IJCRR - 5(6), March, 2013
Pages: 51-58
Date of Publication: 30-Mar-2013
Print Article
Download XML Download PDF
BACTERIOLOGICAL PROFILE AND ANTIMICROBIAL RESISTANCE PATTERN IN EARLY ONSET NEONATAL SEPSIS: CHALLENGE TO THE PHYSICIAN
Author: Kuhu Pal, Arnab Kumar Samanta
Category: Healthcare
Abstract:Objective: Identification of pathogens associated with early onset neonatal sepsis and their resistance pattern so that a guideline for empirical antibiotic regimen can be formulated. Methods: Study was conducted in a teaching hospital in eastern part of Bengal from March 2011 to August 2012. Newborn, age less than 72hours, associated with a clinical diagnosis of sepsis were enrolled in this study. 1 ml of blood was collected maintaining proper asepsis and inoculated in 5 ml of brain heart infusion broth. The broth was incubated aerobically at 370 C and was sub cultured in blood agar, chocolate agar and MacConkey's agar. Isolates were identified by colonial morphology, Gram staining and standard biochemical tests. Antimicrobial sensitivity test was performed by Kirby Bauer disc diffusion method following CLSI guidelines. Result: Among 192 clinically suspected cases of early onset neonatal sepsis, blood culture was positive in 73(38.0%) cases of which Klebsiella pneumoniae (45.71%) was the predominant organism followed by Staphylococcus aureus (20%), Escherichia coli (11.42%), Enterococcus sp (7.14%), Enterobacter sp (5.71%) etc. Most Gram negative organisms were highly resistant to ampicillin (100%), gentamicin (81.25%) and cephalosporin group of drugs. Imipenem (0%) and ofloxacin (31.25%) were the two most effective drugs against these gram negative bacteria. 50% of Staphylococcus aureus were methicillin resistant. Conclusion: This study reflected alarmingly increasing in vitro resistance of isolated organisms towards commonly used antibiotics specially ampicillin, gentamicin and third generation cephalosporins which were given empirically in neonatal sepsis. Therefore this study recommends introduction of fluoroquinolone along with amikacin in empirical treatment of early onset neonatal sepsis.
Keywords: early onset neonatal sepsis, multidrug resistance, fluoroquinolone
Full Text:
INTRODUCTION
Neonatal sepsis is the leading cause of mortality and morbidity in the neonates. The first week of life is a particularly high-risk period when 3/4th of neonatal deaths occur1 . In spite of major improvement in antimicrobial therapy, neonatal life support system and the early notification of risk factors, neonatal sepsis still plays a pivotal role in mortality and morbidity among newborns throughout the world. Symptoms occurring within the age of 72 hrs are considered as early onset sepsis2 . Newborns even though they are born at full term, have relatively immature immune system which is unable to provide a robust defense against virulent pathogens. Therefore neonates are at high risk of developing invasive infections if exposed to pathogenic microorganisms.1
Clinical recognition of neonatal sepsis is not always straight-forward. It is a life threatening emergency and delay in diagnosis and treatment with appropriate antibiotic may have devastating consequences. These neonates therefore usually require aggressive course of parenteral antibiotics. An early etiological diagnosis is essential for appropriate intervention. But microbial etiology of neonatal sepsis is diverse. Several studies on neonatal sepsis have documented the diversity of bacteria and their susceptibility pattern and their temporal variability 3,4,5,6 . In this era of evidence based medicine, today's management may not be acceptable tomorrow. So, the greatest challenge of the day to the pediatrician is the emerging threat of neonatal sepsis coupled with antimicrobial resistance to commonly used drugs. For this reason, active surveillance is needed to identify the pathogens of neonatal sepsis as well as the antibiotic sensitivity pattern for the agents of sepsis in a particular area. This is important in formulating the empirical antibiotic regimen and also to alert clinicians towards emerging pathogens that may pose a threat to the community. So, the study was designed to evaluate the common pathogens associated with early onset neonatal sepsis and their resistance pattern in a newly established teaching institution of rural Bengal and build a treatment policy for early onset neonatal sepsis (EONS).
