IJCRR - 9(13), July, 2017
Pages: 25-29
Date of Publication: 03-Jul-2017
Print Article
Download XML Download PDF
Biomonitoring of Soil Pollution Using Plants on Roadsides of Mysuru
Author: Prakruthi T. R., N. S. Raju
Category: General Sciences
Abstract:Soil pollution assessing capacity using plants with accumulative capacity has been studied. Plant samples were collected from roadsides of traffic and residential sites. The concentration of heavy metals and some physico chemical parameters were analyzed using ICP and standard methods. Correlations were attempted between physicochemical parameters and heavy metals in plants. The heavy metals concentration in soil was in the order Fe>Mn>Zn>Cr>Ni>Cu>Pb>Cd. The uptake of heavy metals by plants depends on the absorption capacity of plants. Calotropis procera showed highest absorption capacity followed by Mangifera indica, Cynodon dactylon, Solanum nigrum and Dalbergia sissoo.
Keywords: Heavy metals, Biomonitoring, Soil, M. indica, D. sissoo, C. procera, S. nigrum and C. dactylon
DOI: 10.7324/IJCRR.2017.9135
Full Text:
Introduction
The increase in pollution in urban areas is mainly due to traffic and industrial establishments. The extent of pollution can be assessed using plants with accumulative capacity. Plant leaf is the most sensitive part that gets affected by pollutants as major physiological processes of plants are concentrated in the leaf (Renjini and Janardhanan, 1989)1. Environmental monitoring using plants is very realistic and useful since it is not only cost effective but they also further assist man in planning the urban cities. The more success is achieved by using the specific plant as biomonitor. The importance and relevance of biomonitors rather than equipment is justified by the statement “There is no better indicator of the status of a species or a system than a species or a system itself. (Tingey and David T, 1989)2. Knowledge about plant uptake and soil levels of pollutants are necessary to interpret the results based on plant leaves. This necessitates the importance of understanding about the level of pollutants in soil. In such situation it is possible to know the capacity of the plants to absorb pollutants. In this study five plant species were selected and used to monitor soil pollution in roadsides of traffic and residential area of Mysore. The plants selected included M. indica, D. sissoo, C. procera, S. nigrum and C. dactylon.
M. indica belongs to the family Anacardiaceae. It is the most economic tropical fruit native to the foothills of Himalaya, Bangladesh and Burma. It grows to a height of 30-100ft and bear evergreen leaves with broad, rounded canopy. D. sissoo is also known as North Indian Rosewood and belongs to the family Fabaceae. It is a slow growing tree native to Indian Subcontinent and Southern Iran. It grows to a height of 82ft. C. procera is a large shrub belonging to family Apocynaceae and grows to a height of 3-6 ft. They are native to Western and Southern Asia, Africa and Indochina. S. nigrum is also known as black nightshade and belongs to the family Solanaceae. It is native to Eurasia and widely distributed in Asia, Africa, Europe, Australia and America. It is a short lived perennial shrub and grows to a height of 2-9ft. C. dactylon belongs to the family Poaceae and is native to Middle East. The leaves are grey green in color and can grow up to 2-15cm with rough edges. The stems are erect and can grow up to 1-30cm.
Materials and methods
Mysuru is the second largest city in Karnataka, India. It has spread across an area of 128.42 sq Km and is located at 12o181N 76o391E 12.30oN 76.65oE. Samples were collected at a distance of 0 to 3 mts from roads having high traffic density and from residential sides of Mysuru. Soil and plant samples of M. indica, D. sissoo, C. procera, S. nigrum and C. dactylon were collected in three different seasons; pre-monsoon, monsoon and post monsoon from roadsides of traffic and residential area of Mysuru. The soil samples were collected from the top 10 cm using stainless steel trowel around the plants which has been sampled. The soil samples collected from traffic area around five plants sampled were mixed together to get a composite soil sample and same has been done in the residential sides. The soil samples were air dried and passed through 2mm sieve and stored in self-sealing plastic bags for further analysis. In each area, leaves were collected from 5-10 plants of each species randomly, then samples of each species were mixed together to get a composite sample of the species and same has been done to all the other plants and packed in muslin bags. They were brought to the laboratory and washed with distilled water to remove adhering dust and extraneous particles. The plant samples were shade dried followed by oven drying at 65-700C for 48 hrs grounded using homogenizer (mixers). After grinding, the samples were mixed thoroughly and dried again at 700 C and passed through 1.5 mm sieve. These samples were stored in screw type plastic bottles for further use. Samples were analyzed for some physico chemical parameters using standard analytical procedures (APHA 2012). The heavy metal concentrations were detected using ICP-OES (Perkin Elmer Optima 8000).
