IJCRR - 9(6), March, 2017
Pages: 34-39
Date of Publication: 31-Mar-2017
Print Article
Download XML Download PDF
A Prospective Study to Analyse Safety of Low Flow Anesthesia for Laparoscopic Procedures
Author: Annu Choudhary, Vaishali C. Shelgaonkar
Category: Healthcare
Abstract:Background: Anesthesia for laparoscopic surgery has developed and advanced significantly, resulting in a technique that is safe and provides better outcome than before. Low flow anesthesia is newer technique which is more economic, ecofriendly and effective. But there is reluctance in combining these two techniques due to risk of hypoxia and hypercapnia. So, this study was conducted to prove that low flow anesthesia is safe in laparoscopic surgeries.
Method: A prospective observational study including 70 patients (ASA I/II, 18-65 years) undergoing various laparoscopic procedures was conducted with the permission of institutional ethical committee and patient's consent. Selected patients were assigned into two groups with fresh gas flow 3L and 0.5L in high and low flow group respectively. The inspiratory and expiratory concentrations of various gases were compared. Also, the increase in soda lime temperature and change in liver/kidney functions were studied.
Result: Demographic data in both the groups were comparable. Inspiratory and expiratory concentration of oxygen, carbon dioxide and sevoflurane were comparable at all intervals of time without any complication. Temperature of sodalime increased in both the groups, but was comparable. Also, there was no significant change in postoperative liver/kidney function tests.
Conclusion: Low flow technique is a safe, efficient technique of general anesthesia for laparoscopic surgery.
Keywords: Low flow anesthesia, Laparoscopy, Sevoflurane
Full Text:
INTRODUCTION
Laparoscopic procedure is a principle technique for minimally invasive procedure and has been currently employed in multiple surgical disciplines. This technique has improved greatly during the past few years towards more patient comfort and safety. The advantages of laparoscopy in comparison to open abdominal surgery include reduced surgical trauma, less pain, fewer post-operative pulmonary complications, and shorter recovery time and a lower incidence of postoperative wound infection1,2. The disadvantages include longer surgical duration and higher equipment cost.1 So, the field of anesthesia must also grow and evolve in order to provide safe anesthesia for these kind of procedures. The anesthesiologist should have an understanding of the pathophysiological consequences from the pneumoperitoneum, to be prepared to prevent, detect and manage the possible alterations that can occur during the intervention.
Pneumoperitoneum causes an increase in systemic vascular resistance, pulmonary vascular resistance, while causing a decrease in cardiac output. However, mean arterial pressure is increased overall because increase in SVR exceeds decrease in cardiac output.3 These effects are proportional to the increase in IAP and can be exacerbated by the reverse trendelenberg position or if patient is hypovolumic. Bradycardia, cardiovascular collapse and asystole in healthy patients have been described, which are attributed to deep vagal reflexes due to sudden insufflations. Pneumoperitoneum transmits upward pressure to thorax and elevates the diaphragm, compresses the lungs and impedes expansion of the lungs and chest cavity (i.e. decreases thoracopulmonary compliance) leading to reduced functional residual capacity and basal atelectasis4. Furthermore, the pulmonary complications like subcutaneous emphysema, pneumothorax, endobronchial intubation, gas embolism can also occur.
In upper abdomen procedures, positioning in different anti trendelenburg degrees causes a reduction in the venous return and therefore in the cardiac output that can reach upto 50% of baseline. In lower abdomen procedures (pelvic, gynecology) trendelenburg position is used, sometimes in an exaggerated degree which makes ventilatory condition worse, but improves venous return and increases cardiac output in healthy patients. Because of venous stagnation, cyanosis and edema in the face and neck may be expected and if this position is maintained for an extended duration, cerebral edema and retinal detachment may occur. Lithotomic position is associated with much higher rise in venous return. All these physiological changes and potential complications makes anesthesia risky. But laparoscopy demands a safer technique of anesthesia to justify its usefulness over open procedures.
