IJCRR - 9(13), July, 2017
Pages: 30-37
Date of Publication: 03-Jul-2017
Print Article
Download XML Download PDF
In silico Characterization of Cellulases from Genus Bacillus
Author: Yogita Lugani, Balwinder Singh Sooch
Category: General Sciences
Abstract:Background: Cellulases are hydrolytic enzymes which hydrolyze \?-1,4-glycosidic linkage in cellulose and these are present in many microorganisms including bacteria, fungi and protozoa. The three types of cellulases involved in complete hydrolysis of cellulose are endoglucanase, exoglucanase and \?-glucosidase. Various structural and functional domains are present in cellulases and among all these domains, cellulose binding and catalytic domains are found to be important for the hydrolysis of cellulose. Cellulases have showed promising applications in different industrial sectors like paper and pulp, textile, laundry, bioethanol production, brewing, detergent and waste management. A major focus has been given in the recent past by researchers to understand the functional domains and catalytic mechanism of this enzyme to make their effective use for industrial applications.
Material and Methods: The protein sequences of cellulases belonging to different Bacillus sp. were retrieved using Uniprot and then physicochemical properties were analyzed using ProtParam and Protscale. Multiple sequence alignment of retrieved sequences was performed using Clustal W and phylogenetic tree was constructed using Mega 6.0 software. SOPMA and GOR IV tools were used for the prediction of secondary structure. The tertiary structure of enzyme was computed using Raptor X.
Results: The molecular weight of cellulases were found to range between 49,263-94,682 Da with hydropathicity ranges between -0.292 to -0.580. The acidic amino acid glutamate was found at the active site and methionone was found at the N-terminal of enzyme. The results have shown that the sequence is highly diversed at N-terminus and C-terminus region between different types of cellulases with conserved sequences in the middle. The phylogenetic tree has showed high similarity amongst retrieved sequences. From the tertiary structure, a great degree of variability in \a-helix, extended strand in \? ladder, hydrogen bonded turn, bend and coil was observed between different types of cellulases.
Conclusion: This study provides insights about the physicochemical properties, hydrohobicity, structure and function of cellulases, which would help to exploit this enzyme at industrial level.
Keywords: Cellulase, Cellulose, Bacillus sp., Endoglucanase, Exoglucanase, ?-glucosidase
DOI: 10.7324/IJCRR.2017.9136
Full Text:
INTRODUCTION
Cellulases are hydrolytic enzymes which can readily hydrolyze both crystalline and paracrystalline structures of cellulose, the largest component of plant residues enters terrestrial ecosystems. Cellulose is present in various lignocellulosic wastes generated from agricultural and industrial processes like sawdust, citrus peel waste, paper mill sludge, industrial waste, paper pulp and municipal solid waste (Maki et al., 2009). The synergistic action of three types of cellulases i.e. endoglucanases (EC 3.2.1.4), exoglucanases (EC 3.2.1.74) and β-glucosidase (EC 3.2.1.21) have been involved for the complete hydrolysis of cellulose (Lugani et al., 2015). Cellulases are industrially important enzymes and are involved in the conversion of lignocellulosic residues for the production of single cell protein, ethanol, bleaching of pulp, fruit juice extraction and for the treatment of waste papers (Shankar and Isaiarasu, 2011). Cellulases are produced by all the microorganisms but mainly by bacteria, actinomycetes and fungi. Among all the microorganisms, members of bacteria have gained intense importance for commercial production of cellulases due to their high growth, wide genetic variability, adaptability and high amendability to genetic manipulations (Patagundi et al., 2014; Lynd et al., 2002). The structure of cellulase composed of carbohydrate binding domain (CBD) at C-terminal which is joined by a short poly- linker region to the N-terminal of catalytic domain. There is presence of two acidic amino acids at the active site of enzyme which catalyze the reaction by acid-base catalysis either through inversion or retention of the configuration of anomeric carbon (Maki et al., 2009). The current focus of most of the researchers has been towards the large scale production of this industrially important enzyme to meet the industrial needs by utilizing various novel bacterial strains. However, a great degree of variability have been observed between different bacterial strains like molecular weight, stability, amino acid composition, family and domain to which they belong, secondary and tertiary structure. Bioinformatics is an interdisciplinary field which is currently used for structural and functional analysis of proteins using various computations tools and databases (Prashant et al., 2010). The information which has been retrieved from available tools and databases about the protein might be useful for the selection of highly efficient bacterial strain for industrial production of enzyme. Moreover, this information may also be helpful for developing new microbial strains with enhanced enzyme production ability by adapting recombinant DNA technology. Keeping in view the above facts about industrial importance of cellulases and use of bioinformatics as an emerging field of molecular biology, the present study was aimed to utilize in silico tools for the characterization of cellulase enzymes from different Bacillus species for their physicochemical characteristics, ancestral relationship and structure determination at various levels.
