IJCRR - 5(5), March, 2013
Pages: 53-62
Date of Publication: 22-Mar-2013
Print Article
Download XML Download PDF
INFECTION OF ACANTHOCEPHALAN PARASITE NEOECHINORHYNCHUS AGILIS SP IN THE GREY MULLET, (MUGIL CEPHALUS) A CANDIDATE SPECIES FROM - CORENTYNE COAST, BERBICE, GUYANA.
Author: S.Rajeshkumar, S.Gomathinayagam, A. Ansari, N.Munuswamy
Category: General Sciences
Abstract:The study describes the infection of the acanthocephalan, Neoechinorhynchus agilis sp. The (grey mullet) Mugil cephalus is highly valued food along the Corentyne coast, Berbice, Guyana. The fish Mugil cephalus were collected from Bush Lot, Whim, 43 Village 63 Beach and 79 Village, Corentyne coast. The infections with the parasites were observed in posterior region of the intestine, liver and muscle, almost blocking the lumen during the examination of M. cephalus. At thee site of the parasite attachment, the surface of the intestine appeared thickened along the mucosal epithelium. A description of the parasites and its clinicopathology is discussed. Though the worm substantially damaged the architecture of the intestinal tissues, no apparent ill effects on the general health condition of the fish were observed. This is the first report of Mugil cephalus of Berbice River, Corentyne coast from Guyana.
Keywords: Acanthocephalans, Spiny headed worm, Neoechinorhynchus agilis sp, Mugil cephalus
Full Text:
Occurrence of disease conditions particularly due to parasites has become a major constraint in aquaculture (Bondad-Reantaso et al., 2005). Besides the direct losses caused by mortality, parasites have considerable impact on growth, resistance to other stressing factors, susceptibility to predation, marketability and pave way for secondary infections (Woo, 2006). Acanthocephalans, known as thorny-headed worms or spiny-headed worms, are characterized by the presence of proboscis, armed with spines, which they use to pierce and hold the gut wall of their gnathostome in the definitive host. Acanthocephalans are obligate endoparasites which infect in host’s intestine (Taraschewski, 1989a and b). They typically have complex life cycles, involving a number of hosts, including arthropods as the intermediate hosts, fishes, amphibians, birds, and mammals as the definitive host (Dudinak and Snabel, 2001). Cases of serious illness or high mortality induced by acanthocephalan infections in fish were seldom reported due to the much lower infection intensity compared with other helminth parasites (Hsiu-HuiShih et al., 2010). Acanthocephalans display the sort of interspecific body size variation that requires explanation among the approximately 1100 described species, adult body lengths vary from 1 mm to more than 60 cm (Bush et al., 2001).
The life cycle of acanthocephalans includes two hosts, an arthropod intermediate host (either an insect or a crustacean) and a vertebrate definitive host a paratenic or transport host in which no development occurs may also be used in some species (Crompton and Nickol, 1985). There is some growth inside the intermediate host and it is thus the size of the last juvenile stage, the cystacanth, which corresponds to the starting size of the parasite when it arrives in the vertebrate host. The final size of the adult worm will depend not only on cystacanth size, but also on the increment in size achieved within the definitive host. Acanthocephalans have thus gained attention from ecologists and environmental toxicologists within the last decade (Taraschewski, 2000). Parasitic infections in fishes are common, especially in wild populations where ecological requirements for intermediate hosts and parasite transmission are met (Feist and Longshaw, 2008). Management of parasitic problems is the major limiting factor in fin fish aquaculture in terms of profitability and environmental health (Costello, 2009; Burridge et al., 2010). Acanthocephalans are a group of endoparasitic helminths commonly found in both marine and freshwater fishes worldwide (Jithendran and Kannappan, 2010). They have a complex life cycle involving arthropods as intermediate hosts and vertebrates as definitive or paratenic hosts and are known to cause pathological conditions in many fin fishes. In severe infections they can cause occlusion of the gut and invasion/migration of the parasites into uncommon locations have also been reported (Nickol, 2006). Besides the drain of valuable nutrients, involvement of toxins and localized toxaemia has also been suggested by some authors (Holloway, 1966). But, diverse views exist regarding the intensity of damage caused by the parasites to the well being of the host and in many cases, apparent changes are not reflected in the general health and condition of the host. Fish parasites are nowadays considered as one of the most inviting fields of research especially after the importance of fishes as a valuable source of protein, in which heavy infection may cause functional disturbances, retard growth, increase the susceptibility of fish for other infection and give the fish an anaesthetic appearance (Paperna, 1980; Mahmoud, 1983). The grey mullet (M. Cephalus) is a commercial marine fish in fish market. This species is omnivorous, feeds on plankton, thus it is more exposed to infection by trematodes than other marine fish, and is therefore selected for the present investigation. In the course of our routine investigation of parasitic disease of finfish, a case of heavy infection of ‘thorny headed worm’ was observed in a wild catch of mullet fish. The present study describes the morphology, taxonomy and clinicopathology of infection.
