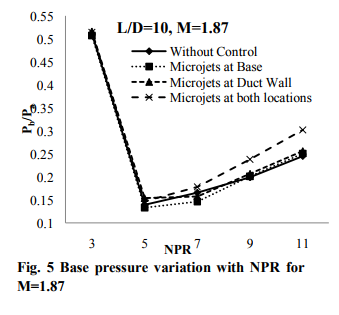
Non-dimensionalized base pressure variation with L/D ratio at Mach 1.87, 2.2, 2.58 for the cases with and without control is compared in Figs. 5 to 7. It is clearly seen that the functional dependence of base pressure with NPR is unaltered by the control. However, the control tends to modify the base pressure level at all NPRs. Also, the control effectiveness in modifying the level of base pressure gets enhanced with increase of NPR. At NPR 3 the control effectiveness is almost insignificant and the effectiveness increases with increase of NPR. For Mach 1.87, the NPR for correct expansion is 6.4. Therefore, up to NPR 6.4 the flow at nozzle exit is over expanded and hence adverse pressure gradient is present when the flow enters the enlarged duct. For NPR larger than 6.4 favorable pressure gradient exists at the nozzle exit. For NPR < 6.4, in the presence of adverse pressure gradient the control effectiveness is only marginal. Also, as the NPR increases from 3, i.e., as the level of adverse pressure gradient decreases, the control effectiveness increases. For the NPRs establishing favorable pressure gradient the control becomes progressively more effective with increase of favorable pressure gradient. Furthermore, it is seen that the control results in decrease of base pressure compared to without control case, up to certain NPR and then increases the base pressure to stay above that for without control case. A closer look at the flow process at the base of the duct will explain the reason for this behavior. The base pressure level is dictated by the expansion level at the nozzle exit and the duct L/D, for a given area ratio. There will be an expansion fan and oblique shock at nozzle lip, for under and over expanded flows, respectively. Thus, the wave at the nozzle lip has a dominant influence on the base pressure level. This causes the control to become more effective at higher NPR for higher Mach numbers, compared to lower Mach numbers.
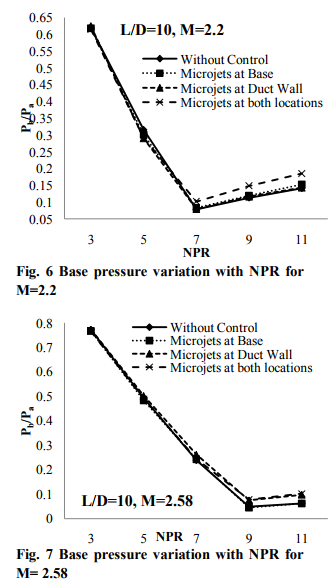
It is important to realize that, even though it appears as though the base pressure increase from its minimum value takes place from NPR 5, 7, and 9 for Mach numbers 1.87, 2.2, and 2.58, respectively, to identify the NPR at which this begins, one has to conduct tests with close steps of NPR. In the present study such tests were not conducted. It is interesting to note that after the limiting NPR, increase in NPR results in increase of base pressure for all Mach numbers. However, the rate of increase becomes a function of nozzle expansion level. Once the flow becomes under expanded the increase be comes larger. Further, the micro-jets become effective in enhancing the base pressure when the nozzle is under expanded. It was found that wall the pressure field with control and without control behaves almost identically. This ensures that the active control in the form of micro jets does not influence the wall pressure adversely rendering it to oscillate violently. This can be considered as one of the major advantages since; the major problem faced while using a control either active or passive the control may augment the base pressure but the control may augment the nature of the wall pressure field in the duct.
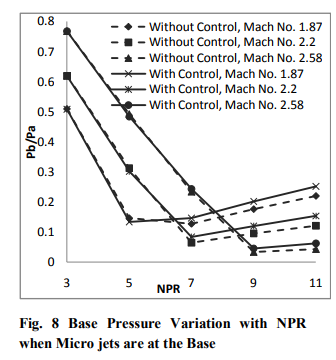
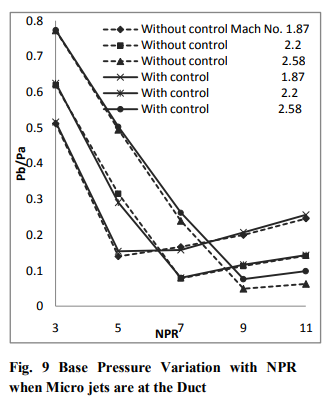
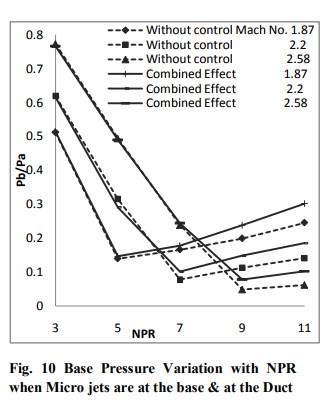
 Non-dimensionalized base pressure variation with NPR for duct L/D = 10 at Mach 1.87, 2.2 and 2.58 for the cases of flow when micro jets are at base, at the duct, and at both the places with and without control are compared in Fig. 8 to 10. Figure 8 presents the results for the case when the micro jets are at the base only. The control becomes effective for the NPRs beyond 5, 7, and 9 for Mach 1.87, 2.2, and 2.58. The reasons for this behavior have been explained above. Further, it is seen in the figure 9 when the micro jets are at the duct alone. The trend remains the as it was seen in figure 8 but the effectiveness is only marginal for Mach 1.87 and 2.2. For Mach 2.58 the micro jets are becoming progressively more effective. Figure 10 presents the results for all the Mach numbers tested for the case when the micro jets are placed at the base as well as in the duct. It is found that once the NPR values are more than the NPR required for correct expansion the base pressure increases progressively with NPR and control also becomes effective.