MATERIAL AND METHODS
Sequence retrieval and alignment
The cellulase protein sequences from different species of Bacillus were retrieved from Uniprot (Universal Protein Resource). The retrieved sequences from Bacillus sp. were Bacillus subtilis, Accession number: P10475; Bacillus akibai,Accession number: P06564; Bacillus thuringiensis, Accession number: M1QQC9; Bacillus pumilus, Accession number: B2ZHC9; Paenibacillus polymyxa, Accession number: E3EEC5; Paenibacillus macerans, Accession number: A0A090Y895. Clustal Omega (version 1.2.4) algorithm was used for the alignment of retrieved protein sequences through multiple sequence alignment.
Physicochemical characterization
ProtParam tool was used to compute different physicochemical properties of retrieving sequences of cellulases like amino acid composition, aliphatic index (AI), pI, instability index (II), number of positive and negative charged residues, grand average of hydropathicity (GRAVY) and extinction coefficient (Kumar et al., 2012). The isoelectric point (pI) is determined based on the pK value of protein during protein migration under denaturation conditions (Bjellqvust et al., 1993). The concentration of purified protein in the sample is evaluated from the value of extinction coefficient (Umang et al., 2012). The stability of protein is calculated from its instability index (II) and the proteins are predicted as stable when their instability index is smaller than 40; however when the value of instability index is greater than 40, the protein is regarded as unstable (Guruprasad et al., 1990). The volume occupied by aliphatic amino acids side chain (alanine, valine, leucine and isoleucine) relative to total volume occupied is called aliphatic index and it determines the thermostability of a globular protein (Walker, 2005).The hydrophilicity or hydrophobicity of protein is determined by grand average of hydropathicity (GRAVY), which is the ratio of sum of hydropathy values of all the amino acids to total number of residues in the sequence (Umang et al., 2012). The hydropathy plots based on Kyte and Doolittle scale for all the retrieved sequences of cellulases were predicted using Protscale tool (Kumar et al., 2012; http://www.expasy.org/tools/).
Phylogenetic analysis
The ancestral relationship between retrieved protein sequences of cellulase for different species of Bacillus was estimated by constructing the phylogenetic tree using Mega 6.0 software (Gouripur et al., 2016). Neighbor joining (NJ) algorithm was used for distance tree building and bootstrap value was set at 1000. The bootstrap value denotes to generation of new data sets with replacements.
Secondary structure prediction
Self optimized prediction method with alignment (SOPMA) and GOR IV tools were used for the analysis of secondary structure and results obtained from these tools were also compared to determine α- helix, β- sheet, turns and loops (Geourjon and Deleage, 1994; http://npsa-pbil.ibcp.fr/cgi-).
Tertiary structure prediction
The tertiary structure of proteins were constructed by using RaptorX structure prediction server, which provides high quality structural model by using the template of primary protein sequence (http://raptorx.uchicago.edu/StructurePrediction/predict/).
RESULTS
Sequence retrieval and alignment
The protein sequences of cellulase enzymes belonging to different strains of Bacillus sp. were retrieved from Uniprot and these sequences were then characterized using Uniprot tool (Table 1). It has been analyzed from data that the molecular weight of enzyme lies between 54,681 to 94,682 Da and they belong to endoglucanase, β-glucosidase and exoglucanase, respectively. Different types of cellulases shows different catalytic mechanism due to variation in multienzyme complex formation.
Thereafter,clustal omega software was used for multiple sequence alignment of these proteins (Fig.1). The cellulase sequences from species of Bacillus were found to be highly diverged at the N-terminal and C-terminal, respectively. However, conserved amino acid sequences with good similarity were found in the middle. The positions with absolute conservation are indicated with asterlink (*), whereas dots (.) represent the position of relative conservation.
