IJCRR - 5(5), March, 2013
Pages: 125-134
Date of Publication: 22-Mar-2013
Print Article
Download XML Download PDF
VALUE OF MODIFIED TRIPLE TEST IN THE DIAGNOSIS OF PALPABLE BREAST LUMPS
Author: Rajan Vaithianathan, Vinoth Sundaresan, Ramachandran Santhanam
Category: Healthcare
Abstract:Background and objectives: Breast lumps in women are a common clinical problem that requires rapid and accurate evaluation with an important aim of excluding any malignancy. The classical triple test includes physical examination, mammogram and fine needle aspiration cytology. We have modified this approach by substituting mammogram with ultrasound for the assessment of breast lesions. The objective of the study was to evaluate the accuracy of this modified triple test (MTT) in the management of palpable breast lumps. Patients and methods: A prospective cross sectional study was conducted at Mahatma Gandhi Medical College and Research Institute. Eighty patients with palpable breast lumps were assessed by all the components of MTT. The results of individual components as well as the overall MTT were compared with the final histopathological examination. Results: Physical examination showed 96.67% sensitivity, 84% specificity and 78.4% positive predictive value for diagnosing malignant breast lumps. Ultrasonography showed 93.10% sensitivity, 95.9% specificity and 93.1% positive predictive value. Fine needle aspiration cytology (FNAC) showed 96.6% sensitivity, 100% specificity and 100% positive predictive value and the modified triple test showed 100% sensitivity, 82% specificity and an accuracy rate of 88.7%. Conclusions: The triple test is 100% accurate in the diagnosis of palpable breast lesions when all three elements were concordant (benign or malignant). Among the three components, FNAC had the highest specificity. MTT is reliable in guiding the clinician in the efficient management of patients with breast lumps. MTT is beneficial in reducing the number of unnecessary open biopsies to confirm the diagnosis. The output of MTT is easily reproducible, making it a valid and reliable diagnostic test in the management of palpable breast lumps.
Keywords: modified triple test, mammogram, breast lump, accuracy
Full Text:
INTRODUCTION
Breast cancer is the most common site specific cancer in women and is one of the leading causes of death from cancer for women, accounting for about 20% of cancer related deaths in women1, 2 . The accurate diagnosis and appropriate management of breast lumps is associated with anxiety and stress, both for the patients and the caring physician. The steps in establishing a diagnosis include clinical examination, mammogram and needle biopsy. The individual components of this triple assessment are not reliable on their own in reaching a diagnosis but when combined, the diagnostic accuracy is nearly 100% and the triple test has been proposed as the gold standard for the diagnosis of breast lumps3- 10 . Breast ultrasound (US) is a very important adjunct to mammography (MMG) in patients with equivocal findings. It is now widely accepted as a diagnostic modality for breast lesions. Using modern high resolution probes, majority of carcinomas of size less than 1 cm can be identified. Potential advantages of breast US are non-invasiveness, easy availability, lower cost and good accuracy rate for diagnosing breast masses11,12. Bassett et al found that MMG was not useful in assessing breast lesions in women less than 35 years due to denser breast tissue. On the contrary, US was helpful in avoiding unnecessary breast biopsies and was recommended as the initial examination in younger women13 . We carried out this study with an aim to assess the diagnostic accuracy of MTT in palpable breast lumps. PATIENTS AND METHODS This was a prospective cross sectional study of 100 female patients diagnosed with breast lumps, presenting to the General Surgery Outpatient Department of Mahatma Gandhi Medical College and Hospital, Puducherry. This study was carried out from Nov 2009 to Jun 2011. The inclusion criteria: 1. All females patients of age > 20 years with palpable breast lump. 2. Patient willing for excision of breast lump The exclusion criteria: 1. Previous breast biopsy 2. Patient refusing surgery 3. Fungating growth Each patient was subjected to the modified triple test(Fig.1). A complete physical examination was performed followed by US of the breast lesions and fine needle aspiration of the lumps. US of the breast was performed by the radiologist using a ESOATE BIOMEDICA AU3 partner ultrasound machine with a 10 MHz probe. The lesions were classified as malignant or benign based on standardized sonologic criteria. Following imaging, FNAC was carried out and smears sent for cytological examination. The results of the modified triple test were then analyzed individually and as a combination. The triple test was considered positive if any one of its components showed a positive report (suspicious or malignant). All patients underwent either excision biopsy or definitive surgery. Patients with concordant malignant reports were treated by definitive surgery. The final histopathological reports were compared to the results of the modified triple test.
