IJCRR - 5(6), March, 2013
Pages: 119-126
Date of Publication: 30-Mar-2013
Print Article
Download XML Download PDF
ROLE OF FATHER IN KEY AREAS OF MATERNAL AND CHILD HEALTH: A CROSS-SECTIONAL STUDY
Author: Swapna S. Kadam, Bhagwant S. Payghan
Category: Healthcare
Abstract:Being in a male dominant society, Indian women are considered responsible for reproductive and child health. Health education activities regarding reproductive and child health are more women oriented. Responsibility of male partner is considered only in family planning. Role of husbands in maternal and child health is undoubtful as they are decision makers and earning members of the family. Knowledge and awareness about the unknown events during pregnancy can make childbirth an extremely enriching and joyful event. Involvement of men in antenatal care can play a vital role in ensuring safe pregnancy, delivery and moral support to wives. Present study was conducted to assess the knowledge, perceptions and practices of men in key areas of maternal and child health like conception, contraception and Maternal and Child Health care. An observational study was conducted in urban area of Chitradurga .A total of 300 randomly selected men, who had child below two years of age were interviewed by using predesigned, pretested, semi structured questionnaire and after seeking verbal consent. The findings pointed out that respondent's opinion about age at marriage, age at first conception, son preference, desired family size, acceptance of male contraceptive were adverse and pointed out gaps in knowledge and awareness. Most of the men were aware about the importance of antenatal care and hospital delivery, however their participation in activities related to it was found negligible. Male involvement in child care is seen to be limited to immunization and seeking medical help in illness. The study pointed out gaps in knowledge and misconceptions among men on key areas of MCH issues and stresses the need for male friendly health education. The findings also suggest the need to change perceptions about couple's role in MCH issues and effective couple communications.
Keywords: Male responsibility, RCH, KAP, Antenatal care.
Full Text:
INTRODUCTION
Every minute, a woman dies of pregnancy-related causes throughout the world, and for every woman who dies; more than 20 others suffer pregnancy - related illness or infection. (1) Because women bear the greatest burden of pregnancy-related and reproductive ill-health, national health programs are women oriented. Ignoring men in policy decisions fails to take in the full spectrum of influence on issues affecting maternal health. Women are usually not the sole decision makers and often not even the principal decision makers about their own contraceptive use, child bearing and caring. (3) Against this background, male involvement is evolving as an important approach for improving maternal and child health. This is partly because men play important roles in reproductive experiences of females and partly because they are often culturally placed as decision makers .Men regulate the household economics and also force their views or choices on females. However patriarchy, ignorance, lack of knowledge and poverty may make it easy for males to take wrong decision or no decision on matters relating to health of their female partners even when obvious need for urgent and appropriate decision exists. (4) Women cannot utilize even free, basic health services against their husbands wish. To bring about equity in gender relations, male participation or male shared involvement in reproductive health is of utmost importance. However, sense of shared and responsible relationship in all aspects of reproductive and child health among men is lacking and needs to be vigorously promoted. Researches in India have found that male involvement is necessary to enhance both use of contraceptives and antenatal care.(16,17,18) Male participation is not simply a question of who will use the family planning method ,men or women .Rather ,it is a question to what extent men can and will expand their support throughout the reproductive cycle of woman. (2) Present study is an attempt to assess the knowledge of men in key areas of MCH, to study their perceptions about their role in MCH care and to study their practices regarding contraception, conception and child care.
METHODOLOGY
This is a cross sectional study conducted in urban field practice area of Department of Community Medicine,BMCH,Chitradurga.The proportion of married men of aged 19-40 is about 25% , with 95% confidence interval and 5% of absolute precision, the required sample size was 288 .( 10 ) .The urban field practice area is having 15 anganwadi centres.List of children below two years of age was obtained from all anganwadi centers .We randomly selected 20 babies from each anganwadi and fathers of these babies were contacted considering unavailability and refusal of respondents. All the fathers were interviewed by using predesigned and pretested semi structured questionnaire after seeking verbal consent. Along with the socio-demographic characteristics, the perceptions and behaviour of men regarding conception, contraception and maternal and child care was studied. Data was analyzed and percentages were used for comparison.
