IJCRR - 4(20), October, 2012
Pages: 26-32
Date of Publication: 20-Oct-2012
Print Article
Download XML Download PDF
STUDIES ON THE YIELDS OF ROSE (ROSA) AND HIBISCUS (ROSAINENIS) FLOWERS IRRIGATED BY DISTILLERY SPENT WASH
Author: S. Chandraju, C. Thejovathi, C. S. Chidan Kumar
Category: General Sciences
Abstract:Yields of Rose (Rosa) and Hibiscus (Hibiscus rosasinenis) flowering plants were made by irrigated with distillery spent wash of different concentrations. The spent wash i.e., primary treated spent wash (PTSW), 1:1, 1:2, and 1:3 spent wash were analyzed for their plant nutrients such as nitrogen, phosphorous, potassium and other physical and chemical characteristics. Experimental soil was tested for its chemical and physical parameters. Rose and Hibiscus sets were planted in different pots (50 cm ht and 30 cm dia) and irrigated with raw water (RW), 1:1, 1:2 and 1:3 spent wash. The nature of yields of flowers was studied at their maturity. It was found that the yields of both flowers plants was very good (100%) in 1:3 SW irrigation, while very poor (25%) in 1:1 SW, moderate (80%) in 1:2 SW and 95% in RW irrigation growth. Soil was tested after harvest of flowers found no adverse effect on soil characteristics. This concludes that the diluted spent wash serves as an eco-friendly in irrigation medium.
Keywords: Distillery spent wash, Rose, Hibiscus, Yields, Irrigation, Soil.
Full Text:
INTRODUCTION
Rose (Rosa) belongs to Rosaceae family. Roses have a long storied history1 . The Chinese and Egyptians are thought to have first cultivated roses, around 5000 years’ ago. Selecting plants on the basis of flower color. During the middle Ages, monks and apothecaries grew roses for their medicinal value 2, 3, 4. The rose has been valued for its beauty and fragrance and has a long history of symbolism and meaning. Rose5 is the national flower of England and the United States, and the state flower of US states. The leaves most rose species are 5-15cm long, pinnate, with (3, 5, 9 and 13) leaflets and basal stipules the leaflets usually have a serrated margin and often a few prickles on the undesirable of the stem. Roses are of great economic importance, both as a crop for florists use and for use in perfumes. They also have minor medicinal uses. Rose perfumes are made from attar of roses are rose oil which is a mixture of volatile essential oils obtained by steam distilling the crushed petals of roses. Hibiscus (Hibiscus rosasinenis) tropical flower, it belongs the family Malvaceae. It gets its name from the Greek words. Hibiscus meaning mallow and rosa-sinessis, meaning rose of China6 . Hibiscus flower are used by malayas as a food dye in cooking toddy, agar-agar, jellies, pineapple slices and cooked vegetables7 . A juice drink made of hibiscus flowers was developed and is marketed together by the Malaysian, Agricultural Research and Development Institute. A decoction of hibiscus roots was offered, in Malaya traditional healing for the relief of venereal diseases and fever. This flower decoction was drunk as an antidote to poison. A preparation from the roots was used as eye drops for sore eyes8 . Molasses (one of the important byproducts of sugar industry) is the chief source for the production of ethanol in distilleries by fermentation method. About 08 (eight) liters of wastewater is generated for every liter of ethanol production in distilleries, known as raw spent wash (RSW), which is known for high biological oxygen demand (BOD: 5000-8000mg/L) and chemical oxygen demand (COD: 25000- 30000mg/L), undesirable color and foul odor9 . Discharge of RSW into open field or nearby water bodies’ results in environmental, water and soil pollution including threat to plant and animal lives. The RSW is highly acidic and contains easily oxidisable organic matter with very high BOD and COD10. Also, spent wash contains high organic nitrogen and nutrients11. By installing biomethenation plant in distilleries, reduces the oxygen demand of RSW, the resulting spent wash is called primary treated spent wash (PTSW) and primary treatment to RSW increases the nitrogen (N), potassium (K), and phosphorous (P) contents and decreases calcium (Ca), magnesium (Mg), sodium (Na), chloride (Cl - ), and sulphate (SO4 2- ) 12. PTSW is rich in potassium (K), sulphur (S), nitrogen (N), phosphorous (P) as well as easily biodegradable organic matter and its application to soil has been reported to increase yield of sugar cane, rice13, wheat and rice, Quality of groundnut14 and physiological response of soybean15,. Diluted spent wash could be used for irrigation purpose without adversely affecting soil fertility16, 17, 18, seed germination and crop productivity19. The diluted spent wash irrigation improved the physical and chemical properties of the soil and further increased soil micro flora20; twelve presowing irrigations with the diluted spent wash had no adverse effect on the germination of maize but improved the growth and yield21. Diluted spent wash increases the growth of shoot length, leaf number per plant, leaf area and chlorophyll content of peas22. Increased concentration of spent wash causes decreased seed germination, seedling growth and chlorophyll content in Sunflowers (Helianthus annuus) and the spent wash could safely used for irrigation purpose at lower concentration. The spent wash contained an excess of various forms of cations and anions, which are injurious to plant growth and these constituents should be reduced to beneficial level by diluting spent wash, which can be used as a substitute for chemical fertilizer23. The spent wash could be used as a complement to mineral fertilizer to sugarcane24. The spent wash contained N, P, K, Ca, Mg and S and thus valued as a fertilizer when applied to soil through irrigation with water25. The application of diluted spent wash increased the uptake of Zinc (Zn), Copper (Cu), Iron (Fe) and Manganese (Mn) in maize and wheat as compared to control and the highest total uptake of these were found at lower dilution levels than at higher dilution levels. Mineralization of organic material as well as nutrients present in the spent wash was responsible for increased availability of plant nutrients. Diluted spent wash increase the uptake of nutrients, height, growth and yield of leaves vegetables26, 27, nutrients of cabbage and mint leaf, nutrients of top vegetables, pulses28, condiments, root vegetables and yields of condiments29, 30, 31 , yields of some root vegetables in untreated and spent wash treated soil132 33, yields of top vegetables (creepers), yields of tuber/root medicinal plants34, 35, yields of leafy medicinal plants, nutrients of creeper medicinal plants36 , yields of leafy medicinal plants in normal and spent wash treated soil nutrients uptake of herbal medicinal plants in normal and spent wash treated soil,nutrients of leafy medicinal plants nutrients of ginger and turmeric in normal and spent wash treated soil nutrients of tubers/roots medicinal plants37 . However, no information is available on the studies of distillery spent wash irrigation on the yields of Rose and Hibiscus flowering plants irrigated by distillery spent wash. Therefore, the present investigation was carried out to study the influence of different concentration of spent wash on the yields of Rose and Hibiscus flowers.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Physico-chemical parameters and amount of nitrogen (N), potassium (K), phosphorous (P) and sulphur (S) present in the primary treated diluted spent wash (1:1, 1:2 and 1:3 SW) were analyzed by standard methods38 . The PTSW was used for irrigation with a dilution of 1:1, 1:2 and1:3. A composite soil sample collected prior to spent wash irrigation was air-dried, powdered and analyzed for physico-chemical properties39-44 . Flowering plants selected for the present investigation were Rose and Hibiscus. The sets were planted in different pots 50cm(h), 30cm (dia)] and irrigated (by applying 5-10mm/cm2 depends upon the climatic condition) with raw water (RW), 1:1 SW, 1:2 SW and 1:3 SW at the dosage of twice a week and rest of the period with raw water as required. Trials were conducted in triplicate; in each case yields of flowers were recorded.