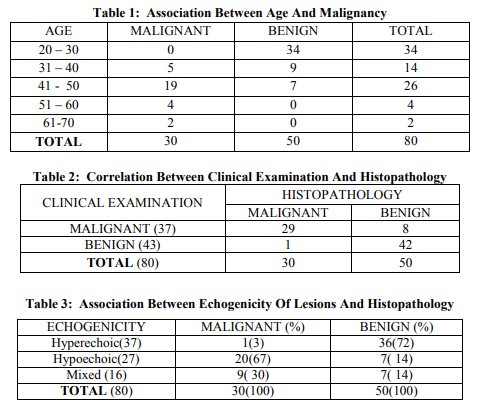
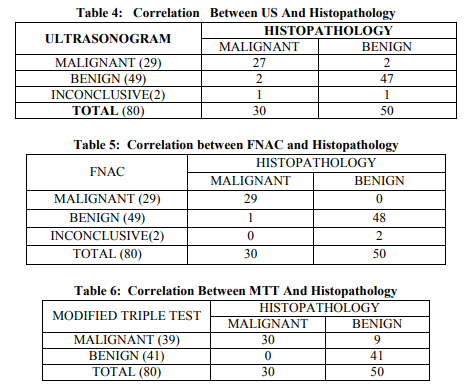
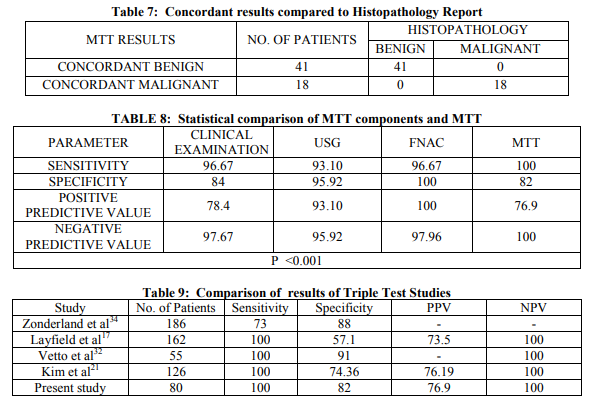
Based on the complete clinical examination findings, 37 patients were diagnosed to have malignant breast lump, 43 patients had benign lesion. Out of the 37 patients with clinically diagnosed malignant breast lump, 29 were confirmed malignant by histopathology report, and remaining 8 revealed benign lesion. Out of the 43 patients with clinical diagnosis of benign breast lump, 42 were confirmed to have benign histopathological lesion and the remaining one had malignancy (table 2). Breast US was carried out on all 80 patients as the second component of the modified triple test protocol. US revealed hyperechoic breast lumps in 37 patients, out of which 36 were benign and 1 turned out to be a malignant lesion. 27 patients had hypoechoic breast lumps, 20 were finally confirmed to have malignant lesion and the remaining 7 had benign lesion. The remaining 16 patients had lumps with mixed echogenicity, out of which 9 were of malignant nature and 7 had benign lesion (table 3). US imaging of the breast lump revealed findings that were highly suggestive of malignancy in 29 patients. Out of these 29, 27 (93%) were finally confirmed to have malignant lesion and remaining 2(7%) had benign lesion. Sonologic benign breast disease were found in 49 patients, out of which 47 (96%) were confirmed to have benign histopathology, and the remaining 2(4%) patients turned out to have carcinoma (table 4). FNAC was performed as the final step of the assessment in all the 80 patients. Benign lesions were diagnosed in 49(61%) patients. Malignant cytology was seen in 29 (36%) patients and the remaining 2(3%) patients had inconclusive smears. Out of 49 patients with benign cytology reports, 48 (98%) were found to have benign histopathology report and 1(2%) patient had carcinoma. All the 29 patients who had malignant features on FNAC were found to have carcinoma on histopathological examination. Two patients who had inconclusive cytology report were found to have benign lesion on final histopathology report (table 5). Putting together all the information gathered from the Modified Triple Test assessment, the patients in the study group were categorized into these groups – 41 were concordant benign (all three components with benign result), 18 were concordant malignant, 21 patients had at least one component positive for malignancy. All the 41 patients with concordant benign result had benign histology and the 18 patients with concordant malignant report had carcinoma confirmed by histology. Out of the 21 patients, 12 were proven to have malignant histology and the remaining 9 patients had benign histology (tables 6 & 7). The diagnostic accuracy rate of MTT in concordant cases (benign and malignant) was 100%. The sensitivity, specificity, PPV and NPV of MTT was found to be 100%, 82%, 76.9% and 100% respectively (table 8). Overall, the diagnostic accuracy rate of MTT was 88.7%.
