IJCRR - 4(22), November, 2012
Pages: 109-114
Date of Publication: 24-Nov-2012
Print Article
Download XML Download PDF
EFFECT OF DIFFERENT STRESSORS ON ELECTROCARDIOGRAPHICALLY DERIVED INDEX QT DISPERSION
Author: Sangeeta Gawali, Prreeya Mardiikar, V.G. Jaltade
Category: Healthcare
Abstract:Introduction: Effect of stress on cardiovascular hemodynamics has been addressed in several studies. Epidemiological evidence suggests that there is relationship between stress and cardiac morbidity and mortality in susceptible individuals. Present study was conducted to study the effect of physical and mental stress on various cardiovascular parameters in healthy adults. Methods: The present study comprised of 90 healthy male subjects who underwent thorough clinical examination to rule out cardiovascular diseases. The subjects were exposed to various stressors like 3 minute mental arithmetic calculations, Harward step test, and cold pressor test. Various ECG derived indices like QT interval, Corrected QT interval and QT dispersion were studied before and after inducing stressors. Results: Statistically significant increase in heart rate, blood pressure and decrease in QT interval (P< 0.05) was observed but increase in QT dispersion was not statistically significant (P>0.05). Interpretation and conclusion: Prolonged QT dispersion during different stressors is regarded as a marker of imbalanced distribution of sympathetic nervous system on heart. Despite this known fact QT dispersion is not affected in our subjects strongly emphasizing that prolonged QT dispersion is always associated with cardiac pathology. It was concluded that altered cardiac functions have direct effect on sympathovagal imbalance leading to increase in QT dispersion.
Keywords: Stress, QT interval, QT dispersion. , Active mental stress, Passive mental stress.
Full Text:
INTRODUCTION
The duration of the QT interval on the surface ECG is a global measure of the time the heart takes to depolarize and repolarize. Prolonged QT interval is associated with generation of life threatening rhythm disturbances and sudden cardiac death1 . QT duration is influenced by heart rate (RR interval, cardiac cy'RESULTScle). So heart rate is required in analysis of repolarisation duration. Autonomic nervous system 2 which can act directly at the cellular level or indirectly through modulation of heart rate is another source of QT changes. Both acute and chronic stresses induce Cardiovascular and neuroendocrine responses inducing QT changes and lethal arrhythmias through alteration of the neural transmission to the heart.2 An epidemiological study also suggests that there is a relationship between stress and cardiac morbidity and mortality in susceptible individual. 3,4,5,6 However effect of physiological induced stress on QT interval and QT dispersion in healthy young adult is subject to speculation. Previous reports provided conflicting data on the effect of stress on QT interval and dispersion. Therefore we have accomplished trials assessing the effect of stressors on QT interval and QT dispersion in healthy individuals. We hypothesized that any kind of physical and mental stress leads to increase in QT dispersion even in healthy subjects.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
We conducted three separate studies under laboratory circumstances in the department of Physiology, B.J M.C. Pune to assess the effect of stress on QT interval and QT dispersion. Study protocol was approved by local ethical committee and participants signed a written consent form. Healthy 90 male medical students of first MBBS were enrolled. The subjects were studied under three groups. Each group (n=30) was exposed to 3 minute mental arithmetic test, Harward step test, cold pressor test respectively. No drug or medication was taken. Participants were instructed not to smoke or consume any alcohol, caffeine or to engage in strenuous physical activity 12 hours prior to testing. The arrival of participants was followed by 5 minute briefing session in which nature and purpose of study was explained. The entire group underwent thorough clinical examination to rule out cardio respiratory disorder. History of hypertension, diabetes, smoking and alcohol was ruled out.
Data collection
Volunteers were assuming supine position. Vital parameters like resting heart rate, blood pressure were recorded before and after test. Resting 12 lead ECG was taken in a room with comfortable temperature, (22 to 25 0 C) at the speed of 25mm/sec with gain of 10 mm/ mV before and after the test. Uncorrected QT interval, Corrected QT interval, QT dispersion were calculated from 12 lead ECG. Uncorrected QT interval was calculated as beginning of Q wave to the end of T wave i.e. reaching of T wave to isoelectric line. Corrected QT interval (QTc) was calculated by Bezett?s formula QTc = QT/√RR QT dispersion (QTd) was calculated as difference between shortest and longest QT interval recorded from 12 lead ECG. For manipulation check purpose, immediately after exposure participants were asked to rate perceived level of stress on 7 point Likert scale.7 1=Not stressed at all 7=Extremely stressed.