RESULTS
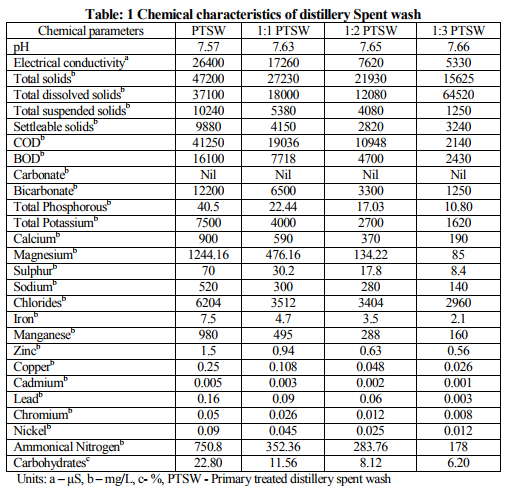
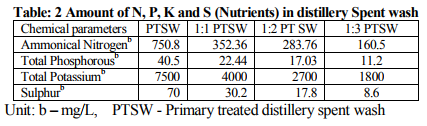
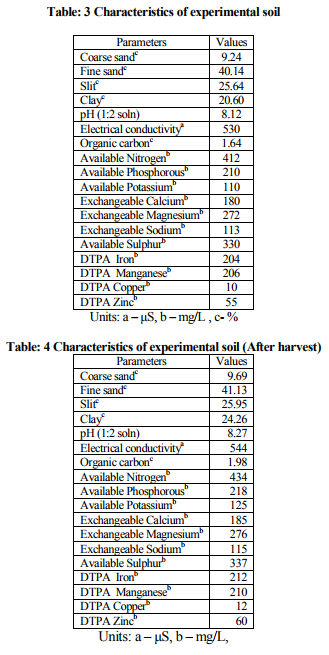
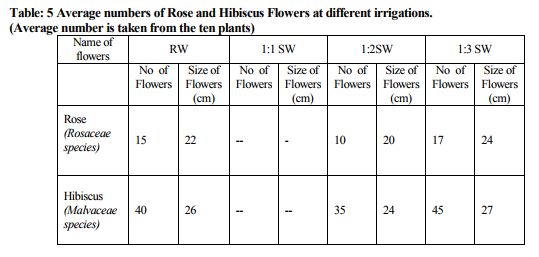
Chemical composition of PTSW, 1:1, 1:2, and 1:3 SW such as pH, electrical conductivity, total solids (TS), total dissolved solids (TDS), total suspended solids (TSS), settelable solids (SS), chemical oxygen demand (COD), biological oxygen demand (BOD), carbonates, bicarbonates, total phosphorous (P), total potassium (K), ammonical nitrogen (N), calcium (Ca), magnesium (Mg), sulphur (S), sodium (Na), chlorides (Cl), iron (Fe), manganese (Mn), zinc (Zn), copper (Cu), cadmium (Cd), lead (Pb), chromium (Cr) and nickel (Ni) were analyzed and tabulated (Table-1). Amount of N, P, K and S contents are presented (Table-2). Characteristics of experimental soils such as pH, electrical conductivity, the amount of organic carbon, available nitrogen (N), phosphorous (P), potassium (K), sulphur (S), exchangeable calcium (Ca), magnesium (Mg), sodium (Na), DTPA iron (Fe), manganese (Mn), copper (Cu) and zinc (Zn) were analyzed and tabulated (Table-3). It was found that the soil composition is fit for the cultivation of plants, because it fulfils all the requirements for the growth of plants. It was found that the yields of both flowers was very good (100%) in 1:3 SW irrigation, while very poor (25%) in 1:1 SW, moderate (80%) in 1:2 SW and 95% in RW irrigation growth.
DISCUSSION
Yields of Rose (Rosa) and Hibiscus (Hibiscus rosasinenis) flowers were very good in both 1:2 and 1:3 spent wash as compared to 1:1 SW and raw water. Irrigations (Table-5). This could be due to more absorption of plant nutrients (NPK) present in spent wash by plants at higher dilutions. No external fertilizer (either organic or inorganic) was required for the cultivation of plants and also it reduces the cost of cultivation. It was also found that no negative impact of heavy metals like lead, cadmium and nickel on the leaves of Rose and Hibiscus plants. The soil was tested after the harvest; found that there was no adverse effect on soil characteristics (Table-4).