MATERIALS AND METHOD
Study area:
The study area was demarcated into 5 different collection points based on the criteria as follow. The temperature and salinity of this Corentyne coast under study ranged between 25- 30 ºC and 25-29 ppt respectively. (Station 1) Whim located in estuarine and coastal areas, spawning and nursery grounds of many marine species, including the commercially valuable shrimps and fish. (Station 2) Bush Lot situated on the western side of the Canje fresh water canal. (Station 3) 43 Village situated near cattle and animal farms, northern tip being closest to influx of contaminants that are directly mixed fresh water from the canal through Corentyne coast. (Station 4) 63 Beach situated towards south west near fresh water canal, an area of maximum inflow of effluents mainly due to anthropogenic sources and outlet located along the length of the Corentyne coast. (Station 5) 79 Village situated in Skeldon, the northern side with the outlet for waste water from the Guyana Sugar Corporation INC (Guysuco), which is also the boundary between Corentyne and Suriname coast (Fig.1).
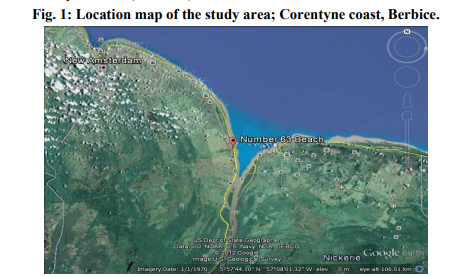
inhabitant of the Corentyne coast, was chosen as the experimental animal for the study according to the Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) species identification sheet (Fischer and Bianchi, 1984). Grey mullets with an average length of 30-32 cm were collected from Whim, Bush Lot, 43 Village 63 Beach and 79 Village of Corentyne coast, Berbice. Fishes were brought to the laboratory on the same day and then frozen at -20 ºC until dissected (Fig.2).

Identification of Parasite: Frozen fish samples
were thawed at room temperature and dissected, intestines removed and placed in physiological saline in Petri dishes. The entire intestine was dissected, opens longitudinally and examined for the presence of acanthocephalan parasites under a Leica S6D sterozoom microscope (Leica, Wetzlar, Germany). Parasites attached firmly to the wall/tissue of the intestine were dissected out with aid of fine needle and forceps. The specimens were then fixed in cold 75% ethanol.
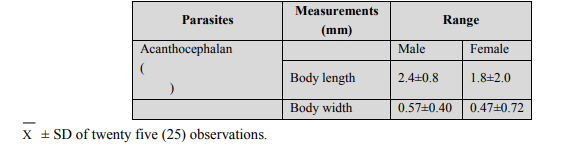
Whole mounts: For preparing whole mounts, specimen were pressed slightly between glass slides, fixed in AFA (alcohol-formal-acetic acid) overnight, stained with Semichons acetocarmine stain and counter stained with fast green (Lasee,2006), (Table 1). Table 1: Measurements of both male and female specimens of Neoechinorhynchus agilis and M. cephalus respectively. Comparison of data from the literature (Petrochenko, 1956 and Govsn, 1969) and specimens from the present research (M. cephalus).