histopathologic examination or clinical followup4,8,17-19 . The triple test result may significantly modify the pre-test probability for a patient. A negative TT(all components negative) suggests that the probability of breast cancer is less than 1%. A positive finding on one of the components of the triple test will steadily increase the probability of cancer. For instance, a patient with a pre-test probability of 5% will, on receipt of a positive triple test, have a post-test probability of 12%. There is strong evidence for the value of using the triple assessment to diagnose cancer in women with breast cancer. A review of 15 follow up studies showed that triple assessment is consistently more sensitive than any single test alone, capable of picking up 95% to 100% of cancers when at least one component is positive. When all three components of triple test are concordant, the diagnostic accuracy is 100%20 . This obviates the need for open biopsy and patients could directly undergo definitive treatment. Although clinical examination has good sensitivity for identifying patients with malignancy, it is the least reliable in the context of a diagnostic clinic providing rapid and accurate results. This has made mandatory the addition of an imaging method (US or MMG) and cytological examination of the breast lesions. Recently, many studies have used US in lieu of MMG in the assessment of breast lumps at the time of one stop clinic visit21-23. US is the first line investigation in young women with mammographically dense breasts. Some malignant breast lesions are not visible on MMG but are detected by US. The false negative rate of MMG in the detection of breast cancer has been consistently reported to be approximately 10%24 . These mammographically occult lesions often occur in women with dense breasts. An US examination is extremely useful in these situations. US used liberally as an adjunct to MMG, increases the cancer detection rate by almost 15%.US is therefore recommended in all cases where there is a clinical suspicion of malignancy even if the mammogram is normal23 . Breast US does not expose the patient to ionizing radiation, is easily available, cheaper and has already proven to be an important adjunct to the other radiological and pathological investigations for breast lesions. In our study, we have replaced MMG with breast US as it is more sensitive in detecting abnormalities in denser breast tissue of younger women, who forms the majority of our patient population (60% in our study). We found that US examination of the breast lesions showed good sensitivity (93.1%), high specificity (95.52%) and high positive predictive value (93.1%). Recent technical advances in ultrasonography have expanded the potential utility of this modality in the evaluation of breast lesions, producing high specificity in diagnosing solid abnormalities and other cystic lesions25-27. Our observations showed high sensitivity and specificity which may be due to the clinical profile of our patients, late presentation with large and locally advanced breast lesions. Fine needle aspiration cytology has a high diagnostic accuracy rate (97%) in the hands of experienced clinical and cytopathologists14. Our study has shown high sensitivity for FNAC (96.67%), high specificity (100%) and high positive predictive value (100%).There were no false positive diagnoses in our study. One patient had a false negative report due to a very hard breast lump that produced acellular aspirate. Final histopathology showed scirrhous type of carcinoma. Overall, there was excellent agreement between the FNAC and the final histopathological report in the majority of cases. Multiple studies have shown that a mass with a concordant benign triple test result can be safely followed up without open biopsy. This is especially helpful in evaluating low-risk masses or multiple masses in a young patient. Similarly, patients with a concordant malignant triple test result can safely proceed to definitive therapy, without undergoing an open biopsy21,22,28-31. In our study, this pattern was found in 18 patients who directly proceeded to definitive procedure, avoiding any open biopsy. We also found that the modified triple test had a diagnostic accuracy rate of 100% among patients with concordant malignant or benign results. Thus, a concordant triple test result can guide treatment with 100% accuracy. In non-concordant cases, we found that FNAC was the single most important investigation to confirm the diagnosis, with high sensitivity, specificity and positive predictive values. Morris KT et al evaluated breast masses in 113 women of younger age, using a scoring system for the modified triple test. This method was found to be a rapid and accurate assessment of breast masses in this population where most cases of breast cancer are missed. The diagnostic accuracy was 100% when score was other than 5 points. Based on the scores, patients could proceed to definitive surgery (≥6 points) or go on to surveillance program (≤4). Open biopsy was required only in 3% of the study group. This approach thus avoided open biopsy in the majority of cases, while identifying all malignancies28 . Two studies had compared the cost effectiveness of TT to traditional method of diagnosis by open biopsy for breast lumps. The authors concluded that TT provided equivalent diagnostic accuracy to that of open biopsy but with a substantially reduced costs32,33 . Another similar study by Vetto et.al31 which included 55 younger women with palpable breast lumps assessed by MTT yielded high diagnostic accuracy. This also led to avoidance of routine open biopsy resulting in an overall cost reduction. In our study, most (60%) of the patients were younger(<40yr) and presented with breast lumps of larger size. This may partly explain the high frequency of concordant results(benign and malignant). The overall sensitivity, specificity and accuracy of the modified triple test in our study was 100%, 82% and 88.7% respectively, which is comparable to other studies(table 9).