CONCLUSION
It is found that the yields of both flowers were largely influenced in case of 1:2 and 1:3 SW irrigations than with 1:1 SW and raw water. In the case of 1:1 SW irrigation, the plant sporting was very poor, this could be due to the formation of thick layer of spent wash on the surface of the soil, which makes the mask on the sets.. But 1:3 SW irrigation shows more uptakes of nutrients when compared to 1:2 SW in both plants. This could be due to the maximum absorption of nutrients by plants at more diluted spent wash. After harvest, soil was tested; found that there was no adverse effect on characteristics. Since external application of fertilizer (either organic or inorganic) was not required for the cultivation of plants by spent wash irrigation media, this minimizes the cost of cultivation and elevates the economy of growers. Also spent wash serves as liquid fertilizer, non pollutant, and eco-friendly irrigation medium. Hence the spent wash can be conveniently used for irrigation purpose with required dilution without affecting environment and soil.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENT
Authors are grateful to The General Manager, N.S.L. Koppa, Maddur Tq., Karnataka, for providing spent wash. Authors also acknowledge the immense help received from the scholars whose articles are cited and included in references of this manuscript. The authors are also grateful to authors / editors / publishers of all those articles, journals and books from where the literature for this article has been reviewed and discussed.
References:
1. Rose plant Britanica.com 2007-11-19.
2. Mabberley, DJ (1997), the plant book, a portable dictionary of the vascular plants. Cambridge university press. Cambridge.
3. Activities and ground nut quality. Journal of Plant Nutrition and soil Science, 166:345-347.
4. Argon, Madison, Wisconsin, USA, pp. 15-72.
5. Rose (Plant) – Britannica online Encyclopedia. Britannica.com.2007-11-19. Retrieved 2009-12- 07.
6. Lawton, Barbara Perry (2004), Hibiscus: Hardy and Tropical plants for the Garde.Timber press p, 36,ISBN 9780881926545
7. Nation’s Restaurant News Hibiscus blossoms as a food drink ingredient.
8. Plants for a future: Hibiscus rosa-Sineasis accessed 07-05-2009.
9. Joshi HC, Kalra N, Chaudhary A, Deb DL (1994). Environmental issues related with distillery effluent utilization in agriculture in India, Asia Pac J Environ. Develop, 1: 92-103.
10. Patil JD, Arabatti SV, Hapse DG (1987). A review of some aspects of distillery spent wash (vinase) utilization in sugar cane, Bartiya sugar May, 9-15.
11. Ramadurai R, Gerard EJ (1994). Distillery effluent and downstream products, SISSTA,Sugar Journal. 20: 129-131.
12. Mohamed Haroon AR, Subash Chandra Bose M (2004). Use of distillery spent wash for alkali soil reclamation, treated distillery effluent for fertile irrigation of Crops. Indian Farm, March, 48- 51.Oxford English Dictionary.
13. Deverajan L, and Oblisami G, (1995). Effect of distillery effluent on soil fertility Status, yield and quality of rice. Madrass Agricultural Journal, 82: 664-665.
14. Amar BS, Ashik B, Sivakoti R (2003). Effect of Distillery effluent on plant and soil enzymatic.
15. Ramana S, Biswas AK, Kundu S, Saha JK, Yadava RBR (2000).Physiological response of soybean (Glycine max L.) to foliar application of Distillery effluent. Plant Soil Research 2: 1-6.
16. Kaushik K, Nisha R, Jagjeeta K, Kaushik CP (2005). Impact of long and short term irrigation of a sodic soil with distillery effluent in combination with Bio-amendments. Bioresource Technology, 96. (17): 1860-1866.
17. Kuntal MH, Ashis K, Biswas AK, Misra.K (2004). Effect of post-methanation effluent on soil physical properties under a soybean-wheat system in a vertisol. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Soil Science. 167(5): 1860-1866.
18. Raverkar KP, Ramana S, Singh AB, Biswas AK, Kundu S (2000). Impact of post methanated spent wash (PMS) on the nursery raising, biological Parameters of Glyricidia sepum and biological activity of soil. Ann. Plant Research, 2(2): 161- 168.
19. Ramana S, Biswas AK, Kundu S, Saha JK, Yadava RBR (2001). Effect of distillery effluent on seed germination in some vegetable crops. Bio-resource Technology, 82(3):273-275.
20. Devarajan L, Rajanna G, Ramanathan G, Oblisami G (1994). Performance of field crops under distillery effluent irrigations, Kisan world, 21: 48-50.