MATERIAL AND METHODS
Study design: This was a hospital based cross sectional study. Study area: Study was carried out in the Neonatal Care Unit, Department of Pediatrics and Department of Microbiology of a newly established teaching hospital acting as a tertiary care centre for eastern part of Bengal. Study population: Blood culture samples of newborn, age less than 72hours with clinical signs of sepsis, including lethargy, refusal of feed, respiratory distress, abdominal distension, vomiting, hypothermia, hyperthermia etc born inside this hospital as well as referred from different centers were enrolled in this study. Exclusion criteria: Babies who had received antibiotics before collection of blood samples, having surgical problems, chromosomal or congenital anomalies were excluded from the study. Study period: March 2011 to August 2012. Study was carried out after getting permission from Institutional Ethics Committee. Procedure: 1 ml of blood was collected maintaining proper aseptic technique and inoculated in 5 ml of brain heart infusion broth with 0.025 % sodium polyanethol sulfonate. The broth was incubated aerobically at 370 C. A blind subculture was done after overnight incubation. If no growth was obtained then blind subculture was done at 48 hrs, 72 hrs, then on 7th day. Any sign of growth in between was followed by subculture. Media used for subculture were 5% sheep blood agar, chocolate agar and MacConkeys agar (Himedia Laboratories).Isolates were identified by colonial morphology, Gram staining as well as standard biochemical tests. Aerobic spore bearers, wherever grown were regarded as contaminants. The remaining isolates were included in the analysis. Antimicrobial sensitivity test was done by Kirby Bauer disc diffusion method following guidelines provided by Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute (CLSI) 7 . Gram negative organisms were subjected to testing for extended spectrum β lactamase production (ESBL). All ESBL producers detected in routine screening test were confirmed phenotypically as per CLSI recommendations. Control strain: Escherichia coli -- ATCC 25922; Staphylococcus aureus -- ATCC 25923; Pseudomonas aeruginosa -- ATCC 27853; Enterococcus faecalis – ATCC 29212 and Klebsiella pneumoniae ATCC 700603 (positive control of ESBL) were used for quality control tests. All the antibiotics, media and control strains were purchased from Himedia laboratories, Mumbai (India) except cefotaxime/clavulanic acid (30µg/10µg) disc which was procured from BD diagnostic laboratory. Statistical analysis was done using Microsoft excel.
RESULTS
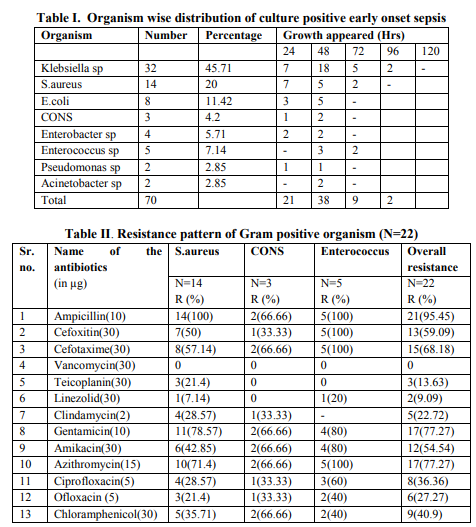
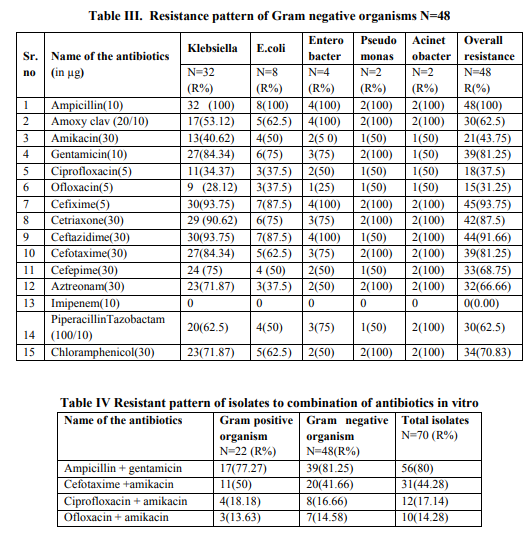
During this one and half year study period 192 blood samples were obtained from clinically suspected cases of early onset neonatal sepsis. Blood culture was positive in 73(38.0%) cases, of which 3 (1.55%) were non albicans Candida and remaining 70(36.45%) were bacteria. All the culture positive cases were monomicrobial. Infection was found to be more common in male newborn with male and female ratio of 1.7:1. 67.12% of culture positive babies were low birth weight. Gram negative bacteria were the most common organisms isolated in present study accounting 68.57% of total isolated bacteria. Klebsiella sp (45.71%) was the most common organism causing early onset neonatal sepsis followed by Staphylococcus aureus(20%), Escherichia coli(11.42%), Enterococcus sp (7.14%), Enterobacter sp (5.71%), coagulase negative Staphylococcus (CONS) (4.2%), Pseudomonas sp (2.85%) and Acinetobacter sp (2.85%). 84.28% growth occurred within 48 hrs of aerobic incubation. Though the cultures were observed for 7 days but no sign of growth was seen after 96 hrs (Table No. I). In vitro antimicrobial susceptibility testing of blood culture isolates of this study revealed that Klebsiella sp was universally resistant to ampicillin (100%), so were S.aureus, E.coli, Enterococcus sp, Enterobacter sp, Acinetobacter sp and Pseudomonas sp. Klebsiella sp was resistant to almost all cephalosporins ranging from 75% towards cefepime to 93.75% towards cefixime and ceftazidime. Resistance to amikacin was less frequent (40.62%) than resistance to gentamicin (84.34%) in these isolates. E.coli also exhibited high resistance against