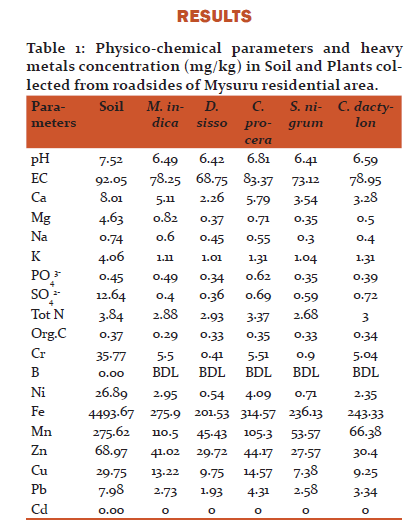
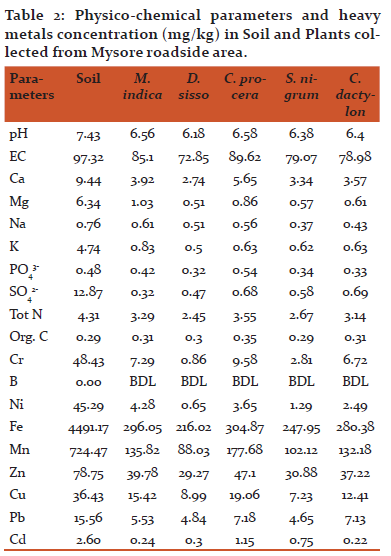
Discussion
Soil
Average pH and EC of soil samples collected from residential and traffic sites were 7.43 and 97.32dS/m, 7.52 and 92.05 dS/m respectively. Soil pH of both places was alkaline. The mean organic carbon concentration was 0.29% and 0.37 % in residential and traffic area respectively. The mean concentrations of some physico chemical parameters and heavy metals in residential and traffic area are given in the Table1 and Table2. Cadmium was absent in residential area soil samples and Boron was below detectable limit in both traffic and residential areas. The source of contamination of soil by heavy metals in roadsides of traffic area may be as a result of industrial activity and traffic density and also heavy metals are naturally present in the soil and are non-degradable (Nriagu 19903, Adeyeye 20054). The heavy metals concentration in soil was in the order Fe>Mn>Zn>Cr>Ni>Cu>Pb>C and higher as compared to plant samples.
PlantsPhysico chemical characteristics
Among Mysuru Residential area plants C. procera contains maximum pH and minimum was in S. nigrum. C. procera and D. sissoo showed maximum and minimum pH respectively in traffic area plants. EC was maximum in C. procera and minimum in D. sissoo in residential and traffic area. Mean Calcium content ranged from 2.26 mg/kg to 5.79 mg/kg and 2.74 mg/kg to 5.65 mg/kg respectively in residential and traffic area. Magnesium content ranged from 0.35 mg/kg to 0.85 mg/kg in residential and 0.51 mg/kg to 1.03 mg/kg in roadsides of traffic. Calcium and Magnesium were above recommended values (GKVK manual 2010)5 in all tested plants. Maximum absorption of Sodium was by C. procera and M. indica in residential and traffic area respectively and it was minimum in S. nigrum in both the places. Mean value of Potassium was 0.5 mg/kg to 1.31mg/kg and it was within the recommended values (GKVK manual 2010)5 in all tested plants. Phosphate was within recommended value (GKVK manual 2010)5 in all plants except C. procera in both residential and traffic areas. All the selected plants in both places showed high sulphate content i.e., above recommended value (GKVK manual 2010)5. Total Nitrogen content was within the prescribed limit (GKVK manual 2010)5 in the plants of both the places. The mean content of organic carbon was 0.29% to 0.35 % and 029% to 0.35 % in residential and traffic site plants respectively.
