IJCRR - 4(20), October, 2012
Pages: 07-14
Date of Publication: 20-Oct-2012
Print Article
Download XML Download PDF
ISOLATION OF CELLULOSE DEGRADING BACTERIA AND YEASTS FROM PINEAPPLE WASTE
Author: Catherine G., Vanitha N.M.
Category: General Sciences
Abstract:There's a current interest in the economic conversion of renewable resources into industrially useful products. For this a large number of agriculture wastes have been harnessed.. Of this pineapple waste is one of them. The ability of different bacterial and yeast strains isolated from ripe pineapple peels waste to degrade cellulose from pineapple wastes was investigated by assessing cellulose decomposition by the method of cellulose Congo red agar media hydrolysis capacity (HC-value). Of the 8 isolates screened for their fermentation ability, 6 showed enhanced performance and were subsequently identified and assessed for cellulose degradation and amounts of glucose produced. Solid state fermentation was carried out in flasks containing pineapple peel waste and pulp wastes as substrates and inoculums of 10% size was cultured in a rotary shaker at a pH of 4.5 and at temperatures ranging from 220 C, 270C, 320C and 350C for 21 days. Cellulose degradation and amounts of glucose produced by 4 test organisms and 1 positive organism in both peel and pulp of pineapple was determined. The highest amount of cellulose degradation and glucose formation was produced by the bacterial isolate PPP04 for peel waste and the yeast isolate YP02 for pulp waste. The present study was undertaken to identify bacteria and yeasts which could degrade cellulose and that which could be used for their degrading ability for commercial production of ethanol and vinegar.
Keywords: cellulose, pineapple wastes, isolates, fermentation, substrates.
Full Text:
INTRODUCTION
Cellulose is a polymer of glucose and is the most abundant organic material in nature. It is however resistant to decomposition. A large number of bacteria, fungi and actinomycetes are known to degrade cellulose. The substrates of compost with primary components of plant material such as cellulose, hemicelluloses and lignin are rather difficult to biodegrade and reduce the availability of other polymers by means of a physical restriction (Ladisch et al., 1983). Several methods for enumerating cellulose utilizing microbes have been described which include liquid media (Smith, R E, 1977) and solid media (Teather and Wood, 1982) for quantification of cellulose utilizing bacteria. Pineapple waste, consisting mainly of cellulose and starch, was suggested as a substrate for production of valuable fermentation and non fermentation products (Tewari et al.1987). In the past, pineapple waste from canneries has been utilized as substrate for bromelin, vinegar, wine, food /feed and organic acid (Dev and Ingle, 1982). Various strains of indigenous yeasts capable of producing ethanol have been isolated from different local sources such as molasses (Rose, 1976), sugar mill effluents (Anderson et al., 1986), local fermented foods (Ameh et al., 1989) and fermented pineapple juice (Eghafona et al., 1999). Pineapple (Ananas comosus) is one of the commercially important fruit crops of India.
Total annual world production is estimated at 14.6 million tonnes of fruits. India is the fifth largest producer of pineapple with an annual output of about 1.2 million tones. (Database of National Horticulture Board, Ministry of Agriculture, Govt. of India, 2002). The objective of present study is therefore to study the potential of cellulose degrading bacteria and yeast on Pineapple wastes, isolated from pineapple peel.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Source of Pineapple fruit
For isolation of microorganisms, Pineapple fruit wastes were obtained from the dump yard of Kalsipalyum, K R Market, Bangalore, while for fermentation, ripe Pineapple fruit was procured from hopcoms, a common vegetables and fruits outlet of Lalbagh Farmers Association, Bangalore. The pineapple fruit wastes from the dump yard were used within 24hrs after collection. When the peels could not be used, they were stored in the refrigerator to prevent deterioration. However, the stored fruit peels were used within 48 hrs.
Isolation of microorganisms from pineapple peel
1g of rotting pineapple peel was serially diluted and plated on two different media viz., a. Nutrient agar and b. Saborauds’s Dextrose agar, using pour plate technique described by Madigan et al., (1997). All the plates were incubated at 300C, for 24 – 48 hrs for bacteria and yeast. Growth of bacteria on SDA was avoided by the addition of 0.003% (w/v) of the antibiotic – streptomycin sulphate. Similarly growth of fungus on nutrient agar was avoided by the addition of 0.004% (w/v) of the antibiotic –actidione (cyclohexamide).