Low-flow anesthesia technique provides conservation of the heat and humidity of the respiratory system, while minimizing cost and preventing air pollution. The physiology of the tracheobronchial environment is protected as mucociliary clearance is better maintained in this technique than in high-flow anesthesia6-9. As the waste gases are reduced- atmospheric pollution is lowered, occupational hazard to operating room staff is decreased and ecological balance is maintained. A number of studies have been conducted evaluating the use of low flow anesthesia in open surgeries, but hardly a few studies conducted including all types of laparoscopic procedures. Potential reasons can be increased incidence of hypoxia, hypercarbia that can make the case difficult. This study was designed to test all those reasons which made anesthesiologist to hesitate in accepting low flow anesthesia technique for laparoscopic procedures of limited duration.
The aim of study was to assess whether low flow technique is compatible with laparoscopic surgery. Primary objectives were to compare the inspiratory and expiratory concentration of various gases at different time interval, to observe the rise in temperature of sodalime canister and compare the preoperative and postoperative kidney/liver function tests to confirm the safety of this technique.
MATERIALS and METHODOLOGY
This prospective observational study was conducted in a tertiary hospital in Maharashtra after approval from the hospital’s ethics committee on 70 patients, age in the range of 18 to 60 years undergoing elective laparoscopic surgeries under general anaesthesia of limited duration (upto 2 hours). Exclusion criteria were patients under ASA III /IV, patients with known hepatic, pulmonary, renal, or neuromuscular disorder, clinically significant laboratory abnormalities, unstable angina, history of myocardial infarction <6 months ,obesity, history of adverse reaction from exposure to any anaesthetic drug, pregnancy or breast feeding..
A detailed pre-anesthetic evaluation and written informed consent was taken from all patients. The patients were allocated into two groups of 35 each randomly by computer generated chits about technique low or high flow in either of the group. Routine investigations were obtained along with serum creatinine, blood urea and aspartate transferase, alanine transferase, alkaline phosphatase, total serum protein, serum albumin, serum bilirubin (total and direct) repeated at 48 hours postoperatively.
Baseline haemodynamic parameters were recorded after 5 minute stabilization period in the pre operative room. Standard protocol of anesthesia induction, maintenance and monitoring were followed in all patients. All patients were preloaded with 500 ml ringer lactate before induction. After preoxygenation with fresh gas flow 6 litres/minute, patients were induced and intubated with appropriate size endotracheal tube connected to Dragger primus anesthesia work station followed by mechanical ventilation with a tidal volume of 8ml/kg at 14 breaths/minute using ventilator and maintained with inhalational agent sevoflurane. Bag and mask ventilation was avoided and ryle’s tube was inserted to deflate stomach. Inspiratory/expiratory ratio was set as 1:2. These respiratory parameters were not modified during procedure unless mandatory due to occurrence of hypercapnia if any. All procedures were performed using the similar type of circle breathing system and vaporizer of sevoflurane by same manufacturer under standard operating room conditions. Accuracy of dual cascaded flow meter was verified by passing the fresh gas flow through dry gas meter. Peak airway pressure, tidal volume and minute ventilation were measured using anesthesia ventilator with respiratory mechanics module. Inspiratory and expiratory concentration of O2, NO2 CO2 and sevoflurane and also MAC (minimal alveolar concentration) were recorded using a multigas monitor with fresh gas analyzer.
Similar patient monitoring equipments were used in all cases for electrocardiograph, non invasive blood pressure, temperature and pulse oximetry. Variables were measured immediately prior to carbon dioxide pneumoperitoneum and every 5 minutes thereafter until the end of surgery. Initially, high fresh gas flow of 6 litres with dial setting of 2% of sevoflurane in both groups were set. In control group (HFA), fresh gas flow was 3 litres with O2:N2O i.e. 1.5 litres: 1.5 litres. In study group (LFA), 500ml of fresh gas flow with O2:N2O ratio 1:1 i.e. 250 ml: 250 ml was kept. During CO2 pneumoperitoneum, intra abdominal pressure was maintained between 12-15 mmHg by calibrated CO2 insufflators. In all cases sevoflurane concentration was adjusted throughout the anesthesia to maintain blood pressure and heart rate within +/-30% of base line values. The temperature of sodalime canister was monitored at every 15 minutes during anesthesia using a temperature monitor and a probe placed in middle of canister, at same site in all cases.
