IJCRR - 4(24), December, 2012
Pages: 89-99
Print Article
Download XML Download PDF
A STUDY ON THE PREVALENCE OF OVERWEIGHT AND OBESITY AND ITS INFLUENCING FACTORS IN RURAL ADOLESCENT SCHOOL GOING CHILDREN IN KERALA, INDIA
Author: Shiny George, Jeffy Binu, Biju Baby Joseph
Category: Healthcare
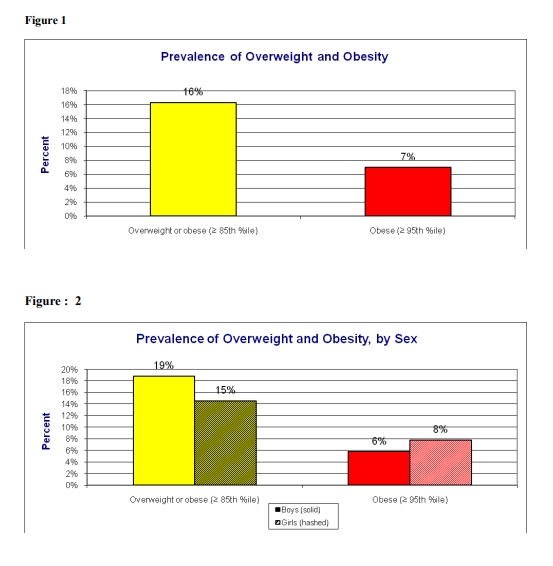
Abstract:Background: Obesity has become a worldwide phenomenon cutting across regional and economic barriers. Childhood and adolescent obesity has emerged as an epidemic not only in the developed countries but also in the developing countries that are in rapid epidemiological transition, and India is no exception. 50-80% of the obese children will continue to be obese adults . However, whether or not obesity persists into adulthood, the obesity in childhood appears to increase the risk of subsequent morbidities . Objective: To assess the prevalence of overweight and obesity and its influencing factors in adolescent school going children in a rural area in Kerala. Research methodology: Height and weight were measured and obesity was assessed using international obesity task force criteria in 173 students of 13 -18 years. Details of influencing factors obtained using a pretested questionare. Results :The study revealed a high prevalence of overweight (16%) and obesity (7%). Prevalence of overweight and obesity was 19% and 6% among boys and 15% and 8% among girls respectively. Among the influencing factors sleeping time and fast food were found to be significant (p=0.01). Conclusion: Increased prevalence of overweight and obesity in rural adolescents emphasizes the need of early recognition of excessive weight gain relative to linear growth and early intervention after an increase in weight-for-height or BMI percentiles in children and adolescents .
Keywords: obesity, overweight, adolescent
Full Text:
INTRODUCTION
Young people in their teens constitute the largest age group in the world, in a special stage recognized across the globe as the link in the life cycle between childhood and adulthood. Excessive amount of adipose tissue in children and adolescents and obesity in particular constitute a growing health problem throughout the world. Childhood and adolescent overweight and obesity are related to health risks, medical conditions, and an increased risk of adult obesity, with attendant impacts on morbidity and mortality. Childhood obesity is a serious health concern affecting over 155 million children in developed countries worldwide. The increasing prevalence of overweight, obesity and its consequences prompted the World Health Organization to designate obesity as a global epidemic1 . Data from NHANES IV indicate that 21% to 23% of children aged 6–17 years are overweight, and 9 to 13% of children aged 6–17 years are obese2 . In the United States, the prevalence of obesity among adolescents aged 12–19 years quadrupled from 1966 to 2003–2006 (from 4.6% to 17.6%) 3,4. Currently one in three (34.9%) U.S. adolescents are overweight or obese4 . It was predicted that by 2010, over 40% of children in the North American and Eastern Mediterranean WHO regions, 38% in the European region, 27% in the Western Pacific region, and 22% in South-East Asian region would be overweight/obese5 . Even in countries like India, which are typically known for high prevalence of under nutrition, a significant proportion of overweight and obese children now coexist with those who are under nourished6. Obesity is a complex condition which is influenced by a wide-range of genetic and non-genetic factors, with interactions between many of these. Obesity may be defined as excess accumulation of adipose tissue in the body7 . It is a chronic disease in which body weight exceeds the normal by at least 20 percent, which becomes a psychosomatic, social economic and aesthetic problem. Some factors in early life are associated with increased risk of obesity in childhood. These are parental obesity, more than 8 hours spend for watching TV per week, very early body mass index, catch up growth, weight gain in first year , birth weight and short sleep duration. Childhood obesity can adversely affect nearly every organ system and often cause serious consequences, including