Heavy metals
Chromium is a toxic heavy metal emitted mainly by heavy traffic and also by burning of coal. Chromium content was above recommended values (GKVK manual 2010)5 in all plants. C. procera showed maximum content of chromium and D. sissoo showed minimum content in both areas. Boron was below detectable limit in all plants irrespective of place. Nickel, iron, manganese, zinc, copper and lead were within the limits in both places (Allen 19896, Kabata Pendias and Pendias19927, Kabata Pendias and Pendias19948, Kabata Pendias and Pendias 20019). Nickel mainly is derived from burning of coal. It is essential in minute quantity for the organisms and plays an important role in insulin production. It can be easily absorbed by the plants (Gunesetal 2004)10. Nickel content was minimum in D. sissoo in both the places. C. procera and M. indica showed maximum content in residential and traffic area plants respectively. Iron is one of the essential microelements for plants which are present in the earth crust naturally. But higher concentration of iron is toxic to plants. In both places Iron content was maximum in C. procera and minimum in D. sissoo. Manganese is also one of the essential microelements for plants. It is necessary for plants in all the stages of development and functions (Marschner 1995)11 and turns to toxic if it is present in excess amounts in the environment. M. indica and C. procera showed maximum content of manganese in residential and traffic area respectively. D. sissoo had minimum amount of manganese. Zinc is one of the essential elements for all living organisms which are very important for the biosynthesis of proteins and enzymes. But a high zinc concentration is toxic to plants (Zhao et al 2003)12. The main source of zinc is by human inputs, from smelting activities and sewage sludge. In all plants zinc absorption was within the prescribed limit (Kabata Pendias and Pendias1994)8. C. procera had higher amount of zinc while S. nigrum and D. sissoo had minimum amounts in both residential and traffic area. Copper is one of the essential microelements for plants. The main source of copper in soil is from traffic movement because it is produced by tire and broken shoe abrasion. C. procera showed maximum amount of copper in both places and S. nigrum had minimum amount of copper. Lead is the most toxic element for the living organisms. The main source of lead is vehicular emissions. Maximum amount of lead was observed in C. procera and minimum amount was in D. sissoo and S. nigrum in residential and traffic area. Cadmium is a highly toxic heavy metal to the living organisms. It is not needed by the plants and animals (Celik. A and A. Aslihan 2004)13. Cadmium was completely absent in all the plants of residential area. In traffic area plants it varied from 0.22 mg/kg to 1.15 mg/kg. In C. procera cadmium content was above recommended level (Kabata Pendias and Pendias1994)8 and other plants had within limits.
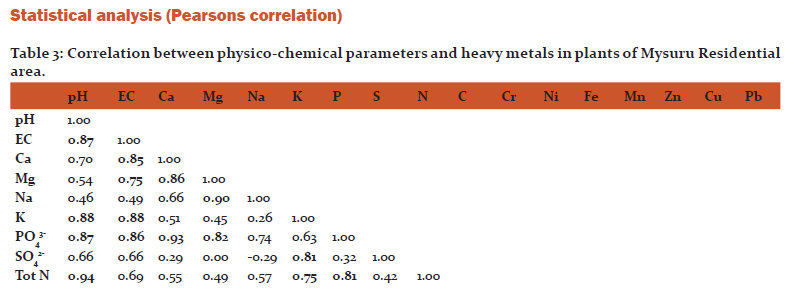
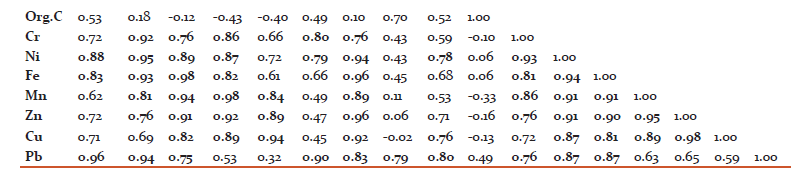
Statistical analysis of Mysore residential area plants showed that pH has highly positive correlation between EC, K, P, N, Ni and Fe while EC showed with Ca, Mg, K, P, Cr, Ni, Fe, Mn, Zn and Pb. Similarly Calcium showed correlations with Mg, P, Cr, Ni, Fe, Mn, Zn, Cu and Pb. Magnesium showed positive correlation with Na, P, Cr, Ni, Fe, Mn, Zn and Cu. Sodium showed positive correlation with Mn, Zn and Cu. Pottasium has correlation with S, N, Cr, Ni and Pb. Phosphate with N, Cr, Ni, Fe, Mn, Zn, Cu and Pb. Sulphur has positive correlation with Pb. Nitrogen with Ni, Cu and Pb. Chromium with Ni, Fe, Mn, Zn and Pb. Nickel has correlation with Fe, Mn, Zn, Cu and Pb. Iron with Mn, Zn, Cu and Pb. Manganese has positive correlation with Zn and Cu. Zinc and Cu also showed highly positive correlations.