Deep venous thromboembolism prophylaxis system was attached to lower limbs of all patients undergoing surgery. Local infiltration with inj. Bupivacaine 0.25% 2 ml at each port was given. At the end of surgery, after removal of port, the vaporizer dial of sevoflurane was turned off and fresh gas flow with 100% oxygen was increased to 6 litres/min along with discontinuation of N2O administration.
The time required for resumption of spontaneous respiration and extubation and for gaining orientation i.e. stating name etc and finally modified aldrete score >8 were used to assess the recovery characteristics. Residual neuromuscular block was antagonized and patients were extubated after return of all reflexes. Total consumption of sevoflurane was recorded from the anesthesia machine software.There was no loss to follow up.
Data was presented as mean and standard deviation.All data were analyzed by specific statistical methods (Chi Square, t-Test, Z-test, Fisher's exact test and Yates' correction) applicable to the various sets of data.
RESULT
There was no significant difference between both groups in terms of demographic data. Patients posted for any type of laparoscopic surgery were selected for the study.
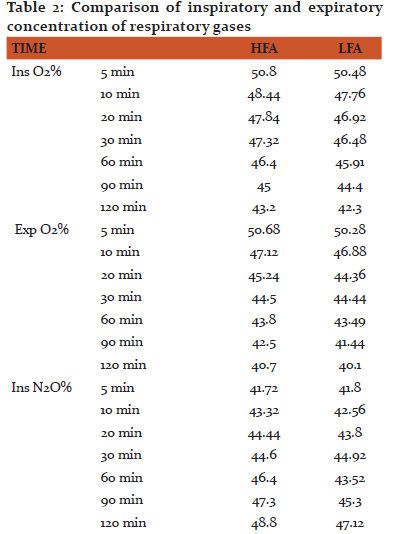
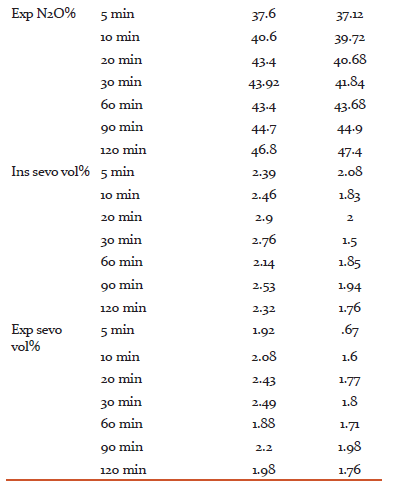
Time to achieve MAC 1.2 i.e. time required to achieve surgical plane of anesthesia was comparable in both the groups (2.92±0.64 in HFA and 3±0.86 in LFA). Intraoperatively, respiratory parameters were comparable. Inspiratory oxygen concentration decreased with time but never dropped below 44.4% in any group. Nitrous oxide was found to be increasing slowly. Also, concentration of sevoflurane was lower in LFA as compared to HFA group. There was no incidence of hypoxia, hypercapnia or arrhythmia in any of the group.
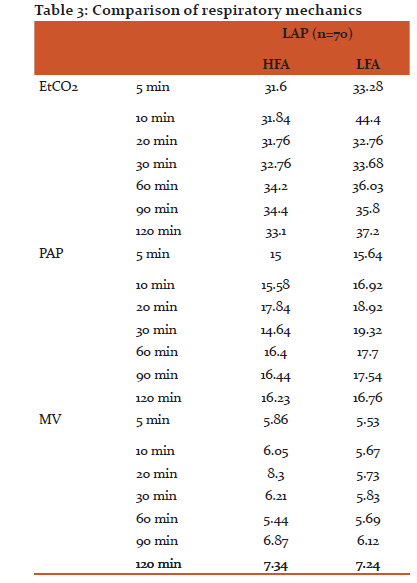
EtCO2, peak airway pressure and minute ventilation were within acceptable range in both the groups at all stages of surgery, although EtCO2 was found slightly higher in LFA group. Mean of EtCO2 in all conditions was less than 45. It is evident that the ventilator parameters remained in the normal range in both the groups with these two different anaesthesia techniques.
Haemodynamically, patients were stable in both the group at all intervals. Stress response of intubation was evident. But later on, gradually settled to near baseline Depth of anesthesia was maintained to overcome surgical stimuli at every point by BIS kept in 40-60.