Physicochemical characterization
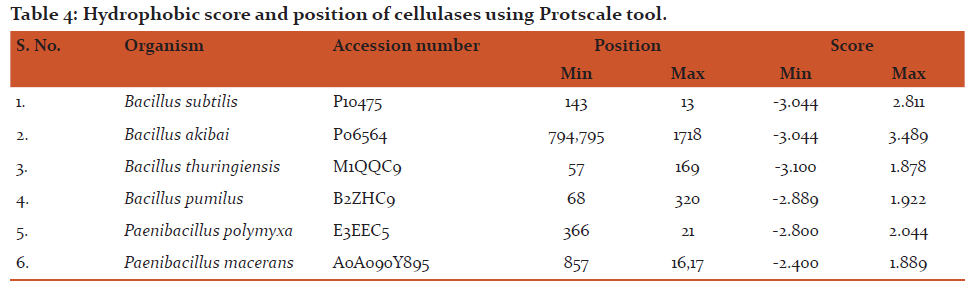
The results of physicochemical properties like pI, number of positive and negative amino acids, extinction coefficient, instability index, aliphatic index, grand average of hydropathicity and total number of atoms for cellulase from different different species of Bacillu sare shown in Table 2. The isolectric point (pI) is the pH value at which mobility of protein becomes zero with more compact and stable conformation. The pI value of cellulase from Bacillus subtilis is more than 7, which means it contains more number of negatively charged amino acids. Whereas, for all the other species of Bacillus, the pI was found to be less than 7 and their cellulases were acidic in nature containing more number of positive charge residues. Expasy’s Prot Param can compute the extinction coefficient for a range of 276, 278, 279, 280 and 282, however 280 nm is more preferred because proteins absorb this wavelength more strongly with minimum interference from other substances. Cellulases from all the selected Bacillus sp. were found to be stable with instability index less than 40. The GRAVY value is negative for all the cellulase sequences and this has showed better possibilities of aqueous interactions. The total number of atoms in different cellulases ranging from 7717 to 13113.The comparison of amino acid composition (%) in different cellulase sequences was also carried out (Table 3) and different amino acids were found to be dominant in different sequences. Protscale tool was used for the construction of Kyte and Doolittle hydropathy plots (Fig.2) and transmembrane region of cellulase from different Bacillus sp. was found to be rich in hydrophobic amino acids as many points lie above the zero baseline. The minimum and maximum hydrophobic position and score for each cellulase sequence was also predicted (Table 4) with minimum and maximum score of -3.100 and3.489, respectively.???????
Phylogenetic analysis
Mega 6.0 software, which provides a subset of substitution model and neighbor joining algorithm for distance tree building, was used for the construction of phylogenetic tree (Fig. 3). Cellulases from Bacillus subtilis P10475, Bacillus pumilus B2ZHC9, Paenibacillus polymyxa E3EEC5, Paenibacillus macerans A0A090Y895 were found to be closely related compared to Bacillus akibai P06564 and Bacillus thuringiensis M1QQC9, which were diverged from many species of Bacillus.
Secondary structure prediction
The secondary structure of different cellulase sequences was estimated using GOR IV and SOPMA tools, the percentage of α-helix, extended strand and random coils incellulase from different Bacillus sp. are shown in Table 5. The presence of amino acid in the helix, strand or coil is depicted from the secondary structure (Ojeiru et al., 2010) and secondary structure of cellulase was depicted by SOPMA (Pradeep et al., 2012). From the results, it has been observed that alpha helix was dominant in Bacillus pumilus B2ZHC9 (46.52%), whereas extended strand and random coil was observed to be dominant in Bacillus subtilis P10475 (26.45%) and Paenibacillus polymyxa E3EEC5 (44.91%), respectively.
Tertiary structure prediction
The tertiary structures of different cellulase sequences were analyzed using RaptorX structure prediction server, which results in modelling of a protein in a step wise manner like template threading, alignment quality assessment and multiple template threading. Different sequences of cellulases showed variability in α-helix, extended strand in β ladder, hydrogen bonded turn, bend and coil (Fig. 4). A high degree of variation was found in the geometric shape and interaction between side chains of amino acids, which lead to differences in their functions.???????
DISCUSSION
The present study showed the industrial importance of cellulases in different sectors such as textile, laundry, bioethanol production, brewing, detergent, waste management, paper and pulp. There are different types of cellulases with different catalytic subunits which are involved in complete hydrolysis of cellulose. In silico studies are very promising tools in the current era for the characterization of industrially important enzymes for various properties for their selection for appropriate industrial application. The different types of cellulases from Bacillus sp. were studied for comparing their physicochemical characteristics, ancestral relationship and structure prediction at different levels. Various computational tools were used for the characterization of cellulases from different Bacillus sp. A great degree of diversity has been observed in molecular weight, family, domain, number of amino acids, positive and negative charged residues, secondary and tertiary structure between the different forms of cellulases. The phylogenetic analysis also showed the ancestral divergence of difference types of cellulases. This study will be helpful for the selection of industrially important bacterial strain with desirable characteristics for particular industrial processes. Moreover, this information can also be useful for designing new microbial strains by applying proteomics, system biology and microarray based strategies. Further, wet lab studies with reduced labour are required to design novel cellulase producing bacterial strains by using in silico data output.