21. Singh Y, Raj Bahadur (1998). Effect of application of distillery effluent on Maize crop andsoil properties. Indian J.Agri. Science, 68: 70-74.
22. Rani R, Sri Vastava MM (1990). Ecophysiological response of Pisum sativumand citrus maxima to distillery effluents. Int. J. of Ecology and Environ. Science, 16-23.
23. Sahai R, Jabeen S, Saxena PK (1983). Effect of distillery waste on seed germination, seedling growth and pigment content of rice. Indian Journal of Ecology, 10: 7-10.
24. Chares S (1985). Vinasse in the fertilization of sugarcane. Sugarcane, 1, 20.
25. Samuel G (1986). The use of alcohol distillery waste as a fertilizer, Proceedings of International American Sugarcane Seminar.245-252.
26. Chandraju S, Basavaraju HC, (2007). Impact of distillery spent wash on Seed germination and growth of leaves Vegetables: An investigation. Sugar Journal (SISSTA). 38: 20-50.
27. Chandraju S, Siddappa and Chidan Kumar CS (2011). Studies on the germination and growth of Mustard and aster seeds irrigated by distillery spent wash, Bio-research bulletin5:110.
28. Joshi HC, Chaudhary A, Chaudhary R, Kalra N, Dwivedi MK (1998). Distillery effluent as soil amendment for wheat and rice. Journal of Indian Society for Soil Science. 46: 155-157.
29. Chandraju S, Thejovathi C, Chidan Kumar CS (2011). Sprouting and Growth studies ofRose and Hibiscus flowering plants irrigated by distillery spent wash. PlantBiology,1(2).
30. Chandraju S, Thejovathi C, Chidan Kumar CS (2011).Studies on the Germination and Growth of Zinnia and Vinca seeds irrigated by Distillery spent wash. SISSTA.
31. Chandraju S, Thejovathi C, Chidan Kumar CS, (2011). Studies on the Sprouting and Growth of Gardenia seeds irrigated by Distillery spent wash.J.Chem.Pharm.Res,, 3(5):376-381.
32. Chidan Kumar CS, Chandraju S, and Nagendraswamy R (2009). Impact of distillery spent wash on the yields of some top vegetables (creepers); An Investigation, World. Appl. Sci. Jour. 6(9): 270-1273.
33. Chidan Kumar CS, and Chandraju S, (2009). Impact of distillery spent wash irrigation on the yields of some condiments; An Investigation, Sugar. Tech. 11(3):303-306.
34. Collins RA, Ng TB Fond wp, Wan CC, Yeung HW (1997). “A comparison of humano deficiency virus type1 inhibition by partially purified aqueous extracts of Chinese medicinal. Herbs”, Life sciences 60(23):PL345-51.
35. Chen K, Shiq MUC, Kikuskie RE, Cheng YC, Lee KH (January 1994). Anti-AIDS agents.
36. Chandraju S, Siddappa and Chidan Kumar CS (2011). Studies on the germination and growth of Cotton and Groundnut seeds irrigated by distillery spent wash, current Botony 2(3):38-42.
37. Sassi AB, Harzallah-Skniri F, Bourgoughom N, Ao uni M (February 2008).
38. Manivasakam N, (1987). Phisico-chemical examination of water, sewage and Industrial Effluent. Pragathi Prakashan, Merut.
39. Jackson ML, (1973). Soil Chemical Analysis. Prentice Hall of India Pvt.Ltd., New Delhi,P.
40. Lindsay WL and Norvel WA (1978). Development of DTPA soil test for Zn, Fe, Mn,and Cu. Soil Science. Soc.Am., J., 42:421- 428.
41. Piper CS, (1966). Soil and Plant Analysis, Han’s Publication, Bombay.
42. Subbiah BV, and Asija CL (1956). A rapid procedure for the estimation of Available nitrogen in Soils. Curr.Sci., 25: 259-260.
43. Walkley AJ and Black CA (1934) .An examination of the method for determining soil organic matter and proposed modification of the chromic acid titration method. Soil Sci., 37: 29- 38.
44. Wolveton Rebecca BC, Donald CMC, and Watkins EA, Jr.Retrieved 2007.
|






 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License