Non-dimensionalized base pressure variation with NPR for duct L/D = 10 at Mach 1.87, 2.2 and 2.58 for the cases of flow when micro jets are at base, at the duct, and at both the places with and without control are compared in Fig. 8 to 10. Figure 8 presents the results for the case when the micro jets are at the base only. The control becomes effective for the NPRs beyond 5, 7, and 9 for Mach 1.87, 2.2, and 2.58. The reasons for this behavior have been explained above. Further, it is seen in the figure 9 when the micro jets are at the duct alone. The trend remains the as it was seen in figure 8 but the effectiveness is only marginal for Mach 1.87 and 2.2. For Mach 2.58 the micro jets are becoming progressively more effective. Figure 10 presents the results for all the Mach numbers tested for the case when the micro jets are placed at the base as well as in the duct. It is found that once the NPR values are more than the NPR required for correct expansion the base pressure increases progressively with NPR and control also becomes effective.
Wall Pressure Distribution
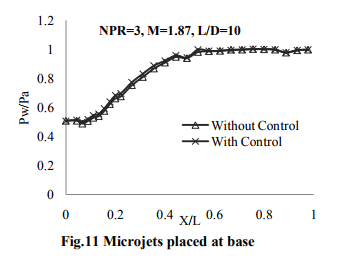
It can be seen from figures 11 to 13 that the location of Microjets at three different locations does not augment the wall pressure. The wall pressure studies are verily required to understand the oscillatory nature of flow which is one of the major problems in active methods of controlling base flows.
CONCLUSIONS
From the above discussion we can draw the following conclusions. The micro jets can serve as an effective controller to control the base pressure, raising the base suction for some combination of parameters. It is found that when the micro jets are employed at the base as well as the duct the control becomes very effective resulting in increase of base pressure and 70 percent increase in base pressure is achieved at Mach 2.58. Further, it is found that when NPR reaches the value required for correct expansion the control becomes effective. This agrees well with the findings of Navin Kumar Singh and Rathakrishnan [7] in the literature who reported that the effectiveness of passive control in the form of tabs in enhancing the mixing increases with increase of favorable pressure gradient. The base pressure level is dictated by the expansion level at the nozzle exit and the Mach number for a given area ratio. There is no adverse effect of the active control on the enlarged duct flow field. The nozzle pressure ratio and the Mach number have a definite role to play in fixing the level of base pressure with and without control at supersonic Mach numbers.
References:
1. Wick, R. S., The effect of boundary layer on sonic flow through an abrupt crosssectional area change, Journal of the Aeronautical Science, Vol. 20, 1953, pp. 675-682.
2. Korst, H., A theory of base pressure in transonic and supersonic flow, Journal of Applied Mechanics, Vol. 23, 1956, pp. 593-599.
3. Anderson, J.S. and Williams, T.J., Base pressure and noise produced by the abrupt expansion of air in a cylindrical duct, Journal of Mechanical Engineering Science, Vol. 10, No. 3, 1968, pp. 262- 268.
4. Rathakrishnan, E. and Sreekanth, A.K., Flow in pipes with sudden enlargement, Proceedings of the 14th International Symposium on Space Technology and Science, Tokyo, Japan, (1984), pp.491-499, 1984.
5. Tanner, M. Base cavities at angles of incidence, AIAA Journal, Vol. 26, No. 3, 1988, pp. 376-377.
6. Kruiswyk, R.W. and Dutton, J.C., Effect of base cavity on subsonic near-wake flow, AIAA Journal, Vol. 28, No. 11, 1990, pp. 1885-1895.
7. Singh Naveen Kumar and E. Rathakrishnan, Sonic Jet Control with Tabs, International Journal of Turbo and Jet Engines (IJT), Vol. 19, No. 1-2, pp. 107- 118, 2002.
8. Khan S. A. and E. Rathakrishnan, Control of Suddenly Expanded Flow, International Journal of Aircraft Engineering and Aerospace Technology (AEAT), Vol. 78, Issue 4, pp. 293-309, 2006.
9. M. Ahmed Ali Baig, F. Al-Mufadi, S. A. Khan and E. Rathakrishnan, “Control of Base Flows with Microjets”, International Journal of Turbo Jet Engines, Vol. 28 (2011), pp. 59-69.
10. M. Ahmed Ali Baig, S. A. Khan and E. Rathakrishnan, “Active Control Of Base Pressure In Suddenly Expanded Flow For Area Ratio 4.84” , International Journal of Engineering Science and Technology, Vol. 4, No. 5, pp 1892- 1902, May 2012.
|






 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License