IJCRR - 4(24), December, 2012
Pages: 124-130
Print Article
Download XML Download PDF
FINE NEEDLE ASPIRATION CYTOLOGY FOR THE DIAGNOSIS OF TUBERCULOUS LYMPHADENITIS
Author: Sumit Giri, Karandeep Singh
Category: Healthcare
Abstract:Background: Tuberculosis is a major public health problem in India and one of the main causes of lymphadenopathy. However, anti-tubercular treatment cannot be given only on clinical suspicion. Cytomorphology with acid fast staining proves to be a valuable tool in diagnosing these cases. Aim: To assess the role of FNAC in diagnosing tuberculous lymphadenitis and also to study the role of repeat aspiration cytology in patients with strong clinical suspicion of tuberculosis. Research Methodology: FNAC were done by cytopathologist after taking a detailed clinical history regarding duration of swelling, site, size, consistency and mobility. The alcohol fixed smears were stained with Papanicolaou stain, air-dried smears stained with May-Grunwald Giemsa (MGG) and Ziehl-Neelsen (ZN) stain for Acid-Fast Bacilli (AFB). Results: Out of 728 cases with lymphadenopathy of various aetiologies, 264 cases were diagnosed as tuberculous (TB) lymphadenitis. Four cytomorphologic patterns were observed: 1) Epithelioid granulomas with caseous necrosis: 142 cases (53.79%). 2) Epithelioid granulomas without caseous necrosis: 73 cases (27.65%). 3) Necrotising lymphadenitis: 38 cases (14.39%), and 4) Necrotising and suppurative lymphadenitis: 11 cases (4.17%). Ninety two cases were diagnosed as reactive lymphadenitis with activated histiocyte clusters and were advised a repeat aspiration after a course of antibiotics. Out of the 41 cases that turned-up for re-aspiration, 27 cases showed subsequent development of epithelioid granulomas, whereas the others continued to reveal features of reactive lymphadenitis. Conclusion: FNAC is a reliable, rapid and cost-effective, outdoor diagnostic procedure requiring minimal instrumentation and is highly sensitive to diagnose tuberculous lymphadenitis and repeat aspiration, after 3?4 weeks helps in providing the correct diagnosis of early tubercular lesions.
Keywords: FNAC, Tuberculous lymphadenitis, AFB, Epithelioid granulomas.
Full Text:
INTRODUCTION Tuberculosis (TB) remains a major public health problem worldwide, especially in the developing countries like India. About thirty percent of the tuberculous infections are extrapulmonal [1]. Peripheral tuberculous lymphadenopathy is the most common manifestation of extrapulmonary tuberculosis, mostly affects the cervical lymphnodes [1,2,3]. Since TB carries a high risk of morbidity and mortality and therefore accurate and timely diagnosis together with effective TB treatment is the mainstay of TB care and control. Open biopsy has been traditionally the standard for the diagnosis of tuberculous lymphadenitis. However, it can be associated with significant morbidity as well as delay in diagnosis. Fine needle aspiration diagnosis of pulmonary and extra-pulmonary tuberculosis is becoming increasingly popular diagnostic tool because of its simplicity, rapidity and performance friendly nature [4,5,6]. Fine needle biopsy (FNB) avoids the physical and psychological trauma occasionally encountered after open biopsy. It is convenient for the patient and the physician as well, useful for outpatients, and relatively painless [7]. FNB has been found to be a safe tool, a quick and inexpensive method of diagnoses with reasonable accuracy of 84.4−89.77% [8,9,10]. The present study was carried out to study the various cytomorphologic patterns in lymph nodes on FNAC and to evaluate the utility of reaspiration cytology for detecting the subsequent development of granulomas.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
This prospective observational study was carried out at the department of pathology, Dr. Hedgewar Arogya Sansthan Hospital, from May 2009 to September 2010. FNAC was performed by cytopathologists on 728 patients who presented with peripheral lymphadenopathy. A detailed clinical history was elicited and a thorough physical examination was done along with relevant laboratory investigations and chest X-ray before subjecting the patients to aspiration. After taking proper consent, aspirations were done using 23 gauze needle with attached 10 ml disposable syringe. In all cases, alcohol fixed and air-dried smears were made: alcohol fixed slides were stained by Papanicolaou (PAP) method and airdried smears were stained by May GrunwaldGiemsa (MGG). Special stain for acid fast bacilli (Z-N stain) was done in all cases where purulent or cheesy material was aspirated. A detailed cytomorphologic patterns were studied. A repeat aspiration was advised after 3−4 weeks in those patients who were diagnosed as reactive lymphadenitis with activated histiocyte clusters.