RESULTS
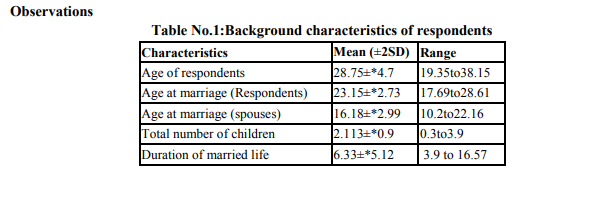
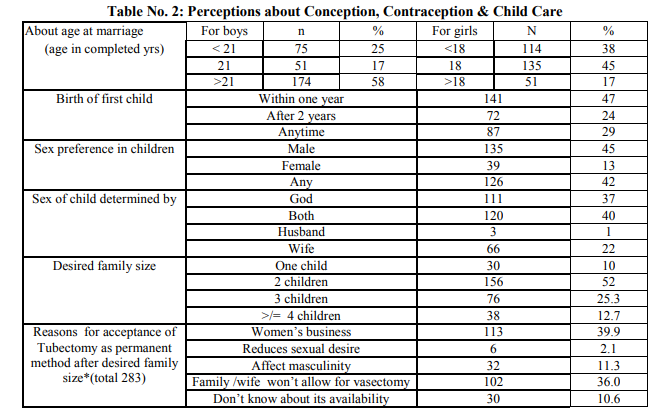
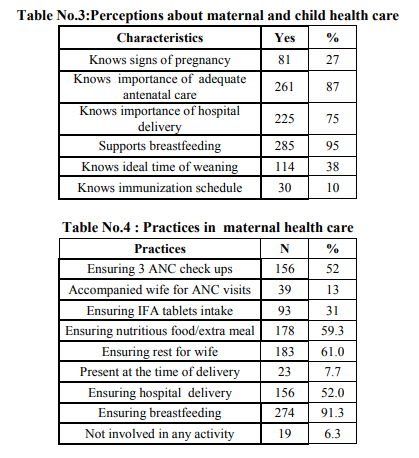
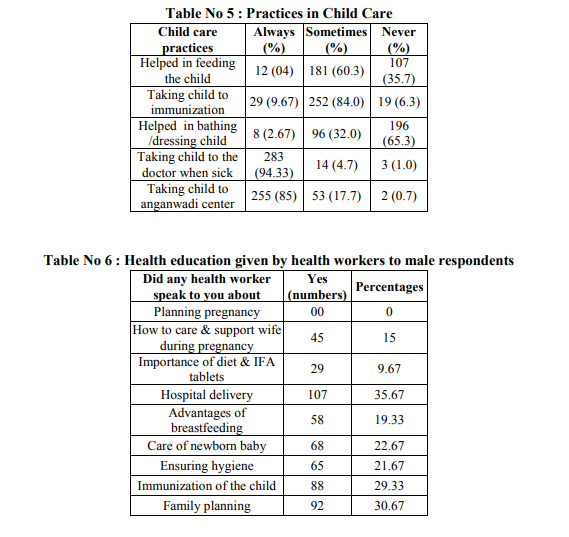
A total of 300 men interviewed, the average age of study subject was 28.75.The minimum age of subject was 19 years. As shown in table no.1.the average age at marriage for the respondents was 23.15 years and for their spouses it was observed 16.18 years. The average number of children per couple was found to be 2.1. and the average duration of marriage was reported 6.33 years. Out of 300 subjects,8.7% were illiterate and most of them (74 %) were studied up to high school level. 61%were Hindu ,32% were muslims.49.33% were from lower middle class and 33% were from lower class according to modified Kuppuswami’s classification. Majority of the respondents (62%) were unskilled labourer.About 70% have nuclear family. As shown in Table No.2, 58% respondents said that boys should marry after 21 years of age while only 17% think that girls should marry after 18 years of age and 3% men didn’t know the legal age of marriage. About the birth of first child after marriage,47% of respondents said that a couple should have child within one year of marriage.Prefered sex of child was male as reported by 45% of respondents. Only 1% knew that male is responsible for sex of the child. The desired number of children per couple was reported two by 52% of respondents and these respondents also wanted at least one son. Only 27% respondents were currently using contraceptives. 283 (94.3%) respondents said that they would prefer tubectomy as a permanent method of contraception. The reasons quoted were didn’t know about availability y of vasectomy services(10.6%), it’s all woman’s business(39.9%), family or wife would not allow them for vasectomy (36%). Table no.3 shows, responses regarding perceptions and knowledge about MCH care. Only 27% men knew signs of pregnancy,87% knew importance of antenatal visits,75% knew the importance of hospital delivery,95% responded that breastfeeding is essential for babies but only 10% men knew the complete immunization schedule and 38% knew about ideal time for weaning. Among practices(as shown in table no.4) ,52% ensured three ANC checkups for wives during pregnancy but only 13% accompanied wife for ANC check up.52% ensured hospital delivery but only 7.7 % were present at the time of delivery. While 6.3% were not involved in any activity related to care during pregnancy. Very few men are involved regularly in day to day activities of child care. Only 4% helped in feeding the child, 2.67% helped in dressing or bathing child, 9% respondents took child to routine immunization sessions regularly.94.33% respondents sought help for sick child and 85% took child to anganwadi center. (Table no.5) Reproductive health issues discussed with men by health workers is shown in table no. 6. Care of antenatal mothers (15%),Importance of diet and IFA tablets (9.67%), Importance of hospital delivery (35.67 % ) advantages of breastfeeding (19.33%),care of new born baby (22.67%), Ensuring hygiene (21.67%), Immunization (29.33%) were discussed with them. Planning pregnancy after marriage was not discussed with any of the respondent.
DISCUSSION
In the study, the mean age at marriage for men is 23.15 and their wives it is reported 16.18 which was no different than reported in NFHS III survey.(2) Most of the respondents opined that the ideal age of marriage for boys is more than 21 yrs while for girls it is 18yrs. A study conducted in Ethiopia showed that 47% men, who were follower of Ethiopian Orthodox Church, opined that ideal age of marriage for boys as 25-29 years and for girls as 20-24 years. (11) Social customs and traditions do play important role in marriage even in modern era and in urban area, especially in lower and middle income group. Marriage in India marks the point in a woman’s life when childbearing becomes socially acceptable. Age at first marriage has a profound impact on childbearing because women who marry early have on average a longer period of exposure to pregnancy and a greater number of lifetime births.