Characterization and Identification
This has been done using procedures described for bacteria and Barnett et al (1983) for fungi and yeast. The identification parameters included – morphological characterization of each isolate that included: color, size, colony characteristics microscopic features like gram staining for bacteria, simple staining for yeasts. The bacterial isolates were further subjected to biochemical tests like IMViC and carbohydrate fermentation which included sugars such as glucose, sucrose, maltose and lactose. This was done to prove the isolates as bacteria.
Maintenance of bacterial and yeast isolates
From the bacterial isolates only the bacterial rods were chosen and further maintained on enrichment media consisting of yeast extract- 0.1% (v/v), peptone-0.5% (v/v), CaCO3 -0.2% (v/v), NaCl0.12% (v/v). The yeast strains were maintained on SDA slants.
Assessment of bacteria and yeasts for attributes of Cellulose degradation
Each bacterial and yeast isolate were further screened by using pure cellulose powder of Himedia grade. For assessing cellulose hydrolysis by the method of carboxymethylcellulose hydrolysis capacity (HC-value), by growing each isolate on the cellulose Congo-red agar medium by streak plate technique, i.e., the ratio of diameter of clearing of zone around the colony (Hankin and Anagnostakis, (1977); Hendricks et al., (1995); Reese et al (1950). The isolates with HC values were selected and maintained on the respective maintenance medium. A positive cellulose degrading bacteriaCellulomonas. uda, NCIM no. 2353, ATCC no. 21399 and an yeast – Saccharomyces. cerevisiae.var.ellipsoides NCIM no. 3494, ATCC no. 24702 was procured from NCL, Pune; and used as standard organism ie., to compare the cellulose degrading activity with that of the isolates.
Pretreatment of Pineapple peel and pulp for fermentation activity
The pineapple was skinned off the peel using a knife that was disinfected with 70% ethanol. The waste substrates used in the study were pineapple peel and pineapple pulp. Both of which were fermented separately with different isolates.
2.7 Processing Specific quantity of Pineapple peel, 100g was taken and mixed with hot sterilized distilled water of equal quantity and mashed in an electric blender to obtain a semisolid mixture. About 200ppm of potassium meta- bi- sulphite was added to further kill away any local micro-flora of the pineapple peel. Similarly, pineapple pulp mash was also prepared by the above mentioned process. Various parameters such as initial cellulose content, Brix content, pH, titrable acidity and volatile acidity were noted before introducing the peel mash and the pulp mash separately into sterilized 250 ml reagent bottles. Three bacterial isolates and the standard organism were then inoculated separately into the peel mash. Similarly four yeast isolates and one standard yeast were inoculated into the pineapple pulp mash. A constant pH of 4.5 was maintained in all the reagent bottles. The organisms were then incubated at four different temperatures viz., 220C, 270C, 320C and 350C. Estimation of Cellulose and glucose content in the pineapple peel and pulp were estimated after 21 days of incubation by anthrone method, Hedge and Hofreiter (1962) and by DNS method, Miller, G.L. (1959), respectively.
RESULTS
Isolation of microorganisms from pineapple peel
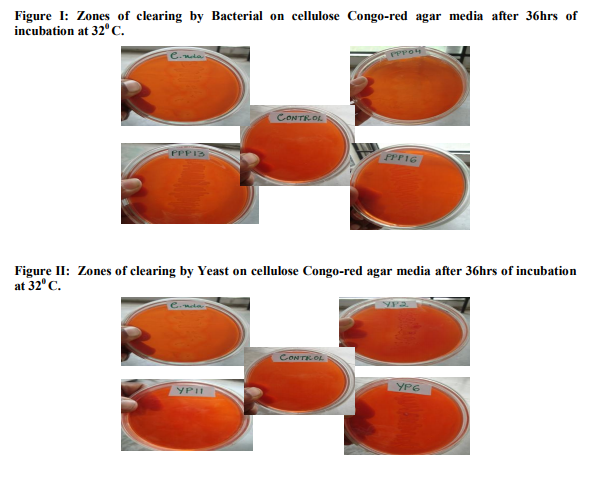
About 22 bacteria have been isolated from Pineapple peel. These bacterial isolates have been named as PPP01 to PPP22. Of the 22 isolates, only six isolates were found to be bacilli, the remaining ones were cocci. From these six bacilli, only three bacilli viz., PPP13, PPP04 and PPP16 is used for the study, depending upon the HC value obtained by the carboxymethylcellulose hydrolysis capacity by cultivating it on cellulose Congo -red agar media. The yeast isolates, have been mentioned as YP01 to YP12. Of the 12 yeast isolates only four yeasts were used for the study, again depending upon the HC value obtained by the carboxymethylcellulose hydrolysis capacity on cultivating it on cellulose Congo -red agar media.