gentamicin (75%), amoxicillin-clavulanic acid (62.5%), chloramphenicol (62.5%), piperacillin - tazobactam (50%) and cephaolosporins. ESBL production was found in 12(37.5%) Klebsiella sp and 2(25%) E.coli. All the gram negative organisms were sensitive to imipenem. Out of 14 S.aureus isolates, 50% were methicillin resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA). No vancomycin resistant Staphylococcus aureus (VRSA) was found in this study. Enterococcus sp was resistant to almost all antimicrobials except vancomycin and teicoplanin. Resistance pattern of Gram positive and Gram negative bacteria are given in table II and table III respectively and overall resistance pattern of isolates to some recommended combination of antibiotics is given in table IV.
DISCUSSION
Studies in different centres of India have revealed an incidence of culture positive EONS varying from 6.1% to 68.93% 6, 8, 9, 10. In this study it was found to be 38.0 %( 73/192). One of the reasons of this great variation may be due to consideration of EONS up to 72 hrs or 7days and it is possible that some anaerobes might be missed in some studies, including the present one. 67.12% of culture positive babies were low birth weight which was just similar to a study in Gujrat9 where 70% of culture positive newborns were low birth weight. Infection was found to be more common in male newborn with male and female ratio of 1.7: 1.A male dominance was observed in almost all studies5, 8, 10 . As per National Neonatal Perinatal Database11 , the most frequent offender of neonatal sepsis was Klebsiella sp(32.5%),followed by Staphylococcus aureus (13.6%).This was supported by the present study where the most frequent isolate was Klebsiella sp (45.71%) followed by S.aureus (20%), Escherichia coli (11.42%), Enterococcus sp(7.14%), Enterobacter sp (5.71%), coagulase negative Staphylococcus (4.2%) etc. This is in accordance with other Indian studies12, 13, 14. But some other Indian studies reported Pseudomonas sp and S.aureus as most common organism of EONS15, 16. The dissimilarity of microbiological pattern of early onset neonatal sepsis can be explained by the regional variation in the spectrum of organisms and the variation in the use of antibiotics. These findings have also implications for therapy and infection control. Empiric therapy for suspected neonatal sepsis must therefore cover both Gram negative bacilli and Gram positive cocci particularly Klebsiella pneumoniae and Staphylococcus aureus. In this study, antimicrobial susceptibility testing from blood culture isolates revealed that Klebsiella and other Gram negative bacilli were universally resistant to ampicillin (100%).Similar high resistance was also established by others also 13, 17, 18 . Klebsiella was highly resistant to Cephalosporin group of drugs ranges from 75% to 93.7%. Resistance to cefotaxime was found(84.34%) almost similar to the studies by Kumar et al17 (83.5%),R. Viswanathan et al4 (81.3%) and S. Begum et al18(94.2%). Klebsiella was found to be quite sensitive towards ciprofloxacin(R=34.37%) and ofloxacin (R=28.12%) in comparison to other groups of drugs. Similar trend was seen by some other studies in India13, 17 and Bangladesh18 . All S.aureus isolates were resistant to ampicillin, whereas resistant to cefoxitin was 50%, Similar high occurrence of MRSA was also established by different studies in India 10, 14, 17. Resistance to amikacin was found in 42.85% cases which were much higher than the study done by Kairavi. J. Desai 12(15.23%). Linezolid, clindamycin, teicoplanin were the drugs to which S.aureus showed least resistance. No VRSA was isolated in this study. Similar low resistance to vancomycin and linezolid was established by different studies10, 12, 13, 17 but in a study in Sikkim, 60% VRSA were observed14 . Thirty three percent isolates of CONS were resistant to cefoxitin, ciprofloxacin, ofloxacin. No resistance was seen against vancomycin, teicoplanin, linezolid, Almost similar type of result were revealed elsewhere in India10,13,17.Sensitivity pattern of E.coli was almost like Klebsiella sp. Number of isolates of Enterococcus, Enterobacter, Pseudomonas were too small to predict any sensitivity pattern. Combination of cefotaxime and amikacin are used as empirical therapy in suspected neonatal sepsis due to multidrug resistant gram negative bacteria in most of the centers in our country, (AIIMS Protocol 200819) including our centre. But it is a matter of great concern that 81.25% of gram negative organisms and 68.18% of gram positive organisms were resistant to cefotaxime leading to overall resistance of 77.14%. The increasing resistance towards this antibiotic is also supported by the study conducted earlier in this country5, 13, 17. 