IJCRR - 4(22), November, 2012
Pages: 66-73
Date of Publication: 24-Nov-2012
Print Article
Download XML Download PDF
A CROSS SECTIONAL STUDY ON MAGNITUDE OF RISK FACTORS OF CARDIO-VASCULAR DISEASES AMONG AUTO RICKSHAW DRIVERS OF DAVANGERE CITY. KARNATAKA, INDIA
Author: Raghavendraswamy Koppad, Santosh Kumar A., Naveen Kotur, Umakanth A.G.
Category: Healthcare
Abstract:As we slowly advance into the 21st Century, we find that the challenges posed by non- communicable diseases (NCDs) present an imminent threat to people worldwide. Cardiovascular diseases (CVD) are leading cause of death in developing countries including India. The huge burden of CVD in Indian subcontinent is the consequence of the large population and high prevalence of cardiovascular risk factors. Objectives: To know the magnitude of and risk factors of Cardio vascular diseases (CVDs) among auto rickshaw drivers. Methodology: Study Design: Questionnaire based cross-sectional study. Duration of study: (3months) July 1st to November 30th 2011. Participants: 200 auto rikshaw drivers of Davangere city. Statistical test: Chi square test. Materials and methods: A pre-designed and pre-tested questionnaire was used to collect the data and anthropometric measurements were done for the study population.. Results: The total study population included 200 male subjects. Age range was 16-55yrs years. Proportion of major cardiovascular risk factors was: current smokers 59 (29.5%), alcohol intake 60 (34.5%), obesity and overweight (BMI ? 23 kg/m2) 96 (48%), central obesity 73 (36.5%), hypertension 34 (17%). Conclusion and recommendation: The study results indicated high proportion of behavioral risk factors, central obesity and hypertension in rick-shaw drivers. Because of this high level of risk factors they are at increased risk of getting cardio vascular diseases. We recommend health education for health promotion and periodic examination to identify and manage risk factors
Keywords: Cardio Vascular Disease s, Risk Factors, WHO STEPS.
Full Text:
INTRODUCTION
As we slowly advance into the 21st Century, we find that the challenges posed by noncommunicable diseases (NCDs) present an imminent threat to people worldwide. Cardiovascular diseases (CVD) are leading cause of death in developing countries including India. (1) In India, CVDs account for 31.7% of the total deaths. (2) Nearly 50% of the cardiovascular deaths in India occur in people below 70years of age, compared with just 22% in the western countries. (3) Currently Indians experience CVDs deaths at least a decade earlier than their counterparts in countries with established market economies (EME). The Global Burden of Disease (GBD) study estimates that 52% of CVDs deaths occur in young and middle aged people in India as compared to 23% in EME, resulting in a profound adverse impact on the economy. (4)
At the same time it is the 3rd most common morbidity after infectious diseases and injuries. The incidence of Cardio vascular diseases (CVDs) and other NCDs are greater in urban areas when compare to rural areas in India. (5) The huge burden of CVDs in Indian subcontinent is the consequence of the large population and high prevalence of cardiovascular risk factors. (2) There is not enough data available on risk factors of CVDs among focused groups like auto rickshaw drivers (work force). Now-a- days World Health Organization (WHO), is promoting more researches on work forces. Auto rickshaw drivers are at more risk for CVDs because of their common life style like irregular eating habits, addictions, extravagance when the money is available and work related sedentariness. With this back ground descriptive, observational study with cross sectional design was conducted to assess the magnitude of CVDs risk factors among auto rickshaw drivers of Davangere city.