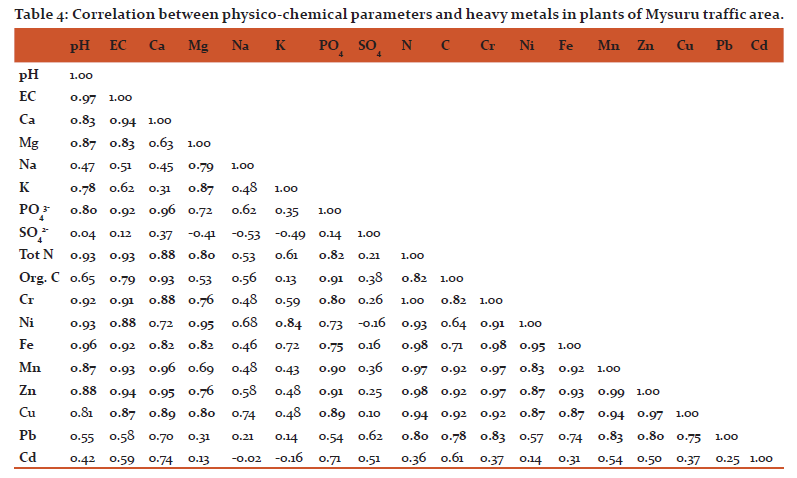
Statistical analysis of Mysore roadside plants showed that pH has highly positive correlation between EC, Ca, Mg, K, PO4, N, Cr, Ni, Fe, Mn, Zn and Cu while EC showed with Ca, Mg, PO4, N, C, Cr, Ni, Fe, Mn, Zn and Cu. Similarly Calcium showed correlations with PO4, N, C, Cr, Fe, Mn, Zn and Cu. Magnesium showed positive correlation with Na, K, N, Cr, Ni, Fe, Zn and Cu. Potassium has correlation with Ni; Phosphate with N, C, Cr, Fe, Mn, Zn and Cu. Tot Nitrogen with C, Ni, Fe, Mn, Zn, Cu and Pb. Org Carbon with Cr, Mn, Zn, Cu and Pb. Chromium with Ni, Fe, Mn, Zn, Cu and Pb. Nickel has correlation with Fe, Mn, Zn and Cu. Iron with Mn, Zn and Cu. Manganese has positive correlation with Zn, Cu and Pb. Zn with Cu and Pb. Cu and Pb also showed highly positive correlations.
Conclusion
The study showed that, plants can accumulate heavy metals and macro elements and thus they can be recommended to use as indicators to determine the pollution level in the environment. The main cause for the heavy metals concentration in plants on roadsides of traffic area may possibly due to the traffic density. In the present study C. procera showed highest absorption capacity followed by M. indica, C. dactylon, S. nigrum and D. sissoo. By increasing the number of plant species for testing purpose, it is possible to get better results for the absorption of different heavy metals and other elements by plants. A list of common sensitive plants, for using them routinely for monitoring environmental pollution can be prepared.
Acknowledgements
The author (T. R. Prakruthi) is thankful to DST, Ministry of Science and Technology, Government of India for providing financial assistance under INSPIRE Fellowship.
References:
- Rejini MBJ, Janardhana K. Effect of heavy metals on seed germination and early seedling growth of groundnut, sunflower and Ginger, Geobios, 16 : 164-170, 1989.
- Tingey, David T, Bioindicators in Air Pollution Research -- Applications and Constraints. Biologic Markers of Air-Pollution Stress and Damage in Forests. Washington, DC: National Academies Press, 1989: 73–80, 1989.
- Nriagu, J.O, Global metal pollution: Poisoning the biopher. Environment Envtar, 32 (9): 7-11, 28-33, 1990.
- Adeyeye, E.I., Trace metals in soils and plants from Fadama farms in Ekiti state, Nigeria, Bulletin of chemical Society of Ethiopia 19: 23-24, 2005.
- GKVK manual 2010
- Allen S.E. Analysis of Ecological materials, 2nd ed. Blackwell scientific publications, oxford 1989.
- Kabata – Pendias, A. and H. Pendias, Trace elements in soils and plants. Boca Raton, FL: CRC press, pp. 365, 1992.
- Kabata – Pendias, A and H. Pendias, Trace element in soil and plants, second edition. Boca Raton, Florida. CRC. PP: 365, 1994.
- Kabata – Pendias, A,;Pendias H., Trace elements in soils and plants. 3rd Ed., Crc Press Inc., Boca Ralon, Florida, USA, 2001.
- Gunes A, Alpaslan M, Inal A, Plant Growth and fertilizer. Ankara University. Agriculture Publications No: 1539, Ankara, 2004.