CONCLUSIONS
- Clinical examination of breast lumps has high diagnostic error especially in smaller breast lumps.
- Additional imaging and cytological examination is of paramount importance in the assessment of breast lesions.
- Breast ultrasonography and FNAC in best of hands can produce results with good sensitivity, specificity and better concordance rates.
- A definitive diagnosis can be made with 100% accuracy when the components of Modified Triple Test concur.
- The output of the Modified Triple Assessment is easily reproducible, making it a valid and reliable diagnostic approach in the management of breast cancer.
- Based on the study, we conclude that the Modified Triple Assessment reliably guides effective management of palpable breast lumps and avoids unnecessary open biopsies.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
Authors acknowledge the immense help received from the scholars whose articles are citied and included in references of this manuscript. The authors are also grateful to authors/ editors/publishers of all those articles, journals and books from where the literature for this article has been review and discussed. The authors also thank all the residents and staff in the Department of Surgery, Departments of Pathology and Radiology, Dean and Vice Chancellor of Mahatma Gandhi Medical College & Research Institute for their support.
DISCUSSION
Breast cancer is the commonest cause of cancer related deaths among women worldwide. The incidence is increasing in the intermediate and low risk population of the South-East and South Asian countries14. In South-Asian countries like India, patients present with breast cancer at an earlier age but often at an advanced clinical stage compared to western countries15 . The Triple Test (TT), initially described in the mid 1970s, is the evaluation of palpable breast masses by physical examination, MMG, and fine needle aspiration16 . Generally, the triple test is deemed to give a positive result if any of its components is reported as suspicious or malignant. One large-scale prospective trial and several smaller studies of TT followed by selective confirmatory open biopsy found that concordant benign TT results (all 3 components benign) correctly predicted the absence of malignancy, as determined either by
References:
1. Baum M. Carcinoma of breast. In Recent Advances in surgery, London. Churchchill Livingston; 1984. p.241-58. 2.
2.Kirby IB, Samuel WB. The Breast. In Schwartz’s Principles of Surgery, McGraw Hill; 2005. p.475-77.
3. Dixon JM, Anderson TJ, Lamb J, Nixon SJ, Forrest AP. Fine needle aspiration cytology, in relationships to clinical examination and mammography in the diagnosis of a solid breast mass.Br J Surg.1984;71:593–6.
4. Hermansen C, Skovgaard PH, Jensen J, et al. Diagnostic reliability of combined physical examination, mammography, and fineneedle puncture (‘‘triple-test’’) in breast tumors. A prospective study.Cancer.1987;60:1866–71.
5. Hansell DM, Cooke JC, Parsons CA. The accuracy of mammography alone and in combination with clinical examination and cytology in the detection of breast cancer. Clin Radiol.1988;39:150–3.
6. Kaufman Z, Shpitz B, Shapiro M, Rona R, Lew S, Dinbar A. Triple approach in the diagnosis of dominant breast masses: combined physical examination, mammography, and fine-needle aspiration. J Surg Oncol.1994; 56:254–7.
7. Vetto J, Pommier R, Schmidt W, et al. Use of the ‘‘triple test’’ for palpable breast lesions yields high diagnostic accuracy and cost savings. Am J Surg.1995;169:519–22.
8. Steinberg JL, Trudeau ME, Ryder DE, et al. Combined fine-needle aspiration, physical examination and mammography in the diagnosis of palpable breast masses: their relation to outcome for women with primary breast cancer. Can J Surg.1996;39:302–11.
9. Irwig L, Macaskill P, Houssami N. Evidence relevant to the investigation of breast symptoms: the triple test. Breast. 2002;11:215–20.
10. Ariga R, Bloom K, Reddy VB, et al. Fineneedle aspiration of clinically suspicious palpable breast masses with histopathologic correlation. Am J Surg.2002;184:410–3.14.
11. Hardy JR, et al. how many tests are required in the diagnosis of palpable breast abnormalities? Department of Radiology, Royal Marsden Hospital, Sutton, Surrey, UK. Clin Oncol (R Coll Radiol) 1990 May; 2(3): 148-52. 12.
12.Tresserra F, Feu J, Grases PJ, Navarro B, Alegret X, Frenadez Cid A. Assessment of breast cancer size. Sonographic and pathologic correlation. J Clin Ultrasound 1999; 27: 485-91.