hypertension, dyslipidemia, insulin resistance/diabetes, fatty liver disease, psychosocial complications8 , increased risk of cardiovascular disease in adulthood9 ,Pulmonary disorders including obstructive sleep apnea and reactive airway disease10 . Higher BMI and greater adiposity have been associated with lower vitamin D levels in children11,12. Overweight/obese children are also at least two fold more likely to be iron-deficient than normal weight children13 . Complications of childhood obesity include acceleration in the timing of thelarche and menarche in girls,14 pubertal advancement in boys15 and adverse effects on maturation and alignment of developing bones in both16 . Serdula found a risk for adult obesity at least twice as High in obese children as in nonobese ones; approximately one-third of preschool children and 50% of school-age children become obese adults.17 Height- and weight-based anthropometric measurement is an excellent tool to gauge general nutritional status in a Population. Commonly used cut points for childhood overweight and obesity include: 110% or 120% of ideal weight for height; weight-for-height Z-scores of >1 and >2, and BMI at the 85th, 90th, 95th, and 97th percentiles.5 Studies from the rural areas in India mainly emphasized on under nutrition, and data on overweight/obesity was not available. We attempted to document the prevalence of obesity and overweight among adolescent school children of a rural area in Kerala and to identify the factors which influenced adolescent overweight and obesity.
MATERIALS AND METHOD
The present cross sectional study was undertaken in the Nehru Memorial Public School which is one of the private unaided school in Kaithakuzhy ,a rural area in Kollam district, Kerala state. 173 students in the age group of 13-18 years, who were studying in class IX to XII, were enlisted for the study. This study was carried out from June to August 2012.
A prior informed consent for the study was taken from the school authorities . A predesigned and pretested questionnaire was used to interview the study participants to elicit the information on their family characteristics like economic status, education and occupation of the parents. Information on individual characteristics like age, sex, eating habits, and time spent for television viewing , hours of sleeping , intake of junk food and fast food , time spent on outdoor games and indoor games were also collected. We administered the questionnaire to all children who attended school on the day of the survey. Children who were absent from school because of sickness or other reasons were not followed-up. During the data collection, the class teachers were asked to accompany the students. Data on weight and height were collected for each through direct physical examinations. Body weight was measured (to the nearest 0.5 kg) with the subject standing motionless on the weighing scale with feet 15 cm apart, and weight equally distributed on each leg. Height was measured (to the nearest 0.5 cm) with the subject standing in an erect position against a vertical scale. Height and weight were measured using standard procedure and the body mass index (BMI) was calculated as the weight in kilogram/height in meter2 . Overweight and obesity were assessed by considering the BMI for a particular age and sex. International Obesity Task Force (IOTF) classification was utilized for the estimation of overweight and obese subjects. Students who had a BMI for age-sex ≥ the 85th percentile to < the 95 percentile of the reference population were classified as overweight and who had a BMI for age-sex ≥ the 95th percentile of the reference population was classified as obese . The number of underweight, normal, overweight and obese was calculated.
Statistical Analysis
The data were entered into an Excel 2007 Microsoft spreadsheet and were analyzed using SPSS 15.0.1 (SPSS for windows, version 15.0.1.2001.) The continuous variables were presented as mean ± SD . Prevalence of overweight and obesity is presented as percentage. The associations were assessed by using the Pearson Chi-square test. For all the statistical tests, a p value of <0.05 was considered as statistically significant.