- Marschner, H,: Mineral Nutrition of Higher plants. Academic press, London, 1995.
- Zhao F J, Lombi E, McGraht S P, Assessing the potential for Zinc and cadmium phytoremediation with the hyperaccumulator Thlaspicaerulescens. Plant soil, 249: 37-43, 2003.
- Cleik, A. and A. Aslihan, Determining the heavy metal pollution in Denizli (Turkey) by using Robinia pseudo acacia L. 31 (1): 105-112, 2004.
- Alam A and Srivastava S.C. (2009): Marchantia Paleacea Bert – As an indicator of heavy metal pollution. Indian journal of Forestry 32 (3). 365-470.
- Alloway, b.j, Heavy metal in soils. Halsted press, John Wiley and sons Inc., London, 1996
- Bargagli, R., Trace elements in Terrestrial plants. An Ecophysiological Approach to Biomonitoring and Biorecovery. Springer verlag, Berlin, 1998.
- Bergman W, Nutritional Disorders of plants. Gustav Fischer, New York, 1992.
- Bonnet M, camares O, Veisseire P, Effect of Zinc and influence of Acremoniumlolli on growth parameters, chlorophyll a fluorescence and antioxidant enzyme activity of ryegrass. Exp Bot. 51: 945-953, 2000.
- Bowen HJM, Environmental chemistry of the elements. Academic press, New york, PP: 333, 1979.
- Chatterjee, J., Chatterjee, F, Phytotoxicity of chromium, cabalt and copper in cauliflour. Environmental pollution 109: 69-74, 2000.
- Ducic, T. and Apolle: Transport and detoxification of manganese and copper in plants. Braz J, Plant physiol., 17, 103-112,2005.
- Elekes, C.C., Dumitriu, I., Busuioc, G., Iliescu, N.S, The appreciation of mineral element accumulation level in some herbaceous plants species by ICP-AES method. Environmental Science and Pollution Research 17: 1230-1236, 2010.
- Ellen, S.E., Chemical analyses of ecological material, 2ndedn. Blackwell scientific, London, P. 367, 1989.
- Fleming G and Parle P, Heavy metals in soils, herbage and vegetables from an industrialized area west of Dublin city. Irish Journal of Agricultural research 16, 35-48, 1977.
- Lindroos, A.J, J. Derome, H. Raitio and P. Raution: Heavy metal concentration in soil solution, soil and needles in a Norway spruce stand on an acid sulphate forest soil. Water Air Soil Pollution. 180, 155-170, 2007.
- M. Miclean, M. Senila, C. Roman. T. Frentie, E. Cordor, Plant uptake factors for 55 elements in a rural mining area, NW Romania, metal elements in Environment, Medicine and Biology, 162-165, 2009.
- Madyon p, Murillo JM, Maranon T, Cabrera F, Lopez R, Bioaccumulation of As, Cd, Cu, Fe and Pb in wild grasses affected by the Aznalcollar mine spill (Sw Spain). The Science of the Total Environment 290, 105-120, 2002.
- Markert, B, Plant as biomoniotors / Indicators for heavy metals in the terrestrial environment – weinbeim VCH. Press: 670. White poplar (Popular alba) as a biomonitor of trace element in contaminated riparian forest. Environ. Pollution, 132: 145-155, 1993.
- Markert, B.A, Breure A.M, Zechmeister, H.G, Definitions, strategies and principles for bioindication / biomonitoring of the environment. Elsevier Science Ltd, 2003.
- Pilgrim, W. Hugher, R.N, Lead, cadmium, arsenic and Zinc in the ecosystem surrounding a lead smelter. Environmental monitoring and Assessment 32, 1-20, 1994.
- Prasad, M.N.V., Freitas, H.M.O, Metal hyperaccumulation in plants – Biodiversity prospecting for phytoremediation technology. Electronic Journal of Biotechnology 6 (3): 285-321, 2003.
- Ross, S.M, Toxic metals in soil-plant systems John wiley and sons, chichester, 1994.
- Sesli, M: A study of lead contamination in tobacco leaves sampled from alongside motor road in the rapidly industrializing city of Manisa, Turkey J. Biological Sci., 4, 768-770, 2004.
- Wittig, R, General aspects of biomonitoring heavy metals by plants. In: Plants as Biomonitors / Indicators for Heavy metals in the Terrestrial environment. Markert B., VCH publisher, Weinheim, 3-28, 1993.
- Wright D.A, welbroun, P, Environmental Toxicology Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, 2002.
|






 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License