CONCLUSIONS
The present study concludes that cellulases are industrially important enzymes due to their ability to utilize agricultural wastes for the production of industrially important products. In recent years, various researchers have adapted genetic engineering approach to develop novel microbial strains with enhanced enzyme producing ability. However, such processes are very tedious and time consuming, which is the major obstacle for adapting such processes for commercial enzyme production. Such limitations can be overcome by initial screening through in silico studies to understand the structure, function and physicochemical properties of the enzyme. These computational studies would be promising tool to design enzymes with desirable characteristics for exploiting them at industrial level.
Conflict of interest: There is no conflict of interest between the authors regarding the publication of this article.
Acknowledgements: The authors acknowledge the immense help received from the scholars whose articles are cited and included in references of this paper. The authors are grateful to al authors/ editors/ publishers of all those articles, papers, journals and books from where the literature for this article has been reviewed and discussed.









References:
- Bjellqvust B, Hughes GJ, Pasquali C, Paquet N, Ravier F, Sanchez JC, Frutiger S, Hochstrasser D. The focusing positions of polypeptides in immobilized pH gradients can be predicted from their amino acid sequences. Electrophoresis 1993; 14(1):1023-1031.
- Geourjon C, Deleage G. 1994. SOPM: a self optimized method for protein secondary structure prediction. Protein Engineering 1994; 7(2):157-164.
- Gouripur GC, Kaliwa RB, B.B. Kaliwal BB. In silico characterization of beta-galactosidase using computational tools. Journal of Bioinformatics and Sequence Analysis 2016; 8(1):1-11.
- Guruprasad K, Reddy B, Pandit MW. Correlation between stability of a protein and its dipeptide composition: a novel approach for predicting in vivo stability of a protein from its primary sequence. Protein Engineering 1990; 4(2):155-164.
- Protein secondary structure prediction http://npsa-pbil.ibcp.fr/cgi- [Accessed on 15/03/2017].
- Protein tertiary structure prediction, http:// raptorx.uchicago.edu/ StructurePrediction/predict/ [Accessed on 12/03/2017].
- Physicochemical characterization of proteins http://www.expasy.org/tools/ [Accessed on 19/03/2017].
- Kumar NV, Rani ME, Gunaseeli R, Kannan ND, Sridhar J. Modeling and structural analysis of cellulases using Clostridium thermocellum as template. Bioinformation. 2012; 8(22):1105-1110.
- Lugani Y, Singla R, Sooch BS. Optimization of cellulase from newly isolated Bacillus sp. Y3. Journal of Bioprocessing and Biotechniques 2015; 5(11):1-6.
- Lynd LR, Weimer PJ, Zyl, WH, Pretorius IS. Microbial cellulase utilization: fundamentals and biotechnology. Microbiology and Molecular Biology Reviews 2002; 66(3):506-577.
- Maki M, Leung KT, Qin, W. The prospects of cellulase producing bacteria for the bioconversion of lignocellulosic biomass. International Journal of Biological Sciences 2009; 5(5):500-516.
- Ojeiru FE, Kazuya T, Yuki H, Mohammed SM, Shunsuke M. Circular dichroism studies on C-terminal zinc finger domain of transcription factor GATA-2. Yonago Acta medica 2010; 53:25-28.
- Patagundi BI, Shivasharan CT, Kaliwal BB. Isolation and characterization of cellulase producing bacteria from soil. International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences 2014; 3(5):59-69.
- Pradeep NV, Anupama, Vidyashree KG, Lakshmi P. In silico characterization of industrial important cellulases using computational tools. Advances in Life Science and Technology 2012; 4:8-14.
- Prashant VT, Uddhav SC, Madura SM, Vishal PD, Renuka RK. Secondary structure prediction and phylogenetic analysis of salt tolerant proteins. Global Journal of Molecular Sciences 2010; 5(1):30-36.
- Shankar T, Isaiarasu L. Cellulase production by Bacillus pumilus EWBCM1 under varying cultural conditions. Middle East Journal of Scientific Research 2011; 8(1):40-45.
- Umang M, Astha J, Aastha C, Neha A, Vibha R. Computational structural and functional characterization of protein family: Key for the hidden mystry. Journal of Pharmacy Research 2012; 5(7):3643-3649.
- Walker JM. The Proteomics Protocols Handbook: Humana Press, 2005, Chap. 52.
|






 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License