RESULTS
Prevalence and intensity:
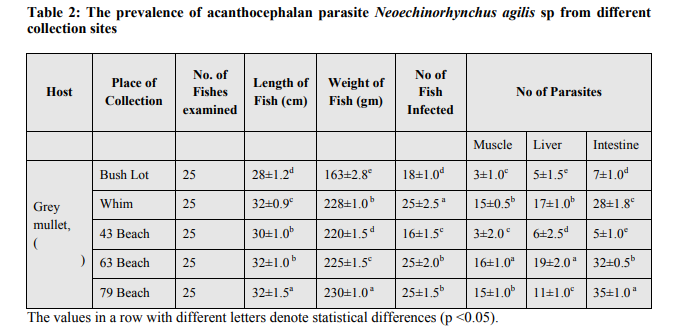
The examination of the different tissues of M. cephalus revealed the presence of heavy infection with the parasite (Fig.3a). All the fishes collected from Corentyne coast, infections were recorded from Neoechinorhynchus agilis, the worms that were reddish yellow to orange in colour and were seen attached to the posterior region of the intestine, liver and muscle (Fig.3a-c). The intensity of infection varied from (5-30) in Neoechinorhynchus agili. Besides, only Bush Lot and Whim fish specimens of M. chephalus were examined from Corentyne coast and intensity of infection was very low with only (5- 8) parasites recorded (Table 2).
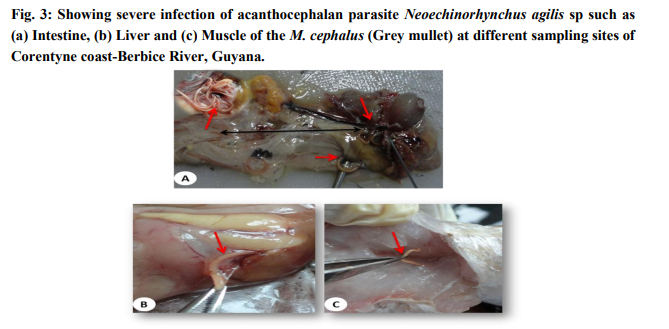
Morphology: The taxonomy of the worms were attempted by clearing the specimens and identified as acanthocephalan parasite using photomicrographs taken using Leica S6D stero zoom microscope (Leica, Wetzlar, Germany). On microscope examination, the metasoma of the parasite was cylindrical, relatively short proboscis was as long as wide, armed with a set of hooks arranged in three circles of six hooks, first rows of hooks largest. The neck was not clearly demarcated. The elongate oval testes lay one behind the other in the middle third of the body. Female worms revealed large number of ovarian balls inside in the ligament sac (Fig. 4ad).
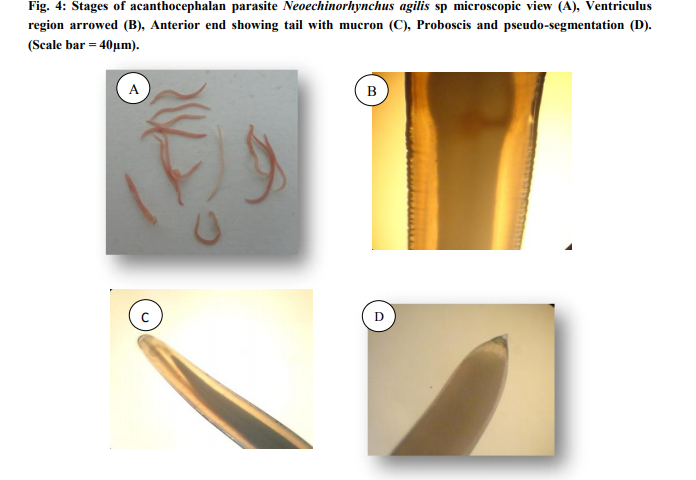
DISCUSSION
The morphological characteristics of the specimen, shape and size of proboscis, the low number and position of the spines on the proboscis clearly place this species within the genus Neoechinorhynchus and conform to the descriptions for Neoechinorhynchus agilis (Rudolphi, 1819, belonging to Acanthocephala: Neoechinorhynchidae (Yamaguti, 1935). The acanthocephalan Neoechinorhynchus sp is a relatively largest with approximately 70-75 species and typically found in freshwater fishes (Ching, 1984). The biodiversity of acanthocephalan species in fish is largely unknown in India (Jithendran and Kannappan, 2010). Acanthocephalan infections depend on various factors such as species of parasite and host nature of the infected tissues and host-parasite interactions the nature and thickness of the various tissue layers, length of the neck and proboscis, presence or absence of a proboscis bulb and the nature of spination also affect the pathological outcome. The mechanical destruction to the host's intestinal tissue is usually followed by host immune responses like proliferation of fibroblasts and granular cell infiltration around the invader, resulting in the formation of a collagenic capsule around it (Schelhaas, 1980), which is very much evident in the present study. The pathology of acanthocephalan parasites in fishes especially with reference to been well documented (Wanstall et al., 1986; Dezfuli, 1991). Usually in acanthocephalan infections, pathology appears to be negligible when parasites are attached to the epithelial mucosa only but deeply embedded forms like Pomphorhynchus spp. can cause serious pathological conditions resulting in extensive granuloma and subsequent fibrosis (McDonough and Gleason, 1981). Extensive inflammation, peritonitis due to perforation of the gut and systemic clinical changes will occur only in massive infections, most often in farmed fish (Bullock, 1963). There are some reports of the Neoechinorhynchus sp from Indian marine fishes (Tripathi, 1959; Chandra et al., 1985) besides other acanthocephalan species, Serrasentis nadakali from Rachycentron canadum and Tenuiproboscis sp (George and Nadakal, 1981) In many marine fish species with aquaculture potential (Sanil et al., 2011) the