Study 1
3 minute arithmetic test— 3 min MA8
Method- In psychophysiology, because of its simplicity and effectiveness 3 min MA test is one of the frequently used active mental stressor. Participants were asked to perform a 1-3 min MA task, which has been shown to induce psychological stress. The task involved fast and correct serial subtraction from a 3 or 4 digit numbers like 7 from 700. In order to increase the perceived importance of stressfulness of the task, participants were told to speak out the results loudly so that the number of correct answer would be recorded. Study 2 Harward step test— Method-it consists of 2 steps of 20 inches in height which the subjects climb up and down at the speed of 30 steps/min for minimum of 4 to 5 minutes. Action of climbing represents actual physical training. The stepping procedure is completed in 4 counts, at counts 1 and 2 the subject steps up to an erect standing position with both feet on the platform, at counts 3and4, subject returns to the standing position in front of the platform. To avoid local muscle fatigue, the leading leg may be changed periodically. The test is terminated when subject is unable to maintain the required rhythm. The rhythm of stepping was regulated by metronome set at frequency of 30 steps /min. Study 3 Cold pressor test Method- Subject was asked to immerse his dominant hand up to wrist in a water bath maintained at 370C for exactly two minutes. After two minutes the subject was asked to put the same hand up to the wrist in an ice water bath saturated with ice cubes and temperature maintained at 2 0 to 40 C. Subject was asked to report the moment at which he first felt pain, cramps, or hurting sensation by saying “yes” and was asked to keep his hand in the same ice cold water for as long as possible or till it became unbearable. Both responses were carefully timed with help of stop watch. Subjects who exceeded four minutes cold pressor tolerance limit were asked to withdraw their hand and test was terminated. ECG was recorded before and immediately after the withdrawal of hand. Statistical analysis-Results are expressed as mean + SD. Paired„t? test was applied to compare QT interval, QTc, QTd before and after stress test. Probability value of less than 0.05 was accepted as significant.
RESULTS
Characteristics of subjects-
Mean age-18.31 + 3.57 yrs
Height-165.72 + 7.25 cm
Weight- 45.52+2.31Kg.
BMI- 27.3 + 6.71 Kg/ m2
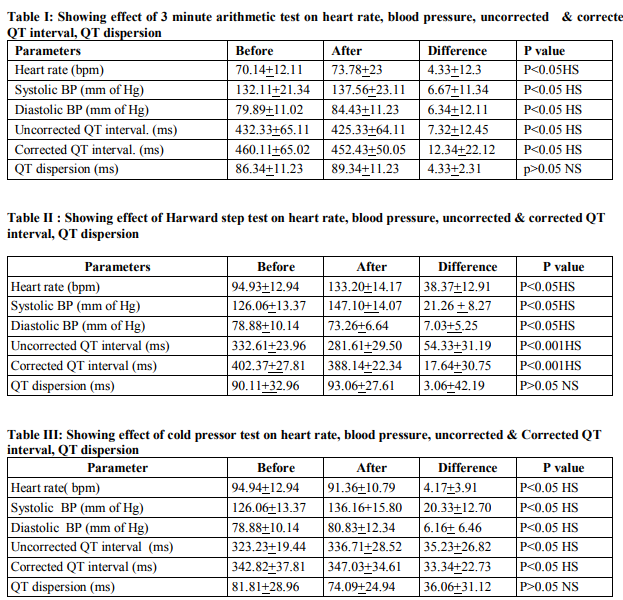
Table I shows significant increase in heart rate, systolic blood pressure and diastolic blood pressure and significant decrease in uncorrected and corrected QT interval (p0.05) after 3 minute arithmetic test. Table II shows significant increase in heart rate and systolic blood pressure (p0.05) after Harvard step test. Table III shows significant decrease in heart rate, increase in systolic blood pressure and diastolic blood pressure, and significant increase in uncorrected and corrected QT interval (p0.05) after cold pressor test.