RESULTS
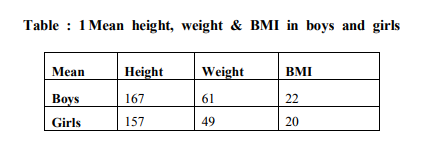
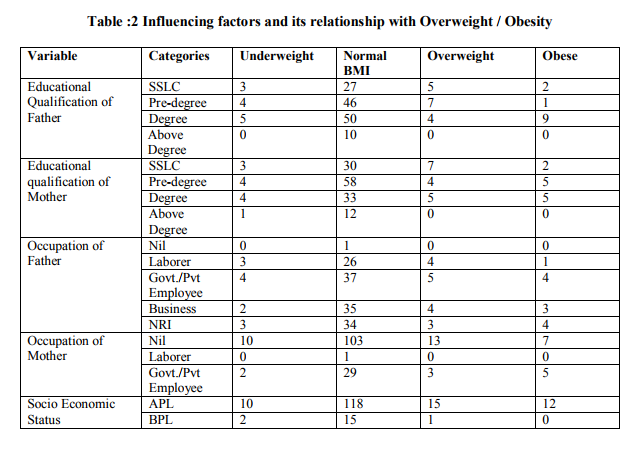
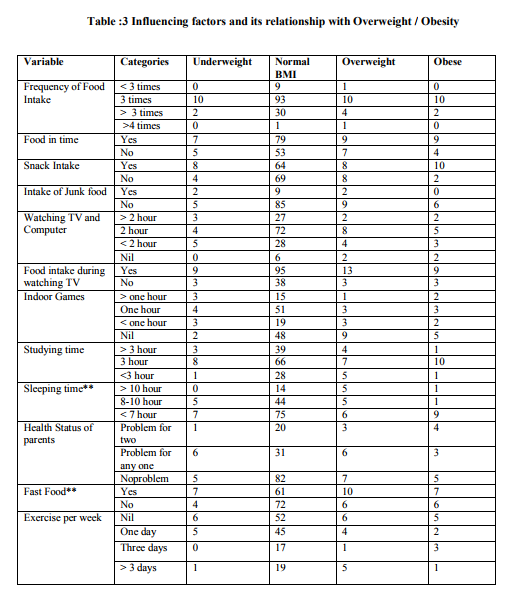
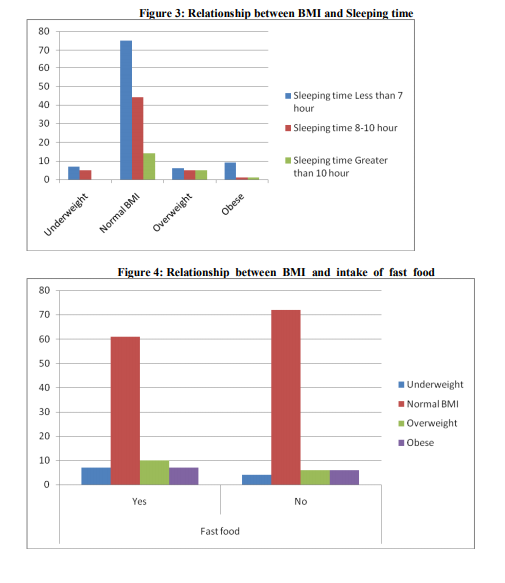
A total number of 173 with age group between 13 -18 years from a school in rural area were screened for their height, weight and body mass index. Out of 173 children 70 were boys and 103 were girls (Table 1). The height, weight and BMI were higher in boys than girls (Table 1). However, these differences were not significantly different with respect to gender at any given age. The overall prevalence of boys and girls having normal BMI were 78% and 76 % respectively. The prevalence of overweight was 19 % among boys and 15% among girls. Prevalence of obesity was 6% in boys and 8% in girls. The prevalence of underweight is 3% in boys and 10% in girls (Fig. 1). There was also a higher prevalence of overweight in boys compared with girls, and obesity in girls compared with boys. An attempt was made to know the influencing factors. The factors studied are educational status and occupation of parents, socioeconomic status, individual characteristics like age, sex, eating habits, and time which was spent for television viewing , intake of food during watching T.V., hours of sleeping , having snacks, junk food and fast food ,time spent for outdoor games , indoor games and exercise. (Table2,3) . Among them sleeping habit and habit of consumption of highenergy foods (fast foods) were found to be the important influencing factors of childhood obesity ( fig.3, 4).