13. Lawrence W. Bassett, MD, et al. Usefulness of mammography and sonography in women less than 35 years of age. Radiology 1991;180: 831-35.
14. Feldman PS, Covell JL. Breast and lung. In: Fine needle aspiration cytology and its clinical application. Chicago: Am Soc Clin Pathol 1985;27.
15. 15.Rasool MI, Malik IA, Luqman M, Ullah K. A comprehensive study of breast cancer. Pak J Med Res 1998; 38:2-7.
16. Johansen C. A clinical study with special reference to diagnostic procedures. Acta Clin Scand. 1975;451(suppl):1-70.
17. Layfield LJ, Chrischilles CA, Cohen MB, et al. The palpable breast nodule: a cost effectiveness analysis of alternative diagnostic approaches. Cancer. 1993;72:1642-51
18. Butler JA, Vargas HI, Worthen N, et al. Accuracy of combined clinicalmammographic-cytologic diagnosis of dominant breast masses. Arch Surg 1990;125:893-96
19. Somers RG, Sandler GL, Kaplan MJ, et al. Palpable abnormalities of the breast not requiring excisional biopsy. Surg Gynecol Obstet. 1992;175:325-28.
20. Nuffield Institute for health /University of Leeds, NHS Centre for reviews and dissemination, University of York/Bulletin on the effectiveness of health service interventions for decision makers/effective health care, the management of primary breast cancer. 2(6): 1-16, 1996.
21. Kim JK, Song YJ, Cho SI, et al. A Study on Modified Triple Test for Palpable Breast - A prospective study. J Korean Surg Soc 2001;61:27-32
22. Bin-Soo Kim, Jin-Kwon Kim,Sung-Il Cho,Donghee Ryu, et al. Diagnosis of Palpable Breast Masses by the Modified Triple Test Score. J Korean Br Can Soc 2002;5:46-51
23. Pande AR, Lohani B, Sayami P, Pradhan S. Predictive value of ultrasonography in the diagnosis of palpable breast lump. Kathmandu University Medical Journal. 2003;1:78-84
24. Seidman H. Gelb S K, Silverberg E, La Verda N. Lubera JA . Survival Experience In The Breast Cancer Detection Demonstration Project. CA Cancer J Clin1987 :37: 258-290 25.
25.Cole-Beuglet C, Soriano RZ, Kurtz AB, Gold bug BB. Ultrasound analysis of 104 primary breast carcinomas classified according to histopathology type. Radiology 1983; 147:191-196.
26. Isabel T, Mutrio MD, Rond HT. Role of ultrasound. Surg Clin N Am 2003; 83: 771- 88.
27. Tresserra F, Feu J, Grases PJ, Navarro B, Alegret X, Frenadez Cid A. Assessment of breast cancer size. Sonographic and pathologic correlation. J Clin Ultrasound 1999; 27: 485-91.
28. Morris KT, Vetto JT, Petty JK, Lum SS, Schmidt WA, Toth-Fejel S, Pommier RF. A new score for the evaluation of palpable breast masses in women under age 40. Am J Surg. 2002 Oct;184(4):346-7.
29. Wai CJ, Al-Mubarak G, Homer MJ, Goldkamp A, et al. A Modified Triple Test for Palpable Breast Masses: The Value of Ultrasound and Core Needle Biopsy. Ann Surg Oncol. 2012 Oct 27. [Epub ahead of print]
30. Morris KT, Pommier RF, Morris A, Schmidt WA, Beagle G, Alexander PW, Toth-Fejel S, Schmidt J, Vetto JT. Usefulness of the triple test score for palpable breast masses. Arch Surg. 2001;136:1008-12.
31. Vetto JT, Pommier RF, Schmidt WA, Eppich H, Alexander PW. Diagnosis of palpable breast lesion in younger women by the modified triple test is accurate and costeffective. Arch Surg 1996;131: 967-72.
32. Morris AM, Flowers CR, Morris KT, Schmidt WA, Pommier RF, Vetto JT. Comparing the cost-effectiveness of the triple test score to traditional methods for evaluating palpable breast masses. Med Care. 2003;41:962-71.
33. Veto J, Use of the Triple Test for palpable breast lesions yields high diagnostic accuracy and cost savings. Am J Surg 1995;169:519-22.
34. Zonderland HM, Hermans J, et al. Triple diagnostic approach versus ultrasoundguided 18 gauge core biopsy in suspicious breast masses. Breast. 1998;7:168-72.
|






 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License