RESULTS
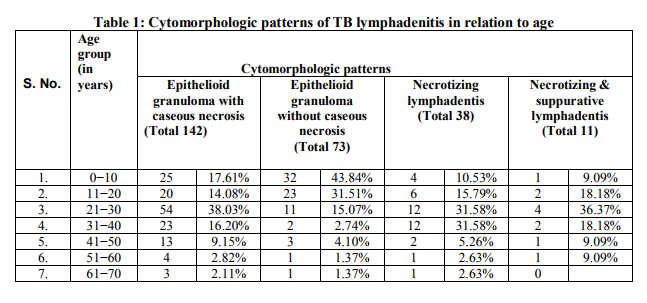
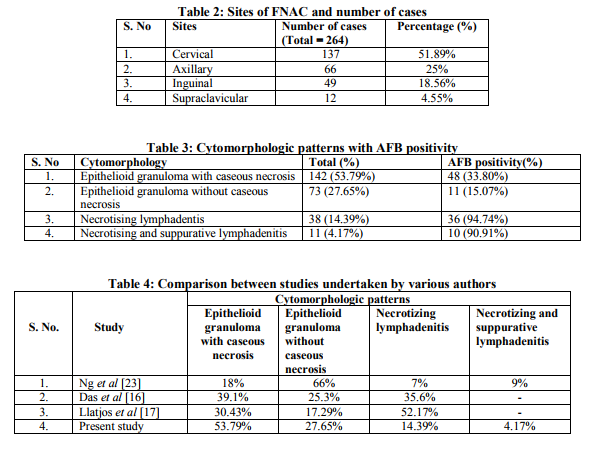
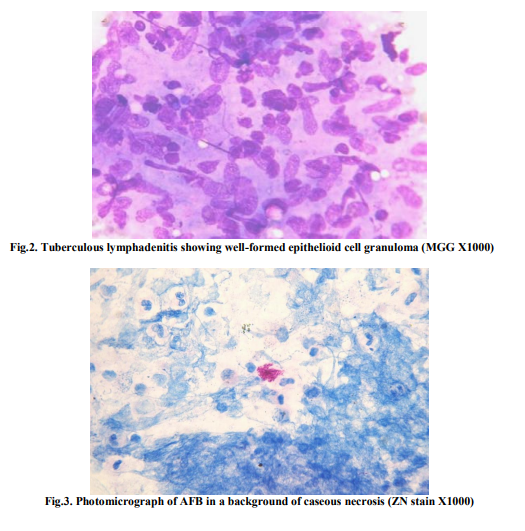
Out of the 728 patients presented with peripheral lymphadenopathy, 264 cases were diagnosed as tuberculous lymphadenitis and 92 cases as reactive lymphadenitis with activated histiocyte clusters. The age of the patient ranged from 4 to 68 years with a median age of 32 yrs. The age group between 21−30 yrs was mostly affected (Table 1). The male: female ratio was 2:1. Among the various sites of lymph node involvements, cervical lymph nodes were the most common-137 cases (51.89%) followed by axillary, inguinal and supraclavicular nodes (Table 2). On the basis of cytomorphological analysis, TB lymphadenitis were categorised into 4 patterns (Table 3): 1. Epithelioid granuloma with caseous necrosis- 142 cases (53.79%) which showed epithelioid granuloma, caseaous necrosis with or without giant cells in a background of lymphoid cells (Fig.1). 2. Epithelioid granuloma without caseous necrosis-73 cases (27.65%) which showed only epithelioid granuloma with or without giant cells (Fig. 2). 3. Necrotising lymphadenitis-38 cases (14.39%) which showed degenerating epithelioid cells in a necrotic background. 4. Necrotising and suppurative lymphadenitis-11 cases (4.17%) which showed degenerating and viable neutrophils in a necrotic background. A definitive cytologic diagnosis of TB lymphadenitis could be considered in the smears with the first two patterns, while the third and fourth could be dismissed as acute suppurative lymphadenitis in the absence of a positive ZN stain. Different patterns showed varied AFB positivity (Table 3). The necrotising lymphadenitis showed 94.74% AFB positivity while necrotising and suppurative lymphadenitis patterns showed 90.91% AFB positivity (Fig.3). The other two patterns i.e., epithelioid granuloma with caseous necrosis and epithelioid granuloma without caseous necrosis had AFB positive only in 48 (33.80%) and 11 (15.07%) cases respectively. Apart from the above four patterns, the present study also showed a fifth cytomorphologic pattern in 92 cases, comprising of ill formed or suspicious epithelioid cells without characteristic necrosis or giant cells. This pattern revealed tiny foci of activated histiocytes in a background of lymphoid cells in various stages of maturation. In such cases a follow-up re-aspiration was advised after 3−4 weeks to look for subsequent development of granuloma. But only 41 cases turned-up for repeat aspiration out of which 27 cases (65.85%) developed epithelioid granuloma, and AFB were seen in 10 cases. Fourteen cases (34.15%) still remained with reactive features.