DISCUSSION
The World Health Organization (WHO) regards obesity as one of the most serious public health problems in the world that can affect young children and adolescents . There are very few reports from the developing world on the prevalence of obesity among children even though in developed countries it has reached epidemic proportions. In countries such as India that undergo nutritional transition, a rapid increase in obesity and overweight is observed. In this study, we have presented the estimates on the prevalence of overweight and obesity in school children who were aged 13-18 years in a rural area in Kollam, Kerala, by using the individual weight and height measures to calculate the BMI. The present study showed that the prevalence of overweight was high among children, 19% in boys, 15% in girls. The obesity was seen in 6% of boys and 8% of girls. The overall prevalence of overweight among the rural adolescent school children was 16% and the prevalence of obesity was 7%.(Fig. 2) Various studies from India have also shown the increased prevalence of obesity in India. A study which was conducted by the Nutrition Foundation of India, found that among 5000 children who were aged 4–18 years in a Delhi private school, 29% were overweight 18. A similar study which was done in south India showed the prevalence of obesity to be 3.1% and that of overweight to be 16.8%.19 Recent studies in India and other countries revealed that obesity is becoming a growing health problem among children and adolescents, especially in urban populations.20 Studies from the rural areas mainly emphasized on under nutrition, and data on overweight/obesity was not available. Therefore we decided to study the prevalence of overweight and obesity in a rural area in Kerala , India. However, a single study conducted by Deshmukh et al21 reported the prevalence of obesity to be 2.2 per cent in the rural Wardha district by using the same definition. In our study, the prevalence which was reported was more than 3 times of that which was reported in Deshmukh’s study. A cross-sectional study which was carried out on school children of the age group of 9-15 years in Punjab, revealed that the overall prevalence of obesity and overweight were 11.1% and 14.2% respectively 22. The reason for the higher prevalence of overweight and obesity among the adolescent populations which were studied in Delhi and Punjab may be that the subjects who were selected for these studies were affluent. In urban areas, considering the necessity of keeping children away from heavy traffic, they are not allowed to ride bicycles and are only allowed to play indoor games or watch television. Therefore, they are not encouraged to participate in outdoor sports and games. Many studies shows that snacks and junk food (bakery items, pizza, burger, cheese, butter, oily items) tends to be more common among overweight and obese adolescents than among normal-weight adolescents.23 In the present study there was no significant relationship between the frequency of food intake, consumption of milk , eggs, snacks and junk food. Our study is for the first time from a rural area in southern part of India . The relatively high prevalence of overweight (16 %) and obesity (7 %) in a rural area is alarming. There was also a higher prevalence of obesity in girls compared to boys. Increase in the prevalence of obesity observed between boys and girls could be explained by higher physical activity level of boys than girls observed in this population. We did not get a significant relationship between SES and overweight/obesity. One possible explanation for the different SESoverweight and obesity relationship in developing countries such as India is that the influence of SES on people’s lifestyles such as diet, food consumption patterns, and public services such as health care and transportation and physical activity may differ. Fathers and mothers education and occupation also did not show a significant relation may be because all of them had studied upto or more than 10th std, as Kerala has high literacy rates.