fishes were apparently healthy except choking of intestinal tract with several live acanthocephalan worms infections, the different organs appeared to be packed with parasites, almost blocking the intestinal lumen, which will adversely affect the movement of digested materials within the intestine and the absorption of nutrients. de Buron and Nickol (1994), reported occlusion and significant distension of M. cephalus infected with the acanthocephalan Neoechinorhynchus sp. Taraschewski (2000) has observed that the pathogenicity of acanthocephalans is mainly caused by two factors, density of worms and depth of parasite penetration into the host tissues. Though the pathological effects are localized around individual worms, in the present case with unusually high parasite load, total destruction of the tissue architecture due to the collective pathological changes had occurred. However, the fish appeared healthy without any clinical manifestations and this observation is in agreement with the views of Hine and Kennedy (1974). In heavy infections the amount of nutrients drained by these worms may be of considerable physiological consequence to the host animals. Severe irreversible damage to the intestinal villi will drastically reduce the absorptive area available for the normal digestive and absorptive functions of the animal while the damages associated with the tissue reactions in the wall of the intestine will alter the nature of the tissues, affecting its functional efficiency and the overall health status of the fish. This study contributes to the knowledge of the acanthocephalans in wild brackish /marine water fish in general as well as to the Neoechinorhynchus sp. in particular. Neoechinorhynchus agilis has been recorded in a study on grey mullets from landing centre near Chennai, Tamil Nadu, India (Jithendran and Kannappan, 2010). Generally, co-infection with nematode parasites has been observed, but the present case showed mono-infection with acanthocephalans alone in the intestinal tract. Usually in acanthocephalan infections, pathology appears to be negligible when parasites are attached to the epithelial mucosa only. Kabata (1985) opined that the number of worms present is important in determining the severity of damage. In severe infected fish acanthocephalans may perforate the gut wall with their proboscis and cause considerable damage with severe local inflammatory reaction. Further, the number of acanthocephalans per fish seemed to increase with the size of the host fish. A similar finding has been reported by various workers in case of other species of acanthocephalans as well (Jithendran and Kannappan, 2010). This is the first study on the detailed pathological manifestations of Neoechinorhynchus sp. and is also the first report of the parasite from M. chephalus. A prevalence of 100% in M. chephalus combined with high intensity of infections in 43 village, 63 Beach and 79 village from Corentyne coast, Whim and Bush Lot indicates that Neoechinorhynchus sp. is less host specific and the ecological requirements for intermediate hosts and parasite transmission are met, favoring the establishment of the parasite. Heavy infections with Neoechinorhynchus sp. capable of causing irreversible damage to the intestinal tissues can seriously affect the health and quality of the M. chephalus brood stock and thereby making the fish unfit for hatchery production. As currently the hatchery production of fin fishes in the region depends solely on brood stock sourced from the wild, further studies are required to understand the intermediate host and life cycle pattern of the parasite and to elucidate possible management measures.