Biochemical tests
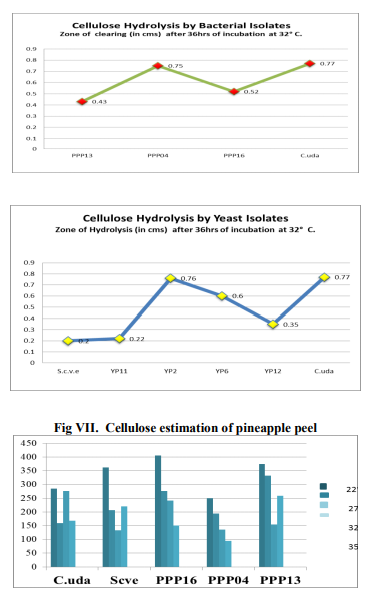
Of the 22 bacterial isolates subjected to biochemical tests viz., IMViC and carbohydrate fermentation – glucose, lactose, maltose and sucrose. All the isolates showed positive tests for one or the other biochemical tests. It has been commonly observed that, all the isolates fermented glucose and maltose producing gas/ acid or both, as evident from gas formation in the Durham’s tube and change in the colour of bromo-cresolpurple (BCP) from purple to yellow colour. It is also noticed that all the 22 isolates of bacteria showed no response in fermenting sucrose and lactose, as the colour of BCP in the test tubes solutions continued to remain purple. The formation of gas in Durham’s tube was absent, but growth could be seen, as evident by the development of turbidity in the test tube, compared to the control. Another important observation made was of the isolate PPP07. This isolate showed negative to all the tests under IMViC and fermentation of sugars, although growth was seen in the test tubes with sucrose, lactose and maltose. This probably points to the isolate PPP07 not being a bacteria. Assessment of bacteria and yeasts for attributes of Cellulose degradation After 36hrs of incubation at 320 C, a clear zone has been formed around the streak of growth for each isolate. The zone of clearing was highest 0.75cm for the bacterial isolate PPP04 and 0.76cm for the yeast isolate YP2.
Cellulose Estimation of Pineapple peel by Anthrone method
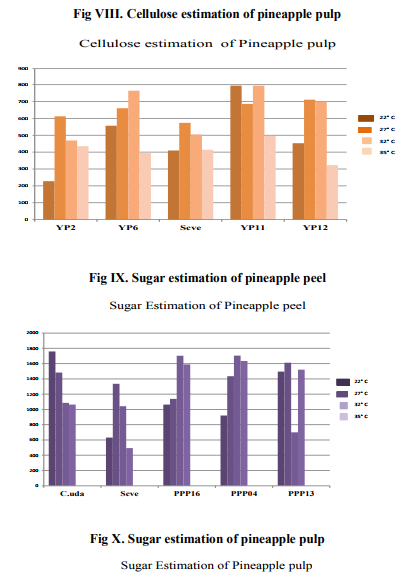
Estimation of cellulose of pineapple peel and pulp was done by the anthrone method using colorimetric estimation at 630nm. The reading obtained, was compared to the initial value of cellulose of peel, which was 1900 µg/ml and pulp 1040 µg/ml before fermentation. After 21 days fermentation, the degradation ability of each isolate was estimated by the anthrone method. Lower the concentration value of cellulose in µg/ml of the given isolate fermentation less was the amount of cellulose remaining after fermentation, indicating to the high cellulose degradation ability of the isolate. Higher the concentration value of cellulose in µg/ml of the given isolate fermentation more was the amount of cellulose still remaining after fermentation, indicating to the low cellulose degradation ability of the isolate.