There was a significant association between sleeping time and overweight/obesity (p= 0.01). Students who were sleeping for less than 7 hours was found to be obese. But hours of watching television and food during watching TV was not statistically significant even though majority of children spent time for watching TV and had the habit of taking snacks while watching TV. Junk food and fast food contains more amount of fat than carbohydrate and protein.24-25 Fat is less satiating than carbohydrate and dietary fat is stored more efficiently than carbohydrate or protein which finally results in obesity or overweight.26 In our study consumption of fast food was positively associated with increased BMI(p=0.01). These results are consistent with other studies which show an association between frequency of restaurant visit and obesity.27 Based on the findings of our study it is recommended that consumption of high fat and high energy food (fast foods) should be avoided by children. Sedentary life style should be discouraged.
Adolescents are at high risk for use of unhealthy weight control behaviors and would benefit from interventions to increase knowledge and social support for achieving and maintaining a healthy weight. Since adolescence is a period of transition from childhood to adulthood, it assumes critical position in the lifecycle of human beings and BMI measurement to detect overweight in older adolescents could identify those at increased risk of developing adult obesity, and its consequent morbidities. Children and adolescents are often considered the priority population for intervention strategies because, firstly weight loss in adulthood is difficult and there are a greater number of potential interventions for children than for adults. Schools are a natural setting for influencing the food and physical activity environments of children.
CONCLUSION
The present study was conducted in 173 adolescent school going children of a rural area in Kerala . The relatively high prevalence of overweight and obesity in a rural area indicates that adolescent obesity is an emerging health problem in rural areas as well and the need of effective preventive measures to halt this epidemic at its beginning. Based on the findings of this study it is recommended that consumption of high fat and high energy food should be avoided by children. Sedentary life style should be discouraged. Increase physical activity like playing outdoor games, walking, cycling should be encouraged in children. Health education should be given to parents, teachers and children regarding dietary habit and sedentary life style.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENT
Authors acknowledge the immense help received from the scholars whose articles are cited and included in references of this manuscript. The authors are also grateful to authors / editors /publishers of all those articles , journals and books from where the literature for this article has been reviewed and discussed.
References:
1. WHO consultation on obesity. Special issues in the management of obesity in childhood and adolescence. In Obesity Preventing and Managing the Global Epidemic, WHO, Geneva, 1998, pp.231– 247.
2. Troiana, R. P., Flegal, K. M., Kuczmarski, R. J., Campbell, S. M. and Johnson, C. L., Overweight prevalence and trends for children and adolescents. The National Health and Nutrition Examination Surveys 1963 to 1991. Arch. Pediatr. Adolesc. Md., 1995, 149,1085–1091.
3. Ogden CL, Flegal KM, Carroll MD, et al. Prevalence and trends in overweight among US children and adolescents, 1999- 2000. J Am Med Assoc 2002;288:1728– 32.
4. Ogden CL, Carroll MD, Flegal KM. High body mass index for age among US children and adolescents, 2003-2006. J Am Med Assoc 2008;299:2401–5.
5. Joan C. Han, Debbie A. Lawlor, and Sue Y.S. Kimm Childhood Obesity – 2010:Progress and Challenges Lancet. 2010 May 15; 375(9727): 1737–1748.
6. Popkin BM., D Horton, S Kim, A Mahal and J Shuigao. Trends in diet nutritional status and diet related non communicable diseases in China and India: The economic costs of the nutritional transition, Nutr Rev. 2001;59:379-90.