OBJECTIVE: ? To know the magnitude of risk factors of Cardio vascular diseases (CVDs) among autorickshaw drivers.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Davangere, Karnataka is the city situated in the middle of the Karnataka with population of 5 lakhs. Even though it has such a huge population, city transport service is still not established according to the need. So, more than a half of the people here are depending on auto rickshaws for their day today works in the city. So the auto rickshaw union is well established and it is one of the main occupation for the part of population here. There are 600 auto rickshaws in the city. We conducted an observational, descriptivecross sectional study on 200 auto rickshaw drivers (30% of total), between July 1st to November 30th 2010 (5months). Simple random sample method was used to collect the information from subjects, there are 40 registered (registered in auto rickshaw union of Davangere) auto rickshaw stands in Davangere, 20 stands were selected by simple random sampling. Every day we visited 3 stands and collected required information from the subjects till required sample size was met. We took all the measures to avoid the duplication. Only those working as full time drivers from last 2 years were included in the study and individual who did not give consent and part time, occasional drivers were not included. The World Health Organization (WHO) step-wise approach was used (adopted after modified to suit the local requirement) to determine the magnitude of cardiovascular risk factors in the study population. The two components of the study were (1) questionnaire based survey for behavioral risk factors and (2) anthropometric measurements. Institutional ethical committee of the S S Institute of Medical sciences, Davangere was approved the study. Free and informed consent was obtained for the questionnaire based interview and anthropometric measurements. We referred newly detected patients with hypertension, obesity to our hospital medicine department (physician) for further management. Data on socio-economic status, tobacco consumption, alcohol consumption, physical activity, anthropometric measurements and blood pressure was collected from all the study subjects. Standard instruments and procedures were used for anthropometric measurements. STEP 1: Information on socio-demographic variables and behavioral NCD risk factors including smoking tobacco, smokeless tobacco, alcohol consumption, physical activity (Job, Leisure time and Travel related physical activities). STEP 2: Physical measurements - Height, weight, waist circumference, and blood pressure were measured using standardized instruments and protocols.
Parameters Used: Height: Height was measured with a standard tape to the nearest 0.1 cm. Subjects were requested to stand without shoes and stand upright with the back against the wall, heels together and eyes directed forward.(6) Weight: Weight was measured using a standard balance to the nearest 0.5 kg. The subjects were asked to wear light clothing. (7) Waist circumference: WC was measured using a non-stretchable fiber measure tape. This measure was taken at the level of the midpoint between the inferior margin of the last rib and the crest of the ileum in the mid-axillary plane. The landmarks were located by palpation, marked and the midpoint found using a tape measure. The measurement was taken at the end of a normal expiration with the arms relaxed at the sides. (7) Blood Pressure: The BP was measured by using a standard mercury sphygmomanometer (appropriately calibrated and maintained). Blood pressure was measured in a quiet room, on the right arm in sitting position. Measurement was done three times over a period of minutes interval, lowest among the readings was recorded. (8) Body Mass Index (BMI):(9) BMI was calculated using the formula: BMI = weight in kgs / (height in meters) 2 . BMI: 18.5 to 22.9 kg / m2 - Normal 23 to 24.9 kg / m2 - Overweight ≥ 25 kg / m2 - Obese Definitions Used In The Study: (10) The definitions used for various parameters were as per the WHO STEPS guidelines. Current Smokers/ Smokeless Tobacco user: Current daily smokers / Smokeless tobacco users were defined as those who were currently smoking daily or using smokeless tobacco daily. Current alcoholic: are those who were taken alcohol within last 12 months. Raised Blood Pressure: Raised blood pressure was defined as systolic blood pressure > 140 mmHg and/or diastolic blood pressure > 90 mmHg or under medication. Body mass index (BMI): BMI was calculated, and overweight was defined as BMI > 23 Kg/m2; abdominal obesity was diagnosed when waist circumference (WC) was [90 cm in men] and [80 cm in women] in accordance with the recommendations of World Health Organization for Asian adults. Physical Inactivity: A person was labeled as inactive if he/ she was inactive in all the three domains of work, transport, and leisure. Statistical analysis After completion of the study, information gathered was analyzed and presented in suitable tabular and graphical forms. Statistical tests: Data was analyzed by using Percentage proportions, Pearson’s Chisquare(X2) tests. For all the tests a ‘p’ value of 0.05 or less was considered for the statistical significance Analysis was done using Statistical Package for Social Sciences (SPSS), version 17.