14(29.16%) Gram negative isolates showed evidence of ESBL production which is higher than that (ESBL= 14%) of an Indian study conducted in Gujrat 10 and this should not be underestimated. On the other hand, fluoroquinolones like ofloxacin and ciprofloxacin showed a superior sensitivity pattern against both Gram positive as well as Gram negative bacteria with overall resistance of 30%(21/70) and 37.14% (26/70)respectively. Moreover, 44.28 %( 31/70) of isolates were found resistant to both amikacin and cefotaxime in vitro. Whereas only 14.28 % (10/70) organisms were resistant to both amikacin and ofloxacin and 17.14% (12/70) were resistant to both amikacin and ciprofloxacin. So, result of our study arises a question towards the rationality of administration of cefotaxime in empirical treatment of neonatal sepsis. Early onset neonatal sepsis with multidrug resistant strains is one of the greatest challenges to the pediatricians. Wise and rational choice of empirical antibiotic is of utmost importance as it takes at least 48 hrs for generation of a proper blood culture sensitivity report. Keeping this in mind, the study strongly recommends introduction of fluoroquinolone in empirical therapy along with amikacin in treatment of EONS in spite of knowing the fact that fluoroquinolones cause arthropathy (arthrosis) and osteochondrosis in juvenile animals of several species. Indications of fluoroquinolone use in pediatric patients have been provided by the American Academy of Pediatrics, which recommends that their use should be limited to the situations where infections have been caused by multidrug-resistant organisms for which there is no effective as well as safe alternative antibiotics are available or as second line therapy in Gram negative neonatal sepsis where first line drugs have failed20. Moreover, in a study including 116 neonates with sepsis, ciprofloxacin were used successfully and no feature suggestive of arthropathy or growth impairment was reported at one year follow up 21 . Though more data from controlled trials to further define the efficacy and safety profile for this class of drugs in pediatric patients especially neonates are desirable, in existing situation of EONS, fluoroquinolones can act as a good alternative to which most of the isolates were susceptible. Moreover, they will also provide some economical relief to the patients over most sensitive carbepenems available in market and we can preserve our last weapon against these notorious pathogens responsible for neonatal sepsis. However, this result was limited to our centre only.
CONCLUSION
This study reveals current data on the pathogens causing sepsis in neonatal care units of this institute but the striking feature is the high rate of in vitro resistance of the isolated organisms to the commonly used antibacterial drugs. This study strongly recommend introduction of fluoroquinolones in the empiric therapy of EONS especially when multidrug resistance gram negative bacteria is suspected to be the causative agent. The present study also emphasizes the importance of periodic surveys of microbial flora encountered in particular neonatal settings to recognize the trend and help in implementation of rational empirical treatment strategy.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
We want to acknowledge the immense help received from the scholars whose articles are cited and included in references of this manuscript and also grateful to authors/editors/publishers of all those articles, journals and books from where the literature for this article has been reviewed and discussed.
References:
1. Guha D.K, Saili A. Guha R, Aggarwal A. Common Infections in the Newborn. In: Neonatology – Principles and Practice. Guha D.K; 3rd ed .Jaypee Brothers Medical Publishers (P) Ltd. New Delhi, India; 2005: 654 – 672.