References:
1. Bondad-Reantaso, M.G., Subasinghe, R.P., Arthur, J.R., Ogawa, K., Chinabut, S., Adlard, R., Tan, Z., Shariff, M., 2005. Disease and health management in Asian aquaculture. Vet Parasitology. 132, 249-272.
2. Bullock, W. L., 1963. Intestinal histology of some salmonid fishes with particular reference to the histopathology of acanthocephalan infections. Journal of Morphology. 112, 23-44.
3. Burridge, L., Weis, J.S., Cabello, F., Pizarro, J., Bostick, K., 2010. Chemical use in salmon aquaculture: a review of current practices and possible environmental effects. Aquaculture. 306, 7-23.
4. Bush, A.O., Fernandez, J.C., Esch, G.W., Seed, J.R., 2001. Parasitism: The Diversity and Ecology of Animal Parasites, Cambridge University Press, Cambridge.
5. Chandra, K.J., 2006. Fish parasitological studies in Bangladesh: a review. Journal of Agriculture and Rural Development. 4 (1and2),9-18.
6. Ching, H.L., 1984. Description of Neoechinorhynchus salmonis sp. n.(Acanthocephala: Neoechinorhynchidae) from fresh water fishes of British Columbia. Journal of Paraistology. 70, 286-291.
7. Costello, M.J., 2009. The global economic cost of sea lice to the salmonid farming industry. Journal of Fish Diseases. 32, 115- 118.
8. Crompton, D.W.T., Nickol, B.B., 1985. Biology of the Acanthocephala, Cambridge University Press, Cambridge University Press, Cambridge.
9. de Buron, I., Nickol, B.B., 1994. Histopathological effects of the acanthocephalan Leptorhynchoides thecatus in the ceca of the green sunfish, Lepomis cyanellus. Transactions of the American Microscopical Society. 113, 161-168.
10. Dezfuli, B.S., 1991. Histopathology in Leuciscus cephalus (Pisces: Cyprinidae) resulting from infection with Pomphorhynchus laevis (Acanthocephala). Parasitol. 33, 137-145.
11. Dudi?ák, V., Snábel, V., 2001. Comparative analysis of slovak and czech populations of Pomphorhynchus laevis (Acanthocephala) using morphological and isoenzyme analyses. Acta Zoologica Universitatis Comenianae. 44, 41-50.
12. Feist, S.W., Longshaw, M., 2008. Histopathology of fish parasite infections -importance for populations. Journal of Fish Biology. 73, 2143-2160.
13. Fischer, W., Bianchi, G., 1984. FAO Identification Sheets for Fishery Purposes. Western Indian Ocean, FAO, Rome.
14. George, P.V., Nadakal. A.M., 1981. Observations on the intestinal pathology of the marine fish, Rachycentron canadus (Gunther) infected with the acanthocephalid worm Serrasentis nadakali (George and Nadakal 1978). Hydrobiologia. 78, 59-62.
15. Golvan, Y.J., 1969. Systématique des Acanthocéphales (Acanthocephala Rudolphi 1801) Première Partie. L’Ordre des Palaeacanthocephala Meyer 1931. Premier fascicule. La Super-famille des Echinorhynchoidea (Cobbold 1876) Golvan et Houin 1963. Memoires du Museum National d’ Histoire Naturelle. Zoologie, Serie A 57, 1- 373.
16. Holloway, J.R., 1966. Prosthorhynchus formosum (Van Cleave 1918) in song birds, with notes on acanthocephalans as potential parasites of poultry in Virginia. Virginia Journal of Science. 17, 149-154.
17. Hine, P.M., Kennedy, C.R., 1974. Observation on the distribution, specificity and pathogenicity of the acanthocephalan Pomphorhynchus laevis. Journal of Fish Biology 6, 521-533.