CO2 absorption by sodalime is an exothermic reaction. This was evident by the observation of increase in temperature of sodalime canister. The temperature of canister was comparable preoperatively, but around 30 minutes intraoperative, there was a significant rise. The mean of temperature were comparable with p value >0.05.
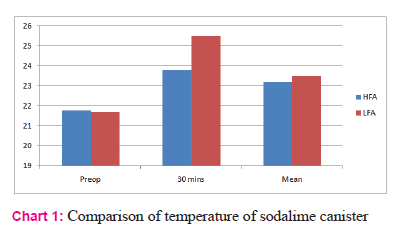
Extubation was uneventful in all cases. Further on observation it was found that a few patient had postoperative complication in terms of nausea, vomiting and agitation, but were easily treated with drugs and counseling.
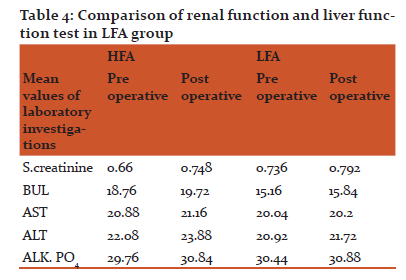
There was no major difference between two groups in preoperative and postoperative kidney function test or liver function test. Patients were also clinically stable and healthy.
DISCUSSION
Laparoscopic surgery is not without its own specific risks, either due to individual laparoscopic techniques or due to the physiological changes associated with the creation of a pneumoperitoneum. As a result, anesthetic techniques for laparoscopic surgery must be refined according to it.4 With the development of modern workstation, monitoring devices, lower solubility inhalational agent and other safe drugs, anesthesia has moved towards a more eco friendly, economic and safer technique. Actually to justify anesthesia of laparoscopy, it must parallel the advantages laparoscopy provides, simultaneously considering the problems it can give birth to. However, anesthesia practitioners, as well as pharmacy and therapeutic committees, are demanding proof that a new more costly drug or technique is superior to preexisting one in achieving the desired effect, enhances efficacy and reduces health care costs.10 In this study, we tried to test the reasons which made anesthesiologists to be reluctant for using low flow with laparoscopic procedures.
Traditionally, anesthesiologists participating in laparoscopic cholecystectomy have been quite cautious about adapting low flow anesthesia due to reason like-
- potential for inducing hypoxia, hypercarbia
- more increase in temperature of sodalime canister
- accumulation of toxic degradation products such as compound A by sevoflurane due to exhaled carbon dioxide rebreathing and administration of small amount of oxygen less than 500ml/min11
EtCO2 helps in controlling the carbon dioxide absorption-elimination equilibrium. In healthy individuals it correlates with PaCO2 from 4-8 mm Hg. In our study inspiratory oxygen never fell below 40% and EtCO2 never rose above 45 mm Hg in LFA group. These findings suggest that clinically significant rebreathing does not occur with a limited period surgery. Similar findings were observed by Young Ho Jang et al11. Also, patients were haemodyanamically stable without any signs of distress. There was no tachycardia, desaturation or increase/decrease in blood pressure at any time interval.
The next concern used to be proportionately more increase in temperature of sodalime canister with lower fresh gas flow. This becomes more significant with sevoflurane, which degrades to compound A, a nephrotoxic substance. Compound A is found to be dose-related nephrotoxin in rats, but renal toxicity, as defined by an increase in serum creatinine or BUN, has not been reported in surgical patients. The literature indicates that for care of surgical patient, the change from preoperative levels in serum creatinine and BUN levels is the most practical predictor of postoperative renal dysfunction and they are widely available, inexpensive, and have been clinically validated as predictive of renal function .12-13 In present study, it was noted that there is increase in temperature of sodalime with time and it was a little more in LFA group because low flow technique preserves heat and humidity in the breathing circuit. But they were comparable as p value was insignificant. To confirm the patient safety pre/postoperative KFT and LFT were recorded. There was no significant change in laboratory investigations suggesting that low flow with sevoflurane is safe for limited hour surgery. For the small variation in a few cases, it can be antibiotics, surgical stress, preexisting renal disease, intraoperative blood pressure, site of surgery, and anesthetics have been implicated in the cause of renal and hepatic dysfunction /injury, but none have been controlled for in prospective studies. 14
Thus, this anesthetic technique offers a means of reducing expenditure without reducing patient care; indeed it could be argued that patient care is increased as a result of the increased monitoring which they receive.15
Conclusion
In conclusion, LFA with sevoflurane using fresh gas flow of 0.5 L with setting of 50% oxygen and nitrous oxide for laparoscopic procedures is safe without any significant likelihood of risks involved.