Sugar Estimation of Pineapple peel by DNS method
Estimation of reducing sugar in Pineapple peel and pulp was done by the DNS method, after 21 days. With the bacterial isolates from peel, varying degree of sugars was formed, with the highest being in isolate PPP04, with sugar formed of 1700µg/ml at 320C, followed by PPP13, 1600µg/ml at temperature of 270C, showed better sugar accumulation. PPP16 showed the least fermentation activity of an average of 1100µg/ml of sugar formation. Similarly, in the pulp, the yeast isolate YP2 showed the highest amount of sugar at all three temperatures of 220C, 270C and 320C, its activity decreased at 350C.
DISCUSSION
The result of this study indicated that both the bacterial and yeast isolates have good cellulose degradative ability, this enhances their use in obtaining useful organic compounds of Pineapple peel and pulp. After fermentation, estimation of cellulose content in the pineapple peel has revealed that PPP04 isolate is able to degrade cellulose much better than all the other isolates as evident from the less amount of cellulose remaining from estimation by Anthrone method after fermentation and the amount of sugar formed as evident from DNS estimation of sugar after fermentation at all the four temperatures, with the vigourous activity seen at 320 C. Altough other isolates degraded cellulose, PPP13 is active only at 320C, its degradation ability is also much lower compared to other isolates. The standard organism C.uda has shown good degradative ability on pineapple peel. The temperature 320C, seemed to be the ideal for all the bacteria. Similarly, the yeast isolate YP2 has shown the highest cellulose degradation compared to other isolates, While 220 C has been the ideal temperature for the degradation for all isolates. YP11 has shown the least amount of degradation ability compared to others. The standard S. cerevisiae also showed a good amount of cellulose degradation. Sugar estimation revealed that all the bacterial isolates are able to form some amounts of sugar. The standard yeast S. cerevisiae has shown the least amount of sugar compared to other organisms; this could be probably due to its fermentative ability. In Pineapple pulp, the yeast isolate YP6 has shown the least amount of sugar compared to the standard yeast and other isolates. This indicates to its vigorous fermentation ability.
CONCLUSION
This study reveals that the three bacterial isolates and four yeast isolates have been able to degrade appreciable amounts of cellulose and produce glucose. A few isolates have also shown the potential for utilizing glucose for further secondary fermentation to obtain industrially important chemical compounds. Further, this study has paved an understanding for scope for utilizing the peel of pineapple or excess of postharvest pineapple as a good substrate for industrially useful products, by harnessing the potential of microbes. Thus in conclusion it may be stated that the isolates could be further harnessed using pineapple fruit wastes, which are of low cost and used in the production of products of high economic value such as alcohol and vinegar.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENT
Authors acknowledge the immense help received from the scholars whose articles are cited and included in references of this manuscript. The authors are also grateful to authors / editors / publishers of all those articles, journals and books from where the literature for this article has been reviewed and discussed.
References:
1. Ali, S., Sayed, A., Sarker R.T., Alam, R. (1991). Factors affecting Cellulase Production by Aspergillus terreus. World J. Microbiol and Biotechnol 7:62-66.
2. Ameh, J. B., Okagbue, R. N. and Ahmad, A. A. (1989). Isolation and characterization of local yeast strains for ethanol production. Nigerian Journal of Technology Research 1:47-52.
3. Anderson PJ, McNeil K, Watson K (1986). High efficiency carbohydrate fermentation to ethanol at temperatures above 40oC by Kluyvero-myces marxianus Var. maxianus isolated from sugar mill. Appl.Environ. Microbiol. 51(6): 1124-1129.
4. Baig, M.M.V., Baig, M.L.B., Baig, M.I.A. and Majeda Y. (2004): Saccharifycation of Banana Agro waste by Cellulolytic Enzymes. African Journal of Biotechnology, 3(9):447-450.