DISCUSSION
A number of possibilities underlie the mechanism by which stress may influence repolarisation homogeneity in the myocardium in absence of ischemia through altered autonomic activity. Animal studies have shown that sympathetic stimulation causes a temporary status during which action potentials shorten non homogenously; thereby creating dispersion of repolarisation 8,9,10,11 Stress promotes differing level of sympathetic and parasympathetic stimulation of the heart, thereby producing difference in heart rate and blood pressure response. According to latest definition of Hans Selye 12, 13 biological stress is the nonspecific response of the body to any demand made upon it. Excessive heat or cold, forced immobilization or exercise, chemical, biological and psychological agent may elicit same neuroendocrine or nonspecific response which consist of increase level of ACTH by pituitary leading to increase release of glucocorticoids from adrenal cortex.12 Stress is both, active and passive, physical and mental. Active stress is one in which the subject is required to actively cope (do something) and perform in a challenging situation.12 3 minute arithmetic test, Step test, Cold pressor test are active mental and physical stress. Passive mental stress is one in which the subject is unable to cope an unpleasant or distressing situation. It is characterized by lack of control over the source of stress. A video clip of distressing images is a kind of passive mental stress. We have studied only active mental stress, as we could not arrange for video clips. Previous studies have shown that passive mental stress has no effect on heart rate and QTd because perceived level of stress achieved is below the midpoint 4 on 7 point Likert scale.13 3 minute arithmetic test and QT prolongation--3 minute arithmetic test is considered to be active mental stress. Adjustment of QTd to changing heart rate is dynamic phenomenon consisting of fast adaptation phase and slow adaptation phase. Franz 14 showed that after rapid change in heart rate, fast adaptation phase of repolarisation usually last 30-60 sec followed by 2 min slow adaptation phase. We proposed that part of QT prolongation we noted was due to delay in heart rate adaptation and only remaining fraction was caused directly by active mental stress. Step test and QT dispersion- We have found increase in heart rate and systolic blood pressure which is due to sympathetic stimulation and increase pumping of the heart which increases cardiac output, thereby increasing systolic blood pressure respectively. Decrease in diastolic blood pressure is due to exercise induced peripheral vasodilatation. Decrease in QT interval is 15 ECG manifestations of ventricular depolarisation and repolarization ionic current that contributes to action potential. Amplitude of this ionic current is influenced by heart rate .Exercise induced increase in heart rate leads to decrease in QT interval as both phase of depolarization and repolarisation shortens. There was no significant increase in QT dispersion though there is sympathetic stimulation. Increase in QTd is an indication of inhomogeneous ventricular repolarisation phase and always associated with cardiovascular disorder. Previous studies have shown QT variability and QTd changes during challenges associated with increase in sympathetic activity in patients with CCF in which there is always autonomic imbalance16. So it appears that autonomic imbalance when associated with cardiac pathology leads only to increase in QTd which may be the reason we have not found significant increase in QTd in our healthy subjects. Cold pressor test and QT dispersion—this study demonstrates increase in blood pressure and decrease in heart rate after CPT. Previous study 16has shown sympathaticoadrenaomedullary secretion of catecholamine is increased during acute cold exposure. One of the immediate local responses to cold is widespread peripheral vasoconstriction which is responsible for increase in systolic and diastolic blood pressure in our subjects.17 We have found decrease in heart rate which is due to reflex baroreceptor response. Pooling of blood from skin surface increases filling pressure which may directly affect pacemaker of the heart. Moderate increase in filling pressure increase the heart rate, but longer increase in filling pressure decrease heart rate which may be the cause of decrease in heart rate in our subjects17 . Prolonged QT interval is regarded as a marker of an autonomic imbalance distribution of sympathetic activity indicating that autonomic neural tone is an important determinant of QT interval and dispersion. 18Release of catecholamine following acute cold exposure is mainly responsible for QT prolongation. Decrease in QT dispersion in our subjects is due to decrease in heart rate which indicates that heart has maintained its rhythmicity despite sympathetic stimulation.
CONCLUSION
Our study has shown -
1. A direct correlation between various stresses induced changes in heart rate and QT dispersion. Increase in heart rate with increase in QT dispersion as seen after step test and 3 minute Arithmetic test. Decrease in heart rate with decrease in QT dispersion as seen after cold pressor test which indicate heart has maintained its rhythmcity.