(2) The median age at marriage for women was 16.7 years. (12)In rural India, 40 percent of girls (ages 15 to 19) are married, compared to 8 percent of boys at the same age. Accordingly, childbearing for women in India is also early; among married women in their reproductive years (ages 20to 49), the median age at which they first gave birth is 19.6 years. (12) The study shows that most of the men (47%) opined that a couple should have child within one year of marriage. Similar findings were seen in studies conducted in India. (8, 13) This is mostly because of the social and family pressure. Marriage is not considered successful till the couple has child. This familial or societal pressure forces couples to become parents as early as possible. Apart from the peer pressure lack of inter spousal communication, knowledge regarding family planning and lack of health education on planned parenthood are the main reasons for early childbearing. (9) A strong son preference for sons has been found to be pervasive in Indian society ,affecting both attitude and behaviour with respect to children.(3)The present study has also revealed a strong son preference (45%) among respondents .Similar findings were seen in study conducted in Delhi(3)and in NFHS III survey.(2) Majority of men (52%) knew that having two children is ideal but in practice they had more than two. A study conducted in Khairwar, MP also showed similar findings. (14) A strong want of son is the main reason for opting for more number of children. About 94.3% of men reported tubectomy as method of choice for permanent contraception. 39.9% feel that this is wife’s business while 36% said that wife/family opposed opting vasectomy. A study conducted in Delhi by M.Dutta et al (3) showed that 34.4% reported opposition from wife as reason for non acceptance of contraception. A study conducted by Abhilasha Sharma also showed similar findings. (15) Knowledge and perception about maternal care in general was good. Most of the respondents were aware about importance of antenatal care and hospital delivery however very few (13%) accompanied their wives for ANC or were present at the time of delivery (7.7%).In India, pregnancy is considered special and care during pregnancy is considered as domain of elder female members of the family therefore for ANC check up usually elderly female accompanies pregnant mother. Considering her experience, it is assumed that elderly female member is the ideal person to take care of a pregnant mother. To ensure proper rest, pregnant mothers are sent to mother’s house for first delivery. Husbands are usually ignored in traditional set up as far as care during pregnancy and post-delivery is concerned. Involvement of husbands in antenatal care was not expected and to some extent was seen as unnecessary interference. (9)Delivery and the postdelivery period were found to be exclusively a woman’s affair. In a study conducted by FRSH(9) , men reported that even talking or inquiring about their wife and baby was not deemed necessary and most husbands were unaware as to whether or not their wives had experienced any problems during childbirth. These men did not see any need to learn about such possibilities, and actually saw such inquiries as unwarranted intrusions into female territory. Similar findings are seen in studies conducted in Kathmandu, Nepal (5), in Pakistan (6), in rural Guatemala (7) and in India. (23, 24) The study shows that very few respondents knew about feeding practices and immunization schedule .But these fathers are more particular about seeking medical help during child’s illness and activities like dropping the child to anganwadi centre. Similar findings are seen in studies conducted by Abhilasha Sharma.