Acknowledgement
My immense gratitude to Dr. S.P. Manjrekar, Professor and Head of Department, IGGMC, Nagpur for her kind support and help to complete this research work.
Authors acknowledge the immense help received from the scholars whose articles are cited and included in references of this manuscript. The authors are also grateful to authors / editors / publishers of all those articles, journals and books from where the literature for this article has been reviewed and discussed.
There is no conflict of interest.
References:
- Smith I. Anesthesia for laparoscopy with emphas is on outpatient laparoscopy. Anesthesiol Clin North Am. 2001;19:21-41.
- Paul Hayden, Sarah Cowman. Anesthesia for laparoscopic surgery Continuing Education in Anesthesia, Critical Care and Pain.2011; vol 1,number 5
- O’Malley C, Cunningham A. Physiology changes during laparoscopy. Anesthesiol Clin North Am. 2001;19:1-19
- John H. Nguyen, Pedro P. Tanaka. Anesthesia for Laparoscopic Surgery
- Barker L. Positioning on the operating table. Update Anaesth. 2002;15:1-6.
- M. Bilgi, S. Goksu, A. Mizrak et al., “Comparison of the effects of low-flow and high-flow inhalational
anaesthesia with nitrous oxide and desflurane on mucociliary activity and pulmonary function tests,” European Journal of Anaesthesiology, vol. 28, no.4, pp. 279–283, 2011.
- P. D. Stevanovic, G. Petrova, B. Miljkovic et al., “Low fresh gas flow balanced anesthesia versus target controlled intravenous infusion anesthesia in laparoscopic cholecystectomy: a cost minimization analysis,” Clinical Therapeutics, vol. 30, no. 9, pp.1714–1725, 2008.
- M. Brattwall, M. Warr´en-Stomberg, F. Hesselvik, and J. Jakobsson,“Brief review: theory and practice of minimal fresh gas flow anesthesia,” Canadian Journal of Anesthesia, vol. 59, n o. 8,pp. 785–797, 2012.
- J.M. Feldman, “Managing fresh gas flow to reduce environmental contamination,” Anesthesia and Analgesia, vol. 114, no. 5, pp.1093–1101, 2012.
- White PF, Smith I. Impact of newer drugs and techniques on the quality of ambulatory anesthesia. J Clin Anesth.1993;5(Suppl 1):3-13
- Young Ho Jang, Sue Rung Ho.Low-flow sevoflurane anesthesia in laproscopic cholecystectomy. Korean J Anaesthesiol.2005 Dec;49(5):1-5
- Mazze RI, Callan CM, Galvez ST, Delgado-Herrera L, Mayer DB. The effects of sevoflurane on serum creatinine and blood urea nitrogen concentrations: a retrospective, twenty-two-center, comparative evaluation of renal function in adult surgical patients. Anesth Analg. 2000 Mar;90(3):683–8. 1.
- Groudine SB, Fragen RJ, Kharasch ED, Eisenman TS, Frink EJ, McConnell S. Comparison of renal function following anesthesia with low-flow sevoflurane and isoflurane. J ClinAnesth. 1999 May;11(3):201–7.
- Sahin SH, Cinar SO, Paksoy I, Sut N, Oba S. Comparison between low flow sevoflurane anesthesia and total intravenous anesthesia during intermediate-duration surgery: effects on renal and hepatic toxicity. Hippokratia. 2011 Jan;15(1):69–74.
- Cotter SM, Petros AJ, Doré CJ, Barber ND, White DC. Low-flow anaesthesia. Practice, cost implications and acceptability. Anaesthesia. 1991 Dec;46(12):1009–12.
|






 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License