2. Stoll BJ. Infection of the Neonatal Infant. In Nelson’s Text Book of Paediatrics; Behrman RE, Kleigman RM, Jenson HB.18th ed. WB Saunders Co.;2006:794-811
3. Ghanshyam D. Kumhar, V.G. Ramachandran, and Piyush Gupta.Bacteriological Analysis of Blood Culture Isolates from Neonates in a Tertiary Care Hospital in India. J Health Popul Nutr 2002 Dec;20(4):343-347
4. Viswanathan R, Singh AK, Mukherjee S, Mukherjee R, Das P, Basu S.Aetiology and antimicrobial resistance of neonatal sepsis at a tertiary care centre in eastern India: a 3 year study. Indian J Pediatr.2011;78 (4):409-12.
5. Bhat Ramesh Y,Leslie Edwars s Lewis and Vandana KE. Bacterial isolates of early onset neonatal sepsis and their antibiotic susceptibility pattern between 1998 and 2004: an audit from a centre in India. Italian Journal of pediatrics 2011; 37: 32-38
6. Zakariya BP, Bhat V, Harish BN, Arun Babu T, Joseph NM. Neonatal sepsis in a tertiary care hospital in South India: bacteriological profile and antibiotic sensitivity pattern. Indian J Pediatr 2011; 78(4):413-7.
7. Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute. Performance standards for antimicrobial disk susceptibility tests. Approved standard M2- A10. Wayne, PA: Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute; 2009
8. Shrestha NJ, Subedi KU, Rai GK. Bacteriological Profile of Neonatal Sepsis: A Hospital Based Study. J Nepal Paedtr Soc 2011;31(1):1-5.
9. Mudey Gargi D, Tankhiwale S. Neelima, Mudey Abhay. Clinical Profile and Haematological Indices of Clinically Diagnosed Early Neonatal Septicaemia: A study Conducted in Teaching Institute Attached to Rural Hospital of Wardha District. International Journal of Current Research and Review 2011;Vol 3(1): 4-8
10. Shah AJ, Mulla SA, Revdiwala SB.Neonatal Sepsis: High Antibiotic Resistance of the Bacterial pathology in a Tertiary Care Hospital.J Clin Neonatol 2012;1:72-75
11. National Neonatology Forum. National Neonatal Perinatal Database. Report for the year 2002 . New Delhi: Dept of Pediatrics.
12. Kairavi. J. Desai, Saklainhaider. S. Malek Neonatal Septicemia: Bacterial Isolates and Their Antibiotics Susceptibility Patterns. NJIRM 2010; Vol. 1(3): 12-15
13. I Roy, A Jain, M Kumar, SK Agarwal et al.Bacteriology of neonatal septicemia in a tertiary care hospital of northern India. Indian J Med Microbiology 2002; 20(3):156-159.
14. Dechen C Tsering, L Chanchal, Ranabir Pal, Sumit Kar.Bacteriological profile of septicemia and the risk factors in neonates and infants in Sikkim.Journal of Global Infectious Diseases 2011;Vol 3(1):42-45
15. Joshi SG, Ghole VS, Niphadkar KB: Neonatal gram-negative bacteremia. Indian J Pediatr 2000; 67:27-32.
16. Karthikeyan G, Premkumar K: Neonatal sepsis: Staphylococcus aureus as the predominant pathogen. Indian J Pediatr 2001; 68:715-717.
17. Kumar S, Rizvi M, Vidhani S, Sharma VK. Changing face of septicaemia and increasing drug resistance in blood isolates. Indian J Pathol Microbiol 2004; 47 (3): 441-446.
18. S Begum, MA Baki, GK Kundu, I Islam, M Kumar, A Haque Bacteriological Profile of Neonatal Sepsis in aTertiary Hospital in Bangladesh. J Bangladesh Coll Phys Surg 2012; 30: 66-70
19. Sankar MJ, Agarwal A, Deorari AK, et al. Sepsis in the newborn. Indian J Pediatr 2008 Mar;75(3):261-266.
20. Committee on Infectious Diseases. The use of systemic fluoroquinolones. Pediatrics 2006;118:1287-1292
21. Drossou-Agakidou Vasiliki, Roilides Emmanuel, Papakyriakidou Koliouska Panagiota et al. Use of ciprofloxacin in neonatal sepsis: lack of adverse effects up to one year. Pediatr Infect Dis J 2004; 23(4): 346-9
|






 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License