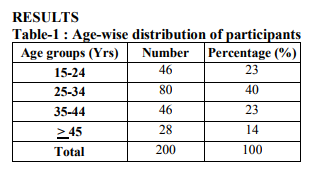
All participants were between the ages of 15 to 55 years, most of the participants were belong to the age group of 25 – 34 years. More than 3/4th of the drivers were of < 45years.
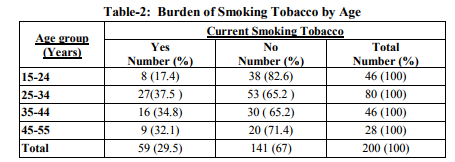
Overall the prevalence of smoking among auto drivers was 29.5%, the prevalence was more in the age group of 25-34years
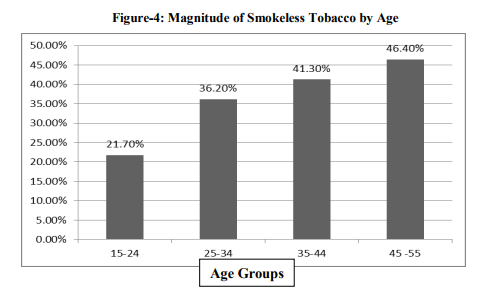
Overall the prevalence of smokeless tobacco was 36.5%, indicates more 1/3rd of the auto drivers were having the habit of using smokeless tobacco. The prevalence was near 50% (46.5%) in the age group of 45-55 years. The prevalence was more in higher age group compared to lower.
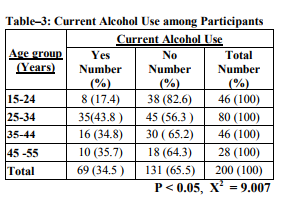
More than 1/3rd (34.5%) of the auto drivers were currently alcoholics. The prevalence was more in the age group of 25-34years. Difference in alcohol prevalence in different age groups is statistically significant.
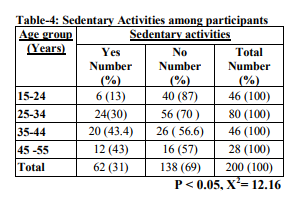
Near one third (31%) of the auto-rickshaw drivers were sedentary (includes work related and leisure time related). Sedentariness was more (435%) among the older age group (35-44years) among the subjects, compared to younger. The difference is statistically significant.
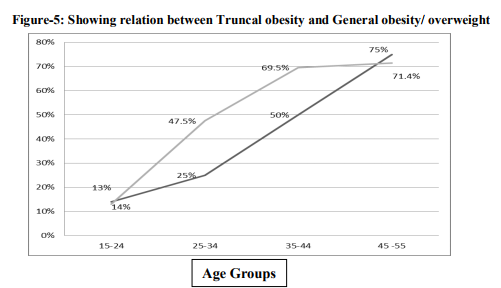
Overall the prevalence of general obesity/ overweight was more (48%) among auto drivers compared to abdominal obesity (36.5%). Both the types of obesity increased with age. Prevalence of general obesity was more among younger age groups compared to older (45-55years)
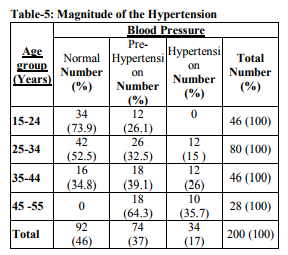
The prevalence of hypertension and prehypertension among auto rickshaw drivers were 17% and 37% respectively. Indicate more than 1/3rd (37%- Pre HTN) of this group is at risk of developing hypertension in the future if not done any intervention, more concerning is among younger age group (15-34 years) near 50% are pre hypertensive and require urgent intervention. Prevalence of hypertension was more among older age group (35.7%; 45-55years).