2. Transient stress induced changes in autonomic balance and ventricular repolarization including transient QT prolongation.
3. Increase in QT dispersion is always pathological.
Study Limitations-Several limitations of the present study need to be addressed. First, the sample size is small. Large sample size may provide an additional insight. The second is the continuous computerized ECG monitoring needed throughout the test. Future directions--Further work is needed to elucidate the mechanism involved for e.g. whether central cortical processing or local sensitivity at the level of myocardial cell may be responsible. New markers like advanced T wave loop variable need to be studied. Measuring the level of catecholamine and cortisol which are the true markers of stress can be measured.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
Authors acknowledge the immense help received from the scholars whose articles are cited and included in references of this manuscript. The authors are also grateful to authors/ editors/ publishers of all those articles, journals and books from where the literature for this article has been reviewed and discussed. The authors also wish to thank all the volunteers who participated whole heartedly in the study. The authors are grateful to all the staff who have contributed and cooperated in the study.
References:
1. Zareba W, Moss .AJ, LE Cessies. Dispersion of ventricular repolarisation and sudden cardia death in coronary artery disease. Am J Cardiology 1994; 74: 550-553.
2. Browne K F, Zipes DP, Hger J J,Prystowky E N. Influence of ANS on QT interval. Am J Cardiology 1982; 59:1099-1103.
3. Kamarck T W, Jenning J R. Biobehavioral factors in sudden death. Psychol Bull 1999; 109: 42-73.
4. Lear J, Poole W K, Kloner R A. Sudden cardiac death trigger by an earthquake. New England J Med 1996; 334: 413-419.
5. Meisel S R,Kutz I, Dayan K I Pauzer H, David D. Effect of Iraqi missile War on incidence of acute myocardial infarction and sudden death in Israeli civilians. Lancet 1991; 338: 660-661.
6. Trichopoulas D,Katsou yanni K,Zavitsanos X . Effect of psychological stress and fatal heart attack: the Atthens, Earthquake natural experiment. Lancet 1981; 1: 441-443.
7. Likert A . A technique for measurement of attitude. Methods Psycho (Frankfurt). 1932;140: 44-53.
8. Andrassy G, Szabo A, Trummer Z, Gyozo A, Tahy A. The application of mental stress to detect impaired myocardial repolarisation reserve. Eur Heart J 2003; 24: 283.
9. Han J, Garcia de Jalan P, Moe G K. Adrenergic effect on ventricular vulnerability. Cir Res1964; 14: 516-524.
10. Schwartz P J . QT prolongation , sudden death and sympathetic imbalance, The pendulum Swings . J cardiovascular electrophysiology 2001; 12: 1074-1077.
11. Schwartz P J, Verrier RL, Lown B. Effect of stellectomy and vagotomy on ventricular refractoriness. Circ Res 1977; 40: 536-540.
12. Selye H. Stress without distress. Mcdelland and Stewart Ltd. Toronto 1974.
13. Selye H. Stress in health and disease, Butterworths, Bosten 1976.
14. Franz M R, Swerdlow CD, Liem LB, Schaefer J. Cycle length dependence of human action potential duration in vivo: effect of single extra stimuli, sudden sustained rate acceleration and deceleration and different study state frequency. J clin invest. 1988; 82:972- 979.
15. Sana Khatib, Nancy Allen, Judith Kramer, Robert Callif. What clinicians know about QT interval. JAMA 2003; 289: 2121-2127.
16. D.S.Raghunandan, Nagraj Desai, Ronald Berger. Increase beat to beat variability in patients with CCF. Indian heart journal 2005;57: 138-142.
17. Abidskov J, A. Aderenergic effect of QT interval on ECG. Am heart J 1976; 92: 210- 216.
18. A. K.Ghosh, J K Ghosh, S Kundu. Heart rate responses to cold water immersion of extremities. Indian J Physiol and Allied Sci. 1975; 29 :64-69.
19. Lo SSS, Muthian CJ, Sutter MI. QT interval and QT dispersion in primary Autonomic failure. Heart 1996; 75:498-501.
|






 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License