18. Hsiu-Hui, S., Hui-Yu, C., Chew-Yuen, L., 2010. Acanthocephalan Fauna of Marine Fish in Taiwan and the Differentiation of Three Species by Ribosomal DNA Sequences, Taiwania. 55(2), 123-127.
19. Jithendran, K.P., Kannappan, S., 2010. A short note on heavy infection of acanthocephalan worm (Neoechinorhynchus agilis) in grey mullet, Mugil cephalus. Journal of Parasitic Diseases. 34(2), 99-101.
20. Kabata, Z., 1985. Parasites and diseases of fish cultured in the tropics (1stEds 1). Taylor and Francis, London, p 318.
21. Lasee, B., 2006. National Wild Fish Health Survey - Laboratory Procedures Manual, Chapter 8 - Parasitology, Section 1, U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service, Washington DC, 3.1 edition., pp. 1-22.
22. Mahmoud, N.A., 1983. Parasitic infestations of some native species of fishes in Cairo markets with special reference to parasites transmissible to man and animals. M. V. Sc. Thesis, Fac. Vet. Med. Cairo Univ. Egypt.
23. Mcdonough, J.M., Gleason, L.N., 1981. Histopathology in the rainbow darter, Etheostoma caeruleum, resulting from infections with the acanthocephalans, Pomphorhynchus bulbocolli and Acanthocephalus dirus. The Journal of Parasitology 67, 403-409.
24. Nickol, B.B., 2006. Phylum Acanthocephala, In: Woo, P.T.K. (Ed.), Fish Diseases and Disorders, Second Edition, Protozoan and Metazoan Infections, Vol. I. CAB International, Wallingford, UK, pp. 444-465.
25. Paperna, I., 1980. Parasites infections and diseases of fish of Africa. Committee for inland fisheries of Africa. CIFA Technical papers 51-62.
26. Petrochenko, V.I., 1956. Acanthocephala of Domestic and Wild Animals. 1. Izdatel’stvo Akademii Nauk SSSR, Moscow. English Translation by Israel Program for Scientific Translations 1971, p. 435.
27. Rudolphi, C.A., 1819. Entozoorum synopsis cui accedunt mantissa duplex et indices loupletissimi. Sumptibus Augusti Rucker, Berlin, Germany, 811 p.
28. Sanil, N.K., Asokan, P.K., John, L., Vijayan, K.K., 2011. Pathological manifestations of the acanthocephalan parasite, Tenuiproboscis sp. in the mangrove red snapper (Lutjanus argentimaculatus) (Forsskal 1775), a candidate species for aquaculture from Southern India. Aquaculture. 310, 259-266.
29. Schelhaas, D.P., 1980. Comparative Histopathology of Acanthocephan Infections in Some Freshwater Fishes. M.Sc. Thesis, University of North Dakota.
30. Taraschewski, H., 1989a. Host-parasite interface of Paratenuisentis ambiguous (Eoacanthocephala) in naturally infected eel and in laboratory-infected sticklebacks and juvenile carp and rainbow trout. Journal of Paraistology. 75, 911-919.
31. Taraschewski, H., 1989b. Host-parasite interface of Neoechinorhynchus rutili (Eoacanthocephala) in naturally infected salmonids. Journal of Fish Diseases. 12, 39- 48.
32. Taraschewski, H., 2000. Host-parasite interactions in Acanthocephala:a morphological approach. Adv. Parasitol. 46, 1-179.
33. Tripathi, Y.R. 1959. Studies on parasites of Indian fishes. 5 Acanthocephala. Rec Indian Mus 54(1–2), 61-99.
34. Wanstall, S.T., Robotham, P.W.J., Thomas, J.S., 1986. Pathological changes induced by Pomphorhynchus laevis Muller (Acanthocephala) in the gut of rainbow trout, Salmo gairdneri Richardson. Zeitscrift. Parasitenkd. 72, 105-114.
35. Woo, P.T.K., 2006. Fish Diseases and Disorders, Second Edition. Protozoan and Metazoan Infections, Vol. I. CAB International, Wallingford, UK. 808 pp.
36. Yamaguti, S., 1935. Studies on the helminth fauna of Japan Part 8 Acanthocephala, International Journal of Zoology. 6, 247- 278.
|






 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License