DISCUSSION
Tuberculosis is a major public health problem in our country. The high rate of tuberculous lymphadenitis is due to low socioeconomic status, illiteracy, incomplete treatment, resistance and increased incidence of HIV. Tubercular lymphadenitis is a common manifestation of extrapulmonary tuberculosis and one of the main causes of lymphadenopathy. Mycobacterial infections are observed among late teens and young adults [11]. Due to high morbidity associated with the disease it affects the earning potential of the individual and their families. Considering the overall prevalence of tuberculosis in the Indian context, the presence of epithelioid cell granulomas is indicative of tuberculosis [12]. FNB has been very useful in the diagnosis of tuberculous lymphadenitis as it was discussed in numerous publications [9, 13−15]. Many authors described three cytomorphologic patterns [16,17]. Whereas some categorized cytologic features of tuberculous lymphadenitis into four groups: (1) epithelioid cell clusters with or without Langhans's giant cells, without necrosis, (2) epithelioid cell clusters with or without Langhans's giant cells, with necrosis, (3) occasional epithelioid cells without characteristic of necrosis nor giant cells, and (4) necrosis without epithelioid cell clusters nor Langhans's giant cells [18,19]. Our study also revealed four patterns similar to the study by Nayak et al [20]. The comparison between various cytomorphologic patterns by different authors is shown in Table 4. The present study showed that every age group of the population was affected by TB and the incidence of the disease was higher in males than in females. This is in correlation with the study by Gupta et al [20]. The cervical group of lymph nodes were the most commonly affected site (51.89%) which was similar to other studies [3,11,22]. The other affected sites were axillary and inguinal group of lymph nodes. These findings were similar to the study by Ng et al [23]. It is observed that there is an inverse relationship between granulomas and the presence of AFB [4,16,24,25]. Our study found higher AFB positivity in smears containing necrotic materials. It was similar to the study by Malakar et al [26]. TB lymphadenitis has unique stages as described by Jones et al [27]. The aspirates from stage one or two tuberculous lymphadenitis usually provide inflammatory cells as seen in reactive lymphadenitis. Thus, FNAC of these stages can only be non-specific reactive. Typical necrotic materials or tubercle bacilli can be seen in the advanced stages in which an abscess is readily formed in the core of the lymph node [8]. So aspirates from an early stage lymph node were the main cause of low sensitivity. If lymph node aspiration was done once in the early stage, the diagnosis is likely to be dismissed as a reactive node. This study shows that re-aspirating after three or four weeks improves the diagnostic efficacy of FNAC. It is therefore necessary to follow the patients whose clinical findings are compatible with TB lesions.
CONCLUSION
To conclude, every case of peripheral lymphadenopathy needs to undergo Fine Needle Aspiration Cytology. This technique coupled with Ziehl-Neelsen staining for Acid Fast Bacilli is an excellent method for diagnosing tuberculous lymphadenitis. It can even provide an important clue about the immune status of the patient. The study also included the significance of repeat aspiration cytology in patients with strong clinical suspicion of tuberculosis.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENT
Authors acknowledge the immense help received from the scholars whose articles are cited and included in references of this manuscript. The authors are also grateful to authors / editors / publishers of all those articles, journals and books from where the literature for this article has been reviewed and discussed
References:
1. Van Altena R, Richter C, 2002. De kliniek en diagnostiek van pulmonale en extrapulmonale vormen van tuberculose. Ned Tijdschrift Med Microbiol 10 C, pp. 46−52.
2. Thompson MM, Underwood MJ, Sayers RD, Dookeran KA, Bell PR, 1992. Peripheral tuberculous lymphadenopathy: a review of 67 cases. Brit J Surg 79, pp.763−764.
3. Bezabih M, Mariam DW, Selassie SG. Fine needle aspiration cytology of suspected tuberculous lymphadenitis. Cytopathology 2002;13(5), pp. 284−90.
4. Nataraj G, Kurup S, Pandit A, Mehta P. Correlation of fine needle aspiration cytology, smear and culture in tuberculous lymphadenitis: a prospective study. JPGM 2002; 48(2): 113−6.
5. Metre MS, Jayram G. Acid fast bacilli in aspiration smears in tuberculous lymph nodes-an analysis of 225 cases. Acta Cytol 1987; 11: 17−9.