5. Beguin, P. and Aubert, J. P. (1994) The biological degradation of cellulose. FEMS Microbiol. Rev., 13, 25–58.
6. Boulter, J. I., Trevors, J. T., and Boland, G. J. (2002) Microbial studies of compost: Bacterial identification, and their potential for turfgrass pathogen suppression. World J. Microb.Biotechnol., 18, 661–671.
7. Burbank, N.C. and Kamagai, J.S. 1965 Study of pineapple cannery waste. Proceedings of the 20th-lndustrial Waste Conference, Engineering Extension Series 118, Vol. 20, pp.365-397.
8. Purdue University.Eghafona NO, Aluyi HAS, Uduehi IS (1999). Alcohol yield from pineapple juice: Comparative study of Zymomonas mobilis and Saccharomyces uvarum. Niger. J. Microbiol. 13: 117-122.
9. EL-Din, S. M. S. B., Attia, M., and AboSedera, S. A. (2000). Field assessment of composts produced by highly effective cellulolytic microorganisms. Biol. Fertil. Soils, 32, 35–40.
10. DEV, D.K. and INGLE, U.M. 1982 Utilization of pineapple by-products and wastes--review. Indian Food Packer 36, 15-22.
11. Hankin L, Anagnostakis SL. Solid media containing carboxymethylcellulose to detect CX cellulose activity of micro-organisms. J Gen Microbiol. 1977 Jan; 98(1):109–115.
12. Hart, T. D., De Leij, F. A. A. M., Kinsey, G., Kelley, J., and Lynch, J. M. (2002) Strategies for the isolation of cellulolytic fungi for composting of wheat straw. World J. Microb. Biotechnol., 18, 471–480.
13. Hedge, J.E. and Hofreiter, B.T. (1962). In: Carbohydrate Chemistry, 17 (Eds. Whistler R.L. and Be Miller, J.N.), Academic Press, New York.Hendricks, C. W., Doyle, J. D., and Hugley, B. (1995) A new solid medium for enumerating cellulose-utilizing bacteria in soil. Appl. Environ. Microbiol., 61, 2016– 2019.
14. Jeffries, T.W., (1996). Production and Applications of Cellulase Laboratory Procedures, 1-10.
15. Ladisch MR, Lin KW, Voloch M, Tsao GT. Process considerations in the enzymatic hydrolysis of biomass. En-zyme Microb Technol 1983;5:82–100.
16. Lu, W. J., Wang, H. T., Huang, D. Y., Qiu, X. Y., and Chen, J. C. (2004) Effect of inoculating flower stalk and vegetable waste with ligno-cellulolytic microorganisms on the composting process. J. Environ. Sci. Health, Part B—Pesticides, Food Contaminants, and Agricultural Wastes, 39, 873–889.
17. Madigan MY, Martinko JM, Parker J (1997). Brock’s Biology of Microorganisms (8th edn.) U.S.A; Prentice Hall International Incorporated.Mandels, M. (1981) Cellulases. Annu. Rep. Ferment.Processes, 5, 35–78.
18. Mandels, M. and Reese, E. T. (1999) Fungal cellulases and the microbial decomposition of cellulosic fabric. J. Ind. Microbiol.Biotechnol., 22, 225–240.
19. Miller, G.L. (1959). Use of Dinitrosalicylic Acid Reagent for Determination of Reducing Sugars. Anal. Chem. 31: 426-428.
20. Rose D (1976). Yeasts for molasses alcohol, Proc. Biochem. 11(2): 10- 12, 36.
21. Sandhu, D. K. and Bawa, S. (1992). Improvement of cellulose activity in Trichoderma. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol., 34/35, 175–192.
22. Smith RE. Rapid tube test for detecting fungal cellulase production. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1977 Apr;33(4):980–981.
23. Teather, R.M. and P.J. Wood, 1982. Use of Congo red-polysaccharide interactions in enumeration and characterization of cellulolytic bacteria from the bovine rumen. Applied Environ. Microbiol., 43: 777-780.
24. Tengerdy, R. P. and Szakacs, G. (2003) Bioconversion of lignocelluloses in solid substrate fermentation. Biochem. Eng. J., 13, 169–179.

|






 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License