DISCUSSION
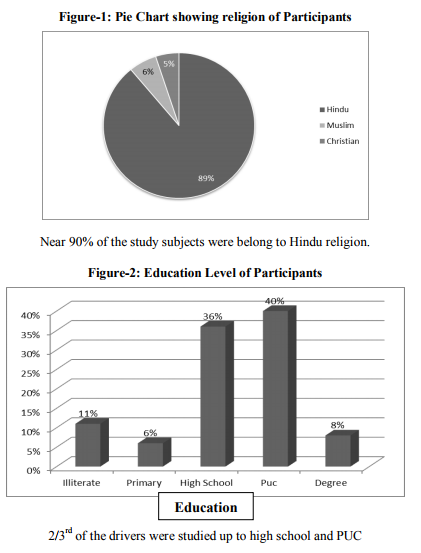
The risk factors of today are the diseases of tomorrow. Identifying these risk factors in populations occupies a central place in the surveillance system because of the importance of lag time between exposure and disease. This study documents the high prevalence of risk factors for CVDs in the study population. Prevalence of smoking is 29.5% in our study is more compared to community based studies conducted in urban settings in other parts of India.(11) Prevalence of smokeless tobacco in our study is 36.5%, this is also more compared study conducted by Joshi et al in general urban community.(12) The prevalence of alcohol use was 34.5% in our study. A multi centric study conducted by Bela shah et al reported that prevalence of alcohol use was 40 – 50% in urban men, is slightly more than our study finding. (13) Our study shows that near one third (31%) of the auto-rickshaw drivers were sedentary (includes work related and leisure time related). This was due to the type of work profile of the auto rick shaw drivers, where the study was carried out. All drivers were full time drivers and driving is sedentary in nature require less physical effort. Prevalence of BMI (48%) and central obesity (36.5%) in our population was higher as compared to other community based studies conducted in urban areas of other parts of India. (14, 1 5) This could be due to more sedentary during working hours and lack of awareness of obesity and its hazards, as most of the drivers studied up to PUC or high school. High prevalence of hypertension in our study was consistent with the recent Indian studies. (16, 17, 18). Prabhakar et al observed the high prevalence of cardiovascular risk factors in industrial settings (Work group) in northern India and expressed it as cause of concern as well as an opportunity for carrying out work place prevention programs. Our results reinforce the need for low-cost workplace (auto – rickshaw association) intervention programs.
CONCLUSION
The study results indicated high proportion behavioral and anthropometric risk factors of cardiovascular diseases in auto rickshaw drivers. It is clear that around 1/3rd of the auto rickshaw drivers are having behavioral risk factors like smoking tobacco, smokeless tobacco, alcohol use and overall sedentary activities. When we come to obesity it is clear that near 50% of the study subjects are having generalized obesity and more than 1/3rd having central obesity this may be because of more sedentariness during there working hours, less of physical activities during leisure time and lack of awareness about hazards of obesity. One of the most concerning observations of this study is more than 50% of the young auto rickshaw drivers (15-35years) are in the pre-hypertensive stage and they are more potential enter the hypertensive stage if proper preventive and promotive care is not taken. This high magnitude of CVD risk factors can put this working group at the risk of increased cardiovascular morbidity and mortality at relatively younger age.
RECOMMENDATION
- Health education programmes for auto drivers to increase awareness about healthy lifestyle.
- Effective implementation of COTPA act [Cigarette and other Tobacco Products Act]
- Strict implementation of anti-alcohol laws.
- Periodic examination of the drivers to identify Risk factors and their management.
Limitations
The results of the study cannot be generalized to the general urban population as the study was done in a focused group (auto rickshaw drivers) that had lower socio-economic status and unique work profile. In addition, study population essentially consisted of males.
Strength
The strength of our study was comprehensive survey of risk factors using WHO stepwise approach ( Step 1, and 2 approach was used after modifying to suit the local requirements) and physical measurements was done using standardized tools.
References:
1. World Health Organization. Preventing Chronic Diseases. A vital investment [Online]. 2005 [cited 2008 Aug 21]; Available from: URL:http://www.paho.org/english/ad/dpc/nc/c mn-po-concept.pdf
2. Kaur P, Rao TV, Sankarasubbaiyan S, Narayana NN, Ezhil R et al. Prevalence and Distribution of Cardiovascular Risk Factors in An Urban Industrial Population in South India: A CrossSectional Study. JAPI 2007 ; VOL 55: 771-776.