7. Guillaume M. Defining obesity in childhood: current practice. Am J Clin Nutr 1999; 70:126S-130S.
8. Daniels SR. Complications of obesity in children and adolescents. Int J Obes (Lond). 2009; 33 (Suppl 1):S60–5. [PubMed: 19363511]
9. Owen CG, Whincup PH, Orfei L, et al. Is body mass index before middle age related to coronary heart disease risk in later life? Evidence from observational studies. Int J Obes (Lond). 2009; 33(8):866–77. [PubMed: 19506565]
10. Gilliland FD, Berhane K, Islam T, et al. Obesity and the risk of newly diagnosed asthma in schoolage children. Am J Epidemiol. 2003; 158(5):406–15. [PubMed: 12936895]
11. Alemzadeh R, Kichler J, Babar G, Calhoun M. Hypovitaminosis D in obese children and adolescents: relationship with adiposity, insulin sensitivity, ethnicity, and season. Metabolism. 2008; 57(2):183–91. [PubMed: 18191047]
12. Yanoff LB, Parikh SJ, Spitalnik A, et al. The prevalence of hypovitaminosis D and secondary hyperparathyroidism in obese Black Americans. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf). 2006; 64(5):523–9. [PubMed: 16649971]
13. Nead KG, Halterman JS, Kaczorowski JM, Auinger P, Weitzman M. Overweight children and adolescents: a risk group for iron deficiency. Pediatrics. 2004; 114(1):104–8. [PubMed: 15231915]
14. Bau AM, Ernert A, Schenk L, et al. Is there a further acceleration in the age at onset of menarche? A cross-sectional study in 1840 school children focusing on age and bodyweight at the onset of menarche. Eur J Endocrinol. 2009; 160(1):107–13. [PubMed: 18974233]
15. Mamun AA, Hayatbakhsh MR, O’Callaghan M, Williams G, Najman J. Early overweight andpubertal maturation-- pathways of association with young adults’ overweight: a longitudinal study. Int J Obes (Lond). 2009; 33(1):14–20. [PubMed: 18982007]
16. Taylor ED, Theim KR, Mirch MC, et al. Orthopedic complications of overweight in children and adolescents. Pediatrics. 2006; 117(6):2167–74. [PubMed: 16740861]
17. Serdula MK, Ivery D, Coates RJ, Freedman DS, Williamson DF, Byers T (1993). Do obese children become obese adults? - A review of the literature. Prev. Med., 22: 167- 177.
18. Chatterjee P., India sees a parallel rise in malnutrition and obesity. Lancet 2002; 360: 1948.
19. Ramachandran A, Snehlata C, Vinitha R, Thayyil M. The prevalence of overweight in urban Indian adolescent school children. Diabetes Res. Clin. Practice 2002; 57: 185–190.
20. Callahan ST, Mansfield MJ. Type 2 diabetes mellitus in adolescents. Curr Opin Pediatr. 2000; 12:310-315.
21. Deshmukh PR, Gupta SS, Bharambe MS, Dongre AR, Maliye C,Kaur S, et al. Nutritional status of adolescents in rural Wardha. Indian J Pediatr 2006;73:15-7.
22. Chhatwal J, Verma M, Riar SK. Obesity among the pre-adolescents and adolescents of a developing country (India). Asia Pac.J. Clin. Nutr., 2004; 13: 231–35.
23. Klesges RC , Klesges LM, Eck LH, Shelton ML. A longitudinal analysis of accelerated weight gain in preschool children. Pediatrics 1995; 95:126-130.
24. Rolls BJ, Kim-Harris S, Fischman MW, Foltin RW, Moran TH, Stoner SA. Satiety after preloads with different amounts of fat and carbohydrate: implications for obesity. Am J Clin Nutr 1994; 60:476- 487.
25. Blundell JE, Burley VJ, Cotton JR, Lawton CL. Dietary fat and the control of energy intake: evaluating the effects of fat on meal size and postmeal satiety. Am J Clin Nutr 1993; 57:772S-778S.
26. Poppitt SD. Energy density of diets and obesity. Int J Obes 1995; 19:S20-S26.
27. Berkey CS, Rockett HR , Field AE, Gillman MW, Frazier AL, Camargo Jr CA, et al. Activity, dietary intake, and weight changes in a longitudinal study of preadolescent and adolescent boys and girls. Pediatrics 2000; 105:56-65.
|






 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License