(15) Traditionally fathers are not involved in child rearing activities; mothers bear the sole responsibility of feeding and caring child. Men are and usually considered as earning member of the family mostly involved in outside activities. As far as health education is concerned, child health seemed to be limited to breastfeeding and immunization and childhood illnesses. Among other maternal care issues only family planning and hospital delivery are focused more.(22) Issues like planning pregnancy support during pregnancy and high risk pregnancy and complications during pregnancy are totally ignored by health workers. Health education has proved to be a cost effective measure .With focused health education men can play important role in maternal and child health care. Maternal morbidity and mortality is more in first three days after delivery due to bleeding or infection .Men can play vital role if they are involved in antenatal care and informed about the complications of pregnancy as they are usually decision makers in the family .They can ensure rest, nutritious diet, hospital delivery and moral support to the wives. (3) Researchers have proved that men are equally important for overall growth and development of the child. (19, 20, 21)
CONCLUSIONS
Role of men in reproductive and child health is totally neglected in traditional socio-cultural set up. Many studies have shown that men can play important role in reducing maternal morbidity, mortality and improving overall development of child. Men should be made aware about their roles and responsibilities in maternal and child health. Strategies, for involving men in RCH, needs to be developed. Appropriate IEC material should be prepared and male friendly approach should be adopted to reach men and address their issues. Efforts should be made to encourage couple communication, acceptance of male contraceptives, Planned Parenthood etc. Women’s education and empowerment are equally important to change their traditional perceptions about gender inequality and the role of husbands in maternal and child health.
LIMITATIONS
Recall bias could have been present even after restricting inclusion to males whose spouses last delivered 24 months prior to the survey. Additionally reporting bias arising from men wanting to provide socially desirable responses especially regarding the care during pregnancy, hospital delivery and child care issues could have been a possible drawback to the study. This could have been overcome by cross confirmation of the men's responses by women interviews. Our study population was largely peri-urban area of tribal district of Karnataka therefore our findings may not be entirely generalizable. However, we gain insights into how similar populations can be targeted to improve male involvement in reproductive and child health. This study design was cross-sectional which limits us from making any causal inferences in relation to the main outcome and independent variables.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
We are thankful to all the interns of 2007 batch, social workers and staff of UHC and Anganwadi workers of Aiyennapethe area, Chitradurga for their help in conducting the survey.
References:
1. Bulletin of WHO, Feb2005, 83(2), 86
2. International Institute for Population Sciences (IIPS) and Macro International. 2007. National Family Health Survey (NFHS-3), India, 2005-06: Volume 1, Mumbai: IIPS
3. M.Dutta, M.C.Kapilashrami, V.K.Tiwari (2004) “Knowledge Awareness and Extent of Male Participation in key areas of Reproductive and child health in an Urban slum of Delhi. Health and Population Perspectives and Issues.27 (2):49-66
4. O.A.Adeleye and J.Chiwuzie (2007) “He does his own and walks away.”Perceptions about male attitude and practices regarding safe motherhood in Ekiadolor, Southern Nigeria. African Journal of Reproductive Health,Vol.2,No.1,pp 76-89
5. Mullany BC. Barriers to and attitudes towards promoting husbands' involvement in maternal health in Katmandu, Nepal. Social science and medicine. 2006: June; 62(11):2798-809.