3. Soumya Deb, Aparijita DasGupta. A Study on Risk Factors of Cardio Vascular Diseases in an urban Health Centre of Kolkatha. Indian Journal of Community Medicine 2008; 33 (4): 271-275.
4. National Cardiovascular Disease Database. Supported by Ministry of Health and Family Welfare. Government of India and World Health Organization [Online]. [cited 2008 Oct 6]; Available from: URL:http://www.whoindia.org/LinkFiles/NMH _Resources_National_CVD_databaseFinal_Report.pdf
5. Srinath Reddy K. Prevention And Control of Non-Communicable Diseases: Status And Strategies. Working paper no.104. Indian Council For Research On International Economic Relations [Online]. July 2003 [cited 2008 Aug 21]; Available from: URL:http:www.icrier.org/pdf/WP104.pdf
6. Deepa R, Shanthirani CS, Premaltha G, Sastry NG, Mohan V. Prevalence of insulin resistance in a selected south Indian population – The Chennai urban population study – 7 (CUPS-7). Indian J Med Res. 2002; 115: 118-27.
7. Integrated Disease Surveillance Project. NCD risk factor surveillance Training manual for field workers and field supervisors. Field manual. [Online]. 2003-04 [cited 2010 July 29] Available from: URL:http://www.whoindia.org/LinkFiles/NCD _Surveillance_ TM02Field_ Manual_ IDSP_NCD_RF.pdf
8. Park K. Textbook of Preventive and Social Medicine. 20thed. Jabalpur: Banarsidas Banot; 2009. p 315-349
9. World Health Organization. The Asia pacific perspective: Redefining obesity and its treatment [Online]. February 2000 [cited 2010 Aug 24]; Available from URL:http://www.wpro.who.int/internet/resourc es.ashx/NUT/Redefining+obesity.pdf
10. Maimoona Aboobakur, Ali Latheef, Ahmed JM, Sheena Moosa, Ravindra MP, Anand Krishnan, Dorairaj Prabhakaran. Surveillance for non-communicable disease risk factors in Maldives: results from the first STEPS survey in Male. Int J Public Health January 2009; 55 (5): 489-496.
11. Thakur JS. Chand?garh: The first smoke-free city in India. Indian Journal of Community Medicine July 2007; 32 (3): 169-170.
12. Yuvaraj BY, Nagendragouda MR, Umakanth AG. Prevalence Awareness and Treatmrnt and control of Hypertension in rural area of davangere City. Indian Journal of Community Medicine January 2010; 35 (1): 138-141.
13. Bela Shah, Prashant amthur. Risk factor Surveillance for Noncommunicable diseases (NCDs): The Multi-site ICMR-WHO Collaborative Initiative. Presentation made at Forum 9; 2005 12-16 September; Mumbai, India
14. Meenakshi Bakshi Mehan, Somila Surabhi, Gautami J. Solanki. Risk factors profile of Noncommunicable diseases among middle –income (18-65 years) free living urban population of India. Int J Diab Der Crres 2006 Dec; 26:169- 76.
15. Mohan V, Shantirani CS, Deepa R. Glucose Intolerance (Diabetes and IGT) in a selected South Indian population with special reference to family history, obesity and lifestyle factorsThe Chennai Urban Population Study (CUPS 14). J Assoc Physicians India 2003; 51:771-7
16. Reddy KS, Prabhakaran D, Chaturvedi V, Jeemon P, Thankappan KR, Ramkrishnan L, et al. Methods for establishing a surveillance system for cardiovascular diseases in Indian industrial populations. Bull World Health Organ 2006;84:460-469.
17. Prabhakaran D, Shah P, Chaturvedi V, Ramakrishnan L, Manhapra A, Reddy KS. Cardiovascular risk factor prevalence among men in a large industry of northern India. The Natl Med J India 2005;8(2):59-65.
18. Gupta R, Gupta VP, Sarna M, Bhatnagar S, Thanvi J, Sharma V et al. Prevalence of coronary heart disease and risk factors in an urban Indian population Jaipur Heart Watch-2. Indian Heart J 2002;54(1):59- 66.
|






 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License