6. Arora B, Arora DR. Fine needle aspiration cytology in the diagnosis of tuberculous lymphadenitis. Indian J Med Res 1990; 91: 189−92.
7. Ponder TB, Smith D, Ramzy I, 2000. Lymphadenopathy in children and adolescents: role of fine-needle biopsy in management. Cancer Detect Prev 24, pp. 228−233.
8. Suh KW, Park CS, Lee JT, Lee KG. Diagnosis of cervical tuberculous lymphadenitis with fine needle biopsy biopsy and cytologic examination under ultrasosographic guides. Yonsei Med J 1993;34(4): 228−333.
9. Dasgupta A, Ghosh RN, Poddar AK, Mukherjee C, Mitra PK, Gupta G, Ganguly U, 1994. Fine needle biopsy cytology of cervical lymphadenopathy with special reference to tuberculosis. J Indian Med Assoc 92, pp. 44−46.
10. Singh JP, Chaturvedi NK, Das A, 1998. Role of fine needle biopsy cytology in the diagnosis of tuberculous lymphadenitis. Indian J Pathol Microbiol 32, pp. 100−104.
11. Grange J, Cristopher C, Yates M. Bacteriological survey of tuberculous lymphadenitis in south-east England. Journal of Epidemiology and Community Health 1982; 36: 157−61.
12. Pandit AA, Khilani PH, Prayag A. Tuberculous lymphadenitis: extended cytomorphologic features. Diagn Cytopathol 1995; 12: 23−7.
13. Masud KU, Wadood AU, Sanaullah, Baloch MA, Mirza JA, Sahibzada NJ, 1999. Role of FNB in the diagnosis of tuberculous lymphadenitis. Biomedica 15, pp. 54−59.
14. Gupta SK, Chugh TD, et al., 1993. Cytodiagnosis of tuberculous lymphadenitis. Acta Cytol 37, pp. 329−332.
15. Khan UF, ul Khan RAH, Ashraf J, Barki NU, 2001. Fine needle biopsy biopsy versus excision biopsy in tuberculous cervical lymphadenitis. J Rawal Med Coll 5, pp. 21−24.
16. Das DK, Pant JN, Chachra M et al. Tuberculous lymphadenitis: correlation of cellular components and necrosis in lymph node aspirate with AFB positivity and bacillary count. Indian J Pathol Microbiol 1990; 33: 1−10.
17. Llatjos M, Romeu J, Clotet B et al. A distinctive cytologic pattern for the diagnosing TB lymphadenitis in AIDS. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr 1993; 6 (12): 1335−8.
18. Gupta AK, Nayar M, Chandra M, 1992. Critical appraisal of fine needle biopsy cytology in tuberculaous lymphadenits. Acta Cytol 36, pp. 391−394.
19. Lau SK, Wei WI, Hsu C, Engzell UC, 1990. Efficacy of fine needle aspiration cytology in the diagnosis of tuberculous cervical lymphadenopathy. J.Laryngol Otol 104, pp.24−27.
20. Nayak S, Puranik SC, Deshmukh SD et al. Fine needle aspiration cytology in the tuberculous lymphadenitis of patients with or without HIV infection. Diagn Cytopathol 2004; 31 (4): 204−6.
21. Gupta S, Rajak CL, Sood BP, Gulathi M, Rajwanshi A, Suri S. Sonographically guided fine needle aspiration biopsy of abdominal lymph node. J Ultrasound Med 1999; 18: 135−9.
22. Bhatt JV, Shah JM, Shah J. Clinicopathological profile of cervical lymphadenopathy. Journal of Applied Basic Medical Sciences 2000; 2(2); 35−9.
23. Ng WF, Kung ITM. Pathology of tuberculous lymphadenitis: A fine needle aspiration approach. J Hong Kong Med Assoc 1990; 42 (1): 18−21.
24. Tripathy SN, Mishra N, Patel NM, Samantray DK, Das BK, Mania RM. Place of aspiration biopsy in the diagnosis of lymphadenopathy. Ind J Tub 1985; 32:130−4.
25. Lenzini L, Rottoli P, Rottoli L. The spectrum of human tuberculosis. Clin Exp Immnunol 1977; 27: 230−7.
26. Malakar D, Jajoo ILN, Kiran S et al. A clinical evaluation of fine needle aspiration cytology in the diagnosis of lymphadenopathy. Ind J Tub 1991; 38: 17−9.
27. Jones PG, Campbell PE. Tuberculous lymphadenitis in childhood: The significance of anonymous mycobacteria. Br J Surg 1962; 50: 302−14.

|






 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License