6. M.Ali, H.Rizwan and H.Ushigima. (2004) Men and Reproductive Health in Rural Pakistan: the case for increased male participation. The European Journal of Contraception and Reproductive Health Care.2004, Vol.9, No.4, 260-266
7. Marion Carter (2002) Husbands and maternal health matters in rural Guatemala: wives reports on their spouse’s involvement in pregnancy and birth. Social science and medicine. Aug 02, 55(3): 437-450
8. Dev A. (1998) Involvement of Husbands in Antenatal Care: Evaluation of Deepak Charitable Trust's Outreach Programme. Population Council, New Delhi, India; 1998; June 23–26
9. Alka Barua. (1998) Young husbands’ involvement in Reproductive Health in Rural Maharashtra. Population Council, New Delhi, India; 1998; June, 6-8.
10. S.K.Lwanga and S.Lemeshow (1991), Sample Size Determination in Health Studies: A Practical Manual, WHO 1991.
11. Antenane Korra, Mesfin Haile (1999) Sexual behaviour and level of awareness onreproductive health among youths: Evidence from Harar, Eastern Ethiopia. Ethiop. J. Health Dev. 1999; 13(2):107-113
12. Pande R., Kurz K., Walia S., Mac Quairrie and S.Jain. (2006) Improving Reproductive Health of Married Youth in India.ICRW publications: Washington DC, USA.
13. Arundhati Char, (2011) Male Involvement in Family Planning and Reproductive Health in Rural Central India. Academic Dissertation submitted to the board of the School of Health Sciences of the University of Tampere.Dec2011.
14. Kalyan B. Saha, Neeru Singh, D.C. Jain, Uma C. Saha. (2004) Men’s Involvement in Reproductive Health: A study among the Khairwar Tribe of Central India. Rural and Remote Health, issue7:605
15. Abhilasha Sharma (2003).Male Involvement in Reproductive Health: Women’s Perspective. The Journal of Family Welfare .Vol 49, No.1, 1-6.
16. Bhalerao, VR, MM Galwankar, SS Kowli, RR Kumar, and RM Chaturvedi. (1984). “Contribution of the Education of the Prospective Fathers to the Success of Maternal Health Care Programme”.Journal of Postgraduate Medicine 30: 10-12
17. Mullany BC, S Becker and MJ Hindin. (2007). “The Impact of Including Husbands in Antenatal Health Education Services on Maternal Health Practices in Urban Nepal: Results from a Randomized Controlled Trial”. Health Education Research 22: 166- 176.
18. Varkey LC, A Mishra, A Das, E Ottolenghi, D Huntington, S Adamchak, and ME Khan. (2004).Involving Men in Maternity Care in India. Washington DC: Population Council. 19.
19 .United Nations Fund for Children (UNICEF). 1998. The state of the world’s children: focus on nutrition. New York, UNICEF.
20. http://www.unmillenniumproject.org/docume nts/Greene_et_al-final.pdf (accessed on 20/12/2012)
21. http://iycn.wpengine.netdnacdn.com/files/IYCN-GM-and-Men-LitReview-060311.pdf (accessed on 20/12/2012)
22. http://paa2010.princeton.edu/papers/100656 (accessed on 20/12/2012)
23. Amarjeet Singh, Arvinder Kaur Arora. How much do rural Indian husbands care for the health of their wives? Indian Journal of Community Medicine.2008; Volume: 33; Issue: 1; Page: 19-25.
24. Abhishek Singh. Faujdar Ram, Men’s Involvement during Pregnancy and Childbirth: Evidence from Rural Ahmednagar, India: Population Review. 2009: Volume 48, Number